Unlike a basement, a cellar can be located outside the building, completely independently on a local area. To do this, its design must provide for the installation of a separate entrance.
Such premises are equipped with an autonomous ventilation system, and there is only artificial lighting. But the basement can be located not only under the main residential building, but also under auxiliary ones. It is very convenient and economical when it is done in the garage.
What does the concept mean?
The ceiling of a cellar or basement is a horizontal load-bearing building structure of a building being built , designed to ensure the tightness and strength of a special room for storing food or equipment located below ground level.
For such structures, it is possible to use various floor structures (from monolithic to wooden), it all depends on what load these floors will bear.
So, for example, for a separately located cellar, it will be insignificant, while basements in the basement or garage can bear significant loads.
At the same time, these floor slabs differ from other types of floors installed in residential buildings, since they work in particularly humid conditions and must ensure not only the strength and durability of the structure, but also a stable temperature throughout the year and standard humidity.
These characteristics will depend on how correctly the walls of the basement and cellar are erected, as well as on the professional thermal insulation of the ceiling and effective ventilation. Only in this case will the most comfortable conditions for storing vegetables and winter preparations be created inside them.
Preparatory activities
To ensure that the room fully performs its assigned functions, before you start building a cellar with your own hands, pay attention to the following points:
- Excavation work is preceded by the development of a room layout, which should be thought through to the smallest detail. This will help avoid unforeseen situations in the future.
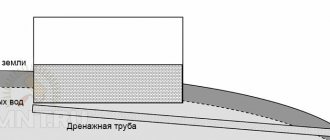
- Assess the groundwater level at the construction site. Ideal if they are located low. When the storage floor is located below a water-saturated layer, take care that water does not penetrate the floor and walls.
Only after reliable protection from moisture can you install a ceiling for the cellar. The task of waterproofing a building is one of the main ones, as it determines the comfortable conditions of the room. How to do it correctly?
Types of basement floors
Such floors are classified according to a number of criteria:
- by location in the building and garage or separately on a personal plot;
- according to the structural scheme - beam and non-beam;
- according to the material of supporting structures - reinforced concrete, wood and steel beams;
- according to the construction method, monolithic, prefabricated, and can also be combined prefabricated-monolithic.
Since the intended purpose of the cellar and basement is located below the ground level, the floor structure must meet the following regulatory requirements:
- Strength, the structure must support not only its own weight, but also the load of all structures above it.
- Stability in lateral stiffness, determined by the original building materials.
- Water resistance, including against flood and groundwater.
- Fire resistance, the ability to hold fire for a long period of time.
- Thermal protection is a necessary characteristic to ensure the desired temperature conditions indoors.
- Seismic resistance.
Type
Types of floors can be basement, basement and ceilings for a separate cellar. In the first two cases, they are the basis for the floor and therefore are presented to them as for standard basement floors of a house, and in the latter, soil is usually placed on the floor, along which the movement of people and cars is not provided.
By design
Depending on the type of structure, there are beam structures that perform a load-bearing function .
They are equipped with beads, slabs, floorings and fillers, heat and moisture-proof materials that impart the required characteristics to such structures. The beams should be spaced at regular intervals and can be made of wood, iron or reinforced concrete.
Most often, in individual housing construction, wooden beams are installed, used for one-story stone, as well as frame housing construction. They are limited in span length to no more than 5 m; iron and reinforced concrete beams have no restrictions.
Beamless structures are formed from load-bearing slabs , which rest on the vertical load-bearing supports of a house or garage or on purlins and crossbars. Slabs are also used that are connected to a vertical support by a load-bearing capital. Beamless structures include monolithic slabs that are both load-bearing and enclosing.
Most often, reinforced concrete floor slabs are used as basement floors - solid ones made of lightweight concrete and multi-hollow ones, in which round holes act as “stiffeners”.
By construction method
Based on the method of construction, floors are divided into prefabricated, monolithic and precast-monolithic. Prefabricated floors are made mainly in the basements of stone houses from factory-made hollow-core slabs.
Dimensions of such slabs: length from 2.4 to 6.8 m, width from 1.2 to 1.5 m, weight from 0.9-2.5 tons. These floors are the most popular, especially for large basements.
Monolithic reinforced concrete structures are made in the form of solid 80-200 mm slabs filled with M 200 concrete. They must rest on load-bearing walls. They are quite heavy; the mass of 1 m2 of monolith, 200 mm thick, weighs approximately 500 kg.
Prefabricated monolithic is the most modern option for installing floors in basements. The 600 mm space between the beams is filled with hollow block structures, after which the structure is filled with M200 concrete.
The weight of a block of expanded clay concrete is 14 kg, polystyrene concrete is 5.5 kg. This allows installation to be carried out without the use of expensive lifting equipment. The weight of 1 m2 of finished prefabricated monolithic floor reaches 380 kg, for expanded clay concrete 320 kg.
Based on materials
Ceilings for basements and cellars are also classified according to source materials :
- asbestos-cement,
- wooden,
- slabs and monolith.
The choice of a specific type of building materials will depend on the location of the structure, load-bearing load and dimensions of the objects.
On asbestos-cement pipes
Not many developers know that instead of basement floor slabs located in low-rise buildings and cellars, asbestos-cement pipes can be installed. This option is resorted to when it is impossible to use lifting equipment to install heavy reinforced concrete slabs.
The advantages of this technology for installing ceilings for basements:
- no lifting equipment is required for installation;
- pipes are well suited for non-standard cellar sizes with a width from 0.5 to 6.5 m and any length;
- can be used for any shape of spans, with the exception of rounded ones;
- simple and quick installation;
- further technological filling of such pipes is intended for the simultaneous formation of a floor if a technical or residential premises is located above the basement.
The disadvantages of using asbestos-cement pipes for basement floors are the high cost of work, approximately 15% compared to traditional reinforced concrete slabs, high labor costs and long periods of construction and installation work.
On wooden beams
Such floors are the most popular, both for wooden residential buildings and for separately located cellars. Floors on wooden beams are not suitable for block and brick walls of multi-story buildings , since they are not able to withstand the high load of wall building materials.
For these houses, in order to strengthen the floors, it is allowed to use steel beams and even used rails. To install them correctly, specific beds are made that reliably fix the steel structures. In this embodiment, the walls become the foundation relative to the beams.
Before laying such floors, all wooden parts must be treated with antiseptic impregnations and fire-resistant solutions, and metal beams must be treated with anti-corrosion compounds.
The main advantages of wooden multilayer floors for basements and cellars:
- high level of thermal insulation;
- high level of sound insulation;
- lightweight design, does not create a significant weight load on the walls and foundation;
- simple installation technology and high maintainability.
The disadvantages include low strength, which, however, does not prevent them from being installed as floors for oversized basements and cellars, as well as increased flammability.
Plates
In order to install the slabs as basement floors, you will need an installation crane. The structures are installed on 250 mm brick walls. For reinforcement, they can be installed on iron beams. After this, the slabs are waterproofed, the tile joints are sealed, and a heat-protective layer of foam is installed. A hole into the basement is made in the ceiling, with a size of approximately 800 x 800 mm.
The advantages of such an overlap:
- high strength;
- quick installation;
- fire resistance;
- heat resistance and water protection.
Disadvantages include the need to use lifting equipment, as well as the standard sizes of finished slabs, which may not coincide with the contour of the cellar or basement.
Monolithic
Such structures do not have inter-tile connections and do not require lifting mechanisms for installation, in contrast to reinforced concrete slabs. A monolithic structure is made in the form of a solid reinforced concrete slab , which is supported by load-bearing walls; if the basement area is large, they are installed on additional support columns.
All parameters of a monolithic slab must be pre-calculated by specialists, and for a basement located in a residential building, this work must be carried out during the house-building design process. An important parameter of such a structure is its thickness, which should not be less than 15 cm and is determined by the largest span from a ratio of 1:30.
For a six-meter span, the minimum thickness is 20 cm; if you need to fill the slab over spans of more than 6 m, you will need to reinforce the structure with stiffeners.
Specifics of installation of prefabricated monolithic slabs
The ceiling in the cellar can be formed using prefabricated monolithic slabs. To carry out construction activities, order special lifting equipment, which will significantly speed up the work.
Precast slabs are blocks that are laid between steel beams and then filled with a small layer of concrete
A number of difficulties arise associated with increased tolerances for the length and width of the slabs. They may simply not correspond to the actual storage dimensions. Considering that the length of the slabs ranges from 9 to 12 meters, before installation you should compare them with the dimensions of the building. If you plan to use monolithic prefabricated slabs, it is advisable to take this into account at the design stage. The width of the basement room must correspond to the parameters of the installed slab.
If the size of the slabs matches the basement, installation is carried out using a crane. Perform the activities in the following sequence:
- connect structural elements using steel profiles;
- fill the cavities in the joints with heat-insulating composition;
- fill the joint planes with concrete mortar;
- lay the roofing material on the surface using bitumen mastic.
Are you having trouble with how to cover a cellar? Use a prefabricated structure made from solid reinforced concrete slabs, which are inexpensive and reduce construction time.
Requirements for parameters and characteristics
Floors are subject to a variety of force loads, primarily from the weight of their own, upper structures, walls, utility networks and equipment.
Under their weight, high stresses appear in them, which lead to deformations and deflections of the beams. The maximum amount of deflection in basements and cellars that is allowed according to the requirements of SNIP: 1/200-1/400 of the span length , more specifically they are established by calculations for the design and selection of building materials.
Developers should strive to minimize the deflection of the floors, although at the same time, such a requirement invariably leads to an increase in the thickness of the slab.
For basements located in residential buildings, it should be the minimum acceptable, as a rule, in the region of 200-300 mm, for the reason that an increase in this indicator leads to an increase in the total construction volume, and therefore the weight of the building, the load on the foundation and the cost of the project.
Basic requirements for the parameters and characteristics of basement floors:
Durability, for built-in basements must correspond to the design life of the main building, for separately located cellars at least 50 years.- Protection from flood and groundwater, high waterproofing characteristics.
- Fire protection, they must correspond to the 1st degree of fire resistance with a fire resistance of at least 1 hour.
- Ease of use, creation of conditions for normal presence of people and storage of products.
- High heat-shielding characteristics to create optimal food storage temperatures.
- The economic component of construction should not lead to a high final cost of the project.
Ventilation
In most cases, the basement floor is used to lay an exhaust ventilation duct. It is designed to remove warm air saturated with moisture, odors and fumes from the room. The pipe should be raised as high as possible to ensure high-quality traction. It is better to install the exhaust vent on the side of the ceiling opposite to where the supply pipe is located. If the roof above the cellar is made of slate or other fragile material, it is advisable to run the pipe along the walls.
The supply channel should be deepened into the ground at least 50 cm. This is necessary so that the air passing through it is heated in winter and cooled in the summer heat. The pipe is brought into the room 5-10 cm above the floor level.
It is recommended to cover the upper sections of the supply and exhaust lines with a fine steel mesh to protect against insects, rodents and amphibians. To prevent water and snow from getting into the pipes during precipitation, umbrellas made of plastic or tin are installed on them. To improve draft, air conditioning systems can be equipped with fans that provide forced pumping of moist air.
Layer diagram and cake
The design of the basement floor depends on what material it is made of, the installation location indoors or its independent location and the characteristics that need to be endowed with such a structure.
For built-in basements, it is better to form a protective floor pie during the construction of the building . In the case when the building has already been constructed, the finishing work has been completed, including the final finishing of the floors, and these floors do not have protective layers for heat and moisture protection, then the protection will need to be installed under the floor slab.
The work is carried out provided that the basement has a sufficient distance to carry out protective work and locate repair and maintenance personnel, that is, at least 2 m.
In built-in basements, the main protection should be organized against moisture penetration and heat loss.
It is formed mainly by the walls and floor of the room and must be completed during the construction of the main building. Standard insulation pie on top of a floor slab for a separate cellar:
- flooring made of cast-in-place concrete, slabs, prefabricated structures or flooring;
- vapor barrier membrane film;
- insulation layer;
- waterproof film;
- roofing;
- bulk soil.
A modern solution for installing a separately located ceiling to create an inversion roof:
This is a relatively modernized type of construction, the pie of which is designed taking into account the disadvantages of traditional options, which suffer from moisture seeping through the heat insulator into the ceiling and destroying it. This design has increased moisture protection, since a reliable waterproof single- or multi-layer carpet is installed between the inner layer of the ceiling and the insulation.
The composition of the inversion roof pie is determined as follows:
- overlap;
- a layer for organizing moisture protection, usually a building primer;
- waterproof carpet;
- laying geotextiles;
- thermal protection, installation of hard plates, for example, extruded polystyrene foam is allowed;
- top layer of geotextile;
- loose gravel ballast layer;
- rigid covering for traffic safety and uniform distribution of ballast.
Fighting condensation
The formation of condensation in the cellar is very often caused by poor ventilation or poor ceiling insulation. It is necessary to combat this harmful phenomenon immediately, since both the room itself and the products stored in it suffer from the presence of condensation.
First of all, measures are taken to insulate the ceiling. To do this, you can use any material that has moisture-absorbing ability and dries quickly. Such materials include forest moss or artificial expanded clay material. Sometimes you have to insulate the walls as well. If this does not help, then condensation and drops from the ceiling are removed using umbrellas made of galvanized iron or plastic film. You can also use drainage plywood. Special gutters are attached to them to drain water and divert it into water intake wells. If the cellar design does not provide for these, you can use a regular bucket. In this case, in the summer the cellar must be carefully examined and repaired.
How to calculate?
In fact, the calculation of the basement floor is based on the use of simple formulas for establishing the bending moment M and the moment of resistance W , and their ratio must satisfy the condition: M/W<=Rd, where Rd is the permissible resistance of the structure in MPa, at a load q that can withstand the beam and its length l. M=(ql2)/8.
According to GOST 26519, published in 1985, a safety factor of 1.3 must be taken into account for beam floors. For basements built into residential buildings with a permissible load of 151.0 kg/m2 with a margin, this value is equal to: 151 x 1.30=197 kg/m2.
Intervals made of light blocks with a layer thickness of 180 mm and D 500 create a load: 500x0.18 = 90 kg/m2 . A reinforced screed with a layer of 55 mm and a density of 2000.0 kg/m3 creates a load: – 2000*0.055=110 kg/m2.
The total floor load will be: 197 +110+90=396.0 kg/m2. The deflection is calculated based on the total load for an I-beam Ry=2000 kg/cm2, span length l=4.5 m
Find Mmax Qmax . Based on the results obtained and Wtr and Itr and rental tables, select the I-beam number:
In this case, I-beam No. 14 is quite sufficient.
What tools and supplies will be needed?
Since floors are made from a variety of materials: reinforced concrete, rolled steel and wood, various tools and materials will be required accordingly.
To install the most common types of wooden floors on metal load-bearing beams, the developer must prepare the following materials and tools:
- I-beam floor beams by number depending on the permissible deflection, the number is calculated depending on the span length and the interbeam distance of at least 600 mm;
- thermal insulation material, mainly mineral wool and Penoplex;
- steam and waterproof membranes and tape for sealing seams;
- lumber for flooring and sheathing, in case of installation of a ventilation gap for mineral wool;
- antiseptic and fire-resistant impregnation for wooden products;
- measuring instruments: angle, ruler, tape measure, level and plumb line;
- jigsaw and regular hacksaw;
- electric drill with drills;
- Bulgarian:
- hammer and set of carpentry tools;
- welding to connect steel load-bearing beams.
For monolithic reinforced concrete floors you will need:
- concrete,
- fittings,
- boards for formwork,
- concrete pump and hoses for pouring mortar.
We are planning to cover the cellar - general tips
The construction of the basement ceiling is carried out after the walls have been erected, the base has been concreted and waterproofing work has been carried out. There are a number of points to consider:
- choose the material for making the ceiling;
- study the technology of performing work;
- calculate the amount of required building materials;
- determine the overall level of costs;
- prepare tools and building materials.
To maintain comfortable humidity, it is necessary to consider the design of the hood. Air exchange is carried out in various ways:
- natural. Ventilation is provided using a supply line and an exhaust pipe due to temperature differences;
- forced. To increase circulation efficiency, a small-sized fan unit is used.
By completing all the activities yourself, you can save a lot of money.
Before making any cellar, the groundwater level is taken into account
Description of device technology features
There are certain features of installing a basement floor, which depend on the source material, type of structure and location of such an object, built-in or separately located.
For built-in basements in a wooden house, the basement is covered with wooden load-bearing beams. This wooden structure serves as the base for the floor of the first floor, so it should be carried out as part of the overall project for the house.
Before its installation, the entire design complex of works for the construction of the zero cycle is carried out, especially the part of the construction of the foundation and waterproofing of the walls.
The basic procedure for installing a ceiling on a basement in a wooden house:
install floor beams, at this stage it is important to observe the design size of the beams in cross-section, the distance between the beams, the depth of embedding in the wall material, as well as perform antiseptic and fire-resistant treatment of the wood;- perform a roll-up device;
- install a vapor barrier membrane secured with a stapler and with an overlap of 100 mm, the seams are taped with special tape;
- install thermal protection from fire-resistant mineral wool insulation materials;
- install the sheathing
- install waterproofing with an overlap of 100 mm and gluing the seams with tape;
- install a ventilation sheathing;
- install a subfloor layer;
- install a finishing layer of the floor;
- perform a finishing layer of ceiling cladding from the basement side.
In order to construct a monolithic ceiling over a separately located cellar, which was not included in the building design, you will need to first perform drawings and calculations for the strength and permissible deflection of the supporting structure. Before installation of the slabs begins, all work on the construction of walls, their waterproofing and thermal protection must be completed.
When assembling formwork for pouring concrete, it is necessary that the slab extends onto the basement walls by at least 10 cm. Only in this case will the strength and durability of the structure be guaranteed.
To perform this work, the developer should first do:
- Steel racks are installed under the beams, mounted at a distance of no more than 1 m from each other.
- Formwork is installed; moisture-resistant plywood laid on durable boards is suitable for this purpose.
- A reinforced frame is made from 10-12mm reinforcement, with a gap between the rods of 15 cm, the mesh is made in 2 layers. The mesh is installed on special spacers so that they do not lie on the bottom layer of concrete; the area covered with concrete of the reinforced structure must be at least 3 cm.
- The formwork must be poured at once and from one batch of M 250, it is better if the concrete is made at the factory, the layer thickness is 20 cm.
- The layer is laid evenly, since it will serve as the ceiling of the basement.
- The poured concrete is vibrocompacted with special equipment or manually by piercing the concrete mass with a reinforcing bar; in this case, air pockets will come out and the slab will be strong, monolithic without voids.
- After 28 days, the formwork is removed; throughout this period, the surface of the concrete must be moistened and covered with film until it gains strength.
- Further work is carried out depending on the chosen insulation pie or inversion roofing.
Use of wood
Are you planning to build a cellar with your own hands? Use wooden beams - a proven, easy-to-work material.
If you are building a house made of wood, you can cover the basement with wooden beams
Perform the activities in the following order:
- Treat all parts of the wood structure with an antiseptic.
- Wrap two layers of roofing felt around the supporting surfaces of the beams.
- Install wooden beams on the top surface of the cellar walls.
- Secure the end part of the beams with small strips, providing a base for the knurling boards.
- Lay the plank and secure it using self-tapping screws.
- Form a heat-insulating contour, coat with mastic, cover with roofing felt or roofing felt.
- Fill the structure with soil if no structure is planned to be built above the structure.
Pay attention to the presence of grooves in the basement walls necessary for installing load-bearing beams.
Possible difficulties and errors during the installation process
The biggest mistakes made by developers are when they start building a basement or cellar without a design and without calculating the strength of the load-bearing structures.
If the basement is built into the building, then its arrangement is carried out according to the construction project, and if this was not provided for at the time, then you will have to order a project for the reconstruction of the house so that the newly constructed basement does not weaken the walls and does not lead to the destruction of the house.
A free-standing cellar also needs design documentation, although of a smaller volume. It is important to provide not only the reliability of the load-bearing elements, but also a reliable ventilation system so that visitors to the cellar are not poisoned by radon or other aggressive gases that can accumulate in underground structures.
The main mistakes that developers make during the installation of basement floors:
poor waterproofing of load-bearing wooden beams when laid on walls, no roofing material at the ends of the logs;- low support of beams on wall structures;
- unacceptable deflection of beams due to their small cross-section;
- the heat-steam and water-protective layer is not completed;
- violation of the technology of pouring and compacting the monolith;
- weak reinforcing frame;
- small thickness of the concrete slab.
Application of rolled metal
Are you deciding what to cover your basement with? It is possible to use ordinary rails. I-beams are used as load-bearing beams and are highly durable.
The installation of railway profiles is carried out in special grooves provided in the walls of the building. This allows you to securely fix the structural elements. The length of the beams must correspond to the dimensions of the basement, the walls of which are the base for them.
Form the load-bearing surface using the following algorithm:
place steel reinforcement bars between the beams and secure them with wire;
- mount wooden formwork, lay a waterproofing coating on it;
- install a power frame under the formwork to support the concrete mass;
- fill the structure with solution, ensuring uniformity of the layer and continuity of work;
- lay the roofing material on the surface.
Cost of work
The final cost of installation of floors over basements and cellars depends on the construction area, the chosen design, the composition and number of layers of the “pie”, the area where the construction site is located, as well as the availability of good access roads.
The average cost of materials and work for installing floors above the basement per 1 m2 is summarized in the table:
| Floor type | Monolithic | Reinforced concrete slabs | Beams made of LVL timber | Regular beams |
| Load-bearing beams | 500 | 190 | ||
| Vapor barrier membrane | 65 | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| Wood flooring | 320 | 320 | ||
| sheathing | 62 | 62 | ||
| Concrete solution with transport costs | 625 | 125 | ||
| Armature | 430 | 63 | ||
| Reinforced concrete slabs | 935 | |||
| Heat protection material | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Concrete mortar | 125 | |||
| Loading and unloading operations | 62 | 125 | 62 | 62 |
| Installation | 875 | 300 | 400 | 400 |
| Material processing | 215 | 215 | ||
| Formwork work | 270 | 70 | ||
| Transport cost | 250 | 375 | 170 | 170 |
| Total costs per 1 m2 of slab installation | 2827 | 2433 | 2044 | 1734 |
Thermal insulation of the structure
Carrying out thermal insulation work
Sand, foam concrete, polystyrene foam, mineral wool boards of varying degrees of hardness and straw mats can be used as thermal insulation materials.
Technology:
- The concrete floor is primed with a mixture of bitumen and diesel fuel (in a ratio of 1:3), which is distributed onto the hot bitumen.
- Sawdust is mixed with a cement composition (1:8), applied in a thick layer and compacted thoroughly.
- After 4-5 days, install a cement screed with sand, with a thickness of at least 30 cm.
A cellar covered according to strict rules can serve its owners for decades. Technologies make it possible to build a basement and use it as additional space for storing food, maintaining a stable temperature and making the most of the free space on the site.