A heat pump is a device for transferring thermal energy from a source to a consumer. Heat is spontaneously transferred from a hot body to a cold one. The pump transfers heat in the opposite direction. The structure consists of a compressor, thermal expansion valve, evaporator and condenser. A typical example of a heat pump is an air conditioner.
The heat pump for heating is currently just beginning to be actively used in private homes. One of the main advantages of this heating method is low electricity consumption, but at the same time high heat generation. The following types of equipment are distinguished, classification is carried out according to the heat source.
To know which type of pump to choose for home use, it is recommended to study the features of each model and their operating principle. Each type also has limitations that are also important to know about.
Operating principle of heat pumps
The operating principle of a device for heating a house is based on the fact that a substance (refrigerant) can give off thermal energy or take it away during a change of state. This idea is the basis for the functioning of the refrigerator (because of this, the back wall of the device is hot).
Thermal pump for heating functions as follows:
- The incoming agent is cooled by 5 degrees in the evaporation section based on the energy from the coolant.
- The cooled agent enters the compressor, which, as a result of operation, compresses and heats it.
- The already hot gas enters the heat exchange compartment, in which it transfers its own heat to the heating system.
- The condensed refrigerant is returned to the start of the cycle.
There are also some models that can provide reverse operation. This means that such devices are used even in summer to cool the building. The heat is sent to storage and then used for heating during the cold season.
Device
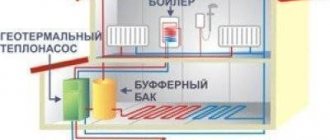
A heat pump for heating a house consists of several main circuit elements:
- a coolant circuit that transfers energy from the heat source;
- a circuit with freon, which periodically evaporates, taking thermal energy from the first circuit, and again settles as condensate, transferring heat to the third;
- a circuit where a liquid circulates, carrying heat for heating.
Operating a thermopump for heating a home is profitable from a financial point of view. The reason for this is that the device does not require high power (accordingly, the electricity consumption is no more than that of a standard household appliance), but it produces 4 times more heat compared to the electricity consumed.
There is also no need to create a separate wiring line to connect the pump.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before deciding whether to use a heat pump or not, you should familiarize yourself with the advantages and disadvantages of its operation. The main advantages of a heat pump include:
- low electricity consumption for heating the house;
- no need for regular inspection and maintenance, which makes the cost of operating a heat pump for heating minimal;
- Installation in any location is allowed. The pump can work with thermal energy sources such as air, soil and water. Therefore, it becomes possible to install it almost anywhere where it is planned to build a house. And in conditions of remoteness from the gas main, the device is the most suitable heating method. Even if there is no electricity, the compressor can operate using a gasoline or diesel drive;
- The house is heated automatically. There is no need to add fuel or carry out other manipulations, as, for example, in the case of boiler equipment;
- absence of environmental pollution with harmful gases and substances. All refrigerants used are completely safe and environmentally friendly;
- fire safety. Home occupants will never be at risk of explosion or damage due to heat pump overheating;
- possibility of operation even in cold winter conditions (down to -15 degrees);
- A quality heat pump for heating a home can last up to 50 years. Compressor replacement is required only once every 20 years.
Is a Heat Pump PROFITABLE or NOT?.. Who Shouldn't Buy a Heat Pump? (BREAK)
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any device, heat pumps have certain disadvantages:
- If the ambient temperature drops below 15 degrees, the pump will not be able to operate. In this case, installation of a second heat source will be required. At very low temperatures, the boiler, generator or electric heater turns on;
- High cost of equipment. It will cost approximately 350,000-700,000 rubles, and the same amount will have to be spent on creating a geothermal station and installing the device. Additional installation work is not required only for a heat pump using air as a heat source;
- It is best to install a heat pump in combination with heated floors or fan convectors, however, in old buildings, redevelopment and possibly even major repairs will be required, which will entail additional time and money. If a private house is built from scratch, there is no such problem;
- When the heat pump operates, the temperature of the soil located around the coolant pipeline decreases. This causes the death of some microorganisms involved in the functioning of the environment. Thus, some damage to the environment is still caused, but it is significantly less than the damage from gas or oil production.
Summarizing
Participants on our portal use a heat pump as a full-fledged heating system (not an auxiliary one). According to our observations, a heat pump is becoming an increasingly popular method of heating a country house. According to reviews from our users, a heat pump works best in houses with low heat loss, so ideally the house should be “tailored” for this device at the design stage. A good option would be a frame structure with all the necessary insulation, membranes and films, or a stone house. Second point: a heat pump is most effective in combination with low-temperature heating devices, so it’s better to immediately focus on heated floors.
On FORUMHOUSE you can find a huge amount of information for those who decide to make a heat pump with their own hands or someone else’s. There are recommendations for the correct design of a geothermal circuit of a heat pump, invaluable tips for making a heat pump yourself, find out how to make the most budget-friendly, “people’s” heating system based on a heat pump, watch our video about a house that is successfully heated with a heat pump.
Use of thermal installations in the world
The practice of using such thermal units in the world goes back more than 50 years. The main driving reasons for this phenomenon were the rise in price of traditional energy resources and the widespread support by the governments of many countries for the use of alternative energy sources.
Therefore, the number of heat pumps is constantly growing at a high rate - up to 10 - 30% per year, despite the high cost of installation. The number of such devices currently amounts to more than 270 pieces. Thermal systems are most actively used in the USA and Canada. They account for up to half of the installations used worldwide.
Russia, despite positive conditions for the use of heat pumps, lags behind global trends in their use. Our belief in a complete supply of natural resources seems to play a role here. At the same time, not all settlements in the country have gas pipelines. World experience in the use of heat pumps indicates positive trends in the development of their use.
How to improve the energy efficiency of the system?
Ready-made factory complexes are good because all their structural parts and components are balanced and adjusted to each other in terms of characteristics. The advantage of independently organizing the system on separate units is that each circuit and operating unit can be upgraded independently of the general infrastructure. Thus, many people abandon the standard heat accumulator, replacing its function with a concrete screed. In this case, geothermal heating will operate with minimal temperature differences in the mixing tank circuit. It is also recommended to experiment with refrigerant and the use of compressors with “floating” capacity. Correct calculation of the load with optimal heat distribution along the operating circuits will increase the efficiency of the system by 15-20%, while minimizing power supply costs.
Heat pump calculation
As we mentioned above, the low-grade heat sources for such pumps most often are the following media:
- Air from the outside with an average temperature of -15 to +25 degrees.
- Air from a heated room, its temperature is +15 - +25 degrees.
- Air from the subsoil probe is heated to plus 4 - 10 degrees.
- Air from geothermal formations, the temperature of which can be 10 degrees or more.
- Air from bottom probes of non-freezing reservoirs with a temperature of 0 - 10 degrees, including that obtained in probes installed on industrial wastewater channels of enterprises.
Calculation method
Any thermal calculation is a complex process, which can only be carried out by qualified specialists. However, it is possible to propose a simplified method that is sufficient to obtain a result that determines the choice of one or another model of the unit.
The calculation comes down to performing a number of steps:
- Determination of the amount of heat loss through the enclosing elements of a building - walls, ceilings, attics, windows, doors, etc. This can be achieved using the following dependency:
Qok = S x (tin – t out) x (1 + ?b) xn : Rt, where
S – total area of all building enclosure elements, m2;
t in – outside temperature, degrees C;
t out – the value of the air temperature in the outer space, degrees C;
n is a coefficient that takes into account the structure of the building; for open buildings it is equal to 1; for buildings with attic spaces it is used at a value of 0.9; for premises located in the basement it is taken equal to 0.75;
b is the coefficient of additional heat losses, depending on the type of building and its location in the climatic zones of Russia, its value can vary between 0.05 - 0.27;
Rt – thermal resistance, which must be additionally calculated using the formula:
Rt = 1( , m2xC/W, where
- calculated values of thermal conductivity of building envelope materials;
- coefficient of heat dissipation from internal surfaces;
- the same for external surfaces.
After preliminary calculations, we determine the total heat loss from various factors:
Qt.pot = Qok+Qi-Qbl, where
Qbl – total heat transfer from the operation of household appliances and human activity;
Qi – energy costs to compensate for heat losses from leaks in the construction of enclosing structures.
- Based on the results obtained, it is possible to calculate the electricity demand throughout the year. To do this, we use the relation:
Qyear = 24x0.63 x Qt.pot x ((dx (tin-tout.sr) : (tin-tout)) (kW/hour) per year, where:
- tin is the desired temperature value in the interior of the house;
- t out – actual external temperature;
- tnar.av – average annual temperature in the region;
- d – length of the heating period, days.
- If you want to have a more reliable idea of the heat pump, you need to calculate the amount of thermal power that will be needed to heat the water in the heating system of the house. This is available using this calculation formula:
Qhor.v = V x 17 kW/ per year, where:
V – volume of daily consumption of water heated to 50o C.
As a result, energy costs to meet the need for heat and hot water will be:
Q = Qyear + Qgv, (kW/hour per year).
It is recommended to increase the obtained result by 10%, taking into account the more intensive operation of the system at peak loads. Preliminary calculation of the power of a heat pump for heating a house allows you to make an error-free choice of installation.
To perform the calculation, you can use a special calculator; they are available in abundance on the Internet.
Types of heat pumps
There are several types of devices depending on what heat source is used. The operating principle of a home heating pump assumes that heat will be taken from sources that are best able to accumulate solar energy throughout the season.
Heat pump. The truth about its effectiveness.
The following types of devices are available for sale:
- ground (earth - water);
- air (air - air);
- air - water;
- aquatic (water - water).
Below we will look at them in more detail.
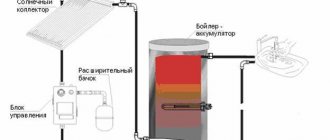
Air - water
Earth - water
Soil is the most stable and therefore popular heat source. At a depth of 4 - 8 meters, the temperature is constant and is 5 - 8 degrees above zero, and already at 10 meters it increases to 10 degrees. There are 2 main methods of collecting thermal energy:
- using a horizontal collector;
- through a vertical geothermal probe.
The first type is a set of pipes through which the coolant moves, laid horizontally. The placement depth must be calculated individually in each case. The calculation is based on the type of terrain, climate and other factors.
In some situations, it is advisable to place the pipeline at the depth of soil freezing (1.4 - 1.8 m), at 2.5 - 3.5 m (if you want to reduce the temperature difference and achieve greater consistency) or at 1 - 1.3 meters (at this depth the soil heats up faster in the spring season ). Sometimes a special collector consisting of 2 layers is even installed.
For such a collector, pipes with a cross-section of 25, 32 or 40 mm are used. They can be laid in different patterns: spiral, lightning, snake, loop, etc. If a snake is implemented, then the pipes should be located at a distance of 0.6 to 1 meter from each other (most often, this is 80 centimeters).
To calculate the heat removal of a pipeline, it is necessary to take into account the type of soil. With dry sand or clay - 10 and 20 W per linear meter, respectively, with wet clay - 25 W, with a high liquid content in the clay - 35 W.
The disadvantage of such a collector is the need to arrange a large area system. If the area of the house for which heating is being installed is 100 sq.m, and the soil of the site consists of wet clay, then to create a collector system you will need 400 sq.m of land, i.e. about 5 acres.
Considering that buildings and other objects cannot be located on the surface (only a lawn with 1-year-old plants can be placed), not all owners will be able to allocate enough free space.
A vertical probe in this case is a more suitable solution. It is a heat exchanger in which pipes are placed into the soil to a depth of 200 m. Depending on the power required for heating, the number of probes to be mounted is determined.
In some cases it is advisable to install 1 u-shaped pipe to a depth of 100 m, and in some cases it is better to choose a set of similar pipes lowered to 20 m to absorb thermal energy on the expanded surface.
Such a pipeline will require significantly less investment. Shallow probes should be spaced approximately 5-8 meters apart. Drilling one pipe 100-200 m is not financially profitable; it is also necessary to obtain permits from the relevant authorities. To avoid this, it is advisable to install several pipes.
Thus, the only disadvantage of vertical structures is the high cost of drilling deep wells. However, despite this, a probe is a more popular solution, because it provides sufficient efficiency in the absence of site area requirements and other limiting factors.
Water - water
Another popular source of heat for heating a home is water. There are 3 types of such structures, depending on where the liquid comes from:
- a collector placed at the bottom of an open reservoir (it should not freeze) - seas, rivers, lakes;
- a collector located in the sewer;
- using water from wells or groundwater.
The first option involves placing pipes with antifreeze under water. To prevent them from rising to the surface, they are secured with additional weight. Due to the increased temperature of the coolant, this method is considered effective, but at the same time economical in terms of financial costs.
Disadvantage - such a structure can only be erected if the reservoir is located no further than 50 m from the site. Otherwise, installation and operation will be unprofitable. However, for coastal residents, the use of a water heat pump will be optimal for heating their home.
When the collector uses purified wastewater and discharged liquid after maintenance. installations can heat multi-storey buildings, industrial facilities and provide hot water supply. For heating private cottages, this system is used quite rarely, because... they are often located far from the central sewer system.
A collector that collects water from wells or ground is rarely used compared to other varieties. This is largely due to the need to build two pits. Liquid is collected from the first, which then transfers its thermal energy to the refrigerant, and cooled water enters the second.
In some cases, a filtration well is built instead of a well. The well for discharging liquid should be located downstream of the groundwater and at a distance of 20 meters from the first.
Such a system is quite difficult to install and maintain. It is necessary to regularly monitor the absence of corrosion damage and contamination of pump elements. It is also important to monitor the quality of incoming water and filter it in a timely manner.
Air - air
Air models have an undeniable advantage over other types of devices. The heat pump uses only air as a heat source, so there is no need to drill ground wells or place water collectors to install such a system. Consequently, air devices will cost much less.
This type has the simplest structure and operating principle. The air mass enters the evaporator, where it transfers heat to the refrigerant. Then it is transferred from the evaporator to the heat carrier directly in the house. Such heating can be represented, for example, by ventilation convectors (fan coils) or a “warm floor” system.
The cost of installing the device is quite low compared to the water or soil version, and the operating efficiency depends mainly on the air temperature. When living in an area with warm winters (at least 0 degrees), this method is considered the most profitable.
If the temperature drops below -15 degrees, then the pump will not be able to provide sufficient heating of the room, therefore, it would be more advisable to use electric or boiler heating of the room.
If it is important to operate an air pump in regions with cold winters, then an additional backup heat source is installed, which will be connected in case of severe frosts. Also, in some cases, it is possible to install an air system if the climate is dry and the temperature does not fall below -15 degrees.
In humid air and frost, an ice crust will form on the device body, which interferes with the operation of the device and can cause its rapid failure.
Process description
The vacuum pump is made as follows:
- First, cut off the top of the compressor with a hacksaw.
- Then the motor suspended on springs is removed from the housing. No tools are needed here - it is not secured.
- The copper tubes located in the housing are connected to oil-resistant tubes, connecting to the “+” and “-” lines on the motor. Excess elements are cut off.
- The opened case must be equipped with a lid. It should be slightly smaller than the sawn-off fragment so that the oil can flow into the container (along its edges). The lid is best made from brass foil using a soldering iron. Its inner side is equipped with stiffening ribs, and its outer side is covered with linoleum (for sound insulation).
During compressor operation, some oil is inevitably lost and is released into the discharge line as oil mist. A tubular level gauge helps track costs. It should be located behind a transparent tube, which is connected to the container using a hose. The tube can be replaced with the body of a ballpoint pen.
The level gauge is covered with a cap to protect it from dust, leaving access for air. Make marks on the mechanism yourself, indicating the maximum and minimum oil levels. The junction of the tube and hose is sealed with sealant.
The finished structure is placed in a box. Its frame is made of a steel angle measuring 2.5x2.5 cm. Any sheet material can act as a cladding. A door should be mounted into the side wall in order to take readings from the level gauge without removing the vacuum pump from the box. A simple latch will be enough to secure it.
Prices and manufacturers
The approximate average market cost of equipment and its installation is:
Horizontal collector:
- Pump – $4500;
- installation - $2500;
- operating cost is $350 per year.
Geothermal probe:
- Pump – $4500;
- installation - $4500;
- operating cost is $320 per year.
Air - for home:
- Pump – $6500;
- installation - $400;
- operating cost - $480 per year.
Water-to-water pump for home:
- Heat pump – $4500;
- installation - $3500;
- operating cost is $280 per year.
The prices shown are not final. The final cost will depend on the country and manufacturer of the device, type of terrain, climatic features, drilling costs, construction conditions, etc. For example, the price of an air pump from a Russian manufacturer will be about $7,000, and from a foreign one – $13,000.
Also, do not forget about the cost of electricity. Despite the fact that the equipment does not consume a lot of electricity, these costs should certainly be taken into account when drawing up an overall estimate and planning a budget.
Which pump to choose
To decide which device to choose, you should consider factors:
- estimated budget - how much money the owner is willing to spend on arranging and connecting the complete system;
- what is the existing or planned heating system inside the house - warm floor, radiator, etc.;
- how many sq.m. is the owner willing to allocate on the site for the creation of a collector;
- Is it possible to drill deep?
- the need for geological expertise (if it is planned to install a geothermal probe) in order to understand how deep the collector should be placed;
- Is it necessary to condition the air flow in summer;
- Will air heating devices be installed?
During the selection process, it is recommended to pay attention to the “heat transformation coefficient” parameter (denoted as ϕ). It determines how effective the device will be. If upon purchase it is indicated that ϕ = 4, then with an electricity consumption of 1 kW, the heat pump will produce 4 kW of heat energy.
When planning your budget, it is important to take into account not only the cost of purchasing a pump, but also future financial costs of operation. Often these parameters differ.
For example, when installing an air-water system, installation costs will be low, but large operating investments will be required due to low efficiency. If you need to minimize operating costs, then you should choose a vertical ground source heat pump.
The cost of a ground or water device and its connection is quite high; a large initial investment will be required. However, after 5-10 years, a heat pump used for heating will pay for itself. Therefore, a decision on the need to purchase this device should be made on the basis of financial capabilities and conditions of construction of the building (type of terrain, climate, etc.).
If, for example, deep drilling on a site is impossible, its area does not allow the placement of a horizontal collector, and there are no bodies of water nearby, the only solution is to install an air source heat pump for heating the house.
The principle of operation of geothermal heating of a private house
To install geothermal heating, you will need the presence of such components as a circuit, reservoirs, equipment in the form of a pump, and a heat exchanger. It is worth noting that a power plant is not needed in this case. Heating from the bowels of the earth can, in its operating principle, resemble the operation of the most ordinary refrigerator, and the system itself continues to gain popularity every day.
The earth is heated by magma, which prevents it from freezing outside. The thermal energy obtained during the operation of the heating system is used for geothermal heating, for which a special heat pump is installed.
The operating principle here is special because:
- The pump is installed;
- Heat exchangers are installed inside the earthen shaft;
- Groundwater is connected to the pump through a water intake;
- The water heats up;
- Sent through the heat exchanger space.
This heating system has an important advantage and is that only 1 kW of electricity is required, and in return you can get energy in the range of 4-6 kW. For example, conventional air conditioners are not capable of converting even 1 kW of electricity into 1 kW of cold. By installing heating from the ground, you can recoup the investment in just a couple of years, however, provided that you have a competent approach to installation and selection of equipment.