Our company offers to buy water heaters, split systems and solar collectors for heating water and autonomous heating systems at a competitive price. The company's catalog presents a large assortment of heating and hot water equipment of various capacities produced in Russia, China and Austria. All solar collectors and instantaneous and storage water heaters (boilers) have a quality guarantee.
Research has established that on a clear day, in 1 hour, 1 m2 of the Earth's surface receives about 1000 watts of energy from the sun. These data are averaged and depend on the latitude and time of year. Modern solar collectors allow you to partially capture this energy and use it for the needs of your home, office, or business. In this case, there is no need to use fuel.
The principle of operation of the solar collector
It's very simple. The panels accumulate solar heat and transfer it to the coolant. It circulates through a coil in the storage tank and releases heat to the water, which can be used for any need. The entire process is controlled by a controller, which starts the pump group if the heat exchanger reaches the required temperature.
How does a solar collector work in general?
. The entire system consists of the following elements:
- the panels themselves in the required quantity according to calculations,
- control controller (including sensors),
- pump group,
- storage capacity (usually a tank of 300-3000 liters),
- mounting elements, pipes and fittings.
It is impossible to remove any element from this scheme; it will not work. The only exception is collectors with flow-through heaters. More on them a little later.
Performance you can count on
Before installing such equipment, it is worth considering such a factor as payback. After all, a bad entrepreneur is one who does not make a profit from his investments. The payback of a collector depends directly on its productivity.
Study of samples
Let's take a closer look at several samples of both types of collectors.
ISolar
Flat-plate collector made in Russia YaSolar.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Absorber material | Copper |
| Light absorbing surface area | 2 m2 |
| Rated thermal power | 1.5 kW at a lighting intensity of 900 W/m2 and an outdoor temperature of 20 °C |
| dimensions | 2065x1073x105 mm |
| Empty mass | 37 kg |
| Internal volume | 1.4 l |
| Glass | Anti-glare, thickness 3.2 mm, translucency 92% |
| Thermal insulation thickness | 60 mm |
| Manufacturer country | Russia |
| Price | 21,700 rubles |
SOKOL-EFFECT-A
Solar collector Sokol-Effect-A.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Rated thermal power | 1.5 kW at a lighting intensity of 900 W/m2 and an outdoor temperature of 20 °C |
| Dimensions | 1093x2008x76.7 mm |
| Internal volume | 1.4 l |
| Empty mass | 32 kg |
| Glass | Anti-glare, thickness 3.2 mm |
| Absorbing surface area | 2.06 m2 |
| Absorber material | Aluminum |
| Manufacturer country | Russia |
| Price | 21900 rubles |
KAIROS VT 15B ARISTON
Vacuum Italian manifold KAIROS VT 15B ARISTON.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Number of tubes | 15 |
| Dimensions | 1910x1840 mm |
| Weight | 51 kg |
| Absorbing surface area | 1.5 m2 |
| Internal volume | 4.6 l |
| External diameter of vacuum tubes | 70 mm |
| Stagnation temperature (stop heating) | 206 °C |
| Operating pressure | 6 atmospheres |
| Price | 77965 rubles |
Absorber, the most important part of the system
The part of the solar collector that receives, accumulates and transfers heat to the coolant is called an absorber. The efficiency of the entire system depends on this element.
This element is made of copper, aluminum or glass, followed by coating. The efficiency of the absorber depends more on the coating than on the material from which it is made. Below, in the photo, you can see what kind of coatings there are and how effectively they can absorb heat.
The description of the system indicates the maximum possible absorption of solar energy incident on the absorber. "α" is the maximum possible absorption percentage. "ε" is the percentage of reflected heat.
By type of structure
Absorbers also differ in the type of device; now there are only two types:
Feather
- are arranged as follows. The plates connect tubes with coolant to each other. The tubes themselves can be interconnected into one system in several ways. This is a simple type of absorber that you can make yourself.
Cylindrical
— in this case, the coating is applied to the glass surface of the flask and used in vacuum manifolds. Thanks to this device, the heat is concentrated more precisely in the center of the tube where the heat extractor, or rod, is located. This system operates with higher efficiency than the pen system.
Operating principle
All types of solar collectors can be used to heat a residential building or other facility, but the principle of their operation, regardless of the design and type of coolant, is the same.
The principle of operation of a solar collector is based on the ability of materials to absorb the energy of the sun in visible and invisible ranges to the human eye, and therefore, within a given material, physical processes begin, molecules begin to move faster, the material (substance) heats up. The heat generated by materials exposed to the sun's rays is transferred to the coolant for subsequent use.
What types of solar collectors are there?
There are two types of such systems: flat and vacuum. But, at their core, their operating principles are similar. They use the sun's heat to heat water. They differ only in the device. Let's look at the operating principles of these types of solar systems in more detail.
Flat
This is the simplest and cheapest type of collector. It works as follows: The metal body, which is internally treated with a highly efficient feather absorber to absorb heat, contains copper tubes. A coolant (water or antifreeze) circulates through them, which absorbs heat. Next, this coolant passes through a heat exchanger in a storage tank, where it transfers heat directly to the water that we can use, for example, to heat a house.
The upper part of the system is covered with high-strength glass. All other sides of the body are insulated with insulation to reduce heat loss.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost panels | Low efficiency, approximately 20% lower than vacuum |
| Simple design | Large amount of heat loss through the body |
Because of their ease of manufacture, such systems are often made even with their own hands. You can purchase the necessary materials at construction stores.
Vacuum
These systems work a little differently, this is due to their design. The panel consists of double tubes. The outer tube plays a protective role. They are made of high-strength glass. The inner tube has a smaller diameter and is covered with an absorber that accumulates solar heat.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any technical device, the solar collector has its pros and cons, both in terms of the possibility of use and operation, and in terms of other parameters and indicators. Depending on the design of the device, the pros and cons vary, so it is necessary to consider them separately from each other.
Flat solar collectors.
Advantages of use:
- When used in southern regions with warm climates, the best indicators in the price-performance ratio;
- During precipitation in the form of snow, they have the ability to self-clean;
- They have high efficiency when used in summer;
- Relatively low cost in comparison with analogues of other designs.
The disadvantages are:
- Significant heat losses caused by the design features of the device;
- Low efficiency when working in the autumn-spring period;
- Difficulty in transporting and installing finished products;
- The high windage of the structure creates a risk of damage to its elements during operation;
- Difficulty and labor-intensive repair work.
Vacuum solar collectors.
Advantages of use:
- When used in regions with cold and temperate climates, the best indicators in the price-performance ratio;
- Insignificant heat losses during operation, in comparison with analogues of other designs;
- Ability to work at low and negative ambient temperatures;
- Ability to work in low solar activity in the morning and evening hours, as well as in the absence of direct sunlight (cloudy weather);
- Easy and convenient installation, transportability of structures;
- Reliability during operation.
The disadvantages are:
- Relatively high cost;
- Strict installation requirements that determine the location of the collector in space in relation to the surface of the earth.
Additional costs associated with operation
Using this does not imply any care or maintenance other than periodic cleaning of dirt and snow in winter (unless it thaws itself). However, there will be some associated costs:
- Repairs, everything that can be changed under warranty can be replaced by the manufacturer without any problems, it is important to buy an official dealer and have warranty documents.
- Electricity, very little of it is spent on the pump and controller. For the first one, you can install only 1 solar panel of 300 W and it will be quite enough (even without a battery system).
- Washing the coils will need to be done once every 5-7 years. It all depends on the quality of the water (if it is used as a coolant).
Coolants for solar systems
The main coolant for heating systems is water. However, its use in solar systems is limited by the crystallization temperature of 0°C, which means the use of water as a coolant is limited to climatic zones where there are no negative temperatures. In addition, the salts contained in the water clog the heating surfaces with scale, and the corrosive agent - oxygen - damages the metal parts of heating systems and contributes to the decomposition of the coolant into its component elements. Therefore, a type of coolant was developed for solar systems that is devoid of the above disadvantages.
The basis of this coolant is propylene glycol mixed with water that has undergone water treatment in the form of demineralization.
In addition, to reduce the corrosive and decomposing effects of oxygen, antioxidant additives are added to the coolant, the formation of gas bubbles in the liquid is reduced by the addition of defoamers, and stabilizers added to the coolant help keep the solution chemically homogeneous. As a rule, coolants for solar systems are sold ready-made. The concentration of propylene glycogel in them is 40% and higher, which corresponds to a crystallization temperature of -30°C and lower. The acid-base balance (pH) for the finished coolant is maintained in the alkaline zone (≥ 7.0) to reduce the corrosive effect.
When using solar system coolants, you should not mix coolants from different manufacturers, since compositions that are different in both quantitative and qualitative properties can enter into a chemical reaction, rendering the solar system unusable.
Solar energy in the conditions of the current energy and economic crisis is one of the most promising areas of technology aimed at preserving the irreplaceable resources of our planet.
How to install a solar collector
You can install this system yourself. To do this, you need to understand the main principle of installation - maximum sunlight.
- We choose a place
. It should be on the sunny side. To do this, it is enough to observe for several days which place on the site the sun illuminates for as long as possible (you need to avoid getting into the shadows of trees or buildings). Select a starting point and an ending point, and direct the solar collector to the center of these points. This way we will get maximum coverage of thermal radiation. - Tilt angle
. This is an important stage of installation, on which its effectiveness depends. As a rule, such data is provided by the system manufacturer, but on average it is 45 degrees. It cannot be installed at a larger or smaller angle, as this will reduce the absorbing area. - We connect the rest of the equipment
. This is a pump group with a controller, a storage tank and connecting pipes. This is all connected according to the instructions. There is nothing complicated here, since the principle of the device is quite simple.
Detailed installation video
View all construction myths
Temperature division of water heating equipment
The consumer is offered a lot of different device options, but their main difference lies in the temperatures they achieve. According to this principle, they are made into three main types of collectors:
- The first is low temperatures (they give low temperatures up to 50 degrees Celsius); the main calculation of application is heating a pool or other options when there is no need to heat the water very much.
- Next come medium temperature collectors (they raise the temperature from 50 to 80 degrees) the main calculation of the application is for heating industrial buildings and residential premises.
Medium temperature collectors are used for heating industrial buildings and residential premises.
- The third type is high temperature collectors (used in industry to generate electricity with subsequent distribution to the central electrical network).
A little about the use of systems in practice
I decided to add this section because actual usage data appeared. A good friend of mine installed it 3 years ago (Ukraine, Kiev region).
A solar system is used to heat a house of 100 sq. m and hot water for 6 people. Gas costs for heating and hot water amounted to 33,400 UAH
in year. It was decided to purchase a solar collector.
The kit includes 6 flat collectors and a storage tank of 1000 liters. Result:
- — 100%
for 6 “warm” months according to the DHW load (temperature 55 degrees), - — 50%
during 6 “cold” months according to the DHW load, - — 25%
for 6 “cold” months based on heating load in maintenance mode.
The total savings for the year amounted to UAH 11,300
(in terms of rubles, the amount must be multiplied by 2.2).
The whole system cost 94,000 UAH
. At this cost of gas, it will pay for itself in 8.4 years. Manufacturers provide a 15-year guarantee, so at least 7 years of net profit.
The efficiency of the system could be significantly increased by purchasing vacuum models. Also, low temperature heating systems, such as heated floors, which operate at a temperature of 30-40 degrees, will be more efficient.
Installation Tips
Several recommendations will help increase the performance of the heating collector:
- It is better to install the box with the radiator not rigidly, but with the ability to rotate around a horizontal axis. This will make it possible to position it at right angles to the direction of the sun’s rays throughout the season. In this case, the piping is performed with a flexible liner.
- To bleed air, valves should be inserted into the lower part of the circuit.
- Hot water pipes must be insulated.
- At night, the access of water to the tank should be shut off to avoid heat loss.
Don’t forget to install a valve at the inlet to the front chamber (in front of the float valve). When cold weather sets in, it will need to be shut off and the system drained.
Video description
Video example of the applied use of a solar collector for a country house:
- The light-absorbing panel should not be subject to shadows from nearby objects - houses, trees, pipes, fences, etc.
- When placing the device on the roof of a house, it is necessary to design a mount for it in advance.
- To avoid the accumulation of precipitation on the work surface, the device must be installed as close to a vertical plane as possible, but with minimal damage to capture sunlight.
- For optimal operation throughout the year, the device must be installed on the south side with an angle equal to the latitude of the area.
Reference! It will not be possible to create a completely autonomous heating system based on a solar collector. Since to ensure maximum efficiency, the circuit will need to be equipped with a circulation pump, automation and other equipment that runs on electricity. However, significantly reducing the consumption of the main energy resource - gas, electricity, coal - with its help is a completely feasible task.
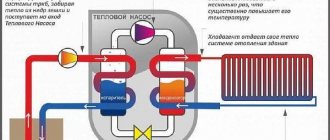
Heat pump efficiency
Many pumps are not only used to produce heat, but also work in reverse mode, cooling the room on a hot day, although this requires additional equipment. To determine the efficiency, we will resort to comparison with traditional systems, i.e. thermal boilers and refrigeration units. The transformation coefficient shows how much thermal power the pump produces per kilowatt of electricity consumed, and depends on several parameters. The smaller the temperature difference in the primary circuit and between it and the heated liquid, the higher it is. Typically, the low-temperature coolant in the heat pump circuit reduces its temperature by 3-5 °C. It is not profitable to take more heat; it is cheaper to increase the pumped volume of coolant.
Vaillant geoTherm water-to-water heat pump
A high-temperature coolant can heat up to a maximum of 50-60 °C, and in many cases 35 °C is sufficient. The transformation ratio is written in the form: B0/W50 or, for example, A35/W20. The numbers indicate the estimated temperature in the primary and heating circuits, the letters indicate the type of coolant (from the English words “brine”, “water” and “atmosphere” - “brine”, “water” and “air”). Thus, in the first case we have a “brine-water” heat pump operating for heating, and in the second case we have an “air-water” heat pump turned on in cooling mode. The average transformation ratio for air-water pumps is 2.5-3.5 (A2/W35), water-water - 5-6 (W10/W35), brine-water - 4-5 ( BO/W35). With a further increase in temperature for each degree, the coefficient decreases by approximately 2.5%.
Stiebel Eltron heat pump in the boiler room of a house
Varieties
Modern solar collectors come in water and air types. The former use water, antifreeze or other liquid with suitable properties as a coolant. Circulating through the internal tubes, it transfers heat to the heat exchanger of the heating system. Inside the air modification, the air flow is heated in a similar way, which is then supplied for heating needs.
Schematic design of a flat solar collector Source tildacdn.com