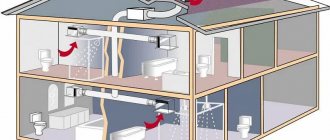
A heating expansion tank (HE) is an element of the heating system that allows you to compensate for changes in the state of the coolant and prevent hydrodynamic damage to the integrity of pipelines, devices and shut-off elements. The efficiency, safety and reliability of the entire heating complex depends on the correct selection, installation and adjustment of the expansion tank. Tanks for liquid expansion of various designs are installed in all types of individual heating systems and almost completely eliminate its loss due to evaporation. Let's look at the types of such tanks.
Types, design and principle of operation of expansion tanks
Expansion tank for open type heating
In open heating systems, the role of RB can be performed by any container located at the highest point in relation to all other elements. In low-rise housing construction, the standard location of the tank is the attic or attic space.
In order to minimize liquid loss during evaporation into the environment, a lid is mounted on the tank. In case the temperature drops to negative values and prevents the liquid from freezing, the tank is insulated on all sides. To prevent the heat transfer fluid in the tank from boiling, a connection is made between the container and a pipe leading into the return circuit. To prevent overflow of liquid and its discharge into the sewer, most designs provide a hose or pipe.
A significant disadvantage of open circuits is the need to periodically top up the liquid that has evaporated into the atmosphere. The problem is solved by installing an automated control mechanism with automatic replenishment, however, the water supply to the tank complicates the design and leads to its increase in cost.
In an open circuit, communication with the atmosphere is carried out through the RB and the air formed as a result of boiling of the liquid is removed. In this case, no increased pressure is created in the heating lines, and water circulation occurs due to convection. In this case, a process of natural convection takes place, in which the cold layers of the coolant sink down and the hot ones rise up.
A simple example of natural convection is heating water in a kettle placed on a lit kitchen stove. When installing an open expansion tank, no shut-off valves are installed between it and the system. Structurally, an open tank can be either cylindrical or rectangular in shape. In typical designs, there is an inspection window on the tank lid to monitor the liquid level. The disadvantages of open-type systems include:
- increased heat loss through the expansion tank;
- increased level of corrosion of system elements due to direct contact of liquid with air;
- mandatory location of the RB above all elements of the contour.
Expansion tank for closed heating
A sealed heating circuit with forced circulation of water or antifreeze does not have the disadvantages inherent in open circuits. There is no air penetration into sealed systems, and compensation for changes in the state of the thermal energy carrier occurs through the use of sealed membrane reservoirs.
Technically, the membrane expansion tank is made in the form of a vessel, the inner part of which is divided by an elastic partition into two sections: liquid and gas. The gas chamber is equipped with a spool to regulate pressure. To prevent contamination, the spool is usually equipped with a protective plastic cap or cover.
A pipe for supplying and discharging liquid is mounted in the liquid part. Most often, membrane tanks are cylindrical in shape, but for small thermal systems round tablet-shaped containers are used. In appearance, RBs are similar to pumped storage tanks (HA) for water supply systems.
As a rule, HAs are painted blue, and expansion tanks are painted red. HA and membrane RB are not interchangeable and their purposes are different. In HA, the membrane has a “pear” shape and is made of a material that allows safe contact with drinking water. Contact with metal parts is excluded. In Belarus, the partition is made of technical rubber and coated with an anti-corrosion compound, which increases its service life.
Installation
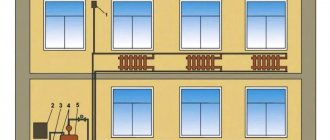
Installation diagram of a tank in a private house system
If you are confident in the calculations and your own abilities, the tank and all materials have been purchased, then you can install the container yourself.
Tools you will need:
- Step and adjustable wrenches;
- Soldering device for plastic pipes;
- Wrench for installing plastic pipes;
- In some cases, a welding machine and an angle grinder are needed.
Before installation, you need to turn off the power to the boiler, turn off the valves and drain the coolant if it is already in the pipes.
The installation is carried out taking into account certain rules.
- The tank must be mounted and installed so that it can be easily approached for adjustment and maintenance.
- The room temperature should not be below 0.
- A pre-shut-off valve must be installed on the supply pipe, which will allow the expander to be removed for maintenance and repair.
After installing the tank, you need to start the entire heating system. If boiling is detected in it, then the reason lies in the incorrectly selected pipe diameter. It's not about the tank. The installation of the expansion tank is described in the following video:
Features of operation of a tank with a membrane
As the volume of liquid in a closed circuit increases, the pressure values increase, and the elastic partition of the expansion tank is affected. It is deformed, affecting the gas environment in the air section, freeing up space in the liquid part of the vessel, into which an excess amount of liquid gradually flows. It should be noted that when operating the RB, it is necessary to monitor the pressure in the gas socket and, if necessary, pump it up. For control, the nipple is usually equipped with a stationary pressure gauge.
Each liquid heating system is quite inertial, and heating and cooling of the liquid does not occur simultaneously. The increase and decrease in the volume of the liquid chamber occurs gradually, which avoids hydraulic shocks that are destructive to all parts of the circuit.
Useful tips when choosing
When purchasing and installing an expander, there are several nuances to consider.
- When choosing a location for installing the tank, it is necessary to take into account that it cannot be installed immediately behind the circulation pump.
- Commercially available tanks come in two colors: red and blue. In the first, the membrane is stronger, but made of technical rubber. Blue tanks are used for water supply; they contain food-grade rubber, but it is less strong and durable.
- When installing, you need to use a special sealant.
- If you decide to go with an open system, then the tank must be placed at the highest point, and when installing the pipeline, the recommended slope must be observed.
- The size of the tank should not be less than the calculated value; a slightly larger volume is allowed. When using forced circulation, the capacity cannot be less than 15 liters.
- Antifreeze can act as a coolant. For a glycol mixture, it is better to choose an expansion tank whose volume is twice as large as the calculated one.
The main advice is to contact professionals, because installing a tank only seems simple. In addition, you cannot do without a special tool.
How to calculate an expansion tank for heating
When calculating the volume of the expansion tank, it is assumed that when the coolant is heated, for every 10 ºC its volume increases by 0.3%. With a household approach, the volume of the expansion tank should be equal to 8-10% of the total volume of coolant poured into the system. To calculate it, it is enough to use a simple method:
- Fill the heating circuit with water;
- Drain the liquid into a vessel whose volume is determined;
- Multiply the resulting volume of liquid in liters by 0.08.
With a heating circuit capacity of 150 liters, we obtain the minimum volume of the expansion tank:
150x0.08 = 12 liters.
In a professional environment, more complex calculation systems are used, taking into account thermal power, equipment efficiency, and other constant and variable quantities. If non-integer values are obtained, a larger tank with the indicator set by the manufacturer is selected.
It follows that when selecting an expansion tank for a closed heating system, the main parameters are its volume and maintainability. Mainly repairable tanks with replaceable membranes are selected. Lastly, tanks are selected based on design features and price.
Calculation methods
Each installation is selected in accordance with the size of the expected load, which will require preliminary calculations.
Knowing how to calculate the volume, the owner will be able to choose the right tank. To choose the right expander, you will need to know:
- heating boiler volume;
- additional devices;
- all pipes included in this heating system.
Next, let’s designate the required indicators with any letters, for example, A is the desired value, B is the efficiency of the membrane equipment, C is the constant expansion rate of the coolant water, and AO is the total volume of the heating system. Next, we calculate using the following formula: A = (AO * C) / B.
Sizing
The final value is rarely absolutely accurate, so approximate calculations are made, and the resulting number will be a guideline for choosing a unit, which should be taken with a margin to the obtained number, leaving at least 3% for the increase in volume during heating.
If a membrane type has been selected, the operating potential of the membrane may be indicated by the manufacturer, but you can make your own calculation. To do this, take the most permitted indicator of pressure inside the system (AB), data on the pressure of the initial filling of the expander (BC) and calculate the desired value (T). Use the following formula: T = (AB – BC) / (AB + 1).
If you do not make calculations and take the equipment “at random,” you may encounter some problems during operation of the device. The main purpose of the expander is to pump out excess liquid with a strong increase in pressure (moisture expands, requiring the excess to be removed from the pipeline). After everything has stabilized, the liquid is compressed back, it must be returned to the pipes, otherwise there will not be enough of it to maintain the temperature. Therefore, identifying differences in the internal pressure of the heating system indicates an imminent breakdown.
Tank too small
If the volume of the installed expander is insufficient, the pressure will increase too much and the automatic valve will operate. It will remove excess moisture, stabilizing the operation of the system. But then everything will return to normal, and the water will no longer be enough to continue proper heating. Additional refueling will be required. A lack of heating fluid will lead to the boiler shutting down, since at low levels the device cannot continue to function. Because of this, pipes may freeze in winter. Breakdowns will occur again and again until the optimal size expander is installed.
Excessively large tank
Installing a tank that is too large is also dangerous. When taking part of the moisture from the pipes, the expander must maintain the optimal permissible operating pressure, which is simply impossible if the dimensions are too large. The unit will constantly show the maximum permissible load without crossing the very line when the valve should operate. This means that the device operates at its maximum potential level, which will quickly lead to breakdown.
General connection rules
A water tank is installed on a prepared site: a concrete base tied to the foundation, or a reinforced metal frame made of profiled pipe. The design must withstand one and a half weight of the tank and the water in it when completely filled.
The inlet pipe can be of any suitable diameter, water is supplied under pressure. The outlet pipe and pipe to the water supply system are chosen with a diameter one and a half to two times larger than the cross-section of the main line. The optimal size is 32 mm.
Even the best quality insulation only slows down the decrease in temperature in the tank. To prevent water from freezing when installing the tank in an unheated attic or on the roof, you should use any suitable heating system for the pipes and the tank itself.
For autonomous water supply
As with centralized water supply, there are several connection options.
Water tower
The storage tank is installed at a level of 15-20 meters above ground level on a reinforced tower or attic. Water from a well pump or pumping station is supplied directly to the tank, and from it is distributed to the bathroom and kitchen in the house. The pressure in the system is provided by the height difference between the water level in the tank and the mixer tap in the house.
The disadvantage is the constant flow of water through the tank, which will cause sediment to accumulate over time, even if you first install a filter system.
The advantage is the simplicity of the design and the minimum of expensive elements, with the exception of the tower design itself and the mandatory insulation of the tank to protect it from freezing, even when it is placed in the attic.
Bottom connection of storage tank
The tank is installed level with the pumping station or on the first floor of the house. It is filled during normal operation of the pump using water from the well. The limiter is a float switch.
This option saves you in case of excessive water consumption and a decrease in the water level in a well or well. However, it is useless when the electricity is turned off, since a pump is required to supply the end user with water from the reserve.
Scheme of the lower connection of the storage tank