- The first step is to develop a diagram.
- Load-bearing beams are installed and sheathing is laid on them.
- The roofing material is attached to the latter.
- Next comes the installation of wooden sheathing and rafters (metal ones are also used, this will extend their service life).
From the outside the building looks traditional, but inside it feels cozy, warm and reliable. Look at the photo below. Isn’t it a beautiful view of such a two-story house with a picturesque balcony?
Hip roof
The unusual name of a hip roof should not confuse you. This variety is a hybrid that combines trapezoidal and triangular shapes. This creates a hipped roof. The transition from one shape to another gives originality, not to mention the practicality of using additional space. A skillfully created individual project will allow you to combine unusual design with functionality. For example, on the second floor there is an attic floor, a playroom for children or an additional guest bedroom with a small open balcony or loggia. By the way, the use of an attic will make it possible to reveal the potential of a hip roof.
If there is no gazebo on the land, this is compensated by a veranda. On a hot day, the cornice will protect guests from the sun, on an autumn day - from the wind and possible precipitation. A design solution would be to place the chimney as one of the walls on the balcony. This will insulate the room on a cool evening.
Roof covering
The choice of roof type is based on economic and individual (aesthetic) considerations, and also depends on the angle of the roof slope. For example, for soft roofs stability is not guaranteed at slopes greater than 45°.
Today, the most common building materials on the market are:
- ceramic tiles;
- metal tiles;
- corrugated sheeting;
- bitumen slate (ondulin);
- folded sheets;
- roll bitumen roofing.
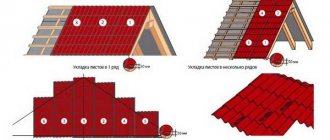
Installation methods vary depending on the material chosen, but in almost all cases the roof is laid from the eaves to the ridge to ensure sufficient overlap and protection from precipitation. Also, the fasteners used must be made of galvanized or stainless steel materials and equipped with an elastic sealing washer.
Comparison of roofing materials - table
Half hip roof
The half-hipped roof option is becoming popular (it gives the building the appearance of a large mansion). The peculiarity is the combination of hip and gable. As a result, we see an original and practical form. Buildings of this type are common in regions with strong winds and harsh climates. The streamlined shape perfectly resists bad weather, the space on the upper floor is used both for utility purposes and as an additional living space. Thanks to the unique angle of the roof, the room will look unique, and with skillful selection of design, even better. Brickwork and a massive wooden porch will give the house the appearance of a country cottage.
When choosing a half-hip roof, be prepared for difficulties, because building this structure correctly is quite difficult and only an experienced team can do it. In addition, due to the large number of beams and partitions, the building acquires significant weight. Therefore, it will be necessary to calculate the additional load on the foundation. All this entails considerable material costs.
Cladding materials
The use of one or another type of material for roof cladding is determined primarily by the climatic characteristics of the region. Even the traditional “issue price” often gives in to common sense - no one has ever managed to save on the quality of a roof. The most popular materials are traditionally:
Roof tiles (metal, bitumen or ceramic)
- Metal shingles are a popular option valued for their durability, low price and ability to withstand impacts, which is especially valuable during loading and transportation. Metal tiles are lightweight (does not create pressure on the foundation) and are easy to attach. The disadvantage is considered to be uneconomical installation (a significant percentage goes to waste) and poor sound insulation, which becomes noticeable in any rain.
- Bituminous (flexible) tiles. This coating has high sound and heat insulation, but requires professional installation.
- Natural (ceramic) tiles. A time-tested material with the advantages of metal tiles, except one. Significant weight requires a reinforced roof.
The tiles can be laid on any roof shape Source dnolchare.blogspot.com
Slate
Slate is the most affordable material containing up to 15% asbestos. This limits its scope of application to commercial buildings. Slate has great strength during bending and impact; it is non-flammable and easy to process (cut with a grinder). The disadvantages are fragility, high hygroscopicity (over time it can become covered with moss) and a health hazard.
Glass roof
A glass roof (especially its spectacular panoramic version) attracts with many advantages. In addition to the original appearance, this design provides excellent weather protection and helps reduce energy bills. The main disadvantage is its cost, including the complexity of design and installation. In addition, in summer the room turns into a greenhouse, and in order not to look sloppy, the glass roof needs regular cleaning.
Green roof
Growing attention to environmental issues has generated interest in the green roof. Modern technical solutions developed in Scandinavian countries make it possible to realize the desire to communicate more often with nature.
Timber frame with eco-roof Source pinterest.com
During installation, layers of hydro- and thermal insulation with a waterproof membrane are laid on the roof, protecting the roof from roots. Then a drainage layer is formed and, finally, a vegetation layer (soil) on which plants can be planted.
An eco-roof serves not only as a decorative element. It maintains a stable microclimate in the house, protects against noise and reduces the load on the sewer system (by absorbing rainwater). At the same time, significant expenses on organization and time for subsequent care are inevitable.
Another option for a “green” roof Source pfpi-co.com
Hip roofs
The hip roofing system involves a hip roof. It is usually used in square houses or similar configurations. 4 triangular slopes are used, which are connected in the center. The triangles must be isosceles (if you look from above, you should see 4 identical triangles inscribed in a square). The origins of such forms go back to ancient civilizations that used the hut. In the Middle Ages, the tent system was common in the construction of palace complexes and castles, where the structures were like a steep slope. Nowadays, it has become popular to erect a square roof not only on private low-rise buildings, but also in cottages and gazebos.
This coating perfectly resists strong winds and the penetration of precipitation into the room thanks to its drainage system. Tall narrow windows with a low-slung house will create the impression of privacy.
Despite the apparent simplicity, the work should only be carried out by a professional team that can properly insulate the connections of beams and rafters. Therefore, the money saved on a small amount of materials will have to be spent on another expense item. In addition, you need to plan for a lot of waste when using most roofing materials, especially metal tiles.
How to calculate the angle
The slope of the slope is used when calculating the elements of the rafter system. It is defined in degrees or percentages, so you need to do some math.
A gable roof in cross-section is an isosceles triangle (if the slopes are the same). It can be conditionally divided into 2 right triangles. One of the sides H is the height to the level of the ridge, the other L is half the span of the house. They are measured against the finished walls and gable. It is necessary to calculate the length of the rafter B, which can be found based on trigonometric formulas.
Tangent of the slope angle relative to the horizontal:
tgα= H/L
Using the Bradis table or using an engineering calculator, we find the corresponding angle value in degrees. For example, the roof height is 3 m, the width of the house is 9 m, half the span is 9/2 = 4.5 m.
tgα=3/4.5=0.6667
This tangent corresponds to an angle of 34°, that is, the roof has an average slope. You can use the cosine function and calculate the length of the rafter as B= L / cos 34° = 4.5/0.829 = 5.42 m.
Also, information about the angle of inclination is needed to navigate roofing materials.
To calculate the length of the rafters (and check), you can use the second method - the Pythagorean theorem:
B²=H²+L²= 9+20.25=29.25, from where B =√29.25=5.41 m is the length of the rafter (without overhang).
To prevent precipitation from getting on the walls, you need to add at least 40 cm for overhang. We obtain for our building a minimum rafter length of 5.81 m with a slope angle of 34°. For convenience, you can take B = 6 m, which corresponds to a standard board.
Mansard roof
The roof under which the living space is located is called an attic. The second name is French. Its shape can be different, but most often it is a variation of a gable roof. For ease of living, the slope line is most often made as a broken line. The design becomes more complicated, but using the space as a living room is more comfortable and practical. A new fashion trend is an additional complication of the coating using concave and convex lines.
If you are interested in such a design due to the reduced cost of construction, then you can’t really count on it. Making a regular pitched roof is much easier. The attic needs to be additionally sheathed with waterproofing, insulation, ventilation outlets, and windows on the façade of the building. Combining a beautiful and convenient option will not be cheap. If you nevertheless decide to build such a roof, then try to make the slope as soft as possible - this will make the building visually more beautiful. The color of the tiles is traditionally burgundy (looks elegant). To complicate the design, you can build in a bay window.
Reconstruction of an old barn into a private one-story house with a gable roof
Conceived as a modern 4600 sqm barn. – This four-bedroom stone and wood family residence sits atop a hilltop in the countryside near Rhinebeck, the culinary epicenter of the Hudson Valley.
“We all like living in a barn. We love the barn's generous interior space, the exposed structure, all that wood. But we don’t like the lack of light, isolation, and comfort. Or dirt! “says the architect of the house.
The form of the local barn - its simplicity and honesty in structure, its form and materiality led to the design process. Research has led to a rich history of local barn archetypes, ranging from the mid-17th century Dutch barn to the English barn.
Research into these archetypes suggested a house design including:
- strong pediment shape,
- cathedral ceilings with attic spaces,
- large sliding doors,
- wooden interior and exterior,
- exposed structural hardwood frame and stone basement.
Similar to traditional barn building events in the region, the double height bent frames were lifted and bolted in place and the entire timber structure was completed in 1 day. To update the barn to 21st century standards, the home uses super insulation. Airtight membranes, in-wall heat exchange ventilation units and triple glazing to provide a comfortable indoor environment with constant fresh air all year round.
Windows and doors are positioned to promote cross ventilation. Heating can be provided by fireplaces and wood stoves or energy-efficient air conditioning systems with multiple heat pumps. All appliances are electric. LED lighting. Daylighting is provided by several skylights. The home features North America's longest residential single-story triple-glazed Passive House certified skylight. Sunshades tilt upward to provide south-facing shade in the summer and close to act as hurricane shades during winter storms.
Endemic tree species on the 120-acre site dictate the choice of materials for the single-story home's interior: white oak for flooring and siding, walnut for millwork, hickory for decorative units. Local granite, slate and domestic stone quarries are chosen for fireplace hearths, wet rooms and foundation masonry respectively. The entire house is clad in wood, including the roof, thanks to a unique, innovative clamping system for the seams of the single-story roof sheeting.
The fully glazed entrance is level with medium sized pine trees. A skylight and a central staircase divide the house between public and living areas. The private areas have varying views of distant hills, a meandering river, nearby forests and wildflower meadows. The living areas feature large sliding glass doors on the verandas, providing wider 180-degree vistas. Upstairs is a bright, multi-purpose white loft space with skylights specially designed for optimal stargazing. Fortunately, an ordinary gable roof of a one-story house provides such opportunities.
Multi-pincer
A special feature of this type of roof is its complicated design, which combines several intersecting slopes to form valleys and internal corners. This form is one of the most difficult, and not every professional team of builders can cope with it. The endova requires particularly careful design, since it is it that will bear the main load during precipitation. The finishing in this area must have reliable waterproofing also because fallen snow will accumulate in these areas.
This design is in demand in cases where the building has an atypical layout and shape, as well as with a multi-level roofing system. This form looks aesthetically pleasing and attractive. But don't try to build it yourself. Firstly, it is necessary to perform all calculations correctly and accurately. Secondly, scrupulousness, patience and professionalism will be required when implementing the plan. Thirdly, when implementing the project you will face considerable financial costs: a large amount of material will be required. If the work is done efficiently, no problems should arise during operation.
Dome and conical
Lovers of everything unusual will certainly pay attention to the domed roof. On the one hand, it is original. It is unlikely that you will see many round roofs on your street, and their shape can be varied. On the other hand, it is functional and practical. The attic space is used rationally, and there are unlimited opportunities to fill the room with light as much as possible by installing a large number of polycarbonate windows. Standing under the dome and looking through the window at the sky is amazing.
One of the types of dome roof is conical. At its base there must be a circle that tends upward to one point. This building looks extravagant, somewhat reminiscent of ancient ethnic buildings. This solution is quite rational: precipitation does not accumulate on the roof, but immediately flows down, and the wind resistance is excellent. The use of the attic space is possible for different purposes: household needs or a living room. In any case, the usable area of the house will expand.
Multi-level roofs
Another type of roof with two slopes. To understand what we are talking about, look at the photo below.
Multi-level gable roofs Source moscow.sk-evrodom.ru
According to its configuration, the roof is gable and covers the entire house. But individually, each slope is a single-slope structure. Usually a load-bearing wall is erected between them, on which both slopes rest.
But at the same time, the larger slope rests on the upper end of the wall, where the ridge beam or mauerlat beam is installed, and the smaller one on its vertical plane, where the load-bearing beam is usually fixed. The construction of such roofs is carried out using the technology of a single-pitched structure.
Pagoda
This is a special Buddhist religious building. It is believed that everything in life happens cyclically, as if in a spiral. This principle was reflected in the design of the first pagodas. The building has the shape of a tower, in which several tiers rise above each other. Each of them has its own roof. At the top, the tiers become smaller, so when there is precipitation, water flows down freely. The material used can be wood, metal or brick.
Slopes of different lengths: for additional extensions
Yes, such a roof looks unusual. But this design has a huge advantage in that for the same gazebo, garage or pool there is no longer a need to build a separate roof or canopy. This is a considerable saving, you see, and also an attractive, memorable design.
The essence of this type of roof is that it has one slope noticeably longer than the other.
Moreover, in terms of construction there is nothing complicated here:
Bubnovaya
The Sudeikin roof (or tambourine) is a historical version of the roofing system. In the structure, beams are located in a certain sequence and places, which form an octagonal dome. A pillar is installed in the middle of the attic, which is the only support. The sediment drainage system is effective due to the steep descent; the presence of the attic provides an effective air layer that retains heat.
With and without an attic: we exchange trash for valuable meters
In fact, what is stored in the attics of ordinary private houses? Of course it's rubbish! And all over the world it has long become fashionable to abandon such a part of the roof in favor of a cozy attic or a real second floor, only with slightly sloping walls. And the attic itself, in its more correct concept as a space for under-roof ventilation, remains, however, under the very covering.
But all this applies only to residential buildings. But for a real Russian bathhouse, it is extremely important to create an air gap between the steam-hot ceiling and the top roofing. Otherwise, in winter the snow on such a roof will constantly melt, and then freeze and hang in icicles. That’s why there should be an attic in such buildings!
Combined roof
A combination of different types of roofs is used in two- and three-story (or more) houses that have an extension to the house in the form of a garage, outbuilding or other non-residential premises. The levels of such a roof vary, so there is a need to arrange transitions. Only an experienced architect can complete such drawings, who will describe all the points in detail. The construction technology is also “star-studded”, so attracting an experienced team of professional builders is a necessity, not a luxury.
Video description
See the following video for interesting types of roofs of private houses:
And also original types of house roofs in the photo:
Symbiosis of a flat and pitched roof of a high-tech style house Source viendoraglass.com
Interesting design solution for a pitched roof Source remontbp.com
A window in the attic was once a complex technical task Source superdom.ua
The absence of a ceiling visually enlarges the room Source music4good.ru
Conical and pitched roofs on one house Source cosmictherap.com
The production of such structures should be trusted exclusively to professionals Source horodom.cx.ua
Combined multi-level roof Source weareart.ru
For such beauty to remain functional, careful calculations are required Source roofcostestimator.com
Classic solution for a two-story house Source za.pinterest.com
In such a design, it is very important to correctly make the points where the roof of the first floor meets the walls. Source houzz.com
Finishing and insulation of different types of roofs
Pitched roofs can be decorated with almost any cladding material. Slate, metal tiles, ondulin, corrugated sheets, seam roofing - the choice depends on the budget and design features. The most expensive in this group are ceramic and slate tiles. These materials justify their price due to their high quality and are used in luxury buildings. The most affordable are corrugated sheets and ondulin. They are not attractive or particularly durable, but there are situations when this is not so important. The optimal solution for finishing the roof of houses with an attic is metal tiles. It has an excellent balance between price and quality.
The insulation of residential and non-residential attics differs significantly: in materials, in the technique of performing work. To summarize, we can say that the main insulation materials in our time are polystyrene foam or mineral wool. The first option has superiority in price. But using it can lead to the formation of a greenhouse effect - the material allows steam to pass through. As a result, the moisture does not leave, and the temperature rises. This promotes the growth of mold and other harmful microorganisms. This will not happen with mineral wool. It retains heat perfectly, allows steam to pass through, and the walls “breathe.” Pay attention to proper waterproofing: if it leaks, the wet insulation will become unusable, so you will have to do the repairs again.
Any house, be it frame-panel or aerated concrete, requires competent and reliable roofing. When choosing it, you should not be guided only by appearance. The roof must be functional. Even in a rustic chalet, you can equip a small staircase along which you can climb to the attic or attic, look at the stars or dream about the future. Think carefully about what exactly you want to see in the end.
Installation of the rafter system
The rafter system is the basis of the entire roof and the strength of the future structure depends on its configuration. According to the principle of structure and nature of application, the support frame differs into two opposite types: hanging and layered .
- Hanging rafters . They rest only on the outer walls of the building, and the triangle-shaped truss remains in a hanging position. Used for lightweight structures.
- Layered rafters . They rely both on the external walls of the building and on the internal ones. The rafter legs “lean” onto the racks, and they, in turn, rest on the bed, which lies on the internal main wall. Used for large and heavy structures.
The functionality and stability of the entire roof depends on the correct choice of the rafter system.
Attaching the rafters to the mauerlat
In private construction, rafters are attached to the mauerlat in the two most common ways: rigid and sliding connections.
In brick and stone houses, the rafters are fastened to the mauerlat in a rigid way using a mortise and non-mortise connection . In the first case, tight fixation is achieved by creating a gash in the rafter leg, and in the second, a support beam is used that supports the beam from the reverse side. These are the most labor-intensive, reliable and universal fastening methods - applicable for both layered and hanging rafter systems.
Slip joints are most often used in timber structures because they exhibit the greatest shrinkage. The rafters are fastened using “floating” fasteners - slides, which avoids deformation of the roof when the position of the upper row of beams changes.
Fastening the rafters in the ridge
Today, only three main methods of installing the upper part of the rafters are actively used:
- Overlapping . In this case, half the cross-section of the adjacent elements is cut out to create a groove and a hole is prepared for the bolted connection.
- Butt . The upper ends of the beam are cut to obtain an ideal vertical joint, and metal plates or wooden linings (notches) are used as fastening elements.
- For a run . The rafter legs are laid close to each other and connected directly to the support beam.
How to strengthen the system?
In order to strengthen the roof frame with a span length exceeding 6 m, it is necessary to reduce the free span of the rafters. This can be achieved by creating an additional horizontal support beam (beam) on the internal load-bearing wall and installing inclined posts.
To add additional rigidity and to reduce the expansion of the rafters, tie-downs are used. They are attached to both sides of the rafter beam using self-tapping screws, nails, and studs at a distance of approximately 1/4 from the top.
To prevent the created frame from being torn off by a strong gust of wind, the rafters themselves can also be attached to load-bearing walls. To do this, twists based on two wires with a diameter of 4 mm are used - they are wrapped around the legs, and then connected from the inside and fixed with an anchor at a distance of 4-5 rows before the cut.
If you are not sure about the reliability of your structure, we recommend not only reading the step-by-step instructions for building a house roof with your own hands, but also contacting specialized specialists.