Russia has vast territories that are located in different climatic zones. Climatic conditions in most parts of the country do not allow harvesting throughout the year.
The natural wisdom and ingenuity of the Russian people made it possible to significantly increase the growing season of plants. By productively using greenhouses of various shapes and designs, amateur gardeners have the opportunity to obtain early and late harvests.
A more competent approach to greenhouse construction will allow you to obtain crops throughout the year. In this article we will try to tell you how to make a greenhouse with your own hands.
Design features
A greenhouse made into reality, made with one’s own hands, occupies an important place on a summer resident’s plot. A greenhouse made by yourself does not mean that it will be less effective in its functionality.
Photos and drawings of greenhouses for making with your own hands can be viewed and studied on thematic websites. The design of the greenhouse and its shape will depend on the purpose of the object.
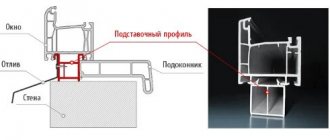
The most popular materials for the construction of greenhouses are fiberglass or galvanized metal profile pipes, which serve as a load-bearing role for the structure. Glass, polyethylene film, polycarbonate can be used as a coating.
Video description
The video shows the sequence of assembling the profile for the greenhouse:
So, the galvanized profile frame is ready, all that remains is to install the polycarbonate. This material is also interesting because when laid on the frame it creates a sealed surface, because the material includes a special joining element, which closes the joint of the polycarbonate sheets from above.
The sheets are laid on top of the frame in even rows and secured to it with self-tapping screws with rounded heads. A neoprene rubber washer must be placed under the latter, which does not crack at both sub-zero and positive temperatures.
Joining polycarbonate sheets Source pinterest.ch
Exterior of the greenhouse
Typically, a greenhouse is designed according to the botanical species of the plant. Factors such as the light transmission capacity of the covering material and maintaining the required temperature inside the room are taken into account.
The shape of the greenhouse is:
- with one slope. This could be a winter garden or a greenhouse. A passage is provided along the entire length, usually adjacent to the southern wall of the house;
- with two slopes. This is the most common form throughout Russia. Offers a variety of interior design options;
- in the form of a drop. A fairly stable design, but difficult to install;
- domed. It has a very impressive appearance with a modest consumption of materials;
- polygonal shape. They look great in a garden plot and can easily withstand strong winds.
How to place vegetables correctly
Placing cucumbers
Immediately, everyone may have a certain impression that there should not be any difficulties with planting vegetables in a greenhouse.
However, one should take into account the fact that there are also certain subtleties in this issue.
Sometimes seedlings can grow too large or stretch in a certain direction.
Most professional gardeners try to place such seedlings in holes to allow the roots to deepen.
However, it is highly undesirable to perform such procedures without any professional skills. When the stem is covered with soil, so-called additional shoots are formed. As a result, the flowers of the plant begin to fall off, and the process of development of the vegetable crop ends here.
To plant dried sprouts, you will have to dig two small holes. The stem should be placed in one, and the root system of the plant should be carefully placed in the other. After some time, all the seedlings will definitely take root properly. All seedlings must be laid out according to the most ordinary pattern. The seedling is carefully placed in a pre-prepared hole, after which it is sprinkled with earth.
The process of growing various vegetable crops in polycarbonate greenhouses always implies the need for certain experience, skills and dexterity.
Consequently, gardeners starting their practice will always experience certain difficulties in the process of combining different varieties of vegetable crops in one greenhouse. To acquire the first skills, it is advisable to decide on one type of vegetation, after which you can already practice on others.
Classification of greenhouses
Objects that ensure the maintenance of an artificial climate within themselves can be classified as collapsible and stationary greenhouses. Folding greenhouses quickly occupied their niche in the market for gardeners.
The ultra-light frame has standardized parts that can be assembled and disassembled by a person without special training. The price of such a kit will not put serious pressure on the family budget.
The coating for this design is usually a special polyethylene film. If handled carefully, it can be used for several years.
A stationary greenhouse design is considered a kind of classic for summer residents. In this case, the steel supporting frame rests on the foundation structure. Window windows are installed for ventilation, at equal intervals of wall glazing sections.
This design has proven itself to be a long-liver in the garden. Ease of manufacture and minimal operating costs are the undoubted advantage of this design.
Greenhouses are also divided according to the type of characteristic features depending on the author of the project. The design of the greenhouse, the author of which is Kurdyumov, provides for watering the plants using the drip method. Greenhouses also have the ability to maintain the desired range of temperature and air humidity.
The greenhouse design, authored by Mittleider, is a durable structure made of natural wood. As a rule, such greenhouses are installed in the direction of the sun. This ensures better illumination for the plants.
Other materials for constructing greenhouses
What else can you use to make a greenhouse inexpensively with your own hands? In principle, there are not many materials:
- Wooden blocks that are assembled according to the type of building with a gable roof. That is, it is the same as a greenhouse made of polypropylene pipes or galvanized profile. Only here you can use either self-tapping screws or nails as fasteners. Perforated elements are increasingly being used.
- From old window frames. In general, an interesting cheap option if you got the windows themselves for free. Let's look at this type of greenhouse.
Greenhouse made of wooden blocks Source es.dreamstime.com
Greenhouse made from old windows
Let's start the analysis with the same question as the other options - how to make a greenhouse correctly. Here the word “correct” is the most important. The thing is that old windows are heavy material; they cannot stand assembled without a frame. Therefore, the first thing to do is to build this very frame. Why do you need beams and boards, the width of which is no less than the width of the window frames:
- The beams are assembled into a box at the site of the greenhouse construction and fastened together with perforated fasteners and self-tapping screws.
- A frame made of boards is installed on the assembled box. These are the racks and the top trim. The type of fastener is the same. Here it is important to install the racks in increments equal to the width of the frames. That is, the latter must fit clearly between the posts to which they will be attached.
- This will need to be done at this stage, having first removed the glass.
Greenhouse made from old window frames Source in.pinterest.com
Attention! Old frames are not new, with all the elements intact. Therefore, after installing the windows, gaps will remain in the frame. The latter can subsequently be filled with polyurethane foam.
As for the size of the greenhouse, the height of the structure can be increased. That is, this is not necessarily the height of one frame. You can stack the windows on top of each other, you can trim one of them and mount the cut part onto the whole one located below.
A greenhouse made from window frames has one big advantage - the windows are ready-made and openable. That is, if, using other materials to build greenhouses, you have to make openings, which is not always easy. With a frame greenhouse everything is much simpler.
As for the roof, the easiest option is to cover it with plastic film. To do this, you need to make a roof structure if a gable roof is chosen. Or form a deck located at an angle of at least 15° - you get a pitched roof.
The film on the roof is secured with slats Source homeli.ru
Preparatory work
In order to make the simplest greenhouse by hand, it is necessary to carry out the necessary preparatory measures.
When choosing a location for a greenhouse, you should be guided by the fact that there is no interference with direct sunlight. The site should be as level as possible, and it is advisable to have protection from strong winds.
News site- Features of electrical wiring installation in houses made of SIP panels
- How to choose a cast iron bath
Please note that you will need water for irrigation and electricity for lighting. Therefore, the greenhouse should be located on the site within acceptable proximity to these sources.
Foundation
The type of greenhouse chosen determines its foundation. First, markings are made - the sides form a right angle. For a seasonal structure, a wooden base made of timber (10x15 or 15x15 cm) treated with an antiseptic or water-repellent compound is suitable to last longer. Place it on the ground, but preferably on a cushion of compacted sand or on concrete slabs.
For a permanent building you will have to dig a pit. You can make a strip foundation - a trench 30x30 cm. Sand is poured onto the bottom, crushed stone on top (all 50-70 cm thick). They put up formwork from boards, lay roofing felt and fill it with concrete. It needs to be pierced with a shovel and knocked on top to remove the air. The base is raised above the ground by 20-50 cm. Support posts or pieces of metal corners are embedded in the foundation.
Installation of the supporting frame of the greenhouse and covering
A reliable frame design will be the key to protecting plants from the hot rays of the sun and heavy rains.
After the concrete in the foundation has gained the necessary strength, the frame elements can be prepared for assembly. The elements of the lower chord and the stand are connected to each other with bolts.
The elements of the upper chord and roof slopes are sequentially connected into a spatial structure with rigid connections. The entrance door is located on the leeward south side.
Effective swirl ventilation should be ensured by placing opening vents in the roof structure.
Clinker brick- Barrel sauna and its features
Apartment renovation
When covering a greenhouse with your own hands from polycarbonate, the sheets are attached to the frame with anodized steel screws. A rubber sealing gasket is placed between the polycarbonate sheet and the frame element.
Glass coating is the most traditional material. However, high operating costs have pushed it out of the greenhouse materials market.
Film coating is characterized by low price and ease of use. It should be noted the low durability of this material.
What to cover
The main covering material for greenhouses and greenhouses is film. It is used on both small and large-sized structures. Glass was previously used for year-round use, but its high price and fragility led to the fact that it is used very rarely - the resulting shelter is expensive. And the large weight of the glazing requires a solid frame.
There are two new items. The more familiar polycarbonate, which is used for gazebos and canopies, and the relatively new one is spunbond non-woven covering material.
Now about everyone in more detail.
Film for greenhouses and greenhouses
Available in different polymers and different thicknesses. The most common are polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride. There are also reinforced ones.
Polyethylene films are the most inexpensive, but they are also the most short-lived. Even with the most careful treatment, they do not last more than a year: they become fragile under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, and the cold kills them. However, they are most often bought: cheap.
Available in sleeve form. By cutting it on one side, we get double width. There is no point in using uncut film: the service life will remain the same, but the consumption will be exactly twice as much. There is only one feature: the film breaks quickly along the fold. It is difficult and almost useless to seal it afterwards: the tape sticks very poorly to a dusty surface. Therefore, this fold is taped with tape before use. It turns out reliable.
Thickness and types
The optimal thickness of polyethylene film for summer cottages and greenhouses is 150 microns. If you take a thicker one, its service life will still be one season, but 150 characteristics will be enough.
The reinforced film differs in appearance: the cage is clearly visible
Reinforced film is more durable. Manufacturers provide a 3-year warranty. It is easy to distinguish by its appearance: it is checkered. Fibers of other polymers or the same polyethylene, but processed differently, are woven into polyethylene fabric. Thanks to stronger fibers, such a film greenhouse can withstand wind and snow loads well (to a certain extent). Reinforced film is available in different densities; for greenhouses and greenhouses at dachas and personal plots, 120 g/m2 to 200 g/m2 is more suitable.
There are also polyvinyl chloride films. They can be used for up to 7 years. But they are expensive. The material is also good because it transmits sunlight well (80-90%) and almost does not transmit infrared light (5-10%), that is, it does not allow the greenhouse to cool down overnight. If you need a warm greenhouse that maintains temperature well at night, this is your choice.
There are also films called perennial. Most often it is polyethylene with various additives. Some other polymers are less common. Typically, perennial films have some special properties:
- less destroyed by ultraviolet radiation - light-stabilizing;
- transmits less thermal radiation - heat stabilizing;
- prevents condensation drops from forming on the film - hydrophilic;
- reflects thermal radiation, glows in the dark, absorbs ultraviolet light - these properties depend on the type of additives, but are called light-converting.
These properties can be combined in one film. This is how you can find a long-term hydrophilic heat-stabilizing film, etc. One more thing. Such films usually have some kind of tint: yellow, greenish, blue...
Perennial films have different colors
When choosing a multi-year film, be sure to check its service life. It can be from two seasons to 3 years. Note. If it says 2 seasons, it means it needs to be removed for the winter. If 2 years, then this is a film for year-round use. Sellers often manipulate these concepts, saying that two seasons mean two years.
See photo reports on the construction of greenhouses with your own hands here.
Polycarbonate
This cellular material has many advantages: it is lightweight, transmits light well, retains heat, bends, and is easy to install. The disadvantage is the relatively high cost. However, if the greenhouse will be used for more than one year, such investments will pay off: even without additional heating, the growing season will increase significantly.
But polycarbonate varies in structure and thickness. The most commonly used types in the construction of greenhouses are in the table.
The structure of polycarbonate and its thickness
For normal conditions (average snow load and wind), single-chamber sheets are used to cover greenhouses. For regions with a lot of snow, it makes sense to take reinforced ones.
The optimal thickness of the sheets is 6 mm or 8 mm. You shouldn’t take less: the sheets are too fragile and their characteristics are not very good (see table). Polycarbonate 4 mm thick can be placed on small greenhouses. It will not withstand heavy loads.
Characteristics of polycarbonate of different thicknesses
Polycarbonate still needs to be fastened correctly: the cells must be oriented from top to bottom, the open edges must be sealed with a special tape or tape, secured with special thermal washers or bolts with a large metal washer, under which a rubber or plastic lining must be placed.
Spunbond
This is no longer the same material. There are many brands: Agril, Lutrasil, Spantex, Agrospan, AgroSUF, etc. It’s just that Spunbond appeared first and now all similar materials are called that way, and also “non-woven covering material” or “agrofibre”. This is a non-woven polypropylene fiber that has unique characteristics: it allows air, light and moisture to pass through, while simultaneously saving plants from overheating or freezing. Feedback from a practice on using this material in a video.
Agrofibre is characterized by density. The lowest is 17 kg/m3, the highest is 60 kg/m3. For seasonal greenhouses and greenhouses from spring to autumn, the optimal density is 30-40 kg/m3; for winter ones, 60 kg/m3 is needed.
Read about how to organize drip irrigation here.
Plumbing, electricity, greenhouse heating
After the greenhouse frame, covering, and ventilation are completed, you can begin installing the electrical network, heating and water supply.
Considering that the humidity in the greenhouse will be high, all electrical work must be performed taking into account the requirements of the relevant standards and rules for performing special work.
Stove heating, electric energy, or gas can be considered as a heat source for the room. The issue of efficiency will depend on the regional location of the facility.
For productive work, it is advisable to bring water into the greenhouse. For this, a plastic pipe with a diameter of 1.5 inches is usually used. The riser is located at the entrance to the room.
Vegetable selection
Bell pepper
A wide variety of vegetable crops can be grown in closed soil.
It is advisable to choose vegetables whose growing season is considered the shortest.
Planting such varieties provides the opportunity to achieve the earliest possible harvest.
Rare late-ripening varieties of vegetable crops can be planted in greenhouses equipped with a heating system. If you plant plants directly in the ground, the yield will be quite high compared to placing them on special racks.
At the same time, it is not recommended to use so-called hydroponic technologies, which will greatly help reduce material costs, but will significantly worsen the taste properties of the vegetation.
In most examples, vegetable crops are grown in greenhouses, which have special requirements for humidity levels, sufficiently high temperatures, preventing exposure to parasites, as well as harsh chemical exposure, and poor environmental conditions.
Among the most popular vegetable crops are:
- Today there are many varieties of tomatoes that have been cultivated specifically for closed soil. These plants respond well to light, nutritious soil, normal distribution of moisture during watering, and a sufficient amount of fresh, moderately dry air mass. To increase productivity, you can use potassium and phosphorus fertilizers. It is not advisable to overuse nitrogen if this substance is used as a fertilizer. Organic substances are also recommended for use when growing these varieties of tomatoes.
- Cucumbers are considered a fairly heat-loving vegetable crop that does not respond well to too sudden temperature changes. Such vegetables definitely need a sufficient amount of moisture, good lighting, and a high level of environmental humidity. In order for the quality of grown cucumbers to be high enough, it is advisable to feed them with organic fertilizers. If you organize conveyor planting, cucumbers will produce fruit constantly.
- In order to plant peppers, it is necessary to ensure nutritional value, lightness and a sufficient level of looseness of the soil. At the same time, it is not recommended to plant hot and sweet peppers next to each other, since there is always the possibility of changing the taste characteristics of this type of vegetation.
- Eggplants are a type of vegetable crop imported to our region from other regions. To ensure a sufficiently high level of yield, it is imperative to water the plants in sufficient quantities, as well as ensure a flow of fresh air into the greenhouse. Eggplant does not have the opportunity to receive the necessary supply of nutrients from the soil for independent development. Therefore, it is imperative to use organic fertilizers when planting eggplants. If you combine eggplants with other vegetable crops in the same greenhouse, only tomatoes are best suited for this.
- A polycarbonate greenhouse is great for growing onions or some other greens. When planting onions, even a novice gardener can count on fairly good yields. Onions are also characterized by high frost resistance. Therefore, it will not be absolutely difficult to organize normal conditions for the development of this type of vegetation.
DIY greenhouse photo
Care
All parts of dismantled structures must be cleaned of dirt and dust at the end of the season. To do this, you can use a solution of potassium permanganate or mustard. After this, they are thoroughly dried and stored in a dry room protected from precipitation.
In the case of stationary structures (with a foundation, glass or polycarbonate), seasonal maintenance should be carried out more thoroughly.
To prevent the proliferation of pests, the walls of the greenhouse are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, the old soil is removed by 10-15 cm, after which new soil is added, and ash, sand, humus, and sometimes wood are added to it. Then it is carefully dug up and treated with a sulfur bomb.
The greenhouse, ready for the new season, is left open until the onset of frost or until the first snowfall. In winter, it is advisable to close the greenhouse tightly to protect it from snow and gusts of wind.
It will be useful to leave some snow in the greenhouse. In spring, melt water can have a beneficial effect on soil quality. In case of heavy snowfalls, the greenhouse must be cleaned with a shovel or broom; in case of moderate precipitation, it can be left alone.