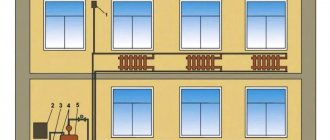
What are the benefits of installing mud traps for a heating system?
There are no questions about the need to install dirt filters for water in centralized heating systems.
Where the coolant is periodically drained and the system is refilled, it is impossible to argue with the necessity of this element in the system - there will always be dirt and foreign impurities. A disdainful attitude towards mud collectors begins with the independent design of small autonomous systems. For example, heating systems of a private house. It just seems that in a small closed circuit there is nowhere for foreign impurities in the coolant to come from.
Dirt filter with tap.
Whatever type of coolant is used, and no matter what initial cleaning it undergoes, it will still be based on water. Water, which begins to interact with the metal components of the system, and there is metal in any system. As a result of this interaction, rust particles are formed that circulate in the system. In certain areas of the system (irregularities inside the pipes, welding sagging, sharp turns, narrowed passages, etc.) these particles accumulate, impeding the movement of the coolant.
Mechanical coarse water filter.
Since the intensity of circulation of the coolant decreases, in order to achieve the desired temperature parameters in the room, its temperature must be increased. This increases the load on the boiler and all other elements of the system, which does not add reliability, economy and efficiency to them. Proper installation of mud filters in the system eliminates most of these problems or, at a minimum, delays the time of their occurrence.
Functions of mud collectors
When operating heating, water supply and other similar lines, one of the most pressing problems is the clogging of various areas with insoluble impurities of organic and inorganic origin - in other words, dirt. In open systems in which water is drawn from an external source, sand, clay particles, silt, etc. most often act as pollutants. In closed pollution systems, rust flakes, scale, separated scale fragments, and mineral deposits also occur. They all have one common property: most of these particles are heavier than the water or coolant circulating in the system.
A section of a pipe with pronounced silting. Accumulating in those places where the fluid flow slows down or changes direction, dirt over time significantly reduces the performance of the system - permeability, heat transfer, etc.; in some cases, serious blockages can lead to system failure. There is a need for mechanical or chemical cleaning (rinsing) of clogged elements. In order to reduce the concentration of dirt particles in the liquid, reduce the rate of blockage formation, and thereby reduce the frequency of complex and expensive cleaning or repair procedures, various filters are used. In particular - the so-called coarse filters, which include mud filters. Sometimes they are called mud collectors, as well as clarifiers: with an effectively functioning mud collector, at the outlet of it, the pumped liquid is even visually much cleaner and lighter than at the inlet.
Peculiarities
A mud filter is a device for filtering and purifying water inside heating systems. Such a filter prevents the formation of deposits on the internal walls; it filters out foreign objects in the pipeline. This device has a number of modifications, each of which has its own characteristic differences. They comply with GOST standards; they are selected taking into account the cross-sectional diameter of the pipes. In general, the purpose of the devices is to clean the coolant before it enters the system itself.
The devices operate on the principle of a colander: water flows through a pipe into the mud pan, at the bottom of which suspensions settle. The purified liquid continues to move through the outlet pipe and enters the heating system. By changing the direction of water flow in the water supply, the mud filter divides the water into clean liquid and dirt, which settles in a special filter container.
This device is functional, you can use it to do the following:
- increase the efficiency of the heating system;
- equalize the thermal output of batteries;
- extend the service life of each element of the heating system;
- reduce home heating costs;
- reduce the risk of emergency situations and leaks;
- Eliminate the need for manual flushing of the system.
Such products protect the main components of the system from dirt and clogging of working channels. They remove dirt from contaminating pipe channels, taps, air valves, and expansion tank pipes. This ensures an increase in high-quality heating of the coolant several times. During normal operation, the water condition will be acceptable for circulation in the system without deposition of lime and alkaline salts. The heat supply inside the pipes will be correct, without wasting energy.
The mud trap is a tool for improving the operation of the system, a unit for expanding the pipeline system by changing the direction of the water flow. Typically, pressure gauges are installed near it, indicating the degree of hydraulic resistance. They are installed on both sides of the filter. A distinctive feature of the installation is the fact that the sump must be directed towards the coolant flow. For ease of installation, manufacturers make an arrow on the body indicating the direction of movement.
Over time, large debris and dirt will accumulate in the sump and will need to be removed. To service the mud pan, first shut off the system, then unscrew the nut located at the bottom of the body. After this, take out a special glass with suspensions. The container is emptied, then put in place and the nut is screwed on. The location of the sump determines the frequency of its cleaning. For example, if a buyer buys a product with a vertical glass, it will have to be cleaned more often.
The principle of operation of the mud collector is extremely simple. This process is cyclical and is repeated many times. However, choosing a product is impossible without at least a superficial understanding of the features of its varieties. After all, not every type of device is suitable in a particular case. And it’s not even a matter of price, but of the different cleaning capabilities of individual modifications.
Where to put the circulation pump?
Most often, the circulation pump is installed on the return side, and not on the supply side. It is believed that there is a lower risk of rapid wear and tear of the device, since the coolant has already cooled down. But for modern pumps this is not necessary, since they have so-called water-lubricated bearings. They are already designed specifically for such operating conditions.
This means that it is possible to install a circulation pump on the supply side, especially since here the hydrostatic pressure of the system is lower. The installation location of the device conventionally divides the system into two parts: the discharge area and the suction area. A pump installed on the supply, immediately after the expansion tank, will pump water out of the storage tank and pump it into the system.
The circulation pump in the heating system divides the circuit into two parts: the injection area into which the coolant flows, and the vacuum area from which it is pumped outIf the pump is installed on the return line in front of the expansion tank, then it will pump water into the tank, pumping it out of the system. Understanding this point will help take into account the characteristics of hydraulic pressure at various points in the system. When the pump is running, the dynamic pressure in a system with a constant amount of coolant remains constant.
It is important not only to choose the optimal location for installing pumping equipment, but also to install it correctly. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the nuances of installing a circulation pump
The expansion tank creates so-called static pressure. Relative to this indicator, an increased hydraulic pressure is created in the discharge area of the heating system, and a reduced one is created in the vacuum area.
The vacuum can be so strong that it will reach the level of atmospheric pressure or even be lower, and this creates conditions for air to enter the system from the surrounding space.
In the area of increased pressure, air can, on the contrary, be pushed out of the system, and sometimes boiling of the coolant is observed. All this can lead to incorrect operation of heating equipment. To avoid such problems, ensure excess pressure in the suction area.
To do this, you can use one of the following solutions:
- raise the expansion tank to a height of at least 80 cm from the level of the heating pipes;
- place the drive at the highest point of the system;
- disconnect the storage pipe from the supply and transfer it to the return after the pump;
- install the pump not on the return, but on the supply.
It is not always possible to raise the expansion tank to a sufficient height. It is usually placed in the attic if there is the necessary space
It is important to adhere to the rules for installing the drive to ensure its trouble-free operation.
We provided detailed recommendations for installing and connecting an expansion tank in our other article.
If the attic is not heated, the storage tank will have to be insulated. It is quite difficult to move the tank to the highest point of a forced circulation system if it was previously created as a natural one.
Part of the pipeline will have to be redone so that the slope of the pipes is directed towards the boiler. In natural systems, the slope is usually made towards the boiler.
An expansion tank installed indoors does not need additional protection, but if it is installed in an unheated attic, care should be taken to insulate this device
Changing the position of the tank pipe from supply to return is usually not difficult to perform. And it’s just as easy to implement the last option: install a circulation pump into the system on the supply line behind the expansion tank.
In such a situation, it is recommended to choose the most reliable pump model that can withstand contact with hot coolant for a long time.
Installation and maintenance of main filters
Installing a carbon filter for hot water or any other type of treatment plant is quite simple
It is only important to follow the step-by-step instructions and be consistent
How to install a filter: step-by-step instructions
The installation process of the main filter consists of the following steps:
- First, you need to stop the water supply to the house, and also drain the remaining liquid from the taps in the kitchen or bathroom. This will get rid of any remaining liquid. However, before performing installation work, you need to install a basin under the insertion point for water that may leak.
- You need to put marks on the wall to fix the filtration system. The fastening must be rigid, since any vibrations can damage the system.
- Using the marks, holes are made into which the plastic pieces of dowels will be placed.
- Next, the filter is connected to the pipes using couplings. To ensure the tightness of the joints, FUM tape is used.
- The device is fixed to the wall using self-tapping screws.
- To assess the quality of installation, you need to restore the water supply and open any tap for a few minutes. During this period of time, the cartridge will be cleaned and the system will be cleared of air.
- From the moment the installation work is completed and the filters are started for the first time, the system’s service life begins to count.
How to change cartridges
Metal water filters are equipped with special removable cartridges. During operation, they may fail and need to be replaced. It is not difficult to carry out such a procedure with your own hands. To do this, you should follow these instructions:
- We turn off the tap at the entrance to the house.
- Relieve the pressure in the system.
- To prevent neighbors from flooding, it is better to place a basin under the flask.
- Using the key from the basic package, you need to unscrew the flask.
- Next, remove the filter part, wash the mesh and attach a new cartridge. The flask is also cleaned of impurities.
- After installing the flask in its original place, you need to make sure that there are no leaks.
Proper and timely replacement of working parts will ensure complete cleanliness of the liquid and eliminate the problem of pressure surges when cartridges become clogged.
How to replace the filler
And although the filling filter with filler has a simple structure, replacing this substance can be difficult. To avoid mistakes, you should follow these instructions:
- First you need to disassemble the filtration column and remove the control valve.
- Next, you should unload the used media and clean the equipment and add new filter media.
- At the next stage, the system is assembled and connected to the water supply.
Installation of a sump for a heating system
In order to install a magnetic filter for heating or a filter of any other type, you should familiarize yourself with the following recommendations that can simplify the entire work process:
- Even before installation begins, it is necessary to carefully prepare the system pipes, cleaning them from rust and other harmful particles.
- When deciding which type of sump design to use for a particular heating circuit, you need to be guided solely by its operational characteristics, in particular, the conditions under which the equipment will be used - operating pressure, temperature readings, etc.
- It is better to choose a location for installing the sump tank where access to the device will be as convenient as possible, taking into account that the filter should be mounted in the area in front of the circulation pump.
- One of the prerequisites for installation is that the cross-section of the filter opening must be identical to the cross-section of the pipe. This measure will ensure the strength of the connection and will prevent the mechanism from subsequently moving aside.
Components of a closed heating circuit
The difference from the gravity system is the need to install specific components. Some of them are necessarily used in a closed system, but are sometimes used in natural circulation. The source of thermal energy is boilers. Some of the wall-mounted gas, pellet, and solid fuel models are immediately equipped with the necessary safety group. If it is not available, it must be purchased separately and installed on the hot water pipe.
The sealed tank maintains pressure and compensates for the volume of coolant. Its efficient movement is ensured by a circulation pump, which is recommended to be installed on the return line near the boiler itself. This arrangement is dictated by the fact that the water in this place is quite cool, the device is less susceptible to overheating. The remaining elements are the same as in the gravitational system: pipelines, radiators or registers.
Cleaning the cartridge filter
Such systems, often installed in country houses, are cleaned in a different way. You will need a filter key, a pan or bucket, a replacement cartridge or a container where you can clean the old one.
First, turn off the valve and make sure that there is no water left in the tap. Then place a bucket underneath: excess liquid from the flask will be drained there. Using a special wrench, you need to unscrew the nut and remove the flask. After this, you can either install a new cartridge, or thoroughly rinse and return the old one to its original place. Then the flask is returned to its place, the nut is screwed back in, and the water is turned on.
Not any cartridge can be reused: this option is only for wound ones. You can wash such a product using strong water pressure (it is recommended to use a hose for this).
How does a mechanical cleaning filter work?
Mechanical cleaning filter device
To understand how to install the filter correctly, let’s take a closer look at what parts it consists of. A detailed diagram of the heating system sump device can be seen in the figure. The body is usually made of brass. Large diameter industrial models may use cast iron. The working part is a fine-mesh steel mesh. As a rule, it can be removed for washing or replacement. The frequency of cleaning the heating system's mud traps depends on various parameters: water hardness in your region, pressure in the pipeline, and the total volume of coolant passing through the filter. There is also a dependence on the materials from which the pipes and components are made. Materials with different corrosion resistance will pollute the coolant at different rates. You can set the required frequency experimentally. The figure shows methods for installing a filter in a pipe with explanations for each of the possible options. As we can see, both with vertical and horizontal insertion, the glass for depositing filtered particles should be at the bottom.
Methods for installing a filter in the system
In conclusion, it should be added that it is often advisable to use a combination of filters to increase the service life of the system. For example, a mud trap for heating and a magnetic filter for a boiler. Or a system of mesh cleaners installed in series.
Popular filter models
Now let's look at the most popular cleaning systems, simultaneously examining the principles by which they operate.
Table 1. Popular models
| Filters, photos | Description |
| Mechanical cleaning | Among the mechanical cleaning filters responsible for coarse filtration, the following models can be distinguished: Atoll AFR (a set of 2 filters), Geyser 1P, BVT Protector, New Voda Prio. Prices for these filters vary from 6,000 to 10,000 rubles. The price of products does not indicate the ultimate superiority of more expensive models in quality - the brand also plays a big role. They buy them often and willingly, since plumbing needs protection from large sand particles. |
| Ionic filters | These filters help disinfect water and provide it with good taste and beneficial substances. They are structurers with bioceramics or tourmaline inside. When heated, tourmaline (a special type of quartz sand) emits electrical impulses that create magnetic fields, due to which the ionization process occurs, killing microbes. Among such filters, products from the companies Novaya Voda, Afwafor, Barrier and Geyser are especially popular. The average cost of an ionizer fluctuates around 2,500 rubles. |
| Reverse osmosis | Since we actually have at least 5 degrees of purification, the price of such equipment will be significantly higher than that of other analogues. Such a system actually consists of three parts. The first is rough cleaning (3 lower cartridges), the second is a membrane filter (the most expensive part), the third is post cleaning and mineralization. The first filters last for 5-6 months. The membrane lasts on average for a year, and post-cleaning can be changed every two years. The prices are influenced by the following parameters: number of degrees, cleaning; presence of a structurer; presence of a UV lamp; material of the storage tank body and its capacity; presence of a pump; quality of workmanship of crane parts and other parts. In general, prices have a very wide spread, starting from 3-4 thousand rubles, and tending upward. The main manufacturers of reverse osmosis, whose products are in demand in the Russian Federation, are: Geyser Prestige, Aquaphor, Atoll. Among other foreign devices, we note the products of the Expert company. |
| Aeration system | Here the producers Geyser, Rosvoda, Runxin stand out. They come in four types: electrochemical, pressure, non-pressure and simplified. We will not go into details, but, in general, the essence is that the water is saturated with oxygen, which causes the oxidation of certain substances, for example, iron, hydrogen sulfide or manganese, turning them from solution into large mechanical inclusions that settle in the system. This also disinfects the water. Ozonation systems work on the same principle, only instead of oxygen, pure ozone is supplied, which causes oxidation processes even better. |
So, we have looked at the different types of filters and understood the purpose for which each of them is included in the drinking water purification system. Now let's see how to install such equipment.
What are filters for heating systems - types
The following types of heating filters are distinguished:
- Rough or pre-cleaning. They must be installed at the stage of connecting to the central water supply (if such a possibility exists). The most reliable model is a sedimentation tank with a flask for the accumulation of pollutants.
- Fine cleaning. Detains contaminants up to 100 microns in size.
- Magnetic devices. They attract metallized components - chips, rust, etc.
Let's take a closer look at each type.
Coarse filters are designed to retain large contaminants and can be installed simultaneously in several areas of the system. Presented in the following modifications:
Mud collector: connects to the central heating system, at branch points (can be flanged, welded, threaded), Sump filter: a more modern model, dirt is retained in a special flask made of heat-resistant plastic (due to the transparency of the flask, you can control its filling level). Fine cleaning – installed as an addition to coarse cleaning devices. The main impact in such devices is taken by the square or cylindrical cassettes installed inside
Such devices can be attached to the wall, which is especially important for plastic pipes. Magnetic filters - consist of two magnets with opposite poles. Metal waste entering a magnetic field is attracted and retained by such a device
The design can also be equipped with a dirt filter. Magnetic models can be either removable and quite easily installed on the pipe, or non-removable. Recommended as an additional cleaning device.
Many people ask the question: is it worth spending money on purchasing all types of filters? Perhaps only a coarse cleaning device will be enough? Experts assure that the most effective protection will be provided by all types of structures that will retain as much possible contamination and impurities as possible. The coarse filter can only cope with large particles, and this is not enough for the heating system to fully operate for a long time.
How often does it need to be cleaned?
Due to water purification and retention of various debris, which does not disappear over time, it begins to accumulate. For this reason, over time, the water filter installed on the pipe becomes clogged. This leads to a decrease in water pressure, and over time, its complete absence. When such situations occur, it is necessary to clean the internal structural elements, for which the device should be removed, disassembled and washed.
Worth knowing! When the filter is sealed along with the water meter, you need to call a technician from the management company who will remove the seals. Once cleaning is complete, it is recommended to install a non-return valve, allowing cleaning to be carried out without the need to call a specialist further.
Why is it worth installing a filter on your heating system?
Many users may quite logically be interested in the question of whether it is necessary to install filters for heating systems? It is worth noting that even without organizing cleaning, the equipment can function normally, another question is how long?
First of all, such an installation is necessary to ensure reliable and uninterrupted operation of heating equipment, eliminating emergency situations and failures.
The price of heating filters is not so high; its timely purchase and installation will cost much less than later repair or replacement of heating elements. Not to mention the fact that an accident in the heating system will lead to such unpleasant consequences as cold and discomfort in the house (after all, it is during the cold season that the thermal regime must be maintained).
The advantages of the installation include:
- reliable protection of the system from blockages;
- it is not necessary to change the water (coolant) so often;
- the service life of heating equipment is extended;
- cost savings;
- confidence in the reliability and uninterrupted operation of the system.
Reticulate
The mesh device is a housing with a mesh filter inside. The most popular option looks like a piece of pipe with a diagonal “spout” (bend), at the end of which there is a screw-off plug. Water, passing through the mesh, leaves suspended matter in it and then goes into the purified system.
From time to time you have to unscrew the plug and remove the filter mesh for washing. Then everything is put back in place, and the device itself does not need to be removed from the pipe. This is the so-called flushing threaded mud sump, but there are many more different types.
According to the type of self-cleaning, the mesh filter can be:
- non-flush - rinsing is carried out after removing the device and disassembling it;
- flushing - to clean, just unscrew the plug and remove the mesh;
- self-flushing - dirt is removed from the mesh by a water flow from the opening of a special drain valve.
Depending on the mounting method, coarse filters differ in:
- welded;
- threaded;
- flanged.
Most heating models have an additional mesh to separate air from the water flow. When it accumulates excessively at the top of the mud trap, the float is activated, and the needle valve allows the gas to exit the device.
The effectiveness of the mesh option directly depends on the smoothness of the increase in hydraulic resistance in the system, both before and after it. Constant changes in pressure in the pipes can cause dirt particles to be forced through the mesh.
You can track the degree of contamination of the mesh by constantly removing it and visually checking it. Or install pressure gauges on both sides of the sump tank and use their readings to monitor how dirty the filter is. There are also variations with a glass bulb for visual inspection.
Classification based on filtering principle
Mesh filters . The most common and familiar type of mud filter for water used in everyday life. In the simplest design, dirt is retained by the mesh and deposited in the accumulation zone. Periodically, the bottom of the glass is turned away and the dirt is removed. The design can be supplemented with a drain valve installed instead of the bottom, and then the mud pan turns from a flushing one into a self-flushing one.
Strainer Danfoss FVR, DN50.
Installing an additional mesh that removes air from the coolant, a float and a needle valve adds the function of protecting the mud pan from gas contamination. The efficiency of the mesh sump depends on the pressure in the line before and after it. If there is a significant difference in these values, solid particles can be forced through the mesh.
A magnetic filter removes metal particles from the coolant flow. When such a filter operates, there is no braking effect on the fluid flow, which is important when operating powerful pumps.
There are also inertial-gravity and subscriber mud collectors. The principle of operation of the former is clear from their name and they are used in large enterprises. Subscriber devices clean the coolant at the entrance to the metering units.
Main types of filters and their design
Today, several designs of mud filters for heating systems have been developed. The principle of operation is similar for all - filtration of a coolant liquid, extraction of solid insoluble inclusions and their accumulation in a filter element or settling tank. Depending on the type of system, there are mud filters for industrial systems, and there are those that are used in individual heating installations, for example, in apartments or private houses.
Classification according to installation and cleaning method
Mud traps for heating systems are most often classified according to the method of installation in the system:
- On a threaded connection;
- Installed using flanges;
- Devices that require welding for installation;
New devices for plastic heating pipes are installed by soldering, so they can conditionally be classified as welded, although today they can be called a separate type of classification.
Classification according to the degree of purification divides filters into coarse filters and fine filters. The former are capable of capturing only large particles, but fine filters are capable of sifting out particles of several microns.
Classification by method of service
There is also a classification according to the method of maintenance, in other words, because the contents of the filter elements are cleaned:
- Self-cleaning;
- Flushing;
- Non-flush;
The former are cleaned by washing the mesh when opening the valve on the filter housing. All contents are simply discharged out through the valve. In washable filters, after removing the lid or flask, the filter element is removed and cleaned first with a brush and then washed with a stream of water. Non-flush ones require complete removal from the system and maintenance in workshops or replacement with a new mud collector.
For a specific heating system, it is also important how the coolant is cleaned. The simplest and most common are mesh filters.
In the body of the mud tank, the coolant passes through a stainless steel mesh and insoluble particles are retained on the metal. To clean the filter itself, rinsing is done by opening the valve on the body or removing the mesh from the filter bowl
The simplest and most common are mesh filters. In the body of the mud tank, the coolant passes through a stainless steel mesh and insoluble particles are retained on the metal. To clean the filter itself, washing is done by opening the valve on the body or removing the mesh from the filter bowl.
Strain filters are installed both in small installations and in industrial heating plants. The advantage of this type of device is its reliability and simplicity of design.
In addition to the usual mesh filter, mesh filters with self-cleaning and with the additional function of an air vent have recently begun to be used. In addition to the coarse filter, a separator filter made of a fine mesh network is installed in the housing, which ensures the separation of gas particles and removes them to the air vent. The operating efficiency of this type of device largely depends on the pressure in the line - the higher the pressure, the more effective the process of cleaning and degassing the coolant.
Magnetic filters are similar in design to mesh filters, the only difference being that magnets are installed around the mesh in the housing, which attract metal particles and rust.
Another type of device provides cleaning of the coolant using gravity. The filter housing is a large-diameter container in which pipes for inlet and outlet of coolant are installed at different heights. When entering a large-diameter settling filter, the liquid changes direction of movement, which results in the formation of numerous flows and turbulences. Heavy particles break off and settle to the bottom of the filter. Such installations are most often used in industrial boiler houses and heating plants.
Operating principle and design
Mud collectors may differ to a certain extent in design, but in their work they use three basic principles:
- inertial-gravitational;
- mechanical;
- magnetic.
These principles can be used individually or together.
1. Inertial-gravitational principle. A typical mud trap is a vertical or horizontal metal cylinder with a diameter significantly larger than the diameter of the pipes in the section of the system in which it is installed. The liquid, entering such a cylinder, instantly loses speed, due to which the heavy particles attracted by it are able to sink to the bottom under the influence of gravity. Some mud tanks also use the inertia of these particles: additional partitions are installed in the mud tank cylinder, directing the liquid along the walls of the cylinder; centrifugal force forces particles toward the walls, after which they themselves sink to the bottom.
Scheme of a vertical gravitational mud trap. To simplify the procedure for cleaning the mud tank, the bottom of the cylinder is made removable, or a separate tap is provided for draining the liquid mud suspension.
2. Mechanical principle. However, gravity and inertia are not able to separate lighter, suspended particles from the liquid. For this purpose, there are mesh filters that mechanically retain all particles with sizes exceeding the size of the mesh cells.
The disadvantage of mesh filters is that if the level of contamination of the filtered liquid is high, they themselves become clogged quite quickly. Therefore, it is logical and expedient to use a mesh filter as a “second-stage” filter - that is, install it in such a way that heavy particles are filtered out first, and then suspended ones.
Vertical and horizontal mud traps with a “cup” of a strainer in front of the outlet pipe. To clean the strainer in the mud pan, it is usually possible to remove it for washing, or to wash it locally using reverse liquid pressure. https://escortcity.co.nz.
3. Magnetic principle. If the working fluid is expected to contain particles with magnetic properties - small metal shavings, scale, etc. – you can add a permanent magnet to the design of the mud pan, which will collect metal debris on its surface. Naturally, it must be possible to clean this magnet - for example, according to the principle of a magnetic plug in the oil sump of a car engine. Actually, the engine crankcase can be conditionally considered a special case of a mud trap.
Installation of a sump for a heating system
In order to install a magnetic filter for heating or a filter of any other type, you should familiarize yourself with the following recommendations that can simplify the entire work process:
- Even before installation begins, it is necessary to carefully prepare the system pipes, cleaning them from rust and other harmful particles.
- When deciding which type of sump design to use for a particular heating circuit, you need to be guided solely by its operational characteristics, in particular, the conditions under which the equipment will be used - operating pressure, temperature readings, etc.
- It is better to choose a location for installing the sump tank where access to the device will be as convenient as possible, taking into account that the filter should be mounted in the area in front of the circulation pump.
- One of the prerequisites for installation is that the cross-section of the filter opening must be identical to the cross-section of the pipe. This measure will ensure the strength of the connection and will prevent the mechanism from subsequently moving aside.
Useful tips
To increase the service life of filters, you should follow these tips:
- evidence that the filter is clogged is a decrease in water pressure in all faucets;
- the more intense the water flow, the more often the structure should be cleaned; it is recommended to do this every 3 months;
- before unscrewing the outlet of the mud trap, you should substitute a basin or bucket, and also open the tap on one of the mixers;
- When cleaning cartridge filters, it is recommended not to wait until the walls of the flask are covered with a brown coating;
- If a stole gasket is used, the plug should be made hot before unscrewing, using a gas torch or a regular lighter.
Having figured out how to remove debris from the filter, it is worth remembering the regularity with which it is important to do this. In the process of clearing the blockage, it is important to take into account the design features of the installed model, as well as maintain the tightness of the threaded connections during reassembly
Prevention
A conventional coarse filter, as a rule, is not installed in an easily accessible place. Therefore, preventative cleaning is difficult. Moreover, its design is designed in such a way as not to allow dirt to pass through, even when it is completely clogged. And the degree of clogging is often determined by the decrease in the intensity of water supply from the mixer.
Attention. If the mud trap is easily accessible and there is no seal on it, then preventive cleaning should be done once every 6 months.
However, the manufacturer recommends cleaning models that provide pressure cleaning (water pressure when opening the valve) or cassette samples at least once every six months . But such specimens often have a transparent body, which helps to visually determine the degree of “clogging” of the filter.
Additional structural elements
The design of the mud pan may also contain other elements that simplify maintenance or increase its functionality:
- in addition to the mentioned drain valve at the bottom, there is an air valve at the top of the mud pan to de-air the system when filling it with liquid;
- at relatively low pressure levels in the system, a transparent window can be provided on the side surface of the cylinder to assess the degree of contamination;
- Pressure gauges can be installed on the inlet and outlet pipes, by the difference in readings of which one can estimate the hydraulic resistance of the mud tank and, as a consequence, the same degree of contamination.
Mud traps can be produced with a flange connection and a “weld” connection. The first option is considered preferable, as it allows the mud collector to be easily replaced if necessary. However, such a replacement is rather an exceptional event: due to the simplicity of the design, mud collectors are extremely reliable, their service life is up to 30 years or more.
Violation of the tightness of system elements
Violation of the tightness of system elements (pipes, connections, twists, welding, etc.) leads to a coolant leak, which, if not eliminated in a timely manner, can cause an emergency and lead to large material costs for its elimination.
In pipelines, leakage occurs due to pipe corrosion, which causes metal destruction, the formation of through holes (fistulas) and pipe ruptures. Corrosion of pipes increases during long-term operation, especially if the system is not flushed. Corrosion also increases when the system is filled with tap water (containing a lot of oxygen), and the system is frequently emptied, which allows air oxygen to enter it.
To prevent accidents in winter, it is necessary to inform the relevant services about any damage detected during the preparation for the heating season. When repairing, require careful pressure testing of the heating system in order to timely identify sections of pipelines weakened by corrosion.
Leaks can occur where pipes are bent, through cracks caused by improper bending. Leak points are eliminated by welding defective areas and replacing faulty areas.
To quickly (but temporarily) eliminate leaks on straight sections of a pipeline with a diameter of no more than 150 mm, install sealing clamps on the damaged section of the pipeline. Use this method when it is impossible to disconnect the damaged section and empty the pipeline. As soon as it becomes possible to disconnect the damaged section of the pipeline, remove the clamp and carry out repairs.
In a threaded connection, coolant leakage through leaks, as a rule, occurs due to poor-quality seals made during installation in the joints between the couplings and locknuts, cracks in the connections, torn and deeply cut threads. After determining the causes of the leak, either reassemble the threaded connection and re-seal it, or replace it.
Eliminate small leaks (fistulas) by welding linings to the pipeline. Fill small fistulas and cracks with welding. In flange connections, leakage occurs as a result of weak tightening of the bolts, aging of the gasket, its being made of low-quality material, or misalignment in the flanges. If, when tightening the bolts, the leak in the flange connection is not eliminated, then replace the gasket.
In a welded joint, leakage can be caused by poor welding quality, which is revealed by temperature expansion. Eliminate this malfunction by additional welding of the defective joint.
Varieties
To reduce the risk of boiler breakdown, increase the accuracy of measuring instruments and ensure a long service life of the equipment, it is important to understand the main types of devices and choose the right one
Polyphosphate
Polyphosphate units are considered a budget option for pre-purification and softening of water entering the boiler.
The operating principle of such a device is to pass liquid through a flask filled with special crystals. They ensure the formation of a protective film on the inner walls of the boiler and also slow down the formation of scale.
Photo 1. Polyphosphate filter for a gas boiler, filled with special crystals. They slow down scale formation.
The devices have a simple design:
- drain;
- flask;
- filler;
- lid.
The liquid enters the flask with filler through the lid, where it is passed through polyphosphate crystals. Next, it goes through the drain into the gas boiler tank.
Any device of this type requires periodic replacement of the filler - sodium salt crystals. As a matter of fact, this is the only difficulty in servicing them. The average lifespan of such a treatment plant is up to one and a half years.
Electromagnetic or magnetic for softening hard water
Electromagnetic devices are expensive, but the price is completely justified: the installation lasts a long time and allows you to obtain perfectly clean water at the output.
The principle of operation is that when the liquid passes through the flask, the salts in it disintegrate. Thus, scale will not settle on the walls of the boiler. Instead, the filter itself will be clogged with tiny salt particles, which is periodically washed.
Photo 2. Three magnetic filters for a heating system boiler; the scale in them breaks down into tiny particles.
Another characteristic is that under the influence of electromagnetic radiation, not only does the scale disintegrate into small particles, but also a thin film is formed that covers the boiler heat exchanger. Thanks to this, it remains protected and does not corrode for a long time.
We should not forget that electromagnetic and magnetic devices are different installations. At the heart of both is a magnet.
Attention! Electromagnetic devices are more powerful because they require connection to an electrical network. Ideal for gas boilers, as they perfectly soften water of any temperature
Magnetic installations are less strong and are not recommended for use with gas boilers if the water hardness is too high.
Magnetic devices consist of a metal case, inside of which there are a large number of strong magnets. Electromagnetic devices are additionally equipped with an electric drive, the operation of which allows the effect of magnets to be greatly enhanced.
Cartridge for cleaning
Cartridge devices have low throughput. The following device types exist:
- Mechanical - traps small debris. Such devices need to be cleaned frequently, and they do not soften the water.
- Coal - purify water due to activated carbon, which acts as a filler. If you do not change it in time, the water will become even more contaminated as a result of passing through the filter.
Photo 3. Four low-flow cartridge filters are needed to purify the water.
- Ion exchange cartridge devices are considered the best, as they change the hardness of water by entering into a chemical reaction with calcium and magnesium ions.
- Osmotic - allow molecules of water and gas to pass through them. This allows you to clean the liquid from metal impurities and harmful microorganisms, but it will not be possible to soften the water by installing such a filter.
- Membrane - purify water from debris and impurities, but do not soften it.
Important! Cartridge filters are not suitable for gas boilers (with the exception of ion exchange devices). They are more focused on purifying the water you are supposed to drink.
Prices for water softeners for a gas boiler
| Manufacturer and model | Type of softener | Cost, rub. |
| Aquaphor Styron | polyphosphate | 290 |
| Unicorn FMP 2P2V 5″ | polyphosphate | 580 |
| New Water B120 | polyphosphate | 1 200 |
| MWS MVS Dy 10 (1/2) | magnetic | 1 490 |
| New Water A032 | magnetic | 1 900 |
| FIBOS mini | magnetic | 4 900 |
Gas boilersInstructionsBoilersEquipment for boiler rooms