When designing and building a private house, it is necessary to correctly select and subsequently install the heating system. In apartment buildings, residents do not have problems with this issue. Since the heating system in the apartment is centralized, all manipulations are performed by the appropriate services.
But private sector developers have to decide for themselves which heating system to choose. And you should find out how to properly configure the heating system of a private house or cottage. As a rule, many criteria are taken into account and the most optimal heating system is selected.
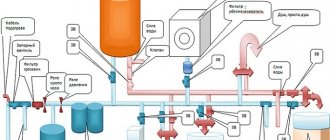
Water treatment for heating system
Ecology of consumption.
Homestead: Water heats the batteries, it makes the turbines work and generate electricity. And if the water quality is low, then constant breakdowns in heating systems are inevitable. The coolant for the heating system is selected at the design stage of the heating system. This is not accidental, since the characteristics of the coolant affect the performance of the entire heating system, which is what you read about in this article and, if necessary, in the next two.
So, what functions does the coolant perform for the heating system, what is it in general, and what are the requirements for it?
The coolant is a liquid poured into the heating system and transfers heat from the boiler to the heating devices. Water and (or) antifreeze are used as coolant.
Water as a coolant for the heating system
Plain water is most often used as a coolant. Why?
Well, first of all, it's accessible.
Water has the highest heat capacity of all substances. That is, when heated, it can accumulate a large amount of energy. And when it cools down, it gives off a large amount of energy, in our case, to the heated room.
Water has a very low viscosity (in other words, good fluidity), making it easy to “move” within the heating system.
Water is an environmentally friendly substance and is not dangerous to our health in case of system leaks.
Disadvantages of water as a coolant
All operating instructions, manufacturers' recommendations and reference books for heating system installers unanimously state: the standard coolant for use in heating systems is distilled purified water.
The latter is not relevant if a house with a water heating system is a permanent place of residence. But what to do if this is a heating system for a summer house, garage, guest house... the risk of water freezing in such heating systems is significant. In this case, there is only one way out: use antifreeze for heating boilers... but that's a completely different story.
Water treatment
If the heating medium is water, then there are also certain requirements for water hardness. Water hardness causes many problems: scale forms in the heating system equipment, which leads to poor performance or failure of this equipment.
Often there is only one way to eliminate the consequences of using hard water: replacing equipment and pipes, which requires significant financial costs.
Typically, ion exchange units are used to soften water, in which calcium and magnesium ions are replaced by sodium ions located in the ion exchange resin.
Ion exchange unit for softening hard water.
As an alternative, magnetic water treatment can be used.
Device for magnetic water treatment.
Magnetic field treatment is economical, affordable, simple and safe. And the taste and salt composition of the water is preserved, and no substances harmful to humans are formed in the water.
The effect of magnetic treatment lasts for twenty-eight days! Magnetic activators can be used in all hot and cold water systems. Magnetic treatment not only prevents the formation of sediment and scale, but also removes scale already deposited on the walls, while the surface is protected by a barely noticeable oxide film. The sediment is gradually removed from the system by the flow of water and settles in filters, from where it is then removed during cleaning.
There are two versions of the magnetic activator produced for domestic needs: with threaded connections from 8 to 32 mm and from 400 to 300 mm with a flange.
There are also ultrasonic anti-scale devices.
Ultrasonic anti-scale device.
They are also designed to prevent deposits on any plumbing and heating devices and assemblies.
The advantages of these devices are the ability to clean large surfaces and the absence of noise during operation.
Ultrasonic anti-scale devices are effective in pipes with a diameter of up to 45 mm or parallel pipes with a diameter of up to 27 mm. Such anti-scale devices are installed quickly and simply, even without cutting into pipes: by winding the wire around the pipe, which, you see, is very convenient.
In addition to softening, these installations also reduce the iron content (about 4 times), due to which the effect of corrosion on equipment is reduced, and this, in turn, leads to savings in energy resources and finances that could be spent on repairing pipes and units heating system.
If you have any questions on this topic, ask them to the experts and readers of our project here.
PS And remember, just by changing your consumption, we are changing the world together! econet
Basic rules for arranging heating make-up
An example of a heating system make-up unit.
What causes the decrease in the volume of water in the pipes? The main source of its leakage is excess operating temperature. As a result of this, a critical expansion of the liquid occurs, after which its excess in the form of vapor escapes through an air vent (closed circuit) or an open expansion tank (gravity).
The installed automatic refill system for the heating system compensates for the lack of water by adding the required volume to the main line. But this is not the only case when prompt addition of coolant to the system will be required:
- Removing air pockets. As a result of opening the Mayevsky valve or air vent, some of the liquid will inevitably leave the system. In a closed circuit, a pressure drop will occur, to which the automatic replenishment of the heating system must respond;
- Micro leaks. A loose fit of pipeline joints and loss of sealing even at a small level will lead to a gradual decrease in the volume of water. It is difficult to identify such defects, but it is necessary. The automatic charging valve for the heating system will only operate after the pressure has dropped to a minimum level;
- Carrying out repair or maintenance work;
- The formation of corrosion on the walls of metal pipes, which leads to their thinning and, as a result, an increase in internal volume. At first glance, this is an insignificant factor. But if the closed heating system is not recharged, the pressure will gradually decrease and air pockets will begin to form.
What should a heating system make-up device consist of? It all depends on the type of heating circuit. Also, the design of adding coolant to the system is influenced by its characteristics: pressure, operating temperature, pipeline layout, number of heating circuits, etc.
Methods for preparing water for heating systems
Some of the shortcomings in preparing water for the heating system are eliminated by preliminary heat treatment and filtration.
In other cases, the coolant is diluted with special additives and reagents, giving it the necessary properties.
What methods can be used to prepare water before filling the heating system?
- Changing the composition of water by adding reagents, that is, chemically active substances.
- Catalytic oxidation to remove excess iron into sediment.
- Application of mechanical filters of various sizes and designs.
- Water softening through electromagnetic wave treatment.
- Heat treatment: boiling, freezing or distillation.
- Sediment of water for a certain period of time.
- Deaeration of water to remove oxygen and carbon dioxide, etc.
Preliminary filtration of water will help remove unnecessary mechanical impurities and suspended particles (stones, sand, fine clay and dirt, etc.).
To purify water with minor contaminants, filters with washable or replaceable cartridge types are used. Heavily contaminated water is passed through filters with a double layer of quartz sand, activated carbon, expanded clay or anthracite.
Why is it necessary to soften water?
Filling the heating system with water that has not undergone the cleaning process significantly increases the risk of premature wear and failure of some elements of the heating system.
Water softening involves reducing the content of magnesium and calcium ions. You can achieve the desired result in several ways.
The use of special filters based on a number of components: slaked lime, sodium hydroxide and soda ash. These substances closely bind magnesium and calcium ions dissolved in water, preventing their further entry into the purified coolant.
No less effective devices are filters based on fine-grained ion exchange resin. The action of this system is to replace magnesium and calcium ions with sodium ions.
Under the influence of magnetic water softeners, magnesium and potassium ions lose their ability to precipitate as solid sediment and are converted into loose sludge, which must be removed from the water.
The choice of one or another method of preparing water for a heating system depends entirely on its type. Each heating system has its own characteristics and recommendations depending on the type and quality of the source material.
Article rating:
(total 1 votes, rating: 4.00 out of 5)
Types of water softening filters
The domestic market is overflowing with offers for water purification filters, both domestic and Western-made. The user needs to understand which softener is best suited for the boiler and autonomous heating system. Next, you will need to select the most appropriate purification method for the initial composition of the water.
Polyphosphate filter
The most affordable and cheapest water softening filter for a boiler, and at the same time a very effective cleaning option. The ion exchange polyphosphate filter module consists of the following basic elements:
- Plastic container in the form of a flask, transparent;
- protective cover for cartridge replacement;
- drainage;
- softening chemical reagent—polyphosphate salt.
Raw or tap water enters the filter container, circulates through a chemical reagent in the form of polyphosphate salt crystals and is impregnated with sodium polyphosphates, forming a phosphate film. It envelops hardness salts, thereby neutralizing their scale-forming properties and protecting boiler heating surfaces from salt deposition.
Polyphosphate is a toxic substance, so after contact with it, water becomes undrinkable. These softeners must be used carefully in hot water supply systems, since due to possible leaks in the structure, water may enter the hot water supply or hot water supply line.
The service life of polyphosphate filters, or rather dissolving polyphosphate salt, is short. The standard consumption of the reagent is 5 grams per 1 ton of water. The reagent is replaced when its volume in the flask is halved. This happens after about six months of filter operation. The cost of polyphosphate ion exchange filters ranges from 500-1400 rubles, and replacing polyphosphates will cost the owner up to 350 rubles.
Magnetic filter
This is the most expensive and effective cleaning method. If you install a compact permanent magnetic filter in front of the boiler, you will not need to constantly regenerate it or change the filter material. It cannot soften water, that is, remove hardness salts from it.
The principle of its operation is different and is based on the transformative effect of a magnetic field on water, as a result of which its structure changes briefly.
Passing through the magnetic filter element, boiler water changes its own physical qualities, while the crystallization process when heating the liquid occurs more intensely, but not on the surface of the heated boiler walls, but in the water column. In connection with this, sludge is formed, which is easily removed by blowing or in a mud pan in front of the boiler.
A characteristic feature of this method of softening boiler water is the temporary nature of magnetization of water, therefore such a filter is installed as close as possible to the boiler unit.
The advantage of this treatment is that when water passes through a magnetic filter, it does not become technical and harmful to humans, therefore it is applicable in double-circuit boilers with hot water heating.
The service life of such softeners is practically unlimited, since the device has no moving or rubbing parts. The cost of installation ranges from 1,500 to 25,000 rubles, depending on the brand, design and hourly productivity of purified water.
Electromagnetic
At a high temperature of hot water in the boiler circuit and a high circulation speed, complete separation of hardness salts from water only with the help of magnetic treatment often does not occur, especially for natural waters with high hardness. To enhance the magnetic effect, electrical treatment of the water is added by placing a specialized electrical treatment on the magnet.
Such a device also functions by treating the source with a magnetic force field, the strength of which is regulated by an effective electrical processor. This pair makes it possible to get a longer lasting effect.
The operation of such a device does not depend on pressure changes and temperature conditions. Transforming hardness salts not only do not harm the boiler, but also act as softening agents for previously deposited scale. Installation cost: from 5,000 to 30,000 rubles.
Preparing water for heating is much more important than it might seem
It just seems that heating networks will not require special water treatment, and technical water, cleared only of stones, sand and algae, will do just fine.
In reality, it turns out that everything is different. Ignoring proper water treatment leads to very unpleasant and costly consequences. First of all, we are talking about hard salts - calcium and magnesium compounds. They can settle on the walls of pipelines through which water flows (the solubility of chemical compounds sharply decreases). Moreover, when heated, this process increases significantly. As a result, we have scale both on pipes and in the middle of heating devices. And thanks to this:
- Reducing the flow diameter of individual elements of the heating system - right up to complete overlap.
- Deterioration in heat transfer - up to twenty percent.
- Increased electrical energy consumption for devices with a heating function (also boilers).
- Detrimental effects on measuring and control equipment. And the problems with the heat generating plant – in this case – are everyone’s problems.
It is also necessary to emphasize the destruction of the walls of the heating system pipes by chemically energetic substances contained in water.
Fighting hardness
So, preparing water for heating includes water softening. This is the most important component that is almost always important. Natural liquid is not ideal. There are enough impurities in it, and calcium and magnesium are in excess due to completely natural reasons - from passing through the strata of limestone rocks and being washed out.
A layer of scale is familiar to all owners of pots and kettles. The same thing happens on the internal surfaces of boilers. It is believed that any millimeter of scale layer reduces the efficiency of the boiler by 1%.
By the way, scale can also be secondary - if, for example, it appeared in the water mass, and then was deposited on the wall (such solid particles are clearly visible). You can combat this using dimeralization.
Ways to fight
Preparing water for heating is an economically viable process. Who wants to change heating devices every 5 years, and change pipes a little less often?
For water purification for the home and heating systems, various devices are used, which we are accustomed to calling filters (not always correctly, but it is clear to everyone).
The most effective and used methods of preparation are:
- Electrolysis exchange - using a special resin that is capable of changing the ions of a number of dangerous substances, while simultaneously restoring the properties of water. The method is perfectly used in household systems - it is compact, easy to use and quite effective.
- Reagent treatment – in other words, the action of chemically energetic substances. Soda liming, liming and treatment with caustic soda are effective against the deposition of hard salts (but due to their complexity, they are used at industrial facilities - the same, as a rule, applies to the following points).
- Catalytic oxidation. Catalyst granules (reaction accelerator) actively oxidize iron and remove it into sediment.
- Magnetic processing. Under the influence of a magnetic field, scale formers (the same CaCO3) crystallize on ferromagnetic particles present in the water mass.
- Diaeration is the removal of dissolved gases.
When selecting a specific method for preparing water for heating, it is necessary to proceed from the required values (each system has its own advice - in some places almost distilled liquid is needed, and in others coarsely filtered liquid will do). In this case, the quality of the initial material and financial opportunities are of fundamental importance. Whatever satisfies all these requirements is acceptable as water treatment!
The need to prepare water for heating will affect everyone. But most of the described methods of water purification are complex and expensive. Enterprises, which in most cases have a professional staff and greater financial opportunities, can afford this. But for small organizations and owners of country houses it is more difficult here. The technical operational level of boiler systems there is usually not high. Very often, small treatment systems are used for water preparation, which are simplified analogues of those described above.
What else to look for when choosing
All softening filters for water of a certain type have the same principle of operation and differ only in the quality of work, less often - in practically insignificant design features. Therefore, there are no specific selection criteria. However, we recommend paying attention to:
- productivity - also throughput, measured in m3/hour or l/hour;
- size - magnetic softeners are slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe, while polyphosphate filters require a lot of space around the pipe;
- thread diameter - must match the diameter of the pipes used in the planned installation location;
- manufacturer - it is better to choose a filter from a well-known manufacturer, preferably in specialized retail outlets that can provide repairs or replacements during the warranty period.
Why not water
Indeed, this is the most popular coolant. Water is cheap, accessible, non-toxic, and has fairly good heat capacity combined with heat transfer.
However, there are a number of serious negative features that make water not an ideal option:
- During frosts, the heating system cannot be turned off without draining the water - it will freeze;
- There is some probability that water in the far parts of the circuit will form ice plugs even without shutting down the system if the frosts hit with all the Siberian force;
- Frozen water means not only traffic jams, but also the risk of pipe rupture due to expansion of the coolant;
- Plaque is deposited on pipes in the form of the well-known scale;
- We must also not forget about corrosion, which does not extend the service life of the pipeline at all.
Ethylene glycol
For the above reasons, we need a non-freezing liquid for heating our home. One of the options is ethylene glycol, or more precisely, antifreeze based on it. The main advantages of such compositions:
- low cost;
- freezing point below -60 degrees;
- no corrosion;
- higher thermal conductivity than water.
However, everything can't be that good. Ethylene glycol is poisonous, so leaks in the heating system can cause serious problems. This is the main reason why ethylene glycol based antifreezes are not used in the home. They are used mainly in industrial facilities.
Non-freezing liquid for heating a home should be safer from an environmental point of view.
Propylene glycol
More expensive antifreezes based on propylene glycol have all the advantages of the previous option, but do not have its main disadvantage - toxicity. From the point of view of its own weaknesses, we can note the high price of compositions with propylene glycol and slightly lower thermal conductivity.
However, environmental safety and low freezing point make antifreezes based on this component quite suitable for home use.
Complex formulations
This group of antifreezes uses various components, which makes it possible to achieve maximum thermal conductivity and a minimum freezing point with complete environmental safety.
As a rule, the price of such compositions is also reasonable.
On the other hand, this group is represented by such a wide selection of antifreezes, the composition of which can vary greatly, that an intelligent choice will require studying the specific name and its composition.
Conclusion
For heating systems of country and country houses (especially those that are not heated in winter on an ongoing basis), it is advisable to choose complex antifreeze compositions, the base component of which is propylene glycol.
Operating principle of ITP Softening water for heating
The first and most important stage of work
The main thing that should be done before planning water treatment measures for a heating system is to conduct a chemical analysis of the composition of the water.
Known (a) and proposed (b) schemes for preparing water for heating: 1 - water heater; 2 — steam-water heater; 3 - refrigerator; 4 - nutrient tank; 5 - high pressure manifold; 6 - low pressure manifold; steam; condensate.
You can carry out tests at home using test kits for aquariums (they are sold at any pet store). However, in order to obtain more accurate values and most effectively prepare water for heating, you should use the services of a certified laboratory.
Water for analysis is collected in a 1.5 liter plastic bottle from non-carbonated drinking water. It is unacceptable to use bottles of sweet carbonated water and other drinks. The cork and bottle are washed well with the same water that is taken for analysis; no detergents should be used. The water is first drained for 10-15 minutes to prevent stagnant water from entering the sample, as this may affect the test results.
To prevent water from being saturated with oxygen dissolved in the air, it is drawn in a thin stream so that it flows down the wall of the bottle. Water is poured under the neck. The bottle is tightly wrapped with a cork to prevent air from entering under it. Oxygen causes chemical processes to occur, and this can also affect test results. If it is not possible to immediately take the samples to the laboratory, then the water can be stored in the refrigerator (not in the freezer!), but no more than two days.
Heating system.
A comprehensive water analysis includes checks for the following indicators:
- rigidity;
- iron;
- manganese;
- pH (degree of acidity);
- permanganate oxidability (indicates the presence of organic substances in water);
- mineralization;
- ammonium;
- oxygen saturation;
- turbidity, color, smell.
If necessary, samples are taken for the presence of microorganisms. Some of them, such as legionella and amoeba, not only can cause serious harm to health, but can also settle inside pipes, forming a slimy microbial film. This promotes corrosion and degrades heating quality.
Related article: How to properly connect an Ariston water heater?
Disadvantages of water as a coolant
All operating instructions, manufacturers' recommendations and reference books for heating system installers unanimously state: the standard coolant for use in heating systems is distilled purified water.
The latter is not relevant if a house with a water heating system is a permanent place of residence. But what to do if this is a heating system for a summer house, garage, guest house... the risk of water freezing in such heating systems is significant. In this case, there is only one way out: use antifreeze for heating boilers... but that's a completely different story.
Best answers
Konstantin Sukhorukov:
Only the heating engineer did not say what would happen to the boiler heat exchanger from the effects of antifreeze. If you want to use anti-freeze, then use liquids based on propylene glycol. And you can pump it without using a water pump, using a regular car pump and a lockable container with two fittings.
Larisa:
pump and hose
Alexander Bakushev:
open the emergency light and fill it until it runs out!
Andrey:
Pump a small container in the usual way and into it a cheap submersible pump, through a hose to the make-up tap, control the pressure using a standard pressure gauge, bleed air, pump and pump. Pre-pressurize the system with network water, check its operation under temperature changes. Evaporation of antifreeze and antifreeze inside a living space is goodbye to health and vision. for these reasons, fill it with an aqueous solution of drinking alcohol (vodka). Moreover, if the system is new and its volume is not very large, get a supply of the strategic product.
Bely Oleg:
Make two fittings in the canister, pour in anti-freeze, one hose goes to the boiler, and pump air into the other with a compressor from the refrigerator. The compressor from the refrigerator presses up to 8 bar - this is definitely enough for you. Productivity is just low. But they cannot pump any electrically conductive liquids - the windings there are not protected in any way...
Denisochka:
Where did the need for glycol coolant come from? When using it, heat transfer is reduced and boiler maintenance becomes more difficult, especially if the boiler is double-circuit with one heat exchanger. For almost any heating system, the best coolant is water.
Modification of surfaces of elements in SCT
There are other known methods for preventing corrosion and scale formation associated with modifying the surfaces of elements in the SCT that are in contact with water. It is possible to use alloy steels for the manufacture of elements of heat exchangers and boilers. This allows you to get rid of corrosion, but the price of SCT elements increases significantly.
Despite the increase in equipment costs, there are such examples. These are pre-insulated pipes for heating networks, or condensing water heating boilers and Viessmann. Or water heating sectional boilers made of aluminum alloys and Bosch-Buderus. IN
It is also possible to use plastics for the manufacture of pipes for heating networks, but only for coolant temperatures not exceeding 95°C. There are known designs of air heaters for boilers made from glass pipes or plastic. All these technologies are still quite expensive and are not widely implemented.
Phosphonates
At the end of the 20th and at the beginning of the 21st century, a large number of compounds were synthesized that found application for the protection of thermal power equipment of small-scale energy facilities, including complexones, in particular phosphonates, which showed a number of advantages over other complexones for the above goals.
Unlike Trilon B, they have a different mechanism of action in preventing scale formation, namely, they inhibit the process of scale formation at the stage of crystal nucleation, therefore they work in substoichiometric ratios, that is, their working concentrations are 1-5 mg/dm3, which makes their use economical profitable.
Such compounds work even on “raw” water, which makes the water softening stage unnecessary, resulting in a sharp reduction in the use of table salt, thereby reducing the amount of waste water, which in turn has a beneficial effect on the environment.
Technologies using complexonates based on organic phosphonates have now become sufficiently developed in the water treatment of small and medium-sized boiler houses, and the production of the corresponding reagents is quite widespread.
But the use of these reagents even for heat supply systems is limited;
- firstly, the alkalinity of the environment: at a pH of more than 8.5, alkaline earth metal complexonates, which are more often than other compounds used to protect heat supply systems from corrosion, for example, zinc complexonates decompose to zinc hydroxide and cease to perform their functions of protecting against corrosion;
- and secondly, the use of complexones based on phosphonates is limited by the concentration of scale-forming ions, mainly Ca2+10 mEq/dm3; thirdly, the lack of regulatory documentation regulating the use of methods for stabilizing water treatment in heat supply systems.
As a result, engineering and technical personnel are not prepared to implement reagent water treatment technologies.
Summary
Thus, complex water treatment requires a number of organizational and technical measures for the implementation of the heat and power complex, in particular in heat supply systems, although the payback of such technologies is quite high; there is evidence that capital costs are paid off during the heating season, or in several months.
Example of an automatic make-up system
There is a lot of equipment on the market to solve the issue of recharging heating systems. Do you want an automatic, trouble-free, reliable installation? It can be “assembled” from the following elements:
- containers with screw caps;
- dosing pump;
- pressure switch;
- rigid suction line with level sensor;
- air valve for releasing air;
- a fitting for pouring coolant into a container, equipped with a plug (prevents solid particles from entering the container);
- injection valve for connection to the circulation system;
- flexible tube;
- low level sensor to signal the absence of liquid in the make-up tank;
- an electric stirrer that prevents possible separation of the coolant into fractions.
A correctly installed unit from the above components will be highly effective in maintaining the required pressure in the heating circuit, and is also fully compatible with the room air conditioning circuit. The installation will automatically “eliminate” all normal losses in systems: connections, pump seals, fittings. It is not at all capricious with regard to the coolant: it works well with both water and glycol-containing liquids.
The volumetric pump used in this automatic make-up unit is capable of overcoming the back pressure in the system without sudden pressure surges when turned on
This unit operates according to the following principle:
- Through the fitting or neck, water/glycol and water in the appropriate proportion/ready solution are poured into the container.
- The pump of the make-up installation is connected to the network and pumps coolant into the system at low output, thereby ensuring its uniform filling.
- When the pressure in the system reaches the set value, pumping automatically stops.
- When the pressure drops, the relay turns on the pump, returning the system to stability.
How to fill a heating system with water
To understand how to fill a heating system operating on the bottom-fill principle with water, you should remember the following algorithm of actions:
- even before filling the heating system in a private house, the valve on the supply pipeline must be pushed in, and the discharge must be opened on the supply section;
- Then on the return pipe you need to slowly open the valve. If the outlet speed of the water in the heating system is high, there is a risk of water hammer, which can lead to the most unpleasant consequences, including the separation of heating batteries;
- Next you need to wait until the water, devoid of air, flows;
- then the discharge is closed, and the supply valve, on the contrary, opens;
- after this, you need to completely de-air all heating areas in the entrance to which you have access, including service premises.
Heating filling quality control
Before filling a closed heating system with water, you need to make sure that all protective elements are present. These include Mayevsky taps, bypasses, and control devices - thermometers and pressure gauges. They are necessary not only to control the pressure in the pipes during the supply of coolant, but are also the main safety measures during heating operation. This is how you can properly fill a heating radiator with water.
When properly filling a closed system with water, the following parameters must be monitored:
- Pressure. Pressure gauges must be installed in key places in the system - the outer radiators and the highest point. After the final release of air, the pressure on all pressure gauges should be the same;
- No leaks.
This is the only way to achieve stable pressure. However, the main verification process occurs when the boiler is turned on. The thermal expansion of water at maximum operating mode should not affect the integrity of the pipelines of the heating elements.
Preparing coolant at home
First, let's figure out how to soften water for heating with our own hands. The simplest and most affordable way to soften a coolant liquid is to boil it. During heat treatment, carbon monoxide is removed from the liquid, which helps reduce calcium hardness. However, a small amount of calcium still remains in the liquid, so boiling does not completely cope with the task of softening the coolant.
You can soften water at home using filters with inhibitors. Essentially, these are scale neutralizers. Inhibitors are soda ash, caustic soda and lime. Hard water is passed through special filters consisting of ion exchange resin. As a result, magnesium and potassium ions are replaced by sodium ions.
A reagent-free way to soften resin is the use of magnetic softeners. As a result of exposure to a magnetic field, the properties of the liquid change so that impurities of magnesium and potassium salts cannot precipitate in the form of a solid sediment, but form loose sludge. However, the sludge still needs additional removal using filters.
Another way to soften the coolant fluid is to use the reverse osmosis method. Its essence is as follows: the liquid is forced through a special membrane, which retains various substances, including magnesium and potassium salts, which contribute to the formation of scale. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost of treatment equipment, as well as excessive water consumption during the purification process (to obtain 1 liter of purified water, 2-10 liters are discharged into the sewer).
If it is decided to use melt or rain water for the heating system, then it should be allowed to settle for several days, and then its acidity should be measured. If it is within 6.5-8, then the liquid can be poured into the heating circuit.
Methods for deferrization of coolant
The concentration of iron in the coolant liquid should not exceed 1 mg/l. The optimal value is 0.3 mg/l. Due to an excess of iron, the internal surfaces of pipelines become silted, and bacteria multiply in the ferrous sediment. Moreover, the process of their active growth is observed already at a temperature of 30-40°C. As a result, heating and hot water systems wear out quickly.
There are the following methods for deferrizing water:
- The simplest technique is settling. As a result of interaction with oxygen, iron oxidizes on its own and forms a rusty precipitate. To carry out the procedure yourself, you will need a tank with a capacity of 200-300 liters, as well as devices for injecting oxygen into the liquid, for example, a compressor.
- Reverse osmosis technology is also suitable. In this case, filters based on ion exchange resins are used. To protect against the proliferation of iron bacteria, chlorination is used. Chlorine is added at the rate that 50 mg is required per liter. However, before doing this, you need to make sure that all elements of the heating system are resistant to chlorine.
- If water from wells is used, the iron concentration may exceed 5 mg/l. In this case, only filters using glauconitic sand, which is enriched with manganese oxide, will help. When passing through the filter, the coolant is cleared of hydrogen sulfide, manganese and iron. All of the above substances precipitate. To clean a clogged filter, use a solution of potassium permanganate, which restores the oxidative capacity of the filter device.
- Mechanical filters for removing peat, sand, dirt, clay, organic matter and zooplankton come with removable or washable cartridges. Pressure filters with granular media are used for heavy contamination.
Dissolved oxygen is responsible for the corrosiveness of the coolant. The standards for this parameter are the same for closed and open heating systems and amount to 0.05 mg/m³. Columns and deaeration units are used to remove dissolved oxygen.
To eliminate the possibility of oxygen entering the system in other ways, it is necessary to monitor the tightness and integrity of all elements of the heating circuit. Filling with water should be done slowly to avoid the formation of air pockets. Pipelines made of gas-permeable materials (polypropylene, polyethylene) are protected with an anti-diffusion aluminum layer.
Filling methods built-in mechanism and pumps
Heating filling pump
How to fill the heating system in a private house - using the built-in connection to the water supply using a pump? This directly depends on the composition of the coolant - water or antifreeze. For the first option, it is enough to pre-flush the pipes. Instructions for filling the heating system consist of the following points:
- It is necessary to make sure that all shut-off valves are in the required position - the drain valve is closed as well as the safety valves;
- The Mayevsky tap at the top point of the system must be open. This is necessary to remove air;
- The water is filled until water flows from the Mayevsky tap, which was opened earlier. After this it is blocked;
- Then it is necessary to remove excess air from all heating devices. An air valve must be installed on them. To do this, you need to leave the system filling valve open, making sure that the air comes out of the specific device. As soon as water flows from the valve, it must be closed. This procedure must be done for all heating devices.
After water has been filled into a closed heating system, you need to check the pressure parameters. It should be 1.5 bar. Subsequently, pressing is performed to prevent leaks. It will be discussed separately.
Filling heating with antifreeze
Before you begin the procedure of adding antifreeze to the system, you need to prepare it. Usually 35% or 40% solutions are used, but to save money it is recommended to purchase a concentrate. It should be diluted strictly according to the instructions, and only using distilled water. In addition, it is necessary to prepare a hand pump to fill the heating system. It is connected to the lowest point of the system and, using a manual piston, coolant is pumped into the pipes. During this, you need to monitor the following parameters.
- Air outlet from the system (Maevsky valve);
- Pressure in pipes. It should not exceed 2 bar.
The entire further procedure is completely similar to that described above. However, you should take into account the operating features of antifreeze - its density is much higher than that of water
Therefore, special attention should be paid to calculating the pump power. Some glycerin-based formulations may increase the viscosity coefficient with increasing temperature
Before pouring antifreeze, it is necessary to replace the rubber gaskets at the joints with paronite gaskets. This will significantly reduce the likelihood of leaks.
Automatic filling system
For double-circuit boilers, it is recommended to use a device for automatically filling the heating system. It is an electronic control unit for adding water to the pipes. It is installed on the inlet pipe and operates fully automatically.
The main advantage of this device is the automatic maintenance of pressure by timely addition of water to the system. The principle of operation of the device is as follows: a pressure gauge connected to the control unit gives a signal about a critical decrease in pressure. The automatic water supply valve opens and remains in this state until the pressure stabilizes. However, almost all devices for automatically filling heating systems with water are expensive.
A budget option is to install a check valve. Its functions are completely similar to the device for automatically filling the heating system. It is also installed on the inlet pipe. However, the principle of its operation is to stabilize the pressure in the pipes with the water make-up system. When the pressure in the line drops, the pressure of tap water will act on the valve. Due to the difference, it will automatically open until the pressure stabilizes.
In this way, you can not only fuel the heating, but also completely fill the system. Despite its apparent reliability, it is recommended to visually monitor the coolant supply. When filling the heating system with water, be sure to open the valves on the devices to allow excess air to escape.
Features of using water as a coolant
From the point of view of heat transfer efficiency, water is an ideal coolant. It has a very high heat capacity and fluidity, which allows it to deliver heat to the radiators in the required volume. What kind of water should I fill? If so, you can fill the water directly from the tap.
Yes, tap water is not ideal in composition; it contains salts and a certain amount of mechanical impurities. And yes, they will settle on the elements of the heating system. But this will happen once: in a closed system, the coolant circulates for years, and replenishment with a small amount is very rarely required. Therefore, some amount of sediment will not cause any tangible harm.
If the heating is of an open type, the requirements for the quality of water as a coolant are much higher. Here, gradual evaporation of water occurs, which is periodically replenished by adding water. Thus, it turns out that the concentration of salts in the liquid increases all the time. This means that sediment also accumulates on the elements. That is why purified or distilled water is poured into open-type heating systems (with an open expansion tank in the attic).
In this case, it is better to use distillate, but getting it in the required volume can be problematic and expensive. Then you can fill in purified water that has been passed through filters. The most critical is the presence of large amounts of iron and hardness salts. Mechanical impurities are also useless, but they are the easiest thing to deal with - several mesh filters with cells of different sizes will help catch most of them.
In order not to buy purified water or distillate, you can prepare it yourself. First, pour and let sit until most of the iron settles. Carefully pour the settled water into a large container and boil (do not cover with a lid). This removes hardness salts (potassium and magnesium). In principle, such water is already well prepared and can be poured into the system. And then top up with either distilled water or purified drinking water. This is no longer as expensive as the initial fill.
Selecting pressure values in the system and expansion tank
The higher the operating pressure of the coolant, the less likely it is that air will enter the system. It is necessary to remember that the operating pressure is limited to the maximum permissible value for the heating boiler. If, when filling the system, a static pressure of 1.5 atm (15 m of water column) was reached, then the circulation pump with a pressure of 6 m of water. Art. will create a pressure of 15 + 6 = 21 m of water column at the entrance to the boiler.
Some types of boilers have a working pressure of about 2 atm = 20 m water column. Be careful not to overload the boiler heat exchanger with unacceptably high coolant pressure!
The membrane expansion tank is supplied with a factory set pressure of inert gas (nitrogen) in the gas cavity. Its common value is 1.5 atm (or bar, which is almost the same). This level can be raised by pumping air into the gas cavity with a hand pump.
Initially, the internal volume of the tank is completely occupied by nitrogen, the membrane is pressed against the body by the gas. That is why closed systems are usually filled to a pressure level of no higher than 1.5 atm (maximum 1.6 atm). Then, by installing the expansion tank on the “return” in front of the circulation pump, we will not get a change in its internal volume - the membrane will remain motionless. Heating the coolant will lead to an increase in its pressure, the membrane will move away from the tank body and compress the nitrogen. The gas pressure will increase, balancing the coolant pressure at a new static level.
Pressure levels in the expansion tank.
Filling the system to a pressure of 2 atm will allow the cold coolant to immediately press the membrane, which will also compress the nitrogen to a pressure of 2 atm. Heating water from 0 °C to 100 °C increases its volume by 4.33%. The additional volume of liquid must enter the expansion tank. The large volume of coolant in the system gives a large increase in its growth when heated. Too much initial pressure of the cold coolant will immediately use up the capacity of the expansion tank; it will not be enough to receive excess heated water (antifreeze)
Therefore, it is important to fill the system to the correctly determined coolant pressure level. When filling the system with antifreeze, you need to remember that its coefficient of thermal expansion is greater than that of water, which requires the installation of a larger capacity expansion tank
Conclusion
Filling closed heating systems is not just a standard final step before commissioning. Correct or incorrect execution of this step can seriously affect the performance of the system, in the worst case, even destroy it. Compliance with filling technology is the key to obtaining stable heating.
How to implement alternative heating for a private home
Two-pipe heating system for a private house - classification, types and practical design skills
Single-pipe and two-pipe heating distribution in a private house
Creation of a surfactant film
One of the methods for creating a protective barrier against the effects of corrosion and scale formation on the surfaces of SCT elements is the creation of a film of surfactants (surfactants). Surfactants are part of a complex of chemicals used to modify feedwater.
Their addition serves several purposes. The addition of surfactants to solutions of phosphates and phosphonates should stabilize the products of their interaction with hardness salts—suspensions—in water. They should also prevent the accelerated appearance of repeated deposits after washing. But the use of surfactants to achieve these goals is of an auxiliary nature.
The well-known properties of surfactants force us to search among their large range for those that will allow us to simultaneously wash out old deposits and form a protective film that prevents corrosion and scale formation. Surfactants have a prolonged effect and washing of residual deposits continues even after the end of the main process during boiler operation.
Conclusions from experiments
Further experiments led to the conclusion that it is possible to clean the boiler without stopping it if you simply add a certain amount of surfactant to the water.
Depending on the thickness of the deposits, they are completely washed off within one or two months. Observation of the hydraulic resistance of the washed boilers during the next heating season showed that it remained quite stable.
The increase in hydraulic resistance began only in the middle of the second (after flushing) heating season. Visual inspections of the internal heating surfaces after the completion of the heating seasons showed that they were free of deposits after the season when a one-time introduction of a surfactant was made (up to 2% of the volume of water in the system).
New deposits appeared during the next heating season. The system was not subject to thermal deaeration or chemical degassing during all three heating seasons during which the experiment was conducted. Research has also shown that a thin (up to 50 microns) durable gray film appears on the surface, which has dielectric properties.
Considering the electrochemical nature of the corrosion reaction, we can assume that this is what determines its anti-corrosion properties and at the same time prevents the appearance of scale formation centers.
Replacing water with antifreeze
If the system has already used water, and you want to switch to antifreeze, then two circumstances should be taken into account.
Secondly
. It is never possible to completely remove water from the heating system. Some of the water remains. If you simply pour prepared diluted antifreeze, its concentration will be insufficient for reliable protection against freezing. Thus, a concentrate must be used. I usually mix concentrate with diluted antifreeze in a 1:1 ratio. After filling the system, you need to start the circulation pump (for a system with forced circulation) or turn on the boiler (for a system with natural circulation) so that the coolant is thoroughly mixed. Then you need to pour out some coolant and measure its density. There is a device for measuring density that is sold in most car dealerships. This device is used to prepare a car for winter (checking the properties of antifreeze in the engine cooling system), but it is also perfect for our purposes. If the device shows a freezing temperature lower than necessary, for example -50 degrees, it’s okay, but if the temperature is higher than we need, then we will have to drain part of the coolant and replace it with concentrate. The drained coolant must be disposed of carefully; it is poisonous and should not be poured into septic tanks or ditches.
I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that different antifreezes may be incompatible with each other. There is an opinion that red composition should not be mixed with a composition of another color.
This is true, but in fact there are other undesirable combinations. Supplements from different brands may react with each other or simply reduce each other's effectiveness. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate what other antifreezes their product can be mixed with. My advice is to pick one brand and stick with it. If you still need to mix, then mix liquids of the same color and before pouring, pour out a little coolant from the heating system, mix it in a jar with a new composition and see if a sediment forms, if the liquid becomes cloudy, or loses its homogeneity.