Here you will learn:
- What is a heat pump
- Advantages of heat pumps
- Principle of operation
- Types of heat pumps: nuances of operation of the freon-water heat exchanger
- Pros and cons of homemade equipment
- Heat pump from air conditioner
- How to make a DIY heat pump from an old refrigerator
- Manufacturing of geothermal installation
You can make a heat pump for heating your home from an old refrigerator or air conditioner. We offer simple instructions for assembling and installing heat pumps.
Using an old refrigerator
The device of a heat pump from a refrigerator
So, in order to assemble a heating system in a country house, you need to have a heat pump.
Today, such units are not cheap, this is explained by high technical characteristics and painstaking work on their assembly. But, if you wish, you can assemble the heat pump yourself.
You can build a simple heat pump from a household refrigerator. The peculiarity of the technique is that it has two main components of a heat pump - a condenser and a compressor. This will significantly speed up the assembly of the heat pump with your own hands.
So, assembling a pump from an old refrigerator is as follows:
Capacitor assembly. The element is made in the form of a coil. In refrigerators it is most often installed at the back. This well-known grille is the condenser through which heat is transferred from the refrigerant. The capacitor is installed in a container that is highly durable and can withstand high temperatures. To avoid damaging the coil during installation, experts recommend cutting the container and installing a capacitor in it. After this, the container is welded. Next, a compressor is attached to the container. It is almost impossible to make a unit at home. Therefore, it is better to take it from an old refrigerator
At the same time, you should pay attention to ensure that it is in good condition. You can use a regular plastic barrel as an evaporator. After all elements of the system are ready, they are connected to each other. Plastic pipes are used to connect the unit to the heating system. Thus, you can build a heat pump from an old household refrigerator
If you need to pump freon into the system, you need to call a specialist. This kind of work can only be done with the help of special equipment.
Thus, you can build a heat pump from an old household refrigerator. If you need to pump freon into the system, you need to call a specialist. This work can only be done with the help of special equipment.
Take note: refrigerator heat pumps are often used to heat small spaces and domestic buildings. This could be a garage or a small shed.
The first channel will let air into the freezer, and the second will release it. In this case, physical processes occur that cause the capacitor to heat up.
You may also be interested in an article on how to make a Frenette heat pump with your own hands.
You can read about Igor Savostyanov’s Henk System heat pumps here.
Classification by construction type
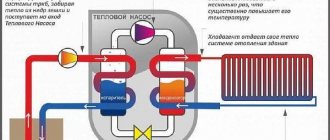
The operating principle of geothermal heating is similar to that of an air conditioner or refrigerator. The main element is a heat pump included in two circuits.
Operating principle of a geothermal (heat) pump
The internal circuit is a traditional heating system consisting of pipes and radiators. External - an impressively sized heat exchanger located underground or in the water column. Both a special liquid with antifreeze and ordinary water can circulate inside it. The coolant takes on the temperature of the medium and, “warmed up,” enters the heat pump, the accumulated heat is transferred to the internal circuit. In this way, water is heated in pipes and radiators.
The geothermal (heat) pump is a key element of the system. This is a compact unit that takes up no more space than a washing machine that is familiar to us. If we talk about performance, then for every 1 kW of electricity consumed, the pump “produces” up to 4-5 kW of thermal energy. While a conventional air conditioner, which has a similar principle of operation, will “respond” to 1 kW of heat for 1 kW of electricity consumed.
Scheme of geothermal heating in a private house
It must be admitted that the installation of this type of heating is the most expensive and labor-intensive to date. The lion's share of its cost is the purchase of equipment and, of course, excavation work. Naturally, a thrifty owner wonders whether it is possible to save money, for example, on installation and make geothermal heating with his own hands? In order to answer this question, it is necessary to understand which systems are used most often and understand the features of their design.
Horizontal heat exchanger
Quite often, a horizontal circuit is used, in which pipes are laid in trenches to a depth greater than the freezing level of the soil in a given area.
The disadvantage of a geothermal heating system with a horizontal circuit is the large area occupied by the collector
The disadvantage is that the area occupied by the circuit must be much larger than the house itself, so to heat a building with an area of 250 m², about 600 m² will go under the pipes. Not every developer can afford such luxury.
In addition, inconveniences arise if the site is already landscaped; for example, you have to observe the distance from trees (1.5 m) and many other nuances.
Vertical heat exchanger
A more compact, but also more expensive option is a vertical heat exchanger. Its installation does not require a large area, but it will require special drilling equipment.
Installation of a vertical heat exchanger requires the use of special drilling equipment
The depth of the well, depending on the technology, can reach 50-200 m, but its service life is up to 100 years. This method is especially relevant when planning geothermal heating of a country house with a developed adjacent territory; it allows you to preserve the landscape almost in its original form.
Water-based heat exchanger
The most economical geothermal installation uses thermal energy from water. It is recommended if the distance to the nearest body of water does not exceed 100 m.
A water-based heat exchanger is the most advantageous and therefore more appropriate for the device
A circuit of pipes in the form of a spiral is laid on the bottom; the depth should be less than 2.5-3 m, that is, deeper than the freezing zone. Reservoir area – from 200 m². The main advantage is that there is no need to perform labor-intensive excavation work, but it is necessary to obtain permission from special services. Having spent significant amounts of money on expensive equipment, you should not skimp on high-quality installation. After all, the quality and efficiency of the entire system will depend on it.
As you can see, installing geothermal heating at home with your own hands is not so easy. Of all the listed types, perhaps only the last option will be quite easy to implement on your own. But even in this case, it is worth weighing all the pros and cons.
Types of structures
- Soil - water
. Heat is drawn from the soil mass. Heat can be collected in two ways: a vertical probe or a horizontal collector. - Water is water.
Heat is taken from the mass of groundwater or an open reservoir. - Air - water
. Heat is taken from the mass of the external air environment. This type of structure is not effective in areas with harsh winters. But air heat pumps for heating a house have an undeniable advantage: there is no need for excavation work to implement them.
Soil-water design
Good heat transfer is guaranteed by soils saturated with moisture.
- Either the entire required area of the site is opened, then the pipes are laid, and after laying they are buried with soil.
- In the second method, trenches are dug under the pipes, into which the collector pipes are laid in rings.
Air-water design
We recommend:
- What is the best heating system for a private home? You will find the answer in the article.
- In the next article we will talk about the features of heating a private house with your own hands.
- All types of heating boilers.
- What types of heating devices are the best? Let's figure it out