November 23, 2021 Stroyexpert Home page » Foundation » Types and types
Diagram of a slab foundation with stiffeners
The most important structural element of the future building, on which its strength, reliability and durability depends, is the foundation. There are many types of foundations used for private housing construction. One of the most reliable foundations for any type of soil, as well as at any level of groundwater, is a slab foundation with stiffeners.
Characteristics of slab foundation
According to the rules for designing foundations, slab foundations with stiffening ribs are used for the construction of structures that are sensitive to uneven precipitation, as well as objects that are built in areas with highly heaving soil.
Slab bases are classified according to technological features. They are divided into:
- Solid.
- Lattice.
- Prefabricated.
- Monolithic.
- With stiffening ribs (up or down).
Classification
There are three types of ribbed slab bases:
- with ribs pointing down (in this case, the monolithic slab rests on a frame in the form of a continuous strip);
- with ribs directed upward (a continuous strip of stiffening elements rests on a monolithic slab on top);
- combined version of the frame arrangement.
The ribs turned upward additionally serve as a base. They must be insulated. Utilities can be laid between them, as well as underfloor heating systems installed. The monolithic tape located on the top of the slab serves as a support not only for load-bearing walls, but also for the materials cladding the facade, as well as roof structures and ceilings.
A foundation with stiffening elements turned downward resembles a shallowly buried strip base, which is rigidly connected to a monolithic reinforced concrete slab laid above. The only difference is that the cross-section of the tape is trapezoidal rather than rectangular.
The technology for constructing a base with ribs pointing down is somewhat simpler than in the second option. The thing is that in this case there is no need to erect hanging formwork. Also, when pouring stiffeners, there is no need to monitor the level of the concrete mixture, which, according to the laws of physics, can begin to rise in the area of contact with the slab.
Basic requirements for burial depth
The slabs are divided according to their depth, which can be:
- Normal (deep), which is laid lower than the soil freezing mark. They are used for the construction of houses with basements or ground floors.
- Shallow (surface or floating), buried to a maximum of 50 cm. The base has the ability to simultaneously move with the movement of the soil.
- Non-buried, which is laid at ground level. It is built after removing the top part of the soil, the thickness of which is equal to the thickness of the sand layer from which the foundation cushion is made.
The depth of laying a slab foundation is influenced by the following indicators:
- Arrangement of the basement.
- Loads that act on the structure.
- The depth of the foundation of the adjacent house or the depth to which communications are laid.
- The topography of the area where construction is taking place.
- To what depth does the soil freeze (this takes into account its type).
Before building a house, geological studies are carried out, the purpose of which is to identify the strength and physical properties of soils, the nature of bedding, possible voids, as well as soil layers that can liquefy and slide over time.
Hydrogeological studies of a construction site make it possible to determine whether there is high water on it, at what depth the aquifers lie and whether the groundwater is aggressive.
When choosing the depth of the foundation, you need to be sure that low-strength layers of small thickness do not pass under the slab, which, if present, are removed. Instead, a thick sand cushion or a deep foundation is used. In order not to spend money on dewatering equipment, the slab is laid higher than the groundwater level.
If the bearing capacity and deformability of the soil are low, it is better to use a pile foundation.
When laying the foundation, you need to take into account the location of groundwater and the freezing point of the soil. When the soil freezes, it increases its volume, and when it thaws, noticeable sediment appears. In areas with water-saturated soil, snow melting is accompanied by the formation of ice of varying thickness. When it begins to melt, the bearing capacity of the soil sharply decreases and deformations begin in it.
If you correctly calculate the depth to which the foundation will be laid, these problems will not be terrible. Reducing this depth is possible with:
- Arrangement of permanent thermal protection of the base.
- Conducting circular soil drainage.
- Complete or incomplete replacement of heaving or non-heaving soils at the construction site.
- Protect the base by coating and gluing roll materials to the horizontal and vertical sides of the base.
Stages of constructing a monolithic foundation with your own hands
Foundation layout diagram
- digging the foundation along strictly marked lines and with a calculated immersion depth;
- filling the base with a sand and gravel cushion;
- creation of a special pipe or drip drainage system along the perimeter of the future foundation or along the external contour of the foundation;
- It is recommended to create an expensive layer of footing in the sand cushion, which protects the basement from water ingress.
That's it, the preparatory work is completed. The pit is ready, a drainage system is provided, the load on the corners of the foundation, as well as the main load points, are correctly calculated. Now it's time to build the foundation itself. And this procedure also consists of a number of stages, because only then will everything work out as correctly and reliably as possible:
- Foundation reinforcement. Depending on the type of building and its mass, horizontal and vertical reinforcement can be considered popular. There is also corner reinforcement using seal welding, but this is popular in the construction of high-rise prefabricated buildings.
- Installation of wooden formwork. It should be slightly wet to ensure optimal adhesion to the concrete mortar. It is also taken into account that mesh formwork always protrudes beyond the width of the foundation. But this is not a problem, because all popular monolithic foundations are buried, so the external contours are subject to waterproofing. The arrangement of formwork is done depending on the type of soil and its characteristics, therefore it is selected individually in each case.
- The main stage is concreting. There are several options here. If it is possible to use several concrete mixers at once, then it is better to simultaneously pour concrete in layers. But if the budget does not allow this, then you can fill the fragments with concrete and connect them with reinforcement. But this technology is a little more expensive.
- Dismantling the formwork and checking the monolithic base for strength. This is the climax.
Types of foundation slabs
There are various schemes for arranging a slab base:
- Classic floating (non-buried) slab. A sand and gravel cushion is used for its arrangement. It is used in areas with a high probability of longitudinal deformation of the soil, causing sliding. It is possible not to use a sand layer when the soil at the construction site has a structure and strength that gives it the ability to withstand transmitted loads, avoiding uneven settlement.
- Foundation laid on piles. Pile foundation support is necessary if the construction site has weak mechanical properties, or the building is built on a slope that cannot be strengthened or terraced.
- A slab base with downward stiffening ribs is used for construction on soils that are characterized by weakness and the ability to slide. The ribs are made in the form of trapezoidal or rectangular thickenings at the bottom and inside the slab. Thanks to them, the horizontal part of the base has a smaller thickness.
The design of the stove may be different. Have:
- One underlying layer of 50 cm, for which sand and crushed stone are used 60:40.
- Two underlying layers of sand and crushed stone, which are not mixed, but are laid and compacted alternately. Crushed stone is placed down, and sand is poured into the spaces between the ribs. If the construction site has waterlogged soil, this is the most reliable method.
- Insulated foundation with ribs down. It is also called Swedish because it was invented by the Scandinavians. It is equipped with crushed stone and sand layers, as well as slab polystyrene foam. Under the places where the ribs rest, extrusion sheets with high rigidity (EPS) are laid, between which cheaper sheets (PSB S) are laid. Used in regions with cold climates in the construction of houses with increased energy efficiency.
- A slab base with stiffeners up is a strip foundation slab laid on top. The monolithic walls of the plinth become the ribs here; the embedded reinforcement located under the external and internal walls of the future building acts as a connecting link. You can also use a shallow depth, and if the house has a basement, then a deep foundation is laid, in which the basement walls will act as stiffeners.
- The base, which has a box-shaped structure, can be considered slab and strip, which is made with expanded cushions merged into one slab. Such foundations are not afraid of any loads; they are suitable for the construction of high-rise buildings. Low-rise buildings are built on such a foundation if the construction site has heterogeneous soils with low bearing capacity. It is also recommended to use such foundations if the construction site is located in an earthquake-prone area. Box-shaped structures can be flat or with ribs, in the spaces between which a sand-gravel mixture or polystyrene insulation is laid, covered with concrete preparation. If the recess is large, between the ribs that serve as the walls of the building, you can arrange a room for a cellar or underground garage. If the ground settlement is uneven, it is not recommended to use walls as ribs. It is necessary to arrange beams intersecting at right angles.
Installation of reinforced concrete slabs
Even if the developer plans to build the walls of the house himself, it is always better to hire a contractor to install the zero cycle, who will competently solve all the issues, from design to quality control of the work. In this case, the customer will not have to think about logistics; searching for performers, organizing their work and work life; installation of temporary access roads; rental of tools and mechanisms. These and other issues will be resolved to the mutual satisfaction of the parties, which will allow the foundation to be formed quickly and in compliance with existing standards
Preparing the area for the foundation
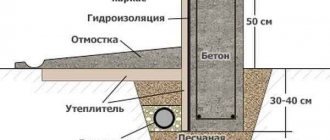
The range of preparatory work may vary slightly, depending on the specific structure of the foundation pie. The difference can be made not only by the thickness of the bulk layers, but also by the presence or absence of concrete. The type of waterproofing used and its location depend on this, which affects the installation technology. Insulation may be present among the preparatory layers, which also makes adjustments to the work process.
In our story, we will rely on traditional technology, which has long become a classic of construction - the option of preparing the foundation with concrete preparation. This is the most reliable way to protect reinforced structures, which:
- prevents the slab from being washed away by groundwater;
- prevents the loss of concrete milk by the main slab monolith;
- creates the best working conditions for fitters;
- is an additional barrier to the forces of frost heaving.
In general, preparation of the base for the foundation is carried out in order to ensure the tightest fit of the slab to the ground. At the initial stage, two main types of work are performed:
- Leveling the soil on the site, including removing the vegetation layer, draining or temporary drainage.
- Construction of a pit and, if required, strengthening of the soil at its bottom. This can be done in different ways: by tamping the bottom, replacing part of the soil with a more durable one. Strengthening by silicatization or cementation is carried out only when all other methods do not give the desired result.
At the initial stage, the contours of the pit are laid out on the ground. The regulations for carrying out this work are a working drawing, on which, in addition to the alignment axes of the building, the dimensions and elevation of the base of the foundation are indicated. It is necessary to carry out the contours of the upper edge of the pit onto the terrain, install the cast-off and secure the building axes and foundation lines on it.
Opening a pit along the marked contour
Bulk cushion device
On average, the thickness of the bulk preparatory layer in an already compacted state is 300 mm, and its area corresponds to the area of the mounted slab. For backfilling, either a ready-made sand and gravel mixture or separately sand and crushed stone are delivered. In the second case, they are unloaded from dump trucks and mixed directly at the bottom of the pit, starting from the far edge, moving towards the entrance.
- In order to evenly distribute the mixture, the bulldozer blade raises it to a height of 15-20 cm, and scatters it in the process of movement “from itself.” The thickness of the filling layer, which must be thicker before compaction begins in accordance with the compaction coefficient, is controlled using a template. Differences are eliminated manually by transferring soil from thicker layers to thinner ones.
- The compaction process may differ depending on what equipment the contractor is provided with. Profile organizations use single-drum vibratory rollers, with each pass of which the compaction line is shifted by a third of its width. Smaller contractors use a vibrating plate for this purpose.
- Compaction of bulk soil should be carried out at optimal humidity. If there is no water at a site under construction, watering machines are used to moisten the sand. Watering is carried out before each penetration, which, coupled with the crushed stone present in the backfill, makes it possible to obtain the highest quality compaction.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Please note: In the technological maps for the installation of soil cushions, there is no mention of geotextiles, which today are actively used as a separating layer. It’s just that when these cards were developed, such material did not yet exist. Its role is to prevent the compacted cushion from moving apart and losing its specified geometric dimensions - most often this happens when forming surface slabs.
Sand cushion placed on top of geotextiles
In the process of installing a sub-foundation cushion, water supply and sewerage pipes are laid and electrical cables are entered.
Installation of a preparatory concrete layer with installation of waterproofing
The cushion prepared for concreting is fenced on all sides with beacon slats, fixing them in a vertical position by driving in reinforcing stakes, followed by checking with a level. The width of the lath should correspond to the thickness of the concrete preparation, so that its top edge will serve as a guide when pouring.
The thickness of the footing is usually 100 m, although it can be slightly less (70 or 50 mm). To fill it, class B7.5 concrete is used; due to its low cement content it is called lean. To make such concrete using M400 cement, for one part you need to take 4.6 parts of sand and 7 parts of crushed stone. The mixture is poured into the formwork and compacted with a vibrating lath, after which vertical reinforcing bars 30 cm high are installed so that when the main slab is poured, they are embedded in its body.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Note: According to existing standards, the concrete base is not reinforced, but practice shows that this still needs to be done. The presence of reinforcement reduces the likelihood of cracking, which can damage not only the integrity of the preparatory concrete layer, but also the waterproofing. For reinforcement, it is advisable to either use factory mesh cards or add polymer fiber to the concrete.
After pouring, the monolith is covered with film and left alone until it gains strength. It is cared for in the same way as the main slab: if the air temperature is above +15 degrees, the concrete base must be shed with water several times a day. After 5-7 days (depending on temperature), when the concrete gains at least 50% strength, the lighthouse slats can be removed and installation of waterproofing can begin.
For this purpose, roll material on a bitumen basis is traditionally used, which is mounted either by gluing to hot bitumen mastic, or by floating method, when the mastic is already applied to the material in the factory, and when rolling out the roll it only needs to be heated with a burner.
The canvases are installed with an overlap of at least 10 cm. Reserves are left at the edges of the footing so that they can be wrapped on the vertical surfaces of the main slab when it is poured. To avoid damaging the waterproofing carpet during the installation of the reinforcement frame, a reinforced polyethylene film is laid on top of it or a thin sand-cement screed is applied.
Construction of the main slab and monolithic reinforced concrete walls of the basement
After installing the waterproofing layer of the foundation pie, you can begin installing the main slab. If the reinforcement is made from individual rods, then the frame is first assembled, and then the formwork is placed - this way it does not interfere with connecting the ends of the rods to each other. If the frame is assembled from ready-made factory meshes, it is easier to install them into already assembled formwork, marking on the sides the levels of the location of the lower and upper rows of reinforcement. In general, in each specific case there is an individual approach.
Reinforcement is carried out in blocks, with mesh or bundles of reinforcement being supplied to the desired point by a crane. The base is first marked using a level, with the orientation to the axis of the formwork and the mark of the top of the slab, which is zero. The axes of the frame are carried out and fixed on the cast-off material, and then, using a plumb line, they are applied with chalk to the concrete base. The bottom row of nets is installed on chair clamps, the height of which provides the required protective layer of concrete.
To fix the top row of meshes, flat frames are pre-assembled. Being installed on the edge every 400 mm, their width sets the required distance between the meshes. The pitch of transverse and longitudinal reinforcement is determined by calculation and depends on the weight of the building. As a rule, for one-story houses it is 200 * 200 mm, but reinforcement is installed under the walls (these are the most loaded areas) more often.
Foundation slab frame with reinforcement reinforcement under the walls
Pouring the slab
Installation of formwork under stiffening ribs
Since in this case the slab is made with monolithic walls of the base, vertical U-shaped clamps are immediately installed along their perimeter, which will become the basis of their frame. The embedded parts will connect the vertical elements of the foundation with the horizontal slab into a single whole. They will be formed using strip formwork, installed after the slab has been poured and reaches half of its design strength.
At the stages of foundation formation, timely delivery of concrete and coordinated work of the team are very important, which will allow the slab to be poured within one day without long downtime. Therefore, the mixture must be distributed using a concrete pump, with breaks in operation for no more than 20 minutes.
Filling is carried out immediately along the entire height, in blocks, starting from the far side of the formwork. The process of concreting, compacting and caring for the monolith at all stages is similar. The only difference is that, unlike the footing, a mixture of a higher grade is used on the main slab - at least B15, but more often B22.5.
Pros and cons of slab foundations
A slab foundation has many advantages:
- If shallow excavation is carried out, excavation work is kept to a minimum.
- More durable and reliable than any other types of bases.
- If properly designed and installed, it will last at least 150 years.
- Has maximum load-bearing capacity.
- Resistant to tip over.
- Can be used in areas with heaving soils.
- It is possible to arrange the ground floor.
- There is no need to install a subfloor.
- Possibility of using a floor heating system.
The only disadvantage of a slab base is the high price, but this is compensated by numerous advantages. True, slabs with ribs downwards have another disadvantage. When using them, it is difficult to form formwork. It should be two-level, and the pit should have cut trenches. This leads to difficulties with reinforcement. In addition, the filling must be carried out within one day.
Foundation design
The stiffening ribs protrude 80 cm under the slab. They have a trapezoidal shape, which will reduce the shear loads taken by the base from the ground. Ribs are placed around the perimeter and inside the slab. The distance between the ribs is determined by the design. Sometimes they are installed under the load-bearing walls of a building. The shape and number of ribs, their depth and location are determined after geodetic research.
Characteristic advantages and disadvantages
- Despite the widespread use of the slab type, it has a significant drawback in the form of a number of channels for laying communication cables and heated floors. Communications must be laid in advance and ensure that they are not damaged before pouring. This is not always practical, since there are many objective factors. If there is a basement, the laying is done along the floor of the structure;
- the need to construct two formworks: one in the form of a trapezoid at the bottom, the second at the top in the form of a rectangle;
- non-standard scheme for structural reinforcement. In each specific case it is necessary to draw up a calculation;
- the need to install waterproofing, since the impact will be from moisture;
- single use;
- difficulties in designing load-bearing and secondary walls due to the large area of the foundation pit.
But, despite many minor shortcomings, there are a number of positive aspects, such as:
- an inverted slab allows you to reduce the thickness of the slab to a minimum of 100 mm, reducing the cost of the estimate;
- flat surface of the basement floor;
- reducing costs for surface leveling;
- the possibility of construction on different types of soil foundations, including heaving ones and with a high level of groundwater.
The quality of the pros outweighs the quality of the cons.
Slab foundation technology
Before laying any type of foundation, a project is drawn up, which is then implemented by a private developer, who must have certain skills. It is impossible to do this work alone, without assistants and special earth-moving equipment, ready-mixed concrete and a concrete pump.
The construction of the slab base is carried out in stages.
- First, a pit is developed. If a slab with stiffeners is laid, it is necessary to dig a pit in which trenches are laid. If the location of the slab is superficial or it is necessary to lay a simple floating slab, the pit is dug to a shallow depth. In the pit, markings are made for the ribs in order to dig trenches along them with a depth that is affected by the thickness of the slab base, the height of the bulk cushion layers and the footing.
When excavation work is being carried out, the soil at the bottom of the pit should not be touched. For this reason, first, using geodetic tools, the required level is determined, and the pegs necessary for orientation are driven in while cleaning the bottom of the pit.
When laying the foundation on wet or porous soil without deepening, before building the bulk layers, geotextiles are laid on it, which prevents the appearance of silt and the spreading of the layer of sand from which the cushion is made. A sand cushion is also placed under the rib by pouring sand onto the bottom of the excavations, which must then be compacted with crushed stone. These pillows are installed around the entire perimeter of the pit.
The formwork for the stiffeners is made permanently, from flat slate, which is a thin material that has sufficient strength and is characterized by high reliability. Thanks to it, the ribs retain the desired geometric shape and are brought to the same height.
- Then waterproofing is performed. To prevent concrete from losing cement laitance, it is necessary to impregnate the soil at the bottom of the trench. For this, heated bitumen is used. You can arrange preparation by laying thin concrete, the thickness of which is 5-6 mm. When the footing has hardened, it must be primed and covered with a sheet of polymer or bitumen material, maintaining an overlap of 15-20 cm. After this, a layer of profile membranes is laid, the edges of which are glued together using special tape. The joints between smooth polymer membranes are welded. Laying of bituminous materials is carried out in two perpendicular layers, glued with mastic or fused using a torch.
The waterproofing carpet must have a fabric that extends beyond the edges of the base. After laying, the protruding ends of the material are wrapped and pasted on the side surfaces.
Stages of manufacturing a monolithic slab
To put all the pieces of the puzzle into one picture, I suggest you understand everything step by step. The technology for constructing a monolithic slab foundation is very difficult. It will be difficult for beginners in this matter to think about specific formulations. But if you have set yourself such a goal, then do not deviate from it.
A house built on such an excellent and stable foundation will be worth much more when it is subsequently sold than a house whose foundation does not consist of a monolithic slab. So:
- A large number of assistants or professional builders dig a pit of a certain depth.
- The entire depression is filled with a sand cushion.
- As mentioned above, a special drainage system will be laid around the foundation in order to protect it and future basement areas from flooding.
- A layer of so-called concrete is made on the sand cushion, which is made in order to place material there that will protect against water ingress.
- Then the main part of the work happens: the reinforcement and foundation slab come into play. After pouring this slab, some of the reinforcement will stick out from it. Thanks to this, future walls will be firmly connected to the slab.
- Then follows a mandatory process, without which it is not possible to make a monolithic foundation. You need to make a strong frame from the reinforcement, the distance between the rods of which should be 25-30 cm. The reinforcement should cover the formwork, do not forget this.
- Clean and slightly wet formwork must be installed to make the walls more durable. The aligned beams together with the bolts finally secure the formwork.
- The climax comes, namely concreting. The average thickness of one layer of concrete is 15 cm. After pouring it, you need to level and properly compact the uncured mixture. We do this until the first water appears on it. Thanks to the leveling bar, which must be moved along the formwork, the gradually cooling concrete will finally assume a level position.
- The last, final stage. This is like an indicator of the work done. Only when the entire concreting process is completed and the concrete has hardened does dismantling of the formwork begin. After this, the monolithic slab is considered complete.
And after this the question arises: are you really ready to sacrifice your family budget for expensive equipment, good equipment? If yes, then we have no right to restrain you. The main thing is to do this consciously, after consulting with your family. We can rejoice in the fact that your house will have the fate of a long-liver - this foundation will stand firmly for about 150 years.
Formation of the structure: formwork, mortgages, reinforcement
After waterproofing, they begin to install removable formwork for a slab with a height of 50 mm higher than the pouring mark. Boards, sheet materials or inventory panels are used for it. I use a level to set the formwork. In addition, the vertical is controlled, and supports are used for better stability.
Along with the arrangement of the formwork, sleeves for utility service entries are laid. The sleeves are closed with plugs and then wrapped with plastic film, so that concrete will not get into the pipes.
Then reinforcement is made to give the base the required strength parameter. The reinforcement is first installed on the ribs, placing 2-4 rods in them, which are connected transversely by the reinforcement, at such a distance that there is a protective layer of concrete of 50 mm on each side. The connection between the ribs and the slab is ensured using special bent elements.
A classic frame for the slab is formed from two horizontal grids - the rods are connected perpendicularly so that the formed cells have a size of 200x250 mm. The rods of one grid are placed on clamps made of plastic, and vertical rods of a certain length provide sufficient distance from the upper grid. The rods are fixed with wire, ties or polypropylene clamps.
The project specifies each reinforcement parameter, the type and diameter of the reinforcement used. All that remains is to carry out the work accurately, according to the drawing, in compliance with the technology.
Slab installation cost
The relatively new technology of using a profiled PVC membrane under the base makes it possible to simplify and speed up the installation of the foundation slab. Due to its excellent mechanical strength and water resistance, it serves as waterproofing and allows you to do without concrete.
Let's consider what the cost of such a foundation slab for an aerated concrete house with an area of 150 m² is at the beginning of 2021. Slab thickness 250 mm, section of plinth walls 600*400 mm:
| Name of materials and works | Unit change | Quantity | Price, rub. | Amount rub. |
| Work to bring the project to the site | complex | 1 | 3730 | 3730 |
| Soil development without removal | complex | 1 | 11220 | 11220 |
| Installation of embedments for sewerage from PVC pipes d110 mm: work | complex | 3730 | 3730 | |
| —“— materials | complex | 1 | 4270 | 4270 |
| Installation of mortgages for water supply from HDPE pipes d32 mm: work | complex | 1 | 7221 | 7221 |
| —“— materials | complex | 1 | 11220 | 11220 |
| Construction of a geotextile separating layer: work | roll | 3 | 749 | 2246 |
| —“— materials | roll | 3 | 2500 | 7500 |
| Sandy base with compaction thickness. 300 mm: work | m³ | 60 | 749 | 44928 |
| —“— materials with delivery | m³ | 60 | 850 | 51000 |
| PVC membrane Planter-standard: work | m² | 120 | 31 | 3744 |
| —“— materials | m² | 145 | 120 | 17400 |
| Built-up horizontal waterproofing: work | roll | 11 | 749 | 8237 |
| —“— materials | roll | 11 | 1565 | 17215 |
| —“— gas cylinder | PC | 2 | 1200 | 2400 |
| Consumables: board and timber for formwork | m³ | 2 | 11000 | 22000 |
| AIII fittings | tn | 2,1 | 50000 | 105000 |
| knitting wire | kg | 42 | 110 | 4620 |
| clamps | PC | 250 | 10 | 2500 |
| technical polyethylene | m.p | 500 | 50 | 25000 |
| Layout of foundation axes | m³ | 21 | 150 | 3150 |
| Installation of a volumetric frame with a cell 200*200 mm | m³ | 21 | 1872 | 39312 |
| Cutting and bending of reinforcement | m³ | 21 | 1495 | 31395 |
| Assembling the slab formwork | m³ | 21 | 299 | 6279 |
| Formation of a slab of B22.5 concrete with delivery: work | m³ | 21 | 2392 | 50232 |
| —“— materials | m³ | 21 | 5100 | 107100 |
| Dismantling the slab formwork | m³ | 21 | 76 | 1596 |
| Formwork for basement walls (lumber) | m² | 42 | 800 | 33600 |
| Removal of the axes of the stiffening ribs (base) | m³ | 6 | 150 | 897 |
| Installation of the plinth frame | m³ | 6 | 1872 | 11232 |
| Cutting and bending of reinforcement | m³ | 6 | 1495 | 8970 |
| Installation of plinth formwork | m³ | 6 | 299 | 1794 |
| Formation of a plinth from concrete B 22.5 with delivery: work | m³ | 6 | 2392 | 14352 |
| —“— materials | m³ | 6 | 5100 | 30600 |
| Dismantling the plinth formwork | m³ | 6 | 75 | 452 |
| Overhead and transportation costs | ||||
| Rent and transportation of a cabin | PC | 2 | 13500 | 27000 |
| Backhoe loader | shifts | 1 | 15500 | 15500 |
| Delivery of fittings | cars | 1 | 13500 | 13500 |
| Delivery of piece materials and boards | cars | 1 | 14000 | 14000 |
| Concrete pump | cars | 2 | 21000 | 42000 |
| Rigging and fastening | 15% | 65614 | ||
| TOTAL ESTIMATED: | 873760 |
Thus, 1 m² of a foundation slab with stiffening ribs pointing upward, and with a profile membrane instead of a footing, costs 5,825 rubles.
The foundation is ready, all that remains is to dismantle the formwork
Concreting
The slab foundation is made of M300 concrete, which is characterized by high levels of compressive strength, mobility and water resistance.
The slab must be poured within one day. For this reason, concrete workers have to work day and night. The work project indicates the correct pattern for laying concrete.
In case of force majeure situations (failure to deliver concrete on time, breakdown of a concrete pump, etc.), it becomes necessary to install working concreting joints, which are sometimes specified in the project if the slab foundation has a large area.
The concrete mixture is laid horizontally, in layers directed in one direction. A concrete pump is used for this. Concrete is laid evenly distributed around the perimeter. It is allowed to raise individual protrusions above the pouring level by a maximum of 10 cm.
Redistribution and leveling of the mixture entering the formwork cannot be done with a vibrator, which is used to compact the concrete after redistribution.
Layers of concrete are laid one at a time before the previous layer begins to harden. If this happens, you cannot do without constructing a working seam. But to continue work it is necessary to wait until the concrete becomes stronger.
The drying speed of concrete depends on the method of cleaning the cement film:
- Washing – strength 0.3 MPa.
- Metal brushes – 1.5 MPa.
- Mechanical cleaning method (sandblasting) – 5 MPa.
Strength is determined in a construction laboratory.
In the absence of force majeure circumstances, the next layer of concrete is compacted using a vibrator. The device is immersed at least 5 cm into the previous layer. The vibrator must not be allowed to come into contact with embedded or reinforcing elements.
The relocation of the vibrating tool should be a distance equal to a maximum of 1.5 of its radius of action. In this case, the compacted area will intersect with the previously compacted one. Vibration is carried out until the concrete stops settling and a shiny cement paste appears on its surface.
All compacted layers must be up to 25 cm high. The foundation slab is poured at a time, and the ribs are poured layer by layer. Their depth parameter is up to 80 cm.
When can you choose a monolithic slab?
A monolithic slab with a grillage upwards can be chosen as a base for a future structure in the following cases:
- Based on the results of geological studies, a large number of problems were found in the soil. For example, too much humidity, bulk soil, the presence of gushing springs underground, flooding of the area with melt water, quicksand, moving soil, etc.
- It is planned to erect a complex architectural structure of large dimensions.
The foundation slab can be erected depending on the initial conditions under the following circumstances:
- Construction of a foundation without deepening the base. In this case, no preliminary work regarding digging pits is done; the foundation is erected directly on the cleaned surface.
- Shallow recessed base. In this case, the foundation is buried into the ground no more than half a meter. This involves digging a pit to fill the concrete solution.
- Monolithic slab, buried to a sufficiently large depth. In this case, a pit is dug to the point where soil freezing extends in winter. As a rule, the depth is about one and a half meters.
How to calculate a monolithic slab foundation
To calculate the foundation slab, you need to use the services of experts. At the design stage, all features of the site should be taken into account. Most math calculations should be done by experts, but light calculations can be done on your own.
So, if you need to build a garage, shed or bathhouse, then it is enough to determine the thickness of the foundation slab. If the parameters are too small, the structure will not be able to cope with bending loads, and if the thickness is excessive, unjustified costs will appear.
Calculation of optimal slab thickness
Calculating the thickness of a slab foundation with your own hands according to step-by-step instructions is carried out after a thorough assessment of the soil at the construction site. For this task, it is better to invite specialists with professional drilling equipment. They will help determine the composition and thickness of the layers, find the location of groundwater and carry out further calculations.
Each soil has its own bearing capacity, which is measured in kilopascals (kPa). The distributed pressure from the mass of the future building should not exceed the load-bearing capacity of the slab.
Calculation of the reinforcing frame and the amount of materials for its manufacture
If you need to reinforce slabs with a thickness of 150 mm, you will need a single-tier knitted mesh with a diameter of 12-16 mm, which is fixed in the central part. If 200 mm structures are used, the reinforced elements are secured in 2 tiers with two meshes with a pitch of 200-300 mm.
For more reliable fixation, the pitch of the rods should be tightened and the mesh should be tied at the points of intersection of the rods using steel wire.
To get accurate parameters, you should use functional online calculators.
Design features
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base
The slab base in the form of a continuous monolithic structure under the house is itself quite strong. But in some cases it is necessary to give the structure additional rigidity. This is achieved through the use of stiffening ribs, which are located along the perimeter of the slab and sometimes stand at a certain pitch along the longitudinal side (if the slab is very long).
Important: among all types of foundations, it is the monolithic slab that ensures sufficient stability of a heavy building on any type of soil, since it has the largest supporting area.
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base. Imagine that a solid monolithic slab was placed on a monolithic strip or, conversely, a monolithic strip was installed on a solid slab base. This is what a slab foundation looks like, equipped with stiffening ribs.
In this case, the slab is a single monolith with a rib structure. This gives the entire structure additional strength, resistance to soil movement and rigidity.
Attention: stiffeners must be installed along the perimeter of the slab part and under all load-bearing walls of the building.
If the building area is large, then the ribs can be located not only across the long side, but also along it, thereby forming a lattice-like structure. The thickness of the slab structure and the height of the strip part are determined by calculations taking into account all loads and soil characteristics.
Some features of the construction of slabs with ribs down
It is imperative to remove a layer of humus over the area of the future building. Expand the perimeter of the trench taking into account the need to add material or cushion. The dimensions of the pit are calculated using the so-called diagonal method.
A sand cushion no thicker than 250 mm thick is placed on the bottom of the earthen layer. If the designed structure has a large area or mass, then the thickness automatically increases to 450 - 500 mm. In this case, it is necessary to compact each layer with a vibrating plate. Simultaneous construction of such thickness is not envisaged.
Calculation of the thickness of the slab and reinforcing frame
When installing a slab foundation with your own hands, it is important to correctly calculate the thickness of the slab. A base that is too thin will not withstand the load. Pouring an excessively thick slab will lead to unnecessary financial expenses.
Please note: each centimeter of slab thickness is 1 cubic meter of concrete mixture per 10 square meters. m area.
The calculation should be entrusted to professionals or a special program should be used. The value is calculated based on the type of soil and loads on the foundation. Therefore, it is necessary to have geological exploration data on the site and a ready-made construction project. The standard thickness of a slab foundation is 200-300 mm.
The reinforcing frame for slabs up to 150 mm thick is made of one layer of mesh, located along the central horizontal axis. For slabs of 200-300 mm, two parallel layers of mesh are required, installed with a distance of 30-50 mm from the bottom and top of the future slab. The diameter of the reinforcement is 12-16 mm, the installation pitch of the rods is 200-300 mm.
Under load-bearing walls, the installation spacing of the rods is reduced due to the sparser arrangement of the elements in the central part of the slab.
It is most convenient to calculate the number of reinforcing bars and clamps for their fastening using a specialized calculator.