the amount of propane - butane gas in a household cylinder is 50, 27, 12, 5 liters
In a household gas cylinder with a volume of 50, 24, 12, 5 liters, according to current regulations, there should be no more than 85% of liquefied gas from the volume of the cylinder.
that is, completely empty cylinders must be filled with the following by the refiller:
50 liter cylinder (22 kg) - 42.5 liters = gas 23.16 kg (summer) or 21.97 kg gas (winter) = full cylinder 35.16 kg (summer) or 43.97 kg (winter).
27 liter cylinder (14.4 kg) - 22.95 liters = gas 12.5 kg (summer) or 11.86 kg (winter) = full cylinder 26.9 kg (summer) or 26.26 kg (winter)
12 liter cylinder (9kg) - 10.2 liters = gas 5.56 kg (summer) or 5.27 kg (winter) = full cylinder 14.56 kg (summer) or 14.27 kg (winter)
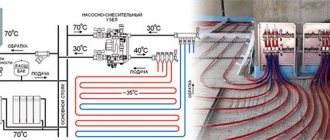
Calculation of main gas flow
The calculation of the required power is carried out on the assumption that the height of the rooms does not exceed 3 m, its area is 150 m2, the condition of the building is satisfactory, and there is insulation. Then, to heat 10 m2 of area, an average of 1 kW of energy is consumed at a temperature lower than –10 0C. Since this temperature on average lasts only half of the heating season, you can take the base value as 50 W*m/hour.
Depending on the thickness of the wall insulation, gas consumption is significantly reduced Source m-strana.ru
Gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 will be determined by the ratio
A = Q / q * ɳ
- Q in the selected example is calculated as 150 * 50 = 7.5 kW and is the required power needed to heat a given room.
- q is responsible for the type of gas and exerts specific heat. For example, q = 9.45 kW (G 20 gas).
- ɳ shows the efficiency of the boiler, expressed in relation to unity. If efficiency = 95%, then ɳ = 0.95.
Let's carry out the calculations and find that the gas consumption for a house with an area of 150 m2 will be equal to 0.836 m3 per hour, for a house measuring 100 m2 - 0.57 m3 per hour. To obtain the average daily quantity, the result obtained is multiplied by 24, for the monthly average - multiplied by another 30.
If you change the boiler efficiency to 85%, 0.93 m3 will be consumed per hour.
How does a liter compare to a cubic meter?
The liter is a measure of capacity that is not included in the international SI system, but is used very widely. Moreover, it is the liter, and not the “abstract” cubic meter, that is the most common unit of volume measurement in everyday life. For example, it is measured in liters:
- capacity of various vessels intended for household use (buckets, pans, bottles, canisters, containers);
- trunk volume of passenger cars,
- internal volume of refrigerators, freezers, microwaves and ovens;
- capacity of city and tourist backpacks.
The "official" definition of a liter has changed several times. From the beginning of the 20th century until 1964, according to the decision of the General Conference on Weights and Measures, a liter was defined as the volume occupied by a kilogram of water. However, this definition turned out to be not very convenient: the ratio of the volume and mass of a liquid depends on many factors - from atmospheric pressure to air humidity. Therefore, experts abandoned the “reference” to the mass of water. And now a liter means a volume that exactly corresponds to a cubic decimeter - the volume of a cube, each edge of which has a length equal to exactly 10 centimeters, which corresponds to 0.1 meters.
Basics of the physical meaning of transformation
The physical meaning of the transformation is not a big problem. In this case, the conversion method for any gas is similar to that for liquids and bulk materials. The calculation is made according to the following method:
1 m³ = 1,000 liters
Accordingly, 1 liter contains 0.001 cubic meters. If the meter shows that natural gas was consumed in the amount of 0.3 m³ during the day, then in liters this value will be 0.3 x 1000 = 300.
Summary
If gas consumption is high, for example, during the gasification of a large industrial facility, you should first of all find all possibilities for connecting to the gas main. Although this may require much more expense than installing gas tanks and related equipment, the costs will be recouped over time due to the low price of fuel.
With moderate gas consumption, for example, when gasifying a private house, a small village, a farm, a small and medium-sized industrial enterprise, an autonomous system using gas tanks would be a more reasonable solution.
Operating and Maintenance Costs
Well-regulated gas equipment requires virtually no maintenance, since neither liquefied nor main gas forms carbon deposits and soot. Preventive maintenance and control inspections are carried out regularly regardless of the type of fuel, and the costs are approximately the same.
Operating costs when using liquefied gas may include electricity costs if the system uses electrically heated evaporators. Evaporators are installed in powerful industrial systems to increase the rate of formation of the vapor phase, as well as with ground-based gas holders, since the natural evaporation of the butane component stops at subzero temperatures.
But electric evaporators are usually used in systems with relatively little gas consumption, and they do not consume as much energy. High-performance systems use liquid-heated evaporators, the heat for which is produced by burning the same liquefied gas.
So, the operating and maintenance costs for systems running on mainline and liquefied gas are almost the same.
How much does heating cost?
The amount of heating depends on the amount of gas consumed and the price per 1 m3 in a given region. By simply multiplying two numbers, you can determine costs per day, per month or for the entire heating season.
In terms of absolute price per m3 (kg), main methane is 3-4 times cheaper than propane-butane mixture. However, when comparing the heating consumption of a building of 100 m2, methane requires an average of about 3000 m3, and only 1000 m3 of liquefied mixture. Therefore, it can be argued that how much liquefied gas costs for heating a house is the same price for main gas, due to higher consumption.
How many liters of water are there in a cube according to the meter?
Online calculator for converting kW to hp
To pay for services, citizens are required to record meter readings. Thus, the amount of cubic meters of water consumed per month is determined.
How it's done:
- Current readings are recorded. If the meter is new, the readings will be reset, but it must pass verification.
- A month later, readings are taken again. The old values are subtracted from the new figure. The total is multiplied by the regional tariff and included in the receipt.
- In some regions, a minimum consumption is established, so if only 5 liters are used, and the norm is 1 cubic meter of water, you will have to pay more. Next month the overpayment will be taken into account.
During the absence of residents in the apartment, the meters do not work, therefore, only mandatory payments will have to be made.
This rule does not apply to residents of regions where standards are set - they need to pay the minimum in any case.
On average, 1 cubic meter of water is used for the following needs:
- taking a bath – 13 times;
- machine washable - 14 times;
- showering – 30 times;
- flushing the toilet – 110 times.
If the house has a small children's pool, 12 cubic meters will be needed for one-time filling. If you have a vegetable garden, there is a need for regular watering, and consumption increases by 10 m3.
In order to save money, some install magnets and seals to reduce readings.
The latter should be mandatory, but magnets are prohibited by law, and the owner may be fined during inspection.
How to pay less
Since you won’t be able to significantly win in price by installing autonomous heating, you need to turn to energy-saving technologies.
- Carry out thorough insulation of not only the walls of the building, but also the roof, floor, foundation, even the basement, if there is one.
- Replace double-glazed windows with energy-saving ones, the profile is frost-proof.
- Install a boiler with maximum efficiency and an electronic thermostat.
- Check the condition of the house's thermal insulation using a thermal imager to identify cold spots and eliminate them.
- Change the ventilation and air conditioning system. Just an open vent or a window set for ventilation takes in more heat than a window opened for 5-7 minutes and a complete change of air in the room.
- Install heated floors , especially in hallways and hallways.
- Install electronic sensors to block heating above the set temperature.
It is very effective to use the smart home system, which will reduce gas consumption by at least 25%. If you follow all the tips, your home will be warm and cozy, and your gas bills won’t be terrible.
The smart home system is easier and more comfortable to control using a remote control Source archidom.ru