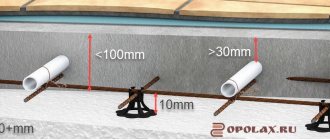
To protect wastewater from freezing, there is a heating cable for sewer pipes. Heating of sewerage is necessary in situations where pipes have to be located in unheated rooms, basements, and basement levels of buildings.
Sometimes it is not possible to lay the system at the required depth, which makes the pipeline susceptible to the risk of freezing drains and the formation of an ice plug. In such cases, it is necessary to insulate the pipes. The best option is a heating cable for sewer pipes, which allows you to solve the problem effectively and reliably. Let's take a closer look at this issue.
Which pipes need heating?
Please note that most sewer pipes do not require heating. If they are located inside a building, then, as a rule, they are not exposed to low temperatures. In addition, the system has a certain slope, thanks to which wastewater quickly passes into the collector and does not linger in the pipes. The temperature of the waste also plays a role - large volumes of water, most often warm, as they are discharged from the bathtub or obtained during washing dishes or laundry.
Sewer heating is only necessary in certain cases:
- for the external part of the system, ensuring the flow of wastewater to the collector or treatment plant;
- pipelines through which clarified wastewater passes to filtration fields or is discharged into filtration wells ;
- for pipelines supplying water to the flushing filters of septic tanks or treatment plants.
The main problem is the difficulty of determining the degree of risk for a particular section of pipes. There are a lot of factors influencing the system, from the level of soil freezing in winter to the depth of soil water. An additional complication is the constant change in conditions and the emergence of new factors that create a threat of freezing for the sewer system. If the installation of the system is carried out correctly, in compliance with all SNiP requirements, there is nothing to fear. But it is not always possible to immerse the pipeline to the required depth - the hydrogeological conditions of the site or the presence of other communications may interfere, preventing the work from being carried out according to all technological rules. The way out is to heat the sewer pipes with a heating cable.
Expert advice
Professionals recommend adhering to the following rules when installing heating systems for sewerage:
- Do not install the cable in narrow pipes, as this may lead to cable breakage or blockage of the line.
- Fasten with aluminum tape, which has good thermal conductivity.
- Do not use metal clamps to secure the wire to the polymer sheath.
Experts advise making a choice in favor of external placement of the cable on the pipeline with subsequent insulation and strengthening.
What is a heating cable
The heating cable is a long-length electric heating device tightly attached to the pipeline and laid together with it in a trench. Somewhat simplified, its design is a conductor that heats up when an electric current passes. The simplest options have a design common to the design of most heating devices.
example
Make it yourself or buy it
If you have special education and experience working with electricity, you can make a heating cable yourself. For this, low-power spirals and wires are used. Metal insulation is carried out using heat shrink tubing. The finished product can be no worse than industrially manufactured analogues.
However, the time and money spent on purchasing materials may not bring tangible benefits and savings.
Tips for choosing
Professionals recommend choosing products with such power that will ensure high-quality heating of the main line when the temperature drops critically. If it is possible to continuously monitor the condition of the cable, then it is advisable to choose a resistive option.
When the system operates in autonomous mode, it is better to install a self-regulating device from inside the highway.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating cable
The advantages of cable heating of sewerage include:
- the ability to eliminate freezing and congestion within the system;
- heating of pipelines allows reducing the volume of excavation work;
- the use of a heating cable stabilizes the operation of the sewer system of a private house, which is not loaded as intensively as public lines and is more susceptible to low temperatures;
- Cable installation can be done with your own hands, without the involvement of expensive specialists.
The disadvantages of a heating cable are:
- creating additional load on power grids;
- the need to pay for used electricity;
- low maintainability;
- significant labor costs when installing a heating system;
- the need to connect additional devices to ensure the operation of the heater.
The disadvantages are quite serious, and the main one is the load on the electrical network. Considering the general deterioration and dilapidation of the power supply system, the use of electrical appliances for heating sewer systems seems to be a somewhat irrational solution. However, in the absence of other methods of protecting pipelines, it is necessary to choose heated pipes for sewerage.
Installation of an external heating cord, recommendations
When installing the wire, two methods are used: linear arrangement along the pipe or tangential wrapping.
Adhesive tape or synthetic cable bandage is used as fastening. The distance between the fastening points should not exceed 200 millimeters.
Often, to increase the efficiency of heat transfer, the pipe is initially wrapped in aluminum foil (this can significantly increase the heating area), to which the heating cable is directly attached. This method is recommended for installation on plastic products, which have low thermal conductivity compared to metal ones.
When laying the heating element, you should avoid creating kinks and make turns at an acute angle to avoid accidental damage to the electrically conductive wires and damage to the insulating layer. The final stage will be the installation of thermal insulation material.
Types of heating cable
There are different designs of heating cable:
Resistive
The simplest design option. It has a strictly defined length and does not allow cutting or connecting several pieces, since the resistance will either decrease too much, which will create an emergency situation for the electrical wire and equipment, or will increase and sharply reduce the efficiency of the cable. There are designs with one and two conductors. The first option requires installation folded in half, since the ends must be connected at one point. The second type can be laid in any way you like, since the double conductor is one wire that simply goes to the end and comes back.
Resistive cable has a lot of disadvantages, but its attractiveness for the user lies in its low cost.
Resistive and zone heating element
Zonal
The zonal design consists of a double insulated conductor, around which a heating nichrome thread is evenly wound. It is connected to conductors at regular intervals, which allows for corresponding heating zones. Such a system does not depend on the length of the circuit and can heat pipelines of any size. The use of a zonal type facilitates the installation of a heating cable on a sewer pipe and provides some advantages:
- there are no starting currents;
- if the nichrome thread is damaged in a separate section, the rest of the cable continues to work;
- heating power does not depend on the length of the circuit;
- characteristics do not change over time.
The disadvantages include the danger of local overheating of the cable section and the possibility of its damage during installation. The price of such a heater is slightly higher than that of resistive types, but significantly lower than that of self-regulating designs.
Self-regulating
The self-regulating cable consists of two conductors onto which a polymer heating matrix is pressed, protected by a double layer of internal insulation, a copper screen and an external protective insulating layer. The peculiarity of its operation is its ability to create its own temperature in different sections of the cable depending on external conditions. The lower the temperature, the stronger the heat release at a given point. A self-heating sewer cable represents the most effective solution to the problem of pipeline freezing, but its cost is significantly higher than that of simpler designs.
Heating film
In the most difficult cases, a heating film is used. It wraps around the pipe, ensuring uniform heating of the entire surface. This allows for maximum heating efficiency, but significantly complicates and slows down installation work. At the same time, the film consumes much less electricity, which can significantly reduce costs. Considering that you have to install the system once, and pay for the resources used constantly, heating sewer pipes using film can be considered a very good option.
You may also like: Sewage system - structure, types and principle of operation
Power wires
Designed to transmit electricity from power plants to distribution transformers and further to the end consumer. In the first case, wires are used that are designed for open-air operation and can withstand voltages of up to 150 kV - the optimal value for transmitting electricity over long distances.
Household power wiring is designed for alternating current with a frequency of 50-60 Hertz and voltage up to 1000 Volts. A classification is often used based on the material of current-carrying conductors, which can be made of aluminum, its alloys or copper. Aluminum ones are cheaper to produce, while copper ones have less resistance to electric current, so they have a smaller cross-section. It is preferable to use copper wiring - it is more durable and reliable, but because of the price, aluminum is still used quite often, and in power lines and in general - almost everywhere.
VVG is the market leader
Cable for laying electrical networks with double polyvinyl chloride insulation - multi-colored on each core and a common cambric. Current-carrying conductors are single or multi-wire, with a cross-section of 1.5-240 mm². It has the following varieties:
- AVVG. The letter “A” before the name indicates that the cable cores are made of aluminum.
- VVGng. Wire insulation does not ignite over a wider temperature range.
- VVGp. It differs only in appearance – its flat shape.
- VVGz. High security cable - all empty spaces inside it are filled with a rubber mixture.
NYM cable
Made according to European standards and although the conductive properties are similar to VVG wires, the insulation class is superior to domestic analogues, since during manufacturing, the voids between the cores are filled with coated rubber. It is manufactured with a number of current-carrying cores from 2 to 5, with a cross-section of 1.5-16 mm². Outdoor installation is permitted, but with additional protection from sunlight, since the insulation is not UV resistant. Unlike domestic analogues, it can be laid with a bending radius of 4 of its diameters.
KG – flexible cable
Without losing its properties, the cable can be used at temperatures from -60 to +50 C°. It is most often used to connect electrical appliances to the network, and its cores are designed for current frequencies up to 400 Hz, which makes it a good choice for use in welding machines. Current-carrying conductors are only copper stranded with rubber insulation. The number can be from 1 to 6, hidden under a common outer shell.
VBBShv – armored
Increased protection against mechanical damage is provided by tapes with which the wires are wrapped before applying the main layer of insulation. Current-carrying conductors are made of copper, separately insulated with PVC, quantity - 1-5 pieces, consisting of one or more wires. Single-core ones are used for direct current transmission.
There is one limitation to using the cable - installation without UV protection is not recommended. The following types are used:
- AVBBSHv – with aluminum cores;
- VBBShvng - when overheated, the insulation does not burn, but smolders;
- VBBShvng-LS – minimum smoke and gases during smoldering.
Which cable to choose?
The criteria for choosing one type of heater or another are:
- size and configuration of the problem section of the pipeline;
- line depth or conditions;
- temperature operating conditions in winter;
- cable cost;
- possibility of repair or replacement.
As a rule, an element for heating sewer pipes is selected based on the totality of these conditions and requirements. It is very difficult to name the most successful option without knowing the specifics and configuration of the system. However, according to experts, resistive types are used less and less, and self-heating cable is used much more often, although it costs users much more.
Heated sewer areas
- A section of external sewer pipe leading to a septic tank, sewer well or other treatment facility.
- Connections of drainage wells, septic tanks.
- Areas of closed storm drainage.
Heating cable installation options
There are two cable placement options:
- outside the pipe;
- inside the pipeline.
Installing the heater outside the pipe is easier. It is usually attached along the pipeline or, if the length allows, wrapped around the pipe for greater uniformity. For fixation to the surface, regular or metallized adhesive tape that is resistant to heat is used. A layer of insulation is put on top. The most correct option is a polystyrene or polyurethane foam shell, which is easy to install and effectively retains thermal energy.
Installing a heating element inside the pipeline allows you to obtain a significantly greater effect. It is used in cases where the system is located close to the surface of the earth or is even located in an open area. A self-regulating heating cable for sewerage inside a pipe allows you to reliably protect both conventional and stormwater systems, which remain practically unused during the cold season. The remaining wastewater freezes, is periodically replenished during warming periods, and ultimately forms an ice jam that can rupture the pipeline. However, the heater can only be installed in pipes of a sufficiently large diameter, otherwise it will cause frequent blockages and instead of benefit will only bring unnecessary worries.
Example of pipe insulation
Shielding
A metal screen is used to protect the electrically conductive part of the cable from moisture. The screen is made of tinned copper, which is resistant to corrosion. Copper has sufficient flexibility and strength to withstand external pressure without losing its tightness.
Budget options for heating systems use aluminum.
Products with aluminum screens are laid outside in a straight line.
DIY installation and connection of a heating cable
Installing a heating element is not particularly difficult. It is most convenient to carry out work during installation of the system, so that you do not have to dig up pipes that are already in use. If you plan to heat the system from the outside, before installing the insulation, lay a heater along the pipeline and secure it with tape. Installing a self-heating cable for sewerage inside a pipe is somewhat more difficult, since it is necessary to combine the installation of the system with the installation of the heater. It is important to bring the element all the way to the drain hole, which is an area exposed to cold.
The connections must be insulated with heat-shrinkable tubing, which is heated with a torch or a hair dryer. For entry, an oblique tee with a plug in which a hole is made is used. A heater is introduced through it, and the outlet is filled with a heat insulator that is resistant to high temperatures. It is necessary to ensure that the heater sections do not intersect anywhere and are located evenly, without clusters or empty areas.
Independent connection to the power grid
Quite often, a malfunction occurs precisely at the connecting junction, which leads to de-energization of the sewer cable. Correct installation is carried out in the following order:
- A large heat-shrinkable tube is placed on the end of the heating cord.
- The outer insulating layer is stripped from the end at a distance of 50 mm, the braid is cut 10 mm from the edge of the insulation.
- The heating cores are separated and the internal insulation of about 6 mm is removed.
- Next, on the cord, as well as on each core, a small-diameter tube and a medium-diameter tube.
- It is necessary to place the twisted braid in a metal tube and crimp it to make a tight connection with the braid.
- The end of the power supply wire is cleared of 80 mm of outer insulation.
- The cores are separated: the ground wire remains as is, and the phase and neutral wires are cut to a length of 35 mm.
- The ends of the wires are freed from secondary insulation by 6 mm.
- The stripped ends of the supply and heating cables are sequentially inserted into heat-shrinkable couplings and connected by heating with a hair dryer or open fire.
- Additionally, each joint must be wrapped with insulating tape.
- The ground wire is inserted into a metal sleeve crimped onto the braid and is also clamped.
- A medium-sized heat-shrinkable tube is moved onto the resulting joint, and after thermite treatment - a large one, followed by heating.
Such a connection completely prevents moisture from entering the connecting joint, so there will be no short circuit in the wiring.