Have you thought about installing water heating in your home? It is not surprising, because a single-pipe heating system for a private house can be traditional and completely energy-independent or, on the contrary, very modern and fully automatic.
But you still have doubts about the reliability of this option - you don’t know which scheme to choose and what pitfalls await you? We will help clarify these issues - the article discusses schemes for arranging a single-pipe system, the pros and cons that await the owner of a house with such a heating system.
The article is provided with detailed diagrams and visual photographs depicting individual elements used in heating assembly. In addition, a video has been selected with an analysis of the nuances of installing a single-pipe system with heated floors.
General information about single-pipe heating schemes
The main areas of application of single-pipe schemes are houses of different heights with a small number of radiators in one circuit. For example, in high-rise buildings no more than three radiators per floor extend from the riser. In the private sector, such systems are most effective in one- and two-story private houses with an area of up to 150 m2.
Advantages and disadvantages
You can choose the right heating system only based on operating conditions, taking into account the positive and negative aspects of all types of construction.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Material savings and lower labor costs compared to two-pipe options | Uneven heating of radiators - the last batteries in the circuit warm up worse than the first (see photo below the table), since the coolant arrives to them already cooled |
| Compact – pipes are easier to hide in the floor or walls | Complex hydraulic calculations, requiring a thorough study of the methodology |
| Hydraulic stability, constant heat transfer of elements | Difficulties with arranging a gravity coolant supply circuit (without installing a circulation pump) |
| Low inertia - filling the lines requires less coolant, which warms up faster | Difficulty in balancing during commissioning - even with accurate hydraulic calculations, sometimes you have to adjust the system |
| Installation of thermostatic fittings on each radiator is allowed | |
| Shut-off valves and battery bypasses allow you to replace the radiator without stopping the system | |
| Simple design, accessible for self-installation with proper hydraulic calculations available |
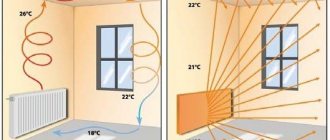
Cooling of the coolant when moving through a single-pipe heating system.
The negative aspects can be minimized by installing radiators with a large number of sections at the end of the circuit, mandatory installation of bypasses, and dividing the system into several branches.
Design Features
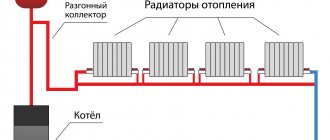
The main distinguishing feature of single-pipe wiring is that all batteries in the circuit are connected in series, and the outlet pipe from the previous battery is connected to the input of the next one. After the last radiator in the circuit, the coolant returns to the boiler.
A pictorial diagram of a typical single-pipe heating system.
In a more competent system, a jumper (bypass) is installed of each
Scheme of a single-pipe heating system with bypass.
It allows:
- balance the system, achieving approximately equal battery temperatures;
- turn off the radiator in case of malfunction or accident;
- regulate the temperature - even with minimal opening of the thermostat tap, the coolant will flow into the next convector.
Heating systems are classified according to several criteria:
- contact between coolant and indoor air – open and closed;
- method of organizing coolant circulation - natural, forced, combined;
- type of coolant supply to radiators - top or bottom;
- layout - horizontal or vertical.
Each of the characteristics and their combinations affect the heating efficiency under specific operating conditions.
Rules for installing double-circuit equipment
Modern double-circuit boilers are equipped with an automatic safety system that controls the heating level and maintains a comfortable temperature in the house. This is a real home boiler room, and its power is enough to provide full heat in the house and a sufficient amount of hot water. At the same time, this is a rather complex device, so it is not immune to breakdowns.
Double-circuit gas equipment
Everyone knows that natural gas requires very careful handling and strict adherence to safety precautions. Basic rules that must be followed when installing any boiler:
- To install the boiler, you need to allocate a separate room (it is often called a furnace or boiler room), and its area must be at least 4 square meters. The boiler room must have at least one window and a sufficiently free doorway.
- When finishing the boiler room, flammable materials must not be used.
- It is necessary to ensure sufficient air flow into the room, for which a through, non-closable vent is installed.
- A separate flue is equipped for the boiler exhaust. It is unacceptable to use the home ventilation system for this, since combustion products can enter the living rooms.
- The outlet of the flue rises above the level of the roof ridge by at least a meter.
- A durable sheet of metal or other non-flammable material with an area of at least one square meter is placed on the floor under the boiler.
- The heating system must withstand pressure testing of at least 1.8 bar.
So, the rules are quite strict, but you can’t joke with gas. If you plan to install this particular type of heating equipment, then you need to strictly follow all the instructions of the specialists.
In a private house, a separate extension is often built for the furnace so that the boiler does not occupy the usable area of the house. It can be equipped with the latest technology, and your home will be absolutely safe.
Boiler room in a private house
Open and closed systems
As it heats up, the volume of the coolant increases. Excess fluid appears that must remain in the system. For heated coolant, expansion tanks are installed. Their volume is chosen at the rate of 10-15% of the total capacity of the boiler, pipes, radiators.
The design determines the type: closed or open.
Open type
Ready-made expansion tank for open-type CO.
In open versions, any container that is resistant to corrosion and temperatures of about 80 ° C is used as a tank. This can be a tank made of stainless steel or corrosion-resistant ferrous metal. The device is installed at the highest point, which prevents the coolant from leaking under the influence of the liquid column.
Important! Open systems are filled only with clean water. When antifreeze evaporates (boils), it releases dangerous or even toxic substances that can be harmful to health.
At the bottom there is a pipe for connection to the pipeline. A hatch is left at the top for adding water.
In other options, topping up the evaporated water is carried out by connecting to the water supply network (see diagram below) and organizing the drainage of the excess into the sewer.
Scheme of an open-type single-pipe system.
To prevent overflow and automatically remove air, the tank is often made airtight, and an automatic bleeder valve is installed in the upper part of the tank. This option is preferable if the tank is located in the attic and access to it is difficult.
Open system tank with automatic air vent.
Closed systems
Design of a membrane expansion tank.
In closed circuits, two types of sealed expansion tanks are used: with a diaphragm or balloon membrane.
Before filling the system, pressure is injected through the nipple in the air chamber to 1.5 atm. Then fill the system with coolant until the pressure gauge reads 1.8-2 atm.
Then the tank operates in automatic mode:
- When heated, the liquid expands.
- The pressure increases, and excess coolant enters the working cavity of the tank through the pipe.
- The separating membrane is elastic, so the working area increases. At the same time, the air pressure in the second compartment of the tank increases.
- After cooling, the coolant decreases in volume and the membrane, straightening under the action of compressed air, squeezes the coolant into the heating system.
There is no contact between the working fluid and room air, so in closed systems you can use any antifreeze and glycols approved by the heating equipment manufacturer.
In closed systems, the expansion tank can be installed anywhere, but preference is given to installation near the boiler: the tank does not spoil the appearance of living quarters, and maintenance is easier.
Scheme of a closed-type single-pipe heating system.
Principle of operation
The functioning of a single-pipe main is carried out by constant circulation of coolant through the branches of the system. As it moves from the boiler to the radiators, it releases heat and warms the room, and then returns to the original tank to repeat the cycle.
The coolant can be steam, antifreeze, air or water. The last option is the most common.
The operating principle of a classic heating system consists of several stages:
- The boiler heats the liquid, causing it to expand and create pressure in the pipes.
- The density of the coolant decreases and it loses weight.
- Cold, heavier water pushes the heated liquid upward. To ensure this process, the pipes coming from the boiler are always installed in the upward direction.
- Under the influence of the resulting pressure, gravity and convection, the liquid flows to the batteries and heats them up.
- Cooling down, the coolant returns to the heating source, repeating the process.
In gravity heating systems, a certain angle of inclination of the horizontal branches is required (per 1 linear meter - 2-3 mm) to ensure stable flow movement.
Heating water increases its volume, which creates hydraulic pressure in the system. But even a slight increase in pressure above normal due to lack of fluid compression can cause pipeline failure. To compensate for the pressure in such schemes, a special expansion tank is installed.
Coolant circulation options
In single-pipe networks, there are three ways to move coolant:
- gravitational;
- using a circulation pump;
- combined.
The option is chosen depending on the configuration of the house and wiring.
Gravity systems
In the case of constructing such networks, the laws of physics are used:
- Thermodynamics - a heated liquid is less dense (light), the greater the difference, the stronger the heating.
- Convection and gravity - light liquid in a closed circuit rises, displacing cooled liquid down.
Heating boilers are used for heating. The organization diagram does not differ from the scheme of an open CO with an expansion tank. Large-diameter pipes are installed in the lifting section (acceleration section), usually 2 times larger than the main distribution. The coolant is cooled in the radiators and enters the boiler.
(Repeat) diagram of an open-type single-pipe system.
Important! Gravity systems can only be open, the coolant is in contact with the air in the expansion tank.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Energy independence | Large pipe diameters to minimize hydraulic resistance |
| No expensive components - a sealed tank and pump | Complex hydraulic calculations |
| Reliability. Fewer parts means less chance of failure | Complex balancing and adjustment at the commissioning stage. |
| Can be used with a solid fuel boiler without a circulation pump | Long warm-up due to slow coolant movement speed |
There is a limitation on the use of gravity circuits - they do not work if the height of the house is more than 7-9 meters and the contour length is more than 30 meters.
Forced circulation circuits
(Repeat) diagram of a closed-type single-pipe heating system.
In closed and spatially distributed open heating systems, pumps are installed to circulate the coolant.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Suitable for long pipelines | Energy dependence |
| Fast warm-up after switching on | If the pump is turned off or broken, circulation stops |
| Easy installation, which does not take into account the slope angles of the connecting pipes | Without reliable power backup it is unacceptable to use with solid fuel boilers |
| Possibility to use different types of wiring | High costs to replace the pump if necessary |
The pump capacity is selected based on hydraulic calculations, allowing for a margin of up to 20%.
Important! Most of the pumps used are built according to the “wet rotor” design. The coolant lubricates and cools the electric motor. Based on this, the pump is installed in the rupture of the “return” pipe, where the coolant is in a cooled state.
Water or antifreeze should not be drained in the summer; the engine must remain filled.
Combined systems
In open types of heating, a combined method of organizing the movement of coolant is often used. To do this, set
Scheme of bypass organization in a single-pipe combined heating system.
There are several options for using the device:
- In mild frosts, when gravity circulation is sufficient to warm up the radiators, open the tap; in this case, the pump is not used.
- If there is insufficient circulation, turn off the tap and turn on the pump.
- When the power supply is turned off, circulation occurs through an open pipe without the use of a pump.
A bypass is required in systems with solid fuel boilers that cannot be stopped quickly. When circulation stops, the working fluid in the heat exchanger quickly heats up, boils, and an explosion due to increased pressure and destruction of the boiler is possible.
How to turn a single-circuit heating boiler into a double-circuit heating boiler?
You cannot make a double-circuit boiler from a single-circuit boiler. Therefore, either leave everything as is or change the boiler. But first of all, think about this type of boiler. Secondly, I know from personal experience that there are constant interruptions in hot water. That is, they turned on the water, but it didn’t immediately get as hot as the boiler, so you still have to drain the water. In winter, when someone bathes or just washes dishes, the heating turns off completely. This is a small minus. Even when a person is bathing and if you turn on the water in another tap, the water for the person who is bathing will start to run cold! Plus, if the water is hard, it will cause more scale; a boiler is better suited to this than a boiler. Gas is now more expensive than electricity. You can install a day-night meter, then using the boiler will become even more profitable. So think about it, maybe you’re lucky, on the contrary, that the boiler is separate and the heating is separate. The only negative is that the boiler takes up a decent amount of space, but it can still be allocated.
Vertical and horizontal wiring
When constructing networks, there are two options for distribution and delivery of coolant: vertical and horizontal.
Scheme of a vertical single-pipe heating system with upper and lower wiring.
The vertical type is installed in houses of two floors and above. In this case, the upper or lower coolant supply to the radiators is used.
For overhead wiring, a horizontal pipe with bends into each riser is placed under the ceiling of the last floor or on the technical floor. The flowing coolant warms up the radiators and collects in the return pipe.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low pipe consumption | Low coolant temperature in the radiators on the first floor |
| Easy to install | Mandatory installation of bypasses on each radiator so as not to stop heating when replacing or removing the battery |
| Applicability for gravity system | It is impossible to install individual heat metering devices in apartments |
| Possibility to hide pipes in the floor with bottom connections | Visible pipes with top connections |
| By installing collectors, you can organize a “warm floor” system |
Vertical wiring allows you to organize a gravity-flow open heating system, independent of the power supply.
Bottom wiring is used in modern multi-apartment and individual residential buildings with forced circulation of coolant. This allows you to hide pipes in the basement or basement, reduces installation costs, and does not spoil the appearance of residential premises.
Hiding the heating pipeline in the basement of the house.
The main disadvantage of this method, as with all single-pipe systems, is the cool coolant in the last radiators of the circuit.
Horizontal wiring is standard and simple; it is used mainly in one-story buildings or on each floor. In the latter case, collectors are installed.
Varieties
There are types - horizontal and vertical. The most common horizontal single-pipe heating system is for buildings with one floor. Liquid supply is realized through a common riser, in stages for each section.
An important advantage is simple wiring with a modest budget for expenses. As a negative point, we can mention air pockets and the inability to adjust the heat flow.
In a vertical single-pipe heating system for a building with two floors, to increase efficiency, it is necessary to provide the possibility of using a special pump. The liquid moves through a common riser into the batteries on the top floor, and then on the bottom. The same temperature level is maintained on all floors of the house.
Horizontal flow:
Vertical:
Leningradka
One of the popular and easy-to-implement schemes began to be widely used in Leningrad, hence the name. Its peculiarity is the way the radiators are connected - in series with bypasses for each battery.
Leningradka open type.
Leningradka closed type.
The scheme is suitable for open and closed systems, with natural and forced coolant circulation. The design can be implemented in vertical and horizontal layout.
Thus, Leningradka is a universal scheme for constructing single-pipe heating systems. It has all the described advantages, but its disadvantages limit its use in large houses.
Possible Solution! In branched networks, several heating branches are made with 3-5 radiators in each. For example, they separate the heating circuits of the first and second floors. For houses with a large area, it is more advisable to use two-pipe systems.
Dependent
This connection scheme, as a rule, provides for the presence of in-house heating points, often equipped with elevators. In the mixing unit of the heating station, superheated water from the main external network is mixed with the return water, thereby acquiring a sufficient temperature (about 100°C). Thus, the internal heating system of the house is completely dependent on external heat supply.
Advantages
The main feature of this scheme is that it provides for the supply of water to the heating and water supply systems directly from the heating main, and the price pays off quite quickly.
- subscriber input equipment is simple and inexpensive;
- heating systems can withstand large temperature changes;
- the diameter of the pipeline is smaller;
- the circuit reduces coolant consumption;
- low operating costs.
Flaws
Along with the advantages, such a connection also has some disadvantages:
- uneconomical;
- temperature control is significantly difficult during weather changes;
- overconsumption of energy resources.
Connection methods
Connection can be made in several ways:
- through direct connection;
- with elevator;
- with pump on jumper;
- with a pump on the return or supply lines;
- mixed method (pump and elevator).
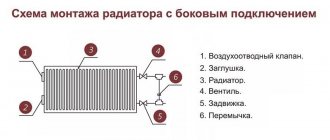
Methods for connecting radiators
The manufacturer indicates the preferred method of connecting radiators to the pipeline in the battery data sheet.
They can be divided into three types:
- diagonal;
- side;
- lower.
The diagonal option is the most effective in terms of heat transfer. However, in single-pipe systems, the method causes increased material consumption and does not look the best.
The side method is suitable for a vertical scheme, when the coolant enters the upper radiator manifold and is removed through the lower one.
For bottom connections, the radiator fittings should be located at the bottom of the device; such products are 10-20% more expensive.
The lower connection reduces the radiator performance by 15-20%, this must be taken into account when calculating the system. At the same time, the bottom connection allows you to hide the wiring as much as possible by pouring pipes into the floor or leading them out through the ceiling of the lower floor. How to actually choose the cheapest heating radiators on the market
Understanding the popularity of aluminum radiators
Thermal calculation
Indoor comfort depends not only on the layout, but also on the amount of thermal energy that the batteries release to the indoor air. Based on this, in order not to freeze in the winter, it is necessary to make the correct thermal calculations. By the way, this is also indicated by the instructions enshrined in the current SNiP.
Thanks to the correct calculation, it is possible to choose:
- a boiler of the required power - not a strong one will not be able to heat the house, a wonderful one will burn expensive energy sources in vain,
- radiators of the required area - this will help to significantly reduce the cost of their purchase.
You can make calculations yourself (using a special computer program) or contact a special engineering company. The second option is more expensive, but this way you will be sure that the data provided to you is correct.
In addition, the engineers of this organization will also prepare a diagram of the heating circuits drawn on the provided design of your house (apartment). This will greatly facilitate installation and will help you purchase the required amount of materials.
Choosing an effective option
Design decisions are influenced by the configuration and area of the house, number of storeys, design requirements, and quality of power supply.
Taking into account the features, we can recommend:
- For one-story houses with a small area - Leningradka with horizontal wiring.
- Two-story buildings in places with intermittent power supplies should be equipped with an open, vertical, gravity system with bypasses and circulation pumps.
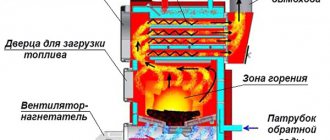
- Systems with boilers using coal, wood and pallets should be built using an open circuit with natural circulation.
- Divide the heating into sections with no more than 5 radiators in each.
Before design begins, local conditions are studied and only after that decisions are made on choosing the type of heating system.
Independent
An independent heat supply system allows you to save consumed resources by 10-40%.
Operating principle
The consumer heating system is connected using an additional heat exchanger. Thus, heating is carried out by two hydraulically isolated circuits. The external heating circuit heats the water of the closed internal heating network. In this case, mixing of water, as in the dependent version, does not occur.
However, such a connection requires considerable costs for both maintenance and repair work.
Water circulation
The movement of the coolant is carried out in the heating mechanism thanks to circulation pumps, due to which there is a regular supply of water through the heating devices. An independent connection circuit may have an expansion vessel containing a supply of water in case of leaks.
This connection method allows you to maintain the circulation of water with a certain amount of heat in case of heating main failures. Those. During an emergency, the temperature in heated rooms will not decrease.
Components of an independent system.
Scope of application
Widely used to connect multi-storey buildings or structures to the heating system, which require an increased level of reliability of the heating mechanism.
Advantages
- possibility of temperature adjustment;
- high energy saving effect;
- possibility of using any coolants.
Hydraulic calculation of a single-pipe system
Hydraulic calculations are carried out to determine the diameter of the connecting pipes in each section of the circuit and the performance of the circulation pump.
Sequence of calculations:
- Determination of heat loss through building structures.
- Calculation of the required heat transfer from radiators for each room.
- Selecting a boiler of the required power.
- Calculation of the diameter of the supply pipes, taking into account the circulation rate of the coolant in the coldest time of the year.
- Selecting a circulation pump if you need a remote option.
Determination of heat loss and calculation of radiators
The heat generated by the boiler is dissipated through the floor, walls and ceiling of the building. They take into account the material of the walls, the number and area of windows and doors, and the quality of insulation.
You can use the calculator on our website:
For small houses, an approximate option is used. It is believed that in the northern regions, to heat 10 m2 of area, 1.5-2 kW of boiler power and radiator heat transfer performance are required. In the middle zone the figure is 1-1.5 kW, in the southern regions - 0.6-1 kW. The data is correct for houses with solid walls and medium or high-quality thermal insulation.
Knowing the dimensions of the house, they obtain the necessary data for subsequent calculations. It is important to determine the required number of radiators for each room. Aluminum and bimetallic radiators in most cases emit from 120 to 210 W per section. By dividing the power required for the room by the performance of the section, the battery dimensions are obtained.
Boiler selection
The heating boiler will work much longer if it does not heat the coolant at maximum mode. In this regard, equipment is chosen that is 10-20% more powerful than the heat loss obtained in the calculations. For example, with a loss of 10 kW, a boiler designed for 12-14 kW is purchased.
Determination of pipe cross-section
The optimal speed of coolant movement through the pipes is from 0.3 to 0.7 m/s. If the parameter is lower, then at low temperatures the radiators may not warm up sufficiently. At higher speeds, the radiators often become airy and noise is heard. Based on the flow rate, pipes with the required internal cross-section are selected.
The required coolant flow is determined by the formula: G=860* q/ΔT , in which:
- G—flow rate kg/h;
- q is the thermal power in the circuit section (kW);
- ΔT is the difference in temperature of the coolant at the inlet and outlet of the radiator, usually taken to be 20 °C.
For example, to ensure heat transfer from a circuit of 2 kW, we obtain the coolant flow rate: 860*2/20=85 kg/h.
Next, special tables compare the flow rate and the generated thermal performance. In our example, for 2 kW radiators, a pipe with an internal cross-section of 8 to 12 mm is sufficient. Highlighted in the table with a red frame.
Table for determining the diameter of pipes of a gravity heating system
Data for each circuit is plotted on a general diagram. By summing up the data obtained, they determine which pipe diameter to choose for connecting to a group of circuits or for each riser.
Pump selection
Modern gas and electric boilers are equipped with a built-in pump. Its performance is selected by the manufacturer based on the boiler power.
The required performance of the remote pump is determined by summing the coolant flows in each circuit. They provide a reserve of 15-20% in performance so that the pump operates in a gentle mode.
Benefits of the magical rite of ritual magic
Specific objects, paraphernalia used in a magical ritual, the spoken words of a spell, the actions of the operator - all this happens in reality. That is, exactly there, in the world that we want to make the way we want. What is added is the power of herbs, the power of components, the power of specially charged and prepared paraphernalia that has been tested more than once, the effectiveness of ancient spell words, the activity of ritual action, and the operator has a different mood in such a special special atmosphere. The world has inertia, changes do not happen immediately, a magical ritual unfolds for a month, or even more, but the changes are persistent, what has changed has changed. A change in a given direction can be seen, experienced, felt - we get our result, the goal of the ritual has been achieved. Energy methods should be considered rather as complementary to the ritual action of a magical ritual.
Magic rituals can be divided according to purpose and method.
Purpose of the ritual
Any area of our life can be subjected to magical operations, because magic is a way of interaction, active dialogue with the World. We always have a choice
- accept the course of events that does not require our intervention,
- or use your will and ideas about life to make a correction in reality.
Magic in relationships - in love (improving existing or creating new connections) - attachments, love spells, interpersonal harmonization (reconciliation or destruction) - rituals for reconciliation, removing anger, interest in oneself, or vice versa - quarrels, backlashes, in business matters (business, money, success, benefits, achieving goals) - for money, from debts, opening roads
In getting rid of the unwanted and interfering - protection, cleaning, transfers and removals - individual tasks of any topic (personal happiness, appearance, health). The list does not claim to be complete. Magic is an active creative activity, and with its help you can work in a variety of directions - invent, try, get your own results and experience.