The foundation is the main structural element of any building. A brick house is no exception. Without a reliable load-bearing foundation, it is impossible to build a durable and comfortable home. An incorrectly laid foundation of a building can cause many troubles, including the destruction of the entire structure. Therefore, it is so important to choose the right and high-quality foundation for a brick house. This article is intended to answer the questions of which foundation is better and how it is poured.
Factors influencing the choice of foundation
The foundation of any building is designed to take on the weight of the structure, support it without deformation and transfer it to the underlying soil. A brick house is one of the most problematic buildings; not all types of foundations are suitable for it. The reason lies in the impressive mass of brick walls.
With an external wall thickness of 640 mm (thermal technical standard) and a height of 3 m, the mass of a linear meter of one floor will be 3460 kg. For comparison, a linear meter of a wall made of foam concrete (500 mm) will weigh 1350 kg, and one made of wood (300 mm) - 470 kg. It is clear that brick walls exert a serious load, and therefore strict requirements are imposed on the choice of foundation.
When designing, the foundation for a brick house is calculated based on several initial data. The calculations are influenced by both the characteristics of the house itself and some external reasons. The following factors are taken into account:
- The load of the house on the foundation (depends on the area, number of storeys, wall thickness).
The walls exert the main load on the base Source bg.decorexpro.com
- Physico-mechanical features of the soil at the building site. The soil can have different densities (which determines the calculation of the permissible load), be natural or bulk. The foundation on heaving soil is designed especially carefully.
- Soil water saturation . It depends on the groundwater level and affects the depth of soil freezing.
Soil properties
The main problem of all foundations is soil heaving. Often this factor has different indicators within one area.
The degree of soil heaving can only be determined based on soil analysis in laboratory conditions. But geological surveys of a building site are expensive and time-consuming, and therefore developers of small houses often use the advice of colleagues from neighboring sites, or use standard recommendations.
The first rule that should be followed for the optimal choice of foundation: a brick foundation must stand on dry soil. A brick foundation is rigid, its strength level decreases sharply under the influence of moisture. That is why a brick base is optimal for dry soils with low groundwater levels.
Important! If this condition cannot be met, then a set of drainage works should be carried out or another solution for constructing the base of the structure should be used.
Shrinkage of brick buildings
Most people are of the mistaken opinion that only wooden structures are at risk of deformation, while brick buildings are free from such problems. In fact, the concept of shrinkage of a brick house is known to all professional builders; This refers to the shrinkage of the foundation. Since the weight of load-bearing walls reaches significant values, shrinkage can also become significant and lead to the appearance of cracks in the walls. The intensity of shrinkage is determined by the properties of the soil - the softer it is, the more the foundation of the house will sink. To reduce negative processes, a cushion is laid under the foundation of the building - a layer of concrete, sand or crushed stone.
Consequences of uneven shrinkage Source stroi-x.com
The period of shrinkage of a brick country house can last for several years (sometimes 5-6 years). To ensure that the process proceeds evenly and does not damage the integrity of the building, the importance of selecting the right foundation becomes obvious. Special technological techniques during the construction of walls also help to avoid cracks. Special expansion joints are left in the brickwork. They last for one to two years and serve as a good preventive measure against the occurrence of not only shrinkage cracks, but also temperature cracks.
After the project has been prepared and a clear understanding of the objective conditions of the construction site has been obtained, the type of foundation is determined. Three types of foundations can support a two-story brick house: strip, pile and slab.
Strip foundation of a brick house
Visually, the strip-type foundation fully corresponds to the name. It has the form of a contour reinforced concrete strip running along the perimeter of the house (under the load-bearing walls) and under the internal partitions. The tape type has become widespread due to the following advantages:
- Ease of execution.
Construction of a strip foundation Source stroy-dom-pravilno.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in foundation repair and design.
- Durability . Service life exceeds 50 years.
- Ability to withstand significant loads without deformation .
- Applicable for any projects . Base strips can be used as wall structures for a basement or ground floor.
The disadvantages of the tape type are its following features:
- Cost . Significant material, time and human resources are required.
- Restrictions . Strip foundations are not used on some soil types. It also imposes restrictions on the choice of architectural form of the building. The depth of the strip foundation for a two-story house is determined for each project individually, based on its features and the characteristics of the site.
The basis of quality is a properly poured concrete mixture Source nearsay.com
There are several types of strip foundations:
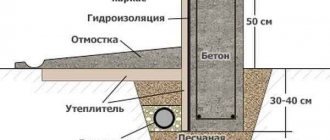
- Monolithic . Solid concrete structure, the most durable and therefore the most common option for brick buildings; the weight of the structure on such a foundation is distributed evenly. A trench is dug along a given perimeter, a cushion of crushed stone and sand is laid on the bottom, a layer of waterproofing is installed, and wooden formwork (bounding surfaces) is installed. A reinforcing belt is installed (steel reinforcement secured in a special way). The concrete solution is poured into the formwork and further compacted. The disadvantage of this method is that you have to wait until the concrete mixture hardens and gets stronger.
- Prefabricated (block) . Finished reinforced concrete blocks are laid in the order specified by the project in a trench and fixed. The disadvantage of this method is the need to use special equipment to move individual elements. A prefabricated base is less durable than a monolithic one
- Shallow-recessed . It is not suitable for two-story buildings made of stone or brick, since it goes into the ground a little more than half a meter.
Scheme of a prefabricated strip foundation Source remoo.ru
A monolithic foundation can be constructed in two ways:
- If the house design includes a basement or basement , then at the first stage a pit is dug, at the bottom of which a reinforced concrete layer is constructed. After it hardens, the basement walls are erected. Such a foundation turns out to be the most reliable; it is designed for two- and three-story brick buildings.
- If the design of a two-story brick house does not include a basement , a standard strip base is installed. Its depth is determined by increasing the depth of soil freezing by 30-40 cm.
Necessary tools for work
To strengthen the structure, you will need a reinforcing mesh.
To make a red brick foundation, in addition to the main material, you need a concrete solution and a reinforcing mesh to strengthen the structure. Separately, you need sand and crushed stone to install the cushion at the bottom of the trench. Masonry tools you will need:
- Master OK;
- cord, jointing;
- hammer-pick;
- shovel;
- construction and hydraulic level, plumb line;
- pegs for marking the territory;
- steel reinforcement.
You can prepare the cement mortar manually, but it is better to use a concrete mixer.
Pile foundation
A pile foundation for a brick house, a two-story or one-story project, is designed for an area with fragile, crumbling soil, and is characterized by the following parameters:
- The use of piles helps transfer the main load from a building to deeper, stronger layers of soil , bypassing the unreliable top layer.
- The upper part of the piles , remaining on the surface, is tied into a single structural element using a reinforced concrete grillage . The building rests on this contour, but most of the load is carried safely on the piles.
Fragment of a pile foundation Source domvita.ru
- The pile method involves the use of special equipment for drilling wells and installing piles. This leads to additional costs, but is compensated by the speed of installation and ease of installation.
- The use of piles is economically justified in areas with dense soil . The method allows you to equip a foundation designed for fairly high loads, and the calculations must be carried out very accurately.
- The use of piles is not economically justified when building on water-saturated soil . In order for the foundation to fully support a two-story brick building, it will need to be strengthened. As a rule, this will require an increase in the number of piles. It will be necessary to use piles of larger cross-section and immerse them to greater depths. In addition, a powerful grillage contour for cutting the piles will be required. Such changes can negate the efficiency of the pile method.
Technical characteristics of red brick
The key parameters of red brick include strength and frost resistance. Strength shows the maximum load this material can withstand. Thus, brick grade M175 is able to withstand a weight of 175 kg per 1 sq. cm.
Frost resistance shows how many freezing cycles it can withstand.
Slab (monolithic) foundation
A good way to arrange the foundation of a two-story brick house. Such a foundation looks like a solid reinforced concrete slab on which the frame of the house is built. It is characterized by the following parameters:
- Laying depth . There are deep foundations (from a meter or deeper), shallow foundations (0.5-1 m) and non-buried foundations (up to 0.5 m).
- Duration of operation . It is the highest when compared with other types; the base is designed for 60-70 years of flawless service.
- Use on problematic soils . An ideal solution for heaving, weak and waterlogged soil.
- Minuses . The slab type is characterized by high construction costs and high time costs.
Which brick to use
For the construction of foundation structures, it is permissible to use red ceramic bricks.
This material is resistant to moisture and is practically not subject to seasonal deformation. To create foundation foundations, it is advisable to lay bricks with frost resistance from 35 to 100. The hardness should be above 175.
Choosing a foundation and ways to strengthen it
The foundation of a two-story brick house is subject to special requirements in terms of strength and depth parameters. In most cases, the choice is made as follows:
- If the soil is not problematic , a strip foundation . It is made deeply recessed, and a wider grillage, according to calculations, is also laid.
- If the soil at a construction site is heaving (changes its volume during the annual freezing-thawing process), preference is given to a pile foundation , which can provide a significant margin of safety. Reinforced concrete pillars with a large cross-section are chosen for it, and only reinforced concrete grillage is laid. If a strip block (prefabricated) foundation is chosen, it is installed below the freezing layer, or the heaving soil is replaced with a backfill of sand or crushed stone.
- If the soil is wet , heaving or crumbling , a deep slab foundation .
Markings and sizes of ceramic bricks
In the designation of red brick, alphanumeric designations are used, they include the following meanings:
By - shows that the brick is hollow; 1NF – shows its dimension. A single brick has the following dimensions - 250x120x65 mm; M250 – indicates the strength grade;
Video description
What types of foundation are there? How is the foundation built and how much does it cost? See all this and much more in this issue:
Scheme of a deep foundation Source kamtehnopark.ru
Sometimes there is a need to strengthen the foundation of a brick house. This can be done in a variety of ways, including:
- Strengthening by injections . The soil around the base is removed, and a cement solution is applied to the exposed base (special equipment is used).
- Reinforcement with piles . Piles are installed along the foundation.
- Reinforcement with reinforced concrete cage . Formwork is installed around the perimeter, a reinforcing belt is installed and concrete mixture is poured.
- Reinforcement with a protective wall . The outer wall is made of concrete, sometimes it rises to a height of up to one meter.
Reinforcement with reinforced concrete slab Source pallazzo.su
Principles of foundation calculations
The foundation for any buildings, including brick ones, is described by several parameters:
- Deepening . It is selected based on an analysis of the soil (density and bearing capacity) and freezing depth. There are tables relating soil type and recommended depth.
- Foundation load . It is calculated based on the total weight of the brick house. To do this, structural (walls, partitions, roofing, floors), internal (people and furniture) and external (snow on the roof) loads are summed up.
- Required (minimum) support area and base width . The total area of the concrete strip is determined by the bearing capacity of the soil and the load on the soil of the building along with the foundation. Knowing the area and perimeter, you can, by dividing the first by the second, calculate the width of the strip base.
A high-quality foundation will give a house a long life Source sever-dom.su