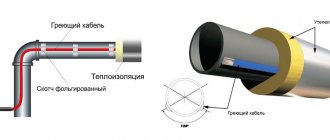
Despite the frequent use of soldering technology for connections, copper pipe is often connected to fittings and fittings using mechanical methods without the use of heat from a gas torch. Moreover, with technological development, mechanical methods of connecting copper pipe assemblies are becoming more and more practical and rational for work. At the moment, connections of copper pipes, fittings and fittings can be made using several proven mechanical methods of detachable connections. Let us consider these options for mechanical assembly without heating in more detail.
Connecting pipes using soldering
Let's consider connecting copper tubes with fittings followed by soldering, which can be low- and high-temperature.
In the first method, soldering is carried out at a temperature of 300 ºC. The second method is used when installing systems with high loads for industrial purposes. Couplings are used as connectors for copper pipes; tin-lead solder and flux are additionally needed.
The pipe soldering technology will be as follows:
- First of all, a pipe of a certain size is cut. This process must be carried out carefully, taking into account the size of the existing fittings.
- The ends of the pipes must be inspected - there should be no defects such as chips, cracks or burrs. If they are not eliminated, there will be problems with the tightness of the connection after all the work is completed.
- After making sure that the ends are clean, you can start connecting. Due to the fact that several pipes will be connected, and they can be of different sections, the fittings must be selected accordingly.
- Next, the end of the pipe and the inner walls of the couplings should be treated with flux, which will degrease the surfaces to obtain the highest quality connection.
- Now the end of the pipe is threaded into the copper tube connector and heated. It must be selected so that the cross-section is 1-1.5 cm larger than the cross-section of the pipe. The pipes are heated with a gas burner. The gap between the pipe and the coupling is filled with molten solder. Currently, you can find any type of solder on the market to suit your needs, so there should not be any problems with the choice.
- After the solder is evenly distributed around the circumference, the parts to be joined must be left until it has completely hardened.
At the final stage, you need to check the connectors for the copper pipes and the entire system by running water into it. At this moment, not only the system will be checked, but it will also be cleaned of flux residues, which over time can cause metal corrosion.
How to choose?
In order to properly install the system, it is necessary to take into account the features of threaded fittings. You must focus on the purpose of the pipes; if you use high-quality materials and carefully follow all the rules, you are guaranteed a high-quality connection for many years. Find out what the sizes and purposes of fittings are, use this when designing.
Selection of fittings
If you need to rotate the structure, you will need corners; if you plan to branch, be sure to purchase tees, crosses, and manifolds. If you just need to connect two pieces of pipe (of the same diameter or of different diameters), stock up on couplings, and, of course, don’t forget to buy plugs.
Installation of various types of fittings
Installation of different types of fittings is carried out in different ways. However, before starting to set up the connection, the following work must be done:
- cut the pipe to the required length, according to the developed project. To cut copper pipes, it is more advisable to use a pipe cutter that does not deform the edges;
- clean off any burrs left after cutting. To do this, you can use a bevel remover or sandpaper;
- if necessary, for example when installing a fitting by soldering, widen the end of the pipe by a few millimeters.
Installing compression fittings
To install a compression type fitting, you will need a wrench of the appropriate size. Installation occurs in the following way:
- a fixing nut and a clamping ring are put on the prepared pipe section;
- the pipe is connected to the selected fitting;
- The connection is fixed first with your hands and then with a wrench.
Installation of compression fitting
In the process of smoothly tightening the nut, the clamping ring fits tightly to the pipe, which makes it possible to achieve a tight connection.
Installation of press fittings
To install a press fitting, you will need to prepare special press pliers or a press gun (the equipment is used by professionals. To connect pipes at home, pliers are sufficient).
The installation diagram is as follows:
- a pipe is inserted into the fitting;
- the maximum depth level is noted so as not to completely block the flow in the pipeline;
- the press sleeve is compressed.
Attaching the Compression Fitting to the Pipe
You can watch the video for more information about installing press fittings.
Installing Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings are installed according to the standard scheme:
- a thread is cut on the pipe using special tools;
Preparing pipe threads
- the threads on the fitting or pipe are sealed with the selected material;
Thread sealing with Tangit Unilok thread
- the fitting is screwed on.
Since copper pipes are quite soft, it is important not to overtighten the threaded connection.
Installing solder fittings
The installation of fittings installed by soldering is completely similar to the process of pipe soldering:
- Flux (a special substance to increase the fusibility of solder) is applied to the prepared section of the pipe;
- the selected connecting element is put on;
- Using a gas torch and solder, the free space in the seam is filled.
Solder fitting installation
When performing work, it is important to strictly follow safety precautions. Soldering is performed in a well-ventilated area
There should be no flammable mixtures or objects nearby.
Thus, you can select and install any type of fittings for copper pipelines yourself.
Labeling and cost
Round copper products for heating and plumbing with walls from 0.8 to 10 mm thick are manufactured in accordance with GOST 617-90. In subsequent years, the document was repeatedly refined, so a different digital value may be indicated in the marking. Depending on the purity of copper, its grades according to GOST 859-2001 are marked as M1, M1p, M2, M2p, M3, M3p. The composition of the material has little effect on the main characteristics of the pipes, so they are allowed to be neglected.
From the standard labeling you can find out:
- Preparation method. Drawn ones are indicated by “D”, and welded ones are indicated by “C”.
- Cross section shape. For the pipes in question, it is round, so it is marked “KR”.
- Precision manufacturing. Normal wall thickness and diameter size are designated “N,” and increased thickness is designated “P.” With normal accuracy of wall thickness and increased diameter, “I” is indicated, and if vice versa, then “K”.
- Length. “ND” is an unmeasured pipe, “MD” is a measured pipe, “KD” is a multiple dimension index, “BT” is a coil.
- About special conditions. Improved characteristics are designated by the letter P. Increased ductility is “PP”, strength is “PT”, accuracy is “PS”, cutting accuracy is “PU”.
Other manufacturing features are not significant
For example, they pay attention to increased accuracy in curvature “K” if they want to install a pipeline with an ideal appearance and are willing to overpay. The standard marking looks like this: DKRNM 30×2.0×2050 M1 GOST 21646-2003
This means:
- the pipe is made of M1 grade copper;
- drawn out;
- round shape;
- manufacturing accuracy is normal;
- soft;
- outer diameter 30 mm;
- wall thickness 2 mm;
- length 2050 mm;
- according to GOST 21646-2003.
According to European standards DIN 1412, copper pipes for installation of water supply and heating systems are marked EN-1057. It means that phosphorus has been added to their composition, which increases oxidation resistance. EN-1057 is the number of the standard to which the pipe is manufactured.
On average, prices for copper products with walls 1 mm thick for heating installation in an apartment or private house, depending on the size of the internal cross-section, are:
| Diameter, mm | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 |
| Price per 1 meter, rub. | 110 | 145 | 180 | 210 | 220 | 235 | 295 | 380 | 600 |
Pipes with walls 1.5 mm thick cost one and a half times more. Prices are indicated for products of Russian manufacturers. Foreign analogues will cost more due to transport and customs costs.
Types of press fittings for pipes
Types of threaded fittings
Depending on the method of application, two groups of such elements are distinguished:
- Compression (crimp fittings for pipes);
- For soldering.
The first ones are intended for making detachable pipeline connections. They can be made in the form:
- Knee;
- Tee;
- Couplings;
- Crane.
Products in this group are characterized by low cost, the ability to be used several times, and ease of installation, which can be performed without any special devices.
In addition, when press fittings are used repeatedly, their reliability decreases.
Types of Compression Fittings
Soldered models are also available in various designs:
- Transition tees;
- Rotations of 45 and 90°;
- Contours;
- Single- and double-socket couplings;
- Plugs;
- Arcs.
They are fastened by capillary soldering using a coaxial overlap connection. In this case, molten solder is sucked into the installation gap, which cools down and makes the joint airtight.
The advantages of compression fittings include their low cost. They are the cheapest of all existing varieties and are made from Cu DHP grade copper. They can be used with both high and low temperature welding.
Let's watch the video, the nuances of installation, testing:
Installing such parts can significantly reduce installation time, but at the same time ensures high strength and reliability of connections. This is what makes copper pipes and fittings popular despite high prices. Only for low-temperature soldering, special parts with a groove along the inner circumference are produced. Solder is placed into it at the factory, and when such an element is put on a pipe coated with flux and heated, the joint will be soldered.
Brief characteristics of threaded fittings
Threaded fitting is one of the main types of pipeline connections.
These are prefabricated parts that are used to repeatedly connect system elements. Their design provides for the presence of external or internal threads. As a rule, this is a cylindrical thread. Threads are provided both on the fittings themselves and directly on the pipes. Their advantage is reusable. Threaded products are suitable not only for connecting elements, but also for installation with plumbing or pipeline fittings. The above fittings can be classified as:
- without coating;
- with zinc coating (galvanized);
- chrome plated (chrome plated);
- with nickel coating (nickel plated).
Naturally, coated fittings provide more reliable anti-corrosion protection.
Threaded fitting is one of the main types of pipeline connections.
The range of threaded elements is huge. These are products of different types and designs:
- squares;
- tees;
- bends;
- nipples;
- couplings;
- plugs;
- fittings and so on.
The material from which threaded fittings are made is also varied:
- cast iron;
- brass;
- stainless steel;
- bronze;
- and finally copper.
This is exactly what the next story will be about copper fittings.
Three main connection methods
Before connecting sections of copper pipes, they must be cut in accordance with the wiring diagram and prepared. You will need a pipe cutter or hacksaw, a pipe bender and a file. And for cleaning the ends, fine-grained sandpaper will not hurt.
Only having a diagram of the future pipeline system in hand can you calculate the required amount of consumables. It is necessary to decide in advance where and what diameter the pipes will be installed. It is also necessary to clearly understand how many connecting elements are required for this.
Option #1: Welding copper pipes
To perform automated or manual welding of copper pipes, electrodes and gas are required to create a protective environment (nitrogen, argon or helium). You will also need a DC welding machine and, in some cases, a torch. The electrode can be graphite, tungsten, copper or carbon.
The main disadvantage of this installation technology is the significant differences in the characteristics of the resulting seam and the pipe metal. They differ in chemical composition, internal structure, electrical and thermal conductivity. If welding is performed incorrectly, the joint may even separate later.
Due to the alloying of copper as a result of the action of the deoxidizer present in the electrode, the weld seam is in many respects very different from the base metal being welded
Only a qualified craftsman can properly weld copper pipes. This requires certain knowledge and skills.
This installation option has a lot of technological nuances. If you plan to do everything yourself, but have no experience working with a welding machine, then it is better to use a different connection method.
Option #2: Capillary soldering
In domestic conditions, copper pipes are rarely connected by welding plumbing fixtures. It is too complex, requires specialized skills and is time consuming. It is easier to use the capillary soldering method using a gas torch or blowtorch.
The technology of soldering copper pipes with solder is based on the capillary rise (seepage) of the latter after melting along the gap between two pressed metal planes
Soldering of copper pipes happens:
- low temperature - soft solders and a blowtorch are used;
- high temperature - refractory alloys and a propane or acetylene torch are used.
These methods of soldering copper pipes do not make much difference in the final result. The connection in both cases is reliable and tear-resistant. The seam with the high-temperature method is somewhat stronger. However, due to the high temperature of the gas stream from the burner, the risk of burning through the metal of the pipe wall increases.
Solders are used based on tin or lead with the addition of bismuth, selenium, copper and silver. However, if pipes are soldered for a drinking water supply system, then it is better to avoid the lead option due to its toxicity.
Image gallery
To implement low-temperature welding, it is not necessary to have special equipment and special skills of the performer. You can do it yourself
Mounting choice: detachable vs permanent
To connect copper pipes into a single pipeline system, you can use several methods of joining them. Various plumbers use crimp and press fittings, welding or soldering. But before you start work yourself, you need to decide whether the pipeline should be permanent or detachable.
There are three installation technologies for connecting copper pipes:
- electric welding;
- soldering using a torch or electric soldering iron;
- pressing.
All these technologies can be used in the formation of both detachable and one-piece systems. Here it is more a matter of using a variety of fittings and adapters or refusing them.
If a structure cannot be disassembled without destroying its individual parts, then it is considered one-piece - it turns out cheaper, but it is more difficult to repair.
If the pipeline system needs to be detachable, and also easier to repair and add new elements, then the connections must be made detachable.
Fittings are used for this:
- compression;
- threaded;
- self-fixing.
It is easier to make detachable connections yourself; you can even do without soldering. They do not require excessively high qualifications from the master.
However, such units require constant inspection and tightening of the nuts to prevent leaks. Changes in pressure and temperature in the system lead to weakening of the fasteners. And from time to time it is recommended to tighten them.
If access to copper pipes is planned to be tightly closed with finishing or concrete screed, then it is best to connect them into an integral structure by soldering or welding. This system is more reliable, durable and resistant to abrasions.
Carvings are prohibited on copper products. This metal is too soft in its structure. When installing a detachable pipeline, all threaded connections must be made using fittings. The latter can be connected to a copper pipe by pressing or soldering.
Before making connections, copper pipes are prepared in a special way:
Image gallery
Photo from
Cutting copper pipe before connection
Removing burrs with a deburring tool
Degreasing and cleaning the external surface
Cleaning the bell of the coupling and fitting
How to connect copper products
- The required section of the product is cut off, as in the previous version;
- The outer and inner parts are cleaned of dirt using a special brush or sponge for copper;
- The pipe is inserted into the capillary fitting as far as possible, flux is applied, the excess of which can be removed with a clean cloth;
- The connection is heated using a gas burner or a special construction hair dryer, and solder is applied. The solder should melt and evenly fill the mounting gap;
- We are waiting for the solder to cool naturally. Remains of flux are removed with a damp and clean cloth.
Now you know how to connect copper pipes in several ways. If anything about copper installation seems unclear to you, you can always study the instructional video. In principle, this work is quite simple and can be done independently, without resorting to the services of professionals.
Even taking into account the fact that polymer pipes are being used more and more often, metal products are still enjoying considerable success. Typically, the metal used is copper, brass and steel. Copper is superior in terms of resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. Actually, the connection of copper pipes will be discussed in this article.
Even though copper pipes are expensive, taking into account all the characteristics of the material, their use is quite justified.
First of all, before connecting copper pipes, you should decide how to connect them, by soldering or another method.
The main advantages and uses of copper pipelines
Copper pipes have an operating temperature from -200 to +250 degrees, as well as low linear expansion, which allows them to be successfully used for the following systems:
- Heating;
- Water supply;
- Air conditioning;
- Gas transportation;
- Obtaining alternative energy, for example, solar systems.
When installing copper pipelines for supplying cold and hot water, you do not have to worry about overgrowing or silting of the internal section. They are also not destroyed by chlorine, which is added in high concentrations to tap water. On the contrary, chlorine creates the thinnest protective layer on the inner wall of pipelines, which significantly extends the life of the pipelines. In turn, a small amount of copper is released into drinking water, which has a beneficial effect on human health.
Amateur Radio Technology
| Internal threads are cut using taps. When cutting threads with a diameter of up to 10 mm, a set of three taps is used manually: rough, medium and finishing, which have one, two and three marks on the cylindrical part of the shank, respectively. Two taps can also be used - rough and finishing, respectively, with one and two marks on the tap. The correct choice of hole diameter is of great importance. If the diameter is larger than it should be, the internal threads will not have a full profile and the result will be a weak connection. If the diameter of the hole is smaller, it is difficult for the tap to enter it, which leads to the breaking of the first threads or to jamming and breakage of the tap. The diameter of the hole for a metric thread can be approximately determined by multiplying the thread size by 0.8 (for example, for an M2 thread, the drill should have a diameter of 1.6 mm, for MZ - 2.4-2.5 mm, etc. (see. table). The drill diameter in the table below corresponds to the standard thread pitch. First, the thread is cut with the first tap, then with the second. To break off the chips, the tap is turned half a turn in the opposite direction after each clockwise turn. To cool the tap and reduce the effort when cutting threads, lubricants are used: for aluminum - kerosene, for copper - turpentine, for steel - emulsion or machine oil. Bronze and cast iron are cut without lubrication. When cutting a blind hole, its depth should be 3-4 mm greater than the length of the required thread. In this case, it is necessary to periodically unscrew the tap to remove chips from the hole. External threads on screws, bolts and studs are cut by hand using dies. The diameter of the rods for external metric threads should be selected according to the table. The threaded rod must have a clean surface; You cannot cut threads on rods covered with scale or rust, as in this case the dies will quickly wear out. Before cutting the thread, the rod is clamped in a vice so that its end protrudes above the level of the vice jaws a little more than the length of the part being cut, and a chamfer is removed at the very end of the rod. When starting to thread, make sure that the die cuts into the rod without distortion. When the die is skewed, the thread profile is distorted and the teeth of the die may break. Cool the die in the same way as the tap. Here your opinion matters — give your rating (rated — 4 times) |
|
- Simple New Year's garland
- Simple testers of thyristors and quartz
- Simple analog frequency meter
- Universal transistor voltage indicator
- What you need to know about the operation of a three-phase electric motor in a single-phase network...
- DIY FM transmitter
- Simple 10 W tube amplifier for 6N2P+6P14P
- TPS2530 – controlled switch with current limiter from Texas Instruments
- A simple transformerless low-frequency amplifier
- VEF TA DM
- TAN-76-4
- TAN-70-4
- Scheme TA K-701
- Ohm's law, formula
- Counter - Digital frequency counter on PC
Sewer plastic pipes diameters, prices
Every owner wants everything in his household to work, nothing to break, and to be easy to maintain and install. And sewerage is no exception. It needs to require as little attention as possible - it’s very inconvenient if it gets clogged, but it’s no less unpleasant to clean it
If you want to have a trouble-free drainage system, pay attention to plastic sewer pipes. They are gradually replacing cast iron ones, and all because they cost less, are easier to install, have a wide range - different diameters and lengths, almost no deposits form on their smooth walls, and even have a service life of about 50 years. This whole bouquet of properties determines their popularity
This whole bouquet of properties determines their popularity.
Plastic sewer pipes are made from various polymers and their compositions
Types of plastic sewer pipes
Products made from different types of polymers are sold under the general name “plastic”:
- polyethylene (PE): high pressure (HDPE) - for internal sewerage distribution,
- low pressure (LHP) - can be laid outside, in trenches (have greater strength),
polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP)
And a number of other thermoplastics and their combinations, but they are rare - people prefer to use already known materials.
The material of plastic sewer pipes is selected depending on the application. For example, polypropylene is more suitable for installing sewerage inside a house or apartment. It has a higher operating temperature range - it normally tolerates environments up to 70°C, and for a short time - up to 95°C. If you have various household appliances that discharge waste hot water into the sewer, this will not be superfluous. PVC pipes, which have lower prices, are more appropriate when laying external sewers - here the drains are usually already mixed, so the temperatures are lower and PVC can withstand them without harm (working up to +40°C, short-term increase to 60°C).
An example of an in-house sewerage system made from plastic pipes
Sewer pipes can also be smooth or corrugated. Moreover, not only siphon bends can be corrugated. There are profiled pipes for sewerage with an internal smooth wall and an external ribbed one. They have greater strength - they can better withstand compressive loads (they have increased ring rigidity) and can be buried to great depths. Available in diameters from 110 mm to 1200 mm.
Dimensions and diameters
Sewage plastic pipes, unlike water and gas pipes, are produced in the form of lengths of 50 cm, 100 cm, 200 cm, etc. - up to 600 cm. The maximum length is 12 meters, but some manufacturers can make longer sections upon request. When laying long routes, this is convenient - there are fewer connections, fewer possible places for problems to arise (leaks or blockages).
Another important characteristics of plastic pipes are diameter and wall thickness. In the markings they usually go side by side: the numbers are 160 * 4.2. What it means: the outer diameter of the pipe is 160 mm, the wall thickness is 4.2 mm. It’s worth remembering here that manufacturers indicate the outer diameter of plastic pipes, and many calculations and planning require knowing the inner one. It is easy to calculate: subtract twice the wall thickness from the outer wall: 160 mm - 4.2 mm * 2 = 151.6 mm. Calculations and tables usually show a rounded result—in this case, 150 mm.
Parameters of sewer plastic pipes
In general, the industry produces plastic pipes for sewerage with a diameter of 25 mm. The maximum cross-section depends on the type of pipe (smooth or corrugated) and the material from which it is made. For example, smooth PVC sewer pipes can have a diameter of up to 630 mm, and profiled two-layer pipes can have a diameter of up to 1200 mm. But these dimensions are of no use to homeowners or apartment dwellers. In private housing construction, diameters up to 100-110 mm are mainly used, rarely up to 160 mm. Sometimes, for a large cottage with a large number of plumbing fixtures, a pipe of 200-250 mm in diameter may be needed.
The organization of sewerage at the dacha is described here.
How to choose a diameter for connecting plumbing fixtures
According to the rules, a calculation must be made; it is fully spelled out in SNiP 2.04.01085. This is a complex matter, a lot of data is required, so few people really think as it should. Over the years, accumulated practice has made it possible to derive the average diameters of polyethylene sewer pipes for each of the plumbing fixtures. You can safely use these developments - all calculations usually come down to these dimensions.
Advantages of copper pipes and their disadvantages
At present, it is impossible to say for sure why copper pipes for water supply are used extremely rarely in the CIS. One of the likely reasons is the high cost of such products, although if we take into account the costs of repairs in one particular apartment, the difference is not so great.
Another factor is the huge variety of alternative options on the building materials market, which can be a worthy replacement for steel pipes, which are prone to oxidation and difficult to install. However, most likely the reason is still in long-rooted habits passed on from generation to generation.
Let's look at the main advantages of copper pipes:
- they are practically not subject to oxidation and corrosion;
- the threshold of permissible temperatures for pipe operation ranges from -110 ℃ to 250 ℃;
- the properties of the material make it possible to avoid the formation of any deposits on the internal walls of the pipes;
- The service life of copper pipes for water supply is quite long, and the costs of their installation and maintenance are extremely low.
However, it is impossible not to note some of the shortcomings of copper pipes for water supply:
- With some metals, in particular aluminum and steel, copper forms a galvanic couple. Therefore, if even a very weak current flows at the point of contact between the thread and the copper pipe, serious complications can occur.
- Copper is an excellent conductor, which in some situations can cause electric shock. This can happen even through no fault of yours - for example, if, as a result of a breakdown of your neighbors’ washing machine, a breakdown occurs between the phase and the ground to the water supply.
- Installing copper plumbing pipes and fittings is quite labor intensive. Although the principle of installing compression fittings will not differ from, say, working with metal-plastic pipes, however, much more effort will have to be applied (read: “How to install copper pipes correctly - expert advice”). If the joining of pipes is carried out using the soldering method, then consumables (solder, flux), a special tool (blowtorch), and also skills will be required.
The nuances of working with copper pipes
To install internal pipelines in the house, you can choose a pipe made of plastic, metal-plastic or stainless steel. But only a copper analog can last for more than half a century without problems or major repairs.
Properly installed copper pipeline systems in practice work properly throughout the entire service life of a cottage or apartment building.
According to accident statistics, the fittings and solder joints used during installation are more reliable than the copper pipes themselves - if a breakthrough in the system occurs, it is only on the wall of the pipe product
Copper pipes are not afraid of long-term heat loads, chlorine and ultraviolet radiation. When they freeze, they do not crack, and when the temperature of the internal environment (water, wastewater, gas) changes, they do not change their geometry.
Unlike plastic analogues, copper pipelines do not sag. This plastic is subject to expansion at high temperatures; this does not happen with copper by definition.
Copper pipe products have two disadvantages - high price and softness of the metal. However, the high cost of the material pays off with a long service life.
And to prevent the walls of the pipes from being damaged from the inside by erosion, filters must be installed in the system. If there are no contaminants in the water in the form of solid particles, then there will be no problems with the destruction of pipelines.
Requirements for pipe processing and welding
When working with copper pipes, the following rules must be observed:
- When installing hot water supply or hot water supply by soldering, you should avoid using lead solder - lead is too toxic.
- The water flow speed should be no higher than 2 m/s, otherwise the smallest particles of sand or other solid substance will gradually begin to destroy the walls of the pipe.
- When using fluxes, after completion of installation, the pipeline system must be flushed - flux is an aggressive substance and will contribute to corrosion of copper pipe walls.
- When soldering, do not allow the joint to overheat - this can lead not only to the formation of a leaky joint, but also to a loss of strength of the copper product.
- Transitions of pipes from copper to other metals (steel and aluminum) are recommended to be made using brass or bronze adapter fittings - otherwise steel and aluminum pipes will quickly begin to corrode.
- Burrs (metal deposits) and burrs at cutting sites must be removed - their presence leads to the formation of turbulent turbulence in the water flow, which contributes to erosion and reduces the service life of the copper pipeline.
- When preparing copper pipes for connection, it is strictly forbidden to use abrasives - particles remaining inside after installation will lead to damage to the metal and the formation of a fistula.
If in the plumbing or heating system in a house, in addition to copper, there are also pipes or elements made of other metals, then the water flow should go from them to copper, and not vice versa. The flow of water from copper to steel, zinc or aluminum will lead to rapid electrochemical corrosion of the latter sections of the pipeline.
Copper pipes can be cut and bent without problems; even a novice master can handle connecting them into a single pipeline system. You just need to select the appropriate tools and follow the instructions
Due to the ductility and strength of the metal, copper pipes can be cut and bent without problems. Rotation of the pipeline can be done either by using a pipe bender or using fittings. And for the installation of branches and connections with various devices, there are many parts made of heat-resistant plastics, brass, stainless steel and bronze.
On the interaction of copper with other metals
In most private homes, domestic water pipes are assembled from steel and aluminum pipes. Heating systems also contain radiators made of steel or aluminum. Incorrect insertion into such copper pipe routing is fraught with considerable problems.
According to building codes, in order to exclude corrosion processes in a pipeline from pipes of different metals, the water flow must be directed towards the copper
The most optimal installation option is to use pipes and devices exclusively made of copper and its alloys. Nowadays you can easily find bimetallic aluminum-copper radiators, as well as corresponding fittings and shut-off valves. It is worth combining different metals only in extreme cases.
If combination is inevitable, then copper should be the final element in the chain of pipeline elements. It is impossible to rid it of its ability to conduct electric current.
And in the presence of even a weak current, this metal creates galvanic pairs with steel, aluminum and zinc, which inevitably leads to their premature corrosion. When installing a water supply system, bronze adapters must be inserted between them.
Another potential problem is oxygen in the water. The higher its content, the faster the pipes corrode. This applies to pipelines both made of the same metal and those made of different ones.
Often, cottage owners make a serious mistake by frequently changing the coolant in the heating system. This only leads to the addition of completely unnecessary portions of oxygen. It is best not to completely change the water, but to add it when the need arises.
Elements for copper pipe connections
Copper fittings, which are used to connect copper pipes, are presented on the modern market in a wide variety of sizes and designs. The most well-known types of such connecting elements are:
- threaded fittings for copper pipes;
- self-locking connecting elements;
- compression or crimp fittings;
- so-called press fittings;
- capillary type connecting fittings.
Of all the listed types of connecting elements, in our time, press fittings for copper pipes are the least used, which is explained by the following reasons: their installation requires the use of complex and expensive equipment: special presses. The design of press fittings was originally developed in order to connect plastic and metal-plastic pipes with their help, so their use for the installation of copper products is not always advisable.
Press fitting pliers
In order for a pipeline in the construction of which copper parts are used to serve as long as possible and be highly reliable, it is advisable to use elements made of homogeneous materials during its installation. Connecting copper pipes with fittings that are made from other raw materials should only be done in rare exceptions.
If it is not possible to avoid the use of fittings made of dissimilar materials when installing pipelines, then this process must be carried out by adhering to the following simple rules:
- copper pipes in communications, for the creation of which elements from different materials are used, are always installed after products made of ferrous metals: in the direction of fluid movement;
- copper parts of pipelines cannot be connected to fittings made of galvanized steel; failure to comply with this requirement will lead to electrochemical reactions occurring in such systems, which will significantly accelerate the corrosion process of steel parts;
- copper elements of pipe structures can be connected to parts made of acid-resistant steel, but if there is such a possibility, it is better to replace such parts with fittings made of polyvinyl chloride.
High pressure crimp connections
Advances in bonded crimp technology and the development of O-ring materials are allowing bonded crimp connections to be used for high pressure applications. However, high pressure systems require a slightly different jaw configuration.
The result of manufacturing a connecting unit using the 360º double crimping technique
Bonded crimp connections for low pressure piping, process piping and non-medical compressed gas lines use a single standard hexagonal pressing shape.
Higher pressure bonding crimp connections require the use of specially designed press fittings and clamping jaws to provide a 360° double crimp on the fitting.
If the connection is leaking
Unfortunately, errors are periodically found in articles; they are corrected, articles are supplemented, developed, and new ones are prepared.
How to distribute responsibilities while hiking... Tips for organizing a tourist trip, selecting participants, optimal…
Making soup - puree from gravilate. Ingredients, composition. Dietary... How to prepare soup - puree from gravilata. Personal experience. Advice. Detailed instructions...
Cladding of walls and ceiling with clapboard…. How to cover with clapboard to make it look beautiful and professional. Practical experience...
Auchan is a chain of shops and hypermarkets. Customer review, prei... Let's talk about Auchan. What do I like to buy in it, what do I prefer to buy...
Copper pipes are connected in three ways: using compression fittings, by capillary soldering and using press fittings. Each of these methods has its pros and cons. It all depends on the exact conditions in which you plan to operate the plumbing system.
Device and purpose
In practice, fittings made of copper, bronze and brass are suitable for installing copper pipelines. Only copper couplings and tees are suitable for soldering.
Fittings are produced according to shape:
- Direct.
- Angular.
- Tees and crosses.
- Transitional (for connecting workpieces of different diameters).
- Combined.
The industry produces many combined types of connectors that allow you to easily install pipelines of complex configurations.
By design there are:
- Threaded.
- Compression (collet)
- Press.
- For welding.
Copper pipe rolling process
When installing heating and plumbing systems, the parts of which are made of copper, such technological operations as flaring or beading of copper pipes are often performed. With this operation, which can be performed using various tools, the geometric parameters of the ends of the connected pipes are changed without changing the performance characteristics of the product.
Flared copper pipes
The simplest tool with which this operation can be performed is a rod with a conical tip, which is inserted into the end of a copper pipe and rotated in it until it acquires the desired geometric shape. Although this device is quite simple to use, it does not allow for high-quality flaring, ensuring uniform pressure on the walls.
A more effective device for performing flaring is a device that consists of a clamp that exerts pressure on the working cone, as well as a stand with several holes or one universal one into which copper pipes of various diameters are inserted. For the installation of heating or plumbing systems consisting of copper elements, home craftsmen most often use just such devices.
Specialists who professionally install communication systems consisting of copper elements use devices for flaring, the design of which includes an eccentric and a safety ratchet. The ends of the pipes, on which the nuts are previously put on, are evenly rolled out on such a device along their inner surface, for which an eccentric is used.
Copper pipe flaring kit
A ratchet, which limits the force exerted on the end of the pipe, is necessary in such a device so that the walls are not pressed through when there is excessive pressure on them. The big advantage of using such a professional device is that when used, small grooves and dents do not form on the inner surface. It is these grooves and dents that occur when using more primitive devices that are the most likely sources of leaks, which ultimately significantly reduce the life of the pipeline.
Connecting elements of compression and self-locking type
Fittings for connecting copper pipes, classified as compression or self-locking, are also called collet or crimp fittings. Such connecting elements are a good alternative to fittings that are connected to copper parts by soldering. A collet-type fitting is an element whose design consists of o-rings and gaskets, as well as a crimp ring, which, when tightened, helps to achieve the tightness of the connection being created. The material for the manufacture of compression or collet fittings can be not only copper, but also brass or metal-plastic.
Brass Collet Male Thread Fitting
Push-in crimp-type connecting elements are the best option for heating and water supply systems, for the installation of which copper pipes of different diameters or tubular products made of various materials are used. Recently, self-locking fittings, which have more preferable performance characteristics, have become increasingly popular.
Self-locking fittings can completely replace soldering in terms of the speed of connection and its reliability. The design of such fittings includes a whole set of rings, one of which is equipped with special teeth. The principle of operation of such connecting elements is based on the fact that when a ring with teeth is acted upon using a special mounting wrench, it is fixed in the adjacent element, thereby creating a reliable and durable connection between sections of copper pipes. Unlike soldering, dismantling a connection made with such a fitting is as easy as receiving it; the same mounting wrench is used for this.
It should be borne in mind that compression fittings are always made of copper, but they can be used to connect elements made of ferrous metal and polymer materials.
Installation work for installing a fitting for crimp type B
This type has approximately the same installation scheme. The cut area is cleaned of contamination, attention is paid to the thread, and the thread is allowed to be lubricated with machine oil.
This makes for an easier connection to the pipe. It is necessary to control the position of the sealing cone; it should be pressed against the workpiece from the inside, while the edge of the pipe should be flared.
It is important to choose the right wrench; it must match the size of the nut so as not to damage it. For example, a 750 mm wrench fits a 54 mm nut.
Installation work for installing a fitting for crimp type A
Installation has step-by-step instructions:
1.select the required element size. The work is easy to do, since all parts are manufactured according to European standards.
2. The workpiece is cut to the required length, and the burrs are removed. All cut ends are checked using a gauge. If necessary, remove dirt from the pipe, grind the damaged edges, and then put on a crimp ring.
Important! The area to be connected is wetted with water to prevent the seal from moving and breaking.
3. The pipe is inserted into the fitting as far as possible, the clamping nut is first tightened by hand, and screwed in until it stops using a wrench.
Important! You should not overdo it, the level of tightness will not change, but the likelihood of tearing off the ring and ruining the reliability of the joint increases.
Upon completion of the work, the rolled pipe may be deformed, this is evidence that the joining was successful and the structure is airtight.