A single-circuit or double-circuit gas boiler is equipment that makes our life in a house or apartment more comfortable. Manufacturers now produce a huge range of gas appliances, differing in power, functionality, and installation method. However, even the most expensive and reliable models can fail. Agree, it’s not very pleasant to be left on a winter evening without heat and hot water.
Having analyzed the possible causes of breakdowns of gas equipment, we came to the conclusion that most often malfunctions occur due to the fact that the pressure in the expansion tank of a gas boiler or water heater is incorrectly adjusted. In this article we will figure out why an expansion tank is needed, how to pump air into it yourself and set the optimal pressure.
Why is an expansion tank needed?
During the heating process, water tends to expand - as the temperature rises, the volume of the liquid increases. Pressure begins to increase in the heating system circuit, which can have a destructive effect on gas equipment and the integrity of the pipes.
The expansion tank (expanzomat) serves as an additional reservoir into which excess water formed as a result of heating is pressed out. When the liquid cools and the pressure stabilizes, it returns through the pipes back into the system.
The expansion tank acts as a protective buffer; it dampens water hammer, which constantly forms in the heating system due to frequent turning on and off of the pump, and also eliminates the possibility of air locks.
To reduce the likelihood of air locks and prevent damage to the gas boiler due to water hammer, the expansion tank should be mounted in front of the heat generator, on the return line
There are two different types of damper tanks: open and closed types. They differ not only in design, but also in the method and location of installation. Let's look at the features of each of these types in more detail.
Open expansion tank
An open type tank is mounted at the top point of the heating system. The containers are made of steel. Most often they have a rectangular or cylindrical shape.
Typically, such expansion tanks are installed in the attic or attic. Installation under the roof is possible. It is imperative to pay attention to the thermal insulation of the structure
The structure of the open-type tank has several outlets: for water inlet, cooled liquid outlet, control pipe inlet, and also an outlet pipe for coolant discharge into the sewer. We wrote more about the structure and types of an open tank in our other article.
Open tank functions:
- controls the coolant level in the heating circuit;
- if the temperature in the system has decreased, it compensates for the volume of coolant;
- when the pressure in the system changes, the tank acts as a buffer zone;
- removes excess coolant from the system into the sewer system;
- removes air from the circuit.
Despite the functionality of open expansion tanks, they are practically not used anymore. Since they have many disadvantages, for example, the large size of the container, the tendency to corrosion. They are installed in heating systems that operate only with natural water circulation.
Closed expansion chamber
In closed-circuit heating systems, a membrane-type expansion tank is usually installed; it is optimally suited for any type of gas boiler and has many advantages.
An expansomat is a hermetic container, which is divided in the middle by an elastic membrane. The first half will contain excess water, and the second half will contain regular air or nitrogen.
Closed expansion tanks for heating are usually painted red. There is a membrane inside the tank; it is made of rubber. A necessary element to maintain pressure in the expansion tank
Compensation tanks with a membrane can be produced in the form of a hemisphere or in the form of a cylinder. Which is quite suitable for use in a heating system with a gas boiler. We recommend that you familiarize yourself in more detail with the installation features of closed tanks.
Advantages of membrane types of tanks:
- ease of self-installation;
- corrosion resistance;
- work without regular addition of coolant;
- lack of contact of water with air;
- performance under high load conditions;
- tightness.
Gas attachments are usually equipped with an expansion tank. But the additional tank is not always configured correctly from the factory and can immediately start heating.
Preventing the problem from recurring
It is easier to prevent problems in the heating circuit than to suddenly look for ways to eliminate them. So before the start of the heating season, communications are checked by testing, especially focusing on dangerous areas.
These include:
- level spans;
- threaded connections and welds;
- zone of joining sections at radiators;
- places of implantation of heating equipment;
- near fittings;
- hard-to-reach areas.
First, everything is checked by eye, then with the circuit running.
Air pressure in the expansion tank
The air or nitrogen pressure in the expansion tank will not be the same for different gas boilers; it all depends on the type of equipment and design features. The standards are indicated by the manufacturer in the product passport.
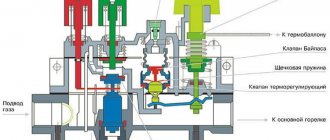
Typically, the pressure in a new damper tank is 1.5 atm. But this setting may not be suitable for a specific heating system. Factory settings are easy to reset. For these purposes, there is a special fitting in the expansion tank housing (for some manufacturers this is a spool valve for pumping), through which the air pressure is adjusted.
The nipple is located on the side of the air chamber of the cylinder. With its help you can release excess pressure or, conversely, pump up the tank
For the normal functioning of a gas boiler, it is necessary that the pressure in the membrane tank be 0.2 atm less than in the system itself. Otherwise, the heated water that has increased in volume will not be able to enter the container.
In small houses and apartments for closed heating systems, the pressure in the expansion tank is usually acceptable in the range of 0.8-1.0 bar (atm). But not less than 0.7 bar, since many gas boilers have protection and the device simply will not turn on.
The tank pressure level should be checked annually. If pressure surges are noticed in the heating system, it means that air has come out of the damper tank and needs to be pumped up.
Advantages and disadvantages
Closed expansion tanks have a number of advantages over open ones:
- Closed analogues do not necessarily need to be installed in the attic; they can be installed near the boiler itself. And open ones must be installed at the highest point of the system.
- In closed tanks, water does not have access to contact with air, which means that oxygen will not dissolve in the water and interfere with the movement of the coolant.
- Most people have converted the attics of their homes into living spaces, so using closed tanks saves space as they can be installed anywhere.
The disadvantages of closed tanks are as follows:
- High price.
- It is necessary to pump air into the device from time to time.
How to set the optimal pressure?
The heating system has pressure gauges that control the pressure in the circuit. On the expansion tank itself there is no fitting for installing a measuring device. But there is a nipple or spool for releasing and pumping air or gas. The nipple is the same as on car wheels. Therefore, you can check the pressure level and adjust it using a conventional car pump with a pressure gauge.
Even a simple automobile hand pump with a pressure gauge or an automatic compressor will be suitable for pumping air into the expansion tank.
Before releasing excess pressure or pumping air into the expansion tank of a domestic gas boiler, it is necessary to prepare the system. The car pressure gauge shows the value in MPa; the data obtained must be converted into atmospheres or bars: 1 Bar (1 atm) = 0.1 MPa.
Pressure measurement algorithm:
- Turn off the gas boiler. Wait until water stops circulating through the system.
- In the area with the hydraulic tank, close all shut-off valves and drain the coolant through the drain fitting. For boilers with a built-in tank, the return flow is shut off, as well as the water supply.
- Connect the pump to the tank nipple.
- Pump up the air to 1.5 atm. Wait a little for the remaining water to pour out, then let the air in again.
- Close the valves of the shut-off valves and use a compressor to pump up the pressure to the parameters specified in the passport or to the level - pressure in the system minus 0.2 atm. If the tank is pumped, excess air is released.
- Remove the pump from the nipple, screw on the cap and close the drain fitting. Fill the system with water.
You can check the correct air pressure adjustment when the boiler reaches operating parameters.
If the tank is inflated correctly, then the needle on the pressure gauge of the device during measurement will show a smooth increase in pressure without any jumps or jerks
If the air pressure in the expansion tank is incorrectly adjusted, the entire heating system may malfunction. If the expansion tank is over-inflated, the compensating properties will not work. Because the air will push excess heated water out of the tank, increasing the pressure in the pipes of the heating system.
And with underestimated pressure readings of the compensating tank, water will simply push through the membrane and fill the entire tank. As a result, when the coolant temperature rises, the safety valve will operate.
Sometimes in double-circuit gas boilers, fuses work even if the pressure of the built-in expansion tank is correctly adjusted. This indicates that the tank volume is too small for such a heating system. In this situation, it is recommended to install an additional hydraulic tank.
Types of heating systems
There are two schemes for building heating networks - open and closed. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
With a more modern closed circuit, an expansion tank of a closed-type heating system with a built-in internal membrane is used.
Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Purpose of an additional tank of a double-circuit boiler
As a rule, built-in compensation tanks in gas boilers have a volume of about 6-8 liters. They are designed to compensate for the expansion of 120 liters of coolant circulating in the heating system. Under normal operating conditions, such an expansion tank is enough for a small apartment or house.
When installing radiators of non-standard shape and size, the heating system must be equipped with an additional expansion tank. Because these batteries hold more water
If the heating area is large, heated floors are installed or there are many radiators in the rooms, the volume of the standard built-in tank will be small, since more water is used.
When heated, excess coolant completely fills the tank. And since there is no free space left in the tank, the water pressure increases in the heating system itself and an emergency release occurs by the safety valve. After this, it is unlikely that the gas boiler will be able to start working automatically.
To avoid such negative consequences, an additional expansion tank with a membrane is installed in the heating system in a design for a double-circuit gas boiler. When the standard tank is completely filled, the water goes into the reserve hydraulic tank. After cooling, the liquid returns to the radiators.
Working with a storage boiler
A storage boiler is a container inside which a coil with hot coolant passes. The difference from a standard heat exchanger is in the volume and method of heating - here the liquid is static, it receives thermal energy in a constant mode.
As water is drawn, the water is replenished and heated again. At the same time, the temperature of the hot water supply is much more even, and the amount of hot water with stable parameters is much greater than that of designs with plate heat exchangers.
Most often, external drives are used, but there are dual-circuit units with built-in capacities . They are efficient, have maximum capabilities and service life.
Experts and ordinary users speak of such designs as the most preferable options.
Calculation of expansion tank volume
It is not difficult to ensure stable operation of the heating system; the main thing is to correctly select the volume of the compensation tank. The volume of the expansion tank should be calculated taking into account the most intensive operating mode of the gas boiler. When heating is first started, the air temperature is not yet very low, so the equipment will operate at an average load. With the arrival of frost, the water warms up more and its quantity increases, requiring more additional space.
It is recommended to select a tank with a capacity of at least 10-12% of the total amount of liquid in the heating system. Otherwise, the tank may not be able to cope with the load.
You can independently calculate the exact capacity of the expansion tank. To do this, first determine the amount of coolant in the entire heating system.
Methods for calculating the volume of water in the heating system:
- Completely drain the coolant from the pipes into buckets or other containers so that the displacement can be calculated.
- Pour water into the pipes through the water meter.
- The volumes are summed up: the capacity of the boiler, the amount of liquid in the radiators and pipes.
- Calculation based on boiler power - the power of the installed boiler is multiplied by 15. That is, for a 25 kW boiler you will need 375 liters of water (25 * 15).
After the amount of coolant has been calculated (example: 25 kW * 15 = 375 liters of water), the volume of the expansion tank is calculated.
There are many methods, but not all of them are accurate and the amount of water that fits into the heating system can be much greater. Therefore, the volume of the expansion tank is always selected with a small margin
The calculation methods are quite complex. For one-story houses, use the following formula:
Expansion tank volume = (V*E)/D,
Where
- D – tank efficiency indicator;
- E – liquid expansion coefficient (for water – 0.0359);
- V is the amount of water in the system.
The tank efficiency indicator is obtained using the formula:
D = (Pmax—Ps)/(Pmax +1),
Where
- Ps =0.5 bar is an indicator of the charging pressure of the expansion tank;
- Pmax – maximum pressure of the heating system, on average 2.5 bar.
- D = (2,5-0,5)/(2,5 +1)=0,57.
For a system with a boiler power of 25 kW, an expansion tank with a volume of: (375*0.0359)/0.57=23.61 l will be required.
And although a double-circuit gas boiler already has a built-in 6-8 liter tank, looking at the calculation results, we understand that stable operation of the heating system will not be possible without installing an additional expansion tank.
What are the advantages of a closed heating system
Despite the fact that many modern devices and systems for space heating have appeared recently, the principle of heat transfer through a liquid with high heat capacity circulating through pipes undoubtedly remains the most common. Water is most often used as a carrier of thermal energy, although in some circumstances it is necessary to use other liquids with a low freezing point (antifreeze).
Water heating is the leader in prevalence
The coolant receives heat from the boiler (furnace with a water circuit) and transfers heat to heating devices (radiators, convectors, “warm floor” circuits) installed in the premises in the required quantity.
How to decide on the type and number of heating radiators?
Even the most powerful boiler will not be able to create a comfortable atmosphere in the premises if the parameters of the heat exchange points do not correspond to the conditions of a particular room. How to correctly calculate the required number of heating radiators is in a special publication on our portal.
But any liquid has general physical properties. Firstly, when heated, it increases significantly in volume. And secondly, unlike gases, this is an incompressible substance; its thermal expansion must be compensated in some way by providing free volume for this. And at the same time, it is necessary to ensure that as it cools and decreases in volume, air does not enter the pipe contours from the outside, which will create a “plug” that prevents the normal circulation of the coolant.
These are the functions that the expansion tank performs.
Not yet in private construction, there was no particular alternative - an open expansion tank was installed at the highest point of the system, which completely coped with the tasks.
Schematic diagram of an open type system
1 – heating boiler;
2 – supply riser;
3 – open expansion tank;
4 – heating radiator;
5 – optional – circulation pump. In this case, a pumping unit with a bypass loop and a valve system is shown. If desired or if the need arises, you can switch forced circulation to natural circulation, and vice versa.
Prices for circulation pumps
A closed system is completely isolated from the atmosphere. A certain pressure is maintained in it, and the thermal expansion of the liquid is compensated by installing a sealed tank of a special design.
Differences between a closed heating system
The tank in the diagram is shown pos. 6, embedded in the return pipe (item 7).
It would seem - why “fence the garden”? A regular open expansion tank, if it fully copes with its functions, seems to be a simpler and less expensive solution. It probably doesn’t cost much, and besides, with certain skills, it’s easy to make it yourself - weld it from steel sheets, use an unnecessary metal container, for example, an old can, etc. Moreover, you can find examples of the use of old plastic canisters.
Open expansion tank
Does it make sense to spend money on purchasing a sealed expansion tank? It turns out that there is, since a closed heating system has many advantages:
- Complete tightness absolutely eliminates the process of evaporation of the coolant. This opens up the possibility of using, in addition to water, special antifreezes. The measure is more than necessary if the country house is not used constantly in the winter, but only occasionally, from time to time.
- In an open heating system, the expansion tank, as already mentioned, must be mounted at the highest point. Very often, an unheated attic becomes such a place. And this entails additional efforts to thermally insulate the container so that even in the most severe frosts the coolant in it does not freeze.
The expansion tank can be placed in an inconspicuous corner
And in a closed system, the expansion tank can be installed in almost any area. The most appropriate installation location is the return pipe directly in front of the boiler entrance - here the tank parts will be less exposed to temperature effects from the heated coolant. But this is by no means a dogma, and it can be mounted in such a way that it does not create interference or disharmonize its appearance with the interior of the room, if, say, the system uses a wall-mounted boiler installed in the hallway or in the kitchen.
- In an open expansion tank, the coolant is always in contact with the atmosphere. This leads to constant saturation of the liquid with dissolved air, which causes increased corrosion in the circuit pipes and radiators, and increased gas formation during the heating process. Aluminum radiators are especially intolerant of this.
- A closed heating system with forced circulation is less inert - it warms up much faster when starting up, and is much more sensitive to adjustments. Completely unjustified losses in the area of the open expansion tank are eliminated.
- The temperature difference in the supply and return pipes in the connection currents with the boiler is less than in an open system. This is important for the safety and longevity of heating equipment.
- A closed circuit with forced circulation to create circuits will require pipes of a smaller diameter - there is a benefit both in the cost of materials and in simplifying installation work.
- An open type expansion tank requires control to prevent overflow when filling, and to prevent the liquid level in it from falling below a critical level during operation. Of course, all this can be solved by installing additional devices, for example, float valves, overflow pipes, etc., but these are unnecessary complications. In a closed heating system, such problems do not arise.
- And finally, such a system is the most universal, as it is suitable for any type of battery and allows you to connect underfloor heating circuits, convectors, and heat curtains. In addition, if desired, you can organize hot heat supply by installing an indirect heating boiler into the system.
Of the serious shortcomings, only one can be mentioned. This is a requirement of the “safety group”, which includes control and measuring instruments (pressure gauge, thermometer), a safety valve and an automatic air vent. However, this is most likely not a disadvantage, but a technological cost that ensures the safe operation of the heating system.
In a word, the advantages of a closed system clearly outweigh, and spending on a special sealed expansion tank looks completely justified.
Features of adjusting the hydraulic accumulator
Expansion tanks for water supply are sold with standard manufacturer settings - often the pressure in the air compartment is already set at 1.5 bar. The permissible pressure is always indicated on the label and the manufacturer does not recommend deviating from the specified parameters, especially in the direction of increasing it.
Before proceeding with the adjustment, the system is disconnected from the power supply and the shut-off valves are closed. The membrane tank is completely emptied by draining the water - an accurate pressure indicator can only be measured when the water compartment is empty.
Next, pressure readings are taken using an accurate pressure gauge. To do this, remove the decorative cap from the spool and bring the device. If the pressure differs from the required one, it is brought into compliance by pumping or bleeding excess air.
Considering that the manufacturer is against deviations from the recommended pressure values, it is necessary to select suitable equipment at the design stage, the parameters of which will not conflict with each other
When adjusting the pressure in the gas compartment of the tank, the manufacturer fills it with an inert gas, for example, dry nitrogen. This prevents corrosion of the inner surface. Therefore, users are also recommended to use technical nitrogen to increase pressure.
Setting the tank pressure in the water supply system
The pressure in a closed tank is always set slightly lower (by 10%) than the pressure level when starting the pump. By adjusting the pressure in the device, you can adjust the water pressure. The lower the gas pressure in the hydraulic tank (but not less than 1 bar), the more water it will hold.
In this case, the pressure will become uneven - strong when the tank is full and increasingly weak when it is empty. To ensure a strong and even flow of water, set the pressure in the chamber with air or gas to within 1.5 bar.
The water pressure in the water supply is set using a relay. When setting the pressure in the expansion chamber, these values must be taken into accountAdjusting the hydraulic tank in the water heater trim
The expansion tank, which is used for hot water supply, should initially not contain water. The pressure in the device is set at a value that is 0.2 greater than the upper pump shutdown threshold.
For example, if the relay is configured to turn off the equipment at a pressure of 4 bar, then the pressure in the gas compartment of the expansion tank should be set to 4.2 bar.
Installed in the water heater piping, the tank does not serve to maintain pressure. It is designed to compensate for expansion when water is heated. If you set the pressure in it to a lower value, then there will always be water in the tank.
Installation of an open type hydraulic tank
An open-type device is used less and less often, as it requires constant user intervention in its operation. An open expansion tank is an unsealed container that serves to generate pressure in the water supply system, accumulate water, and also serves as an expansion chamber.
The tank is connected to: a drain tap, pipes for the recirculation and supply pipes, a control and overflow pipe
The tank is installed above the highest plumbing point, for example, in the attic, water enters the system by gravity. Every meter the device rises increases the pressure in the water supply by 0.1 atmospheres.
To automate the process of providing water, the tank is equipped with a float switch and an automatic relay is installed that will turn the pump on and off.
The container is mounted in a frost-free room, covered with a lid to prevent dust and debris, and the walls are wrapped in mineral wool or other insulation.
This method of organizing water supply requires regular monitoring by the user, otherwise the water may freeze at subzero temperatures (if the room is not heated). The liquid will evaporate, so you will have to constantly add it.
In addition, such a container is bulky and not aesthetically pleasing; it requires an attic space in the house. But the main drawback of the device is that the tank is not designed to work under conditions of high water pressure in the system.