When starting to install a heated floor, the question arises which pipe material is better: cross-linked polyethylene or plastic.
The answer lies in the operating conditions of the heated floor, and the opinions of specialists, experience and reviews of people who have been operating floor heating systems for more than one year will help to understand this issue.
Almost all modern pipes are based on cross-linked polyethylene; only metal-plastic pipes have a metal reinforcing layer with adhesive layers added to the outer and inner layers of cross-linked polyethylene, ensuring the solidity of the product.
Evaluation criteria for pipe materials
I will list the main points of operating a water pipeline for floor heating. Taken into account:
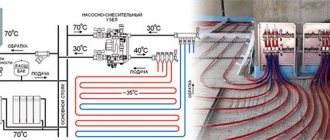
- Heating temperature. It fluctuates in the range of 30...55 °C.
- Constant pressure in the circuit. It will be 1.5-2 bar; when testing the system, a pressure of 6 bar is used.
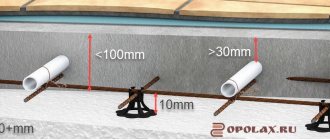
- The pipeline is most often located in a screed, where it is subjected to pressure from the pressure of water and concrete.
Thus, the most important parameters of pipes for heated floors:
- Operating temperature 30...55 °C.
- Pressure up to 6 bar.
- Sufficient thermal conductivity.
Protection against oxygen penetration into the channel, thermal expansion indicators, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation are also important.
Types of HDPE pipe connections
The HDPE pipe has approximately the same connection devices. The most popular is the collet connection. To connect pipes, a coupling is used, in which there is a collet on one side and a thread on the other. To fasten the coupling, the clamping nut is unscrewed and put on the HDPE pipe. The collet is inserted inside the pipe, the clamping nut is put on and tightened well.
Advice! The clamping nut must not be pressed too hard, otherwise it may burst or the collet will crush the edge of the pipe.
After completing the connection of the collet, it is possible to screw another threaded pipe onto the other edge of the threaded coupling to the same diameter.
The flange connection of HDPE pipes is made similar to the connection outlined above. A sleeve is welded to the edge of the HDPE pipe, onto which the flange is attached. And the same device with a slip-on flange, where the connection is installed on the edges of the pipes and pressed with union nuts.
Which is better – cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic for heated floors?
Both polymers are actively used by craftsmen when installing this type of heating. I will describe their pros and cons in more detail in order to fully appreciate the capabilities of each.
Characteristics and properties
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) appeared not so long ago, but has already proven itself to be the best among polymer analogues.
It is obtained by processing (cross-linking) polyethylene. Volumetric transverse intramolecular bonds are formed in the polymer structure. Their quantity in relation to the total mass of raw materials determines the degree of crosslinking. The normalized value is from 65 to 80%.
There are three types of cross-linked polyethylene, each of which has a certain level of cross-linking and corresponding markings:
- PEX-A – degree of cross-linking up to 85%.
There is also a recently introduced polyethylene with higher heat resistance - PE-RT. The crosslinking process made it possible to make polyethylene products more heat-resistant (withstand 95°C), improve their elasticity and strength.
However, the stitching method does not matter much. It is much more important to make sure that what you are looking at is truly cross-linked polyethylene. The letter X just indicates this. There are cases when unscrupulous manufacturers label PEX, but in reality it turns out to be ordinary polyethylene, which cannot be used in heated floors.
Polyethylene pipes are manufactured in different densities from PE32 to PE100. In underfloor heating circuits, craftsmen consider it better to use PEX-B polyethylene bends with a density of 100, which have an oxygen-protective layer, suitable performance characteristics and a lower price.
Cross-linked PEX polyethylene, intended for installation in hidden heating pipelines, is painted red and sold in coils.
The metal-plastic pipe has a five-layer structure. It consists of a thin aluminum layer on which the inner and surface layers of cross-linked polyethylene are fixed with glue. The metal cylinder gives the metal-plastic sufficient strength and 100% protection from oxygen. The marking looks like PEX-AL-PEX.
Metal-plastic can withstand heating up to 95° at a pressure of up to 10 bar, and in emergency situations – up to 130°.
In terms of indicators such as thermal stability, thermal conductivity, and thermal expansion, metal-plastic pipes are leaders among polymer types.
Metal-plastic
Polyethylene pipes with an aluminum layer are used less and less. They are also easy to install, robust, flexible, durable and affordable. The disadvantages of the material are the high price of fittings and low aesthetic properties. Most often, high-quality metal-plastic is used in the construction of heating systems.
Advantages and disadvantages
What are the advantages of both materials when used for underfloor heating contours?
Polyethylene
The service life at an average temperature of 75 °C is 50 years. Such indicators are quite suitable for use in heated floors, where the maximum temperature for heating is 55 ° C.
They have good thermal conductivity - 0.38 W/(m•C). They are superior to polypropylene products in terms of heat transfer.
They are endowed with the property of memory, that is, they are able to restore their original shape after bending.
The material is much more flexible than metal-plastic and bends easily.
Properties such as smoothness of the inner layer, resistance to all types of corrosion, long service life (at least 30 years during normal use) are characteristic of both materials.
The main disadvantage of PEX is its strong thermal expansion when heated. It is capable of elongating by 1 cm per meter when heated to 50 °C. However, proper floor screed completely eliminates this drawback.
Metal-plastic
Thermal conductivity is 0.45 W/(m•C).
The normalized heating of metal-plastic at a pressure of 10 bar is 95 °C.
Linear thermal elongation is the lowest among plastics.
The flow of oxygen through the walls of the outlet is zero.
Metal-plastic bends well. Pipes with a cross-section of up to 20 mm can be easily bent by hand.
Experts include the following disadvantages of metal-plastic:
- Large bending radius (80 mm), as a result of which, if there is an error in installation, creases appear that cannot be corrected. If the pipe is bent, it will break easily. You will have to install a coupling or change the entire circuit.
- Fitting connections in a heated floor under a screed may weaken over time due to systematic temperature fluctuations.
The danger of metal-plastic
It lies, oddly enough, in its multi-layered nature. When heated, all layers of metal-plastic expand with different increases, which leads to deformation of the pipe, primarily at the joints with fittings. Therefore, it is impossible to lay metal-plastic pipes with fittings in a heated floor screed. Otherwise, you will have to break up the concrete by at least half a meter, install a new fitting, and wall up this place without a guarantee that it will not leak again.
Metal-plastic pipe products for floor insulation
Metal-plastic pipes were originally developed for constructing closed floor insulation systems. These materials have a complex, multilayer structure, where the supporting element is aluminum foil. Adding metal to cross-linked polyethylene eliminates its disadvantages, but adds its own characteristics that should be taken into account during installation.
To understand how a metal-plastic pipe works, you need to understand its structure. The material is a “sandwich” of two layers of polyethylene covered with metal. The bonding agent is a special glue that is applied to the metal foil on both sides.
Aluminum inclusion adds metal-plastic to all the advantages of polyethylene pipes:
- resistance to water hammer;
- higher operating parameters - pressure up to 10 atm, temperature up to 95-100 degrees (recommended 93);
- faster and more efficient heating of the room;
- the ability to maintain the bending shape without fixation, which simplifies installation.
When choosing high-quality pipes, you will not encounter any disadvantages. Poor-quality metal-plastic can create problems during installation. A poor adhesive base leads to delamination of the pipe, and thin foil will quickly break at a break.
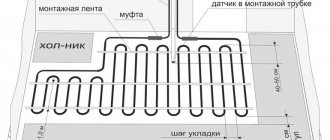
Note! Installation of a metal-plastic floor is carried out at a distance of 35 cm. Closer installation will lead to deformation of the pipe at the bend.
Metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic pipes (MP) are multilayer composite pipes consisting of five layers. The inner and outer layers of polyethylene are tightly connected to the inner layer of special aluminum foil using glue.
This complex pipe has been developed specifically for underfloor heating to offer optimal efficiency in terms of heating output per m², achieving uniform heating of the floor surface with a minimum number of pipes. The aluminum layer results in faster heating times. The inner wall of the pipes is smooth, so calcification does not occur , and the pipes are not subject to corrosion. The unique combination of aluminum and polyethylene ensures durability and provides an alternative to copper pipes. Metal-plastic pipes have their advantages and disadvantages. There are a number of reasons why MP pipes are the best heated floor pipes available.
Advantages of metal-plastic pipes
The advantages of MP pipes include the following characteristics:
- anti-oxygen protection to prevent corrosion of metal parts of the system, such as, for example, a boiler;
- low linear expansion coefficient;
- resistance to corrosion , as well as to chemicals;
- good sound insulation ;
- smooth surface ( less pressure loss );
- keep their shape;
- durability - tests have shown that the service life is up to 50 years and above.
- maximum operating temperature at a pressure of 10 bar up to 95 ºС;
- convenient installation , since MP pipes are easily bent. This allows them to be evenly laid in snakes and spirals with a large number of folds.
The connection of MP pipes is made using various fitting systems using special tools: press jaws, shears for MP pipes, reamers for pipe processing, crimping machine and others.
Disadvantages of metal-plastic
The disadvantages of pipes include the following:
- different linear expansion coefficients for aluminum and polyethylene, which can lead to delamination of pipes;
- when using threaded fittings, scale may build up on the inside of the fittings, so it is better to use press fittings;
- If the fittings are pinched during installation, a cut may appear on the pipe.
Criterias of choice
When choosing a material for the construction of communications, the decisive argument should not be considerations of economic benefit or installation complexity, but the compliance of the technical characteristics of the pipes with the expected operating conditions.
In the case of installing heated floors, the following requirements apply to pipe materials:
- Durability . According to official requirements for pipes for heated floors, it is prohibited to use ferrous rolled metal and seamed pipes. Steel products without special anti-corrosion protection in a walled-up state will not last long. The connecting seam is a “weak” point when hydraulic pressure increases in the heating system. The use of such materials will quickly lead to an emergency situation, the elimination of which will require opening the concrete screed.
- Chemical inertness . For long-term operation without reducing the internal clearance, pipes with a perfectly smooth inner wall are required. The coolant contains salts of alkaline earth metals, which, during long-term operation, are deposited on the inner walls of most pipe materials.
- Resistance to mechanical loads without deformation . The minimum concrete screed exerts a pressure on the pipes equal to 10 kg of weight per square meter. cm. Soft plastic pipes will be deformed under this load, and too hard plastic may burst.
- Resistance to high temperature and pressure of the carrier in the heating system . The minimum required stability parameters are 95 degrees and 10 atm. respectively.
- High level of heat transfer . For efficient heating, it is important that communications are not a barrier between the coolant and the air.
- No connections under the screed . Pipe materials are required that can be laid in one piece up to 120 m long.
- Flexibility and fracture resistance . When laying heated floors, it is important that the pipes are flexible enough to bend without damaging the walls and deforming the internal section with a minimum radius. Large distances between pipes cause cold segments.
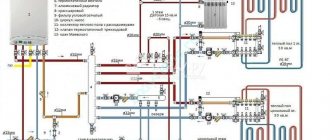
The choice of this or that material is also influenced by the type of heating in the house. If this is a central system, then the heated floor will be subject to more severe loads than with an individual circuit.
Note! Those looking for the ideal option for underfloor heating should consider using copper materials. Copper has a much greater safety margin than is necessary in this case. There are two disadvantages - complicated installation and high price of copper pipes.
Metal-plastic and cross-linked polyethylene are very close in their technical and price characteristics. Comparing their positive and negative sides will allow you to make the right choice in each specific case.
XLPE pipes
XLPE pipes - REX pipes . REX is an abbreviation for cross-linked polyethylene. This flexible, durable material is becoming an increasingly popular material. To give polyethylene strength and resistance to temperature influences, it is processed under high pressure. This leads to the formation of additional molecular bonds . This processing method is called *cross-linking*, which is why polyethylene is called cross-linked polyethylene.
Due to the three-dimensional molecular bonding in the structure of polyethylene, there are a number of advantages compared to traditional metal pipes. Three-dimensional molecular bonding increases the resistance of pipes to thermal deformation, abrasion, scratches, shrinkage, and cracking due to internal stress.
When choosing REX pipes, you should pay attention to the degree of crosslinking . The standard requires a certain degree of cross-linking, at least 65%, ranging from 65% to 80%. The stitching method affects the service life and technical characteristics, as well as the cost of the pipes.
There are three methods for producing cross-linked polyethylene, which affect the degree of cross-linking.
- Pyroxide (REX - a) - pyroxides are introduced into polyethylene. The degree of crosslinking is up to 85%.
- Silane (REX - b) - organosilanides are added to polyethylene. The degree of crosslinking is at least 65%.
- Radiation (REX - c) - degree of crosslinking 60%.
If the degree of crosslinking is 0%, then the pipes become too brittle and prone to cracking. Too little stitching can have equally serious consequences.
Pros of REX pipes
REX pipes have a number of advantages :
- low noise level of pipes due to its flexibility and ability to absorb pressure surges;
- ease;
- ease of installation;
- have *shape memory* , can easily restore their original shape;
- corrosion resistance;
- durability , operation is designed for a period of at least 50 years;
- resistance to freezing in cold weather;
- flexibility;
- minimal probability of *explosions* after defrosting the system;
- withstand high temperature and pressure changes.
XLPE pipes are affordable .
REX pipes are installed using specialized fittings. This allows you to significantly reduce hydraulic losses in the pipeline. The life of the underfloor heating system is increased because fewer fittings are used at kinks, which reduces the risk of leaks and costly repairs in the future.
What to choose
The answer to this question depends on the criteria that will be a priority for the owner:
- Based on the technical characteristics, we can conclude that for floor insulation in an apartment building it is better to use metal-plastic products - they are more resistant to operation under harsh conditions of pressure and temperature differences.
- When installing it yourself, it is also better to pay a little more for metal-plastic, but make the installation work easier for yourself.
- Cross-linked polyethylene will serve faithfully in an individual home. Even if you forget to drain the water and the system freezes, there will be no problem, the quality of the pipes will not suffer.
- A limited budget with professional skills will also allow you to choose more economical polyethylene.
Both materials are guaranteed to last at least 50 years, withstand the average operating parameters of a heating system on a water circuit well, and do not differ critically in cost.
Metal-plastic pipes (MP) and cross-linked polyethylene (PE) pipes are mainly used for underfloor heating and radiator heating systems, but they are also quite widely used in water supply systems. Both types of pipes have earned their widespread use due to the reliability of their operation; the service life of both polyethylene and metal-plastic pipes reaches up to 50 years.
But, each of the presented pipes has its own pros and cons. Now we will take a closer look at each of these pipes, tell you about the strengths and weaknesses of each of them and find out where and how best to use this or that type of pipe.
Polypropylene pipes, PPR or PPRS
The teams that practice installing these particular hoses are popularly called ironers or ironers. The material is considered consumer goods, that is, widely consumed by the people. A crash test of the PPR pipe showed that it explodes at 40-50 bar. By comparison, metal-plastic breaks already at 40 bars. So the offensive word “consumer goods” shows why people love PPR water supply so much. Cheap and good pipe.
How long will it last?
Under normal conditions, in cold water and a pressure of 2.5 - 4 barr, all materials work the same, with a 50 year guarantee. But polypropylene is also used in heating and underfloor heating, and this temperature is already 45 degrees, and if in radiators, then up to 70-90 degrees. Accordingly, the hotter it is, the shorter the shelf life. In radiators, polypropylene pipes last 15-20 years, and even less at high constant pressure.
Installation features
Unpleasant moments: when connecting, soldering is used and many polypropylene manufacturers produce sagging at the cut site; nozzles and adapters do not always fit perfectly, so additional noise occurs during operation. Although plumbers joke that some people even find the sound of water soothing.
Disadvantages of PPR:
- It is believed that polypropylene is obsolete, and it is not comme il faut for professional construction companies to work with polypropylene.
- Large linear extension. For unreinforced pipes, the coefficient of linear expansion is 0.15 mm/mS, for reinforced pipes - 0.03 mm/mS. This means that when used in a heating system, PPR will stretch and sag 5 times more than metal-plastic. Accordingly, apply a load at a different angle to the connecting parts and begin to leak. This is not covered by the warranty and is considered a violation of technical specifications. The master's secret may be to use short sections or supports under the pipeline, which compensates for linear expansion.
- Lots of joints. And this is almost the main disadvantage of PPR pipes. After all, most of the joints are hidden. And that’s why, when answering the question of which plastic pipe is better, I want to place PPR in the very last place.
Conclusion: excellent for regular plumbing in a city apartment.
Do-it-yourself pipe installation
Installation of plumbing and heating systems made of cross-linked polyethylene can be easily done independently. Below is a step-by-step description of the technology for assembling systems from pipes and fittings - simpler and not requiring special skills and equipment.
Required tools and materials
To assemble cross-linked polyethylene pipelines yourself, you will need:
- special scissors for cutting workpieces or an angle grinder (“grinder”) with cutting discs;
- a hammer drill or electric drill for punching holes in the walls;
- calibrator;
- round file with fine notch;
- To install compression fittings, you will need two adjustable wrenches;
- For the pressing method, you will need a manual mechanical press to crimp the fittings.
Drawing and diagrams
It is better to start preparing any work with a design drawing a plan with the exact dimensions of future systems and indicating the connection points for faucets, machines (washing and dishwashing), meters, water heaters or heating units. The plan will help determine the required number of pipes and components.
Work order
Before starting work, it is necessary to prepare tools and materials, cut the pipe into blanks, clean the ends of the blanks from dirt and debris, and remove burrs with a file.
Connecting pipes using compression fittings is done in the following order: unscrew the compression nut and put it on the pipe; insert the workpiece into the fitting; tighten the nut by hand. Then, using wrenches, tighten the nut: one and a quarter turns for pipes with a diameter of up to 25 mm, one turn for pipes with a diameter of 32 mm.
It is convenient to hold the fitting body with one key and rotate the nut with the other.
Assembly using the pressing method is carried out in the following order:6
- Place a crimp ring on top of the end of the workpiece - a press sleeve;
- Insert the inner fitting of the fitting body into the tube;
- put hand press clamps on the sleeve;
- squeeze with force until the press handle stops. Release and remove - ring dents from the press should appear on the sleeve.
Installation video
Our video will help you see all the nuances of assembling pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene:
Installation features
You cannot use the compression assembly of the system when installing a heated floor - this is the least durable connection. Before pouring the screed, be sure to fill the system with water under pressure and check for leaks.
It is quite possible to bend the workpiece by hand. To do this, you should heat it up using a hair dryer, place it in a mandrel made from boards, plywood or other available materials, and let it cool completely. You can use a pipe bender or a Volnova machine.
XLPE pipes
These are thermoplastic hoses, which, when produced in the CIS countries, must comply with the technical specifications of GOST 32415-2013 “Thermoplastic pressure pipes and connecting parts for them for water supply and heating systems.”
It easily holds 95 degrees and high pressure, is chemically resistant, even gas can be passed through it without leakage. They do not conduct electric current - at the dacha you can safely use the remaining piece to insulate the cable. The polyethylene material is perfectly smooth, which prevents salt deposits and dirt from lingering and accumulating.
Performing the stitching process
The crosslinking process is aimed at eliminating one of the main disadvantages - thermoplasticity. The output is polyethylene, which remains flexible but does not deform at temperatures above 80 degrees.
Note! Due to the fact that the basis of the cross-linked polymer is pure carbon, when exposed to temperatures above 400 ºС, the material will begin to melt.
Technical parameters of the product depend on the chosen method of obtaining cross-linking:
- silane;
- peroxide;
- electron beam.
In the first method, a substitution reaction occurs using silane (a reagent). The second method is characterized by preliminary mixing of raw materials and inhibitor, and the crosslinking process is carried out under pressure. The third direction uses irradiation, under the influence of which the formation of additional bonds and substitution occurs.
Video
One example of how to replace a section of a metal pipe with a polypropylene one. Using the same principle, it is possible to connect plastic pipes from different materials:
In these photos you can see how else it is possible to connect plastic pipes:
There are often cases when, while manufacturing a pipeline, one has to face the problem of connecting pipes from different materials. In this article we will look at how to connect a HDPE pipe to a polypropylene pipe.
Some structural features
Conventional non-crosslinked material is produced under low pressure when catalysts are present. It has large polymer molecules with side branches. Most of them are in some kind of free “floating” in the space between molecules. Cross-linking allows you to achieve lateral bonds that create an intermolecular network. As a result, it is possible to obtain a particularly strong structure, which has the appearance of a crystal lattice of solids.
When different cross-linking techniques are used, the result is a substance with a certain number of bonds, indicating greater or less impressive strength. Some versions of cross-linked polypropylene are obtained in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and have the highest percentage of cross-linking, which can reach 85%. The most common and applicable in a wide range of products is silane polymer, which has a 70% bonded structure.
Cross-linking will be 60% if the technology provides for a radiation manufacturing method. In the presence of nitrogen, a material is created with rather complex reaction conditions. As a result, it is possible to achieve the same 70% cross-linking. Cross-linked polypropylene with a high percentage of cross-linking is more expensive and has the greatest crack resistance, high melting point and impressive impact resistance. This cross-linking makes it possible to achieve higher hardness and less ductility of products, which does not mean high quality, but allows you to obtain various materials that will have their own purpose.
Reviews on the use of material for household needs
A warm floor made of cross-linked polypropylene, according to home craftsmen, will be a highly efficient system. Such pipes are considered today the most modern choice, since their characteristics fully meet the requirements. Among the disadvantages here, according to buyers, one can note only low flexibility, due to which the products do not hold their shape well during installation.
Cross-linked polypropylene is also used quite often for heating. However, here, as consumers emphasize, problems may arise due to the oxygen permeability of the material, which may cause the activation of corrosion processes on structural elements. Therefore, for heated floors, for example, experts advise using pipes with diffusion protection.
Combination couplings
While the collet connection for HDPE pipes is clear, the combined couplings (fittings) for polypropylene pipes are varied. Let's take a quick look at them:
- A coupling with an internal thread helps to connect a pipeline with another type of pipe or devices that have an external thread. It consists of a polypropylene blank with an iron coupling pressed inside, on which a thread is cut.
- A male threaded coupling performs the same functions as discussed above. The only difference is that a metal sleeve with external thread is pressed into the polypropylene blank.
- A coupling with a turnkey internal thread is made up of a polypropylene blank into which an iron sleeve is pressed, supporting the edge of the polypropylene with iron edges. The edges are designed for an open-end wrench. The edge is threaded. It is convenient to screw such a bushing onto another thread with a wrench. In addition, there are models of couplings with turnkey edges.
- A coupling with an external thread on a turnkey basis is the same as the coupling outlined in paragraph 3, only it has an external thread.
- A detachable coupling with internal thread is made up of two iron parts under an open-end wrench. Moreover, one iron part is connected to a polypropylene blank. Such couplings are installed in places where it is necessary to disconnect the pipeline or remove devices. Another name for this coupling is American. It unwinds with two keys.
- The detachable coupling with external thread is similar to the previous American type. The only difference is the external thread instead of the internal one.
- The coupling with a union nut is made up of a polypropylene blank into which a fitting with a turnkey union nut is pressed. It is installed in the same way as the American one: in the places of the required pipeline connector.
Combination couplings
While the collet connection for HDPE pipes is clear, the combined couplings (fittings) for polypropylene pipes are varied. Let's take a quick look at them:
- A coupling with an internal thread helps to connect a pipeline with another type of pipe or devices that have an external thread. It consists of a polypropylene blank with an iron coupling pressed inside, on which a thread is cut.
- A male threaded coupling performs the same functions as discussed above. The only difference is that a metal sleeve with external thread is pressed into the polypropylene blank.
- A coupling with a turnkey internal thread is made up of a polypropylene blank into which an iron sleeve is pressed, supporting the edge of the polypropylene with iron edges. The edges are designed for an open-end wrench. The edge is threaded. It is convenient to screw such a bushing onto another thread with a wrench. In addition, there are models of couplings with turnkey edges.
- A coupling with an external thread on a turnkey basis is the same as the coupling outlined in paragraph 3, only it has an external thread.
- A detachable coupling with internal thread is made up of two iron parts under an open-end wrench. Moreover, one iron part is connected to a polypropylene blank. Such couplings are installed in places where it is necessary to disconnect the pipeline or remove devices. Another name for this coupling is American. It unwinds with two keys.
- The detachable coupling with external thread is similar to the previous American type. The only difference is the external thread instead of the internal one.
- The coupling with a union nut is made up of a polypropylene blank into which a fitting with a turnkey union nut is pressed. It is installed in the same way as the American one: in the places of the required pipeline connector.
With such combined couplings, soldered to a polypropylene pipe, it is easy to connect to a HDPE pipe, which has a collet with a similar thread.
Negative features and reviews about them
According to consumers, the described material also has its drawbacks. For example, cross-linked polypropylene exhibits low resistance to solar radiation. If ultraviolet radiation is exposed to pipes for a long time, the material will begin to deteriorate and become brittle.
Buyers also emphasize that polypropylene is destructively affected by oxygen if it penetrates into the molecular structure. However, these problems can be eliminated by protecting products or adding special substances at the product creation stage.
Types of HDPE pipe connections
The HDPE pipe has approximately the same connection devices. The most popular is the collet connection. To connect pipes, a coupling is used, in which there is a collet on one side and a thread on the other. To fasten the coupling, the clamping nut is unscrewed and put on the HDPE pipe. The collet is inserted inside the pipe, the clamping nut is put on and tightened well.
Advice! The clamping nut must not be pressed too hard, otherwise it may burst or the collet will crush the edge of the pipe.
After completing the connection of the collet, it is possible to screw another threaded pipe onto the other edge of the threaded coupling to the same diameter.
Specifications
Cross-linked polypropylene is not inferior in its characteristics to many solid substances, and some varieties are superior to them in resistance to destroyers and long service life. The density of the material is 940 kg/m3. Combustion occurs at a temperature of +400 ˚С, while the material decomposes into water and carbon dioxide. The melting point reaches +200 ˚С.