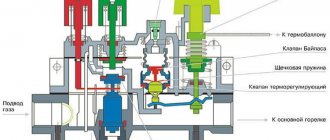
Hot water in the tap and a stable +23 °C in the house, when there is severe frost outside - isn’t it true that these benefits of civilization have already become familiar? Now answer a simple question: was the gas boiler heat exchanger flushed after the previous heating season? If your answer is “no,” you risk being left without heat in the winter.
To prevent this from happening, read our article on fighting scale and preventing the accumulation of mineral deposits. We detail proven methods for combating calcium deposits, which reduce the efficiency of the unit and increase fuel consumption. Our tips will help increase heat transfer and extend the life of the boiler.
How is scale formed and why is it dangerous?
No liquid can compare with ordinary water in terms of specific heat capacity. Depending on temperature and pressure, this indicator varies in the range from 4174 to 4220 Joules/(kg deg). Water is non-toxic, readily available and cheap, making it an almost ideal coolant.
And yet, H2O has a significant drawback - in its natural state it contains salts of the alkaline earth metals Ca and Mg. When heated, they form insoluble carbonate, or, in other words, lime deposits – scale – on the internal surfaces of heat exchange equipment.
Hard water is typical for a large part of Russia and especially for the middle zone, where the degree of mineralization reaches its maximum
The negative consequences of scale formation are as follows:
- efficiency decreases;
- water pressure decreases;
- boiler wear accelerates;
- expenses increase.
Domestic heating boilers and water heaters are mainly equipped with surface heat exchangers, in which heat is transferred through the surfaces of metal walls. But scale has a high thermal resistance, that is, low thermal conductivity.
For this reason, the heat transfer coefficient in contaminated heat exchangers decreases, which leads to a decrease in the temperature of the coolant in the heating circuit and insufficient heating of the water at the outlet of the water heating circuit.
If your boiler does not heat water well, check the condition of the heat exchanger; perhaps it is all about scale, which has caused a decrease in efficiency
Solid deposits as thin as 0.2 mm increase fuel consumption by 3%. If the scale thickness is 1 mm, the excess gas consumption will reach 7%.
When heat transfer decreases, more gas must be used to maintain a given water temperature, which indicates a decrease in efficiency. At the same time, with an increase in fuel consumption, the volume of flue gases increases, and the emission of harmful substances increases, polluting the air around the household and the atmosphere in general.
Deposits completely or partially block the flow area of the pipe, which leads to an increase in hydraulic resistance in the system, disruption of coolant circulation, and a decrease in the supply of hot water at water intake points.
When using water of normal hardness, a layer of scale 2-3 mm thick is formed over the course of a year. With higher mineralization, the rate of carbonate sedimentation increases
Violation of heat transfer leads to overheating of pipes, which causes the formation of microcracks - future sources of corrosion. Due to operation at extreme conditions, the unit fails prematurely.
To prevent equipment damage, scale must be removed periodically. Scheduled cleaning of heat exchangers of gas wall-mounted boilers and floor-standing units is carried out within the time limits established by the manufacturer. A simple procedure helps maintain equipment energy efficiency at its original level, extends the turnaround time, and reduces the overall cost of operation.
Contact a professional or do it yourself
Professional cleaning of heating boilers is an expensive proposition. Depending on the condition of the equipment and the specifics of its operation, amounts can range from several tens to hundreds of dollars. In addition, the masters rarely arrive within the next few hours; sometimes you have to wait for them for several days. It is not comfortable.
The cost of professional cleaning using a special station for washing heat exchangers pays off: the parts are washed from the inside to a shine, and the equipment works much better. But if you want, you can always save money and do the same thing yourself. The result will be no worse, and you will only have to invest your own time and effort.
Professional device for washing heat exchangers
Soot on external surfaces
When gas is incompletely burned, soot, an amorphous allotrope of carbon, deposits on the outer surfaces of the heat exchanger. The heat exchangers of boilers with an open combustion chamber and natural draft suffer more from soot.
One of the reasons for its increased formation is the dustiness of the air in the room from which the combustion air comes. A lot of dust is generated during construction work. If the construction site is located near the entrance of a coaxial chimney, the heat exchanger of the boiler with a closed chamber may also become dirty.
A coaxial chimney consists of an inner and outer pipe. One of them serves to remove combustion products, the other serves to supply air into the closed combustion chamber
Insufficient diameter, incorrect configuration, and blockages of the chimney lead to poor draft. If the draft is poor, the removal of combustion products becomes difficult, and they settle in the form of soot on the lower outer part of the heat exchanger.
Like scale, soot has low thermal conductivity and reduces the efficiency of heat exchange equipment, leads to accelerated wear, and shortens the time between repairs. The efficiency of a heat exchanger contaminated with soot and scale can decrease by 25% or more.
How often should the heat exchanger be flushed?
The cleaning frequency is specified by the equipment manufacturer in the operating instructions. For example, heat exchangers in Neva boilers must be descaled every 12 months.
The concentration of alkaline earth salts in water can vary. If the concentration is high, the water is called hard. When using it, scale forms faster, therefore, unscheduled cleaning may be required. Also, the rate of deposit formation depends on the thermal conditions and intensity of the boiler operation.
The presence of scale in the heat exchanger pipes and soot on its fins is indicated by a decrease in the heating performance of the equipment. To determine whether the actual heating output corresponds to that stated in the documentation, measure the temperature and composition of the flue gases using a gas analyzer.
In the absence of a device, the presence of scale can be judged by indirect signs: a decrease in the temperature and pressure of water leaving the boiler. If there is normal water pressure in the water heater pipeline, and a thin stream flows from the tap, check for deposits on the internal surfaces of the heat exchanger tubes.
Insufficient water heating at standard gas flow and normal pressure also indicates contamination of the heat exchanger.
Note that malfunctions in the operation of complex equipment can be caused by various reasons and the presence of scale is only one of the options.
Causes of failure
A faulty gas boiler can cause a lot of trouble for its owner. Moreover, it is sometimes impossible to figure out the causes of the problem on your own. The list of possible faults is very wide.
When conducting diagnostics, make sure there is gas and electricity, and check water consumption. Does the unit continue to operate intermittently? Carefully inspect the internal and external structure to eliminate possible causes of technical problems.
The most common errors in the operation of gas boilers are considered to be program failures. In such cases, experts advise analyzing the control panel for possible damage. You can also carry out independent adjustment of the device and configure the boiler according to the operating rules.
If, after searching for visible causes of the malfunction, the boiler continues to heat poorly, and you have not found the reason for the poor operation of the device, we can safely say that the unit is covered with foam from chemical compounds and this interferes with its full functioning.
See also: Basic requirements for installing a gas boiler (more details here)
Methods for removing contaminants
To remove scale and soot, mechanical, hydraulic, chemical and other methods or combinations thereof are used.
Mechanical cleaning of heat exchange equipment is carried out using a cleaning rod, wire brush, or scraper. Both hand tools and electric or pneumatic drives are used.
The use of a hydraulic method is only possible if you have a high-pressure apparatus that will supply a powerful flow of liquid that can knock down deposits and bring them out.
The chemical method involves the use of special agents that loosen and dissolve contaminants.
When washing heat exchangers chemically, you can use pumping units to supply the reagent to the water circuit; this is more effective than simple soaking
Magnetic, electromagnetic, and ultrasonic methods are relatively new and involve the use of filter-converters and other technical means.
To clean the heat exchangers of household water heaters and heating boilers, a combination of mechanical and chemical methods is most often used. After soaking (etching) in detergent, the remaining scale is cleaned mechanically. The modern techniques discussed above are also gaining popularity.
Chemicals for cleaning and prevention
Descaling agents contain organic or inorganic acids. In the production of household products, adipic and orthophosphoric acids are most often used. At home, prepare aqueous solutions of citric or acetic acid.
Acids are reagents - they are capable of reacting with alkaline earth salts and forming other water-soluble salts, which are then removed from the heat exchange equipment.
Alkalies are also used, for example, soda ash or caustic soda, which loosen carbonate deposits and soot, facilitating subsequent mechanical and chemical cleaning. Alkaline solutions are also used to neutralize traces of acid remaining in the heat exchanger after descaling.
Most reagents are supplied to customers in the form of highly concentrated aqueous solutions and require additional dilution with water in certain proportions specified in the instructions for use.
It is necessary to follow the manufacturer's instructions for preparing the working solution and not exceed the concentration of the product. Otherwise, contact of heat exchange equipment materials with an aggressive substance will lead to accelerated corrosion.
When choosing products, take into account the material of the heat exchanger. This is usually copper, stainless steel or cast iron. For example, Aminat D is intended for heat exchangers made of stainless and carbon steels. Another reagent from the same series, Aminat D(K), is used to clean copper surfaces.
Many domestically produced boilers have copper heat exchangers installed. When choosing an anti-scale agent, make sure that it is approved for use on non-ferrous metals
Universal products include citric acid, vinegar, Medesk-Plus , Trilon B. They are used for washing heat exchangers made of non-ferrous metals and stainless steel.
Trilon B is the disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. It appears as a white crystalline powder. When Trilon B interacts with alkaline earth salts (scale), calcium and magnesium ions are replaced by sodium ions. As a result, sodium salts are formed, which are highly soluble in water.
Products are produced that have a complex composite composition. They simultaneously contain components that clean scale and prevent its formation.
The KKF composite differs from other chemical agents in its principle of action. It is not a solvent like acids, but in its presence self-cleaning of carbonate deposits (scale) occurs.
Under normal conditions, calcium carbonate crystals form as mineral deposits. This is scale. In the presence of CCF, instead of mineral plaque, another modification of calcium carbonate is formed - aragonite.
Acicular crystals of aragonite destroy calcium deposits as they grow. In contrast, aragonite has weak adhesion to the surface of the heat exchanger and is therefore easily removed by washing with ordinary water.
The active ingredients of CCP already at the initial stage prevent the formation of calcite crystals. As a result, scale formation is significantly slowed down or completely suppressed. This process is called inhibition (translated from Latin: “delay”).
Aragonite is a polymorph of calcium carbonate. Its crystals have a needle-like, pointed shape and easily destroy scale, and are washed away with ordinary water.
KKF inhibits not only scale, but also corrosion due to the formation of a protective film on the metal surface. When purchasing anti-scale products, do not forget to check whether they have Rospotrebnadzor certificates.
Design features of heat exchangers
To properly flush the heat exchanger, you need to know its design. You will find all the information about your boiler in the instruction manual.
Just in case, let us remind you that to organize autonomous heating and hot water supply in apartments and private houses, gas boilers and hot water heaters with the following types of heat exchangers are mainly used:
- shell-and-tube;
- coaxial;
- lamellar.
In the widely used shell-and-tube heat exchangers, water circulates through a pipe that coils around the side walls of the shell in the form of a coil. This type of unit is soldered or welded, that is, non-separable.
The shell-and-tube heat exchanger is one of the most efficient and simplest in design; it is easy to descale it with your own hands
Plate-type heat exchangers are less common. Their main structural part is a metal package in which several plates are assembled.
For example, heat exchangers of Italian boilers Westen Zilmet and Baxi include from 10 to 16 plates. They give up their heat to the water moving between them through channels. Such a device must be disassembled before cleaning.
Diagram of a plate heat exchanger, which shows: pipes for supplying coolant and heated medium (1, 2, 11, 12); fixed and movable plates (3, 8); channels through which the coolant moves (4, 14); small and large gaskets (5, 13); heat exchange plate (6), upper and lower guides (7, 15); rear support and pin (9, 10)
The main element of a coaxial (bithermic) heat exchanger is two coaxial pipes. In its simplest form, it looks like a spiral with tightly fitting turns.
Double-circuit boilers are characterized by the presence of 2-3 heat exchangers. For example, the NEVALUX-8023 boiler is equipped with three heat exchangers, one of which is coaxial, but not of the spiral type, but with links connected in series.
How to descale a plate heat exchanger
Turn off the boiler, turn off the gas and water supplies, drain the water from the heat exchanger and wait until it cools down. Disconnect the pipelines, unscrew the tie rods, move the pressure plate under which the plates are located.
Carefully separate them from each other. Remove each plate separately to avoid injury from sharp edges; wear thick protective gloves. When working with acid, change them to rubber ones.
Prepare a container in which you will soak the plates, taking into account that they should be completely immersed in liquid.
Use the cleaner according to the included instructions. Table vinegar is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 3. Powdered citric acid is diluted in a ratio of 1 to 10. The water for the solution is preheated to 40°C. The plates are immersed in the solution for 1 hour, after which the remaining deposits are removed with a brush under running water.
After dismantling and cleaning, place the plates in a horizontal position so that they lie on a table or other work surface.
To clean the heat exchanger from scale, it is not necessary to buy a booster, it is enough to have a pump, and everything else can be easily done with your own hands
When disassembling the heat exchanger, at the same time inspect the gaskets and sealing elements and, if damaged, replace them with new ones. It is recommended to change all gaskets at once, even if only one of them is worn out. Reassemble all elements in the reverse order of dismantling. Reinstall the heat exchanger.
Neutralization
When you are finally done flushing your boiler or heat exchanger, you will need to neutralize the flushing solution. To do this, stock up on regular soda.
And then there are two options.
Or you pour all the flushing solution into a separate container, call the Ministry of Emergency Situations, and they take the solution to a solid waste landfill (just kidding). Or you start adding a little soda to the intermediate tank. The pump is still running. The soda will react with the acid, fizz, and neutralize the latter. At the same time, you measure the pH, and as soon as it reaches 6-7 units (neutral), this solution can be poured into the sewer. It is advisable, in this case, to add cold water to the intermediate tank and drain the solution with a temperature of less than 50°C. These are the regulatory requirements of one of the RD (guidance document) dedicated to chemical washing. By the way, you need to find this document...
Flushing the shell and tube heat exchanger
Turn off the boiler, turn off the taps on the inlet pipes to save water in the heating system. Drain the heat exchanger. Disconnect the wires from the thermostat and disconnect the hot water pipes. Unscrew the nuts and screws securing the heat exchanger and remove it.
With regular boiler maintenance and proper operation, soot is formed in moderate quantities and can be removed with a regular toothbrush
To flush the shell-and-tube heat exchanger from a thick layer of carbonate deposits, it must be removed from the housing. The dismantling process does not require special skills
Visually inspect surfaces. If there is soot on the fins or other areas, soak the heat exchanger in a detergent containing lye. It can also be a solution of ordinary laundry soap.
Unless otherwise stated in the instructions, soaking should last about 15 minutes. Then use a brush to remove the soot. Rinse the heat exchanger under running water with good pressure.
To remove scale, install the heat exchanger in a basin or other container. Pour a solution of citric acid (concentration 10%) into the pipe. After 12-15 hours, rinse the pipes with clean water. Also clean or replace the hot water circuit filters.
Reinstall the heat exchanger. After cleaning, it is also advisable to replace all gaskets. If the gaskets are rubber, use silicone to lubricate them.
Next, the heat exchanger must be checked for leaks. A saturated soap solution is applied to the detachable connections of the gas circuit. If there are leaks, bubbles will form in the soaped areas.
Having completed flushing the floor-standing boiler, check its tightness, electrical connections and performance in different modes, restore the settings and put it into operation
When checking the water circuit in a double-circuit gas boiler, turn on the heating and hot water supply systems separately and inspect each detachable connection. If a leak is detected, tighten the nut or install a new seal.
Definition
A heat exchanger is a mechanism that directs heat from one coolant (water) to a second (air).
It contains special components and cavities.
If it is exposed to hard water for a long time, then scale, rust and other contaminants form in it. They need to be eliminated promptly.
The regularity of cleaning is determined by the quality of the water and the parameters of the boiler itself, as well as the degree of load on it.
Whatever washing method is chosen, first of all, deposits are removed using mixtures of different acids or special reagents. This is followed by rinsing with water.
If you do not carry out these operations, then:
- The heat exchanger will overheat.
- The efficiency of the boiler will decrease.
- The boiler may break down. In an advanced case, an explosion is not ruled out.
Cleaning and washing of floor-standing boilers
Removal of scale and soot is carried out without dismantling the heat exchanger. A flushing pump (booster) is used. An aqueous solution of citric acid is poured into its container. For 2 liters of warm water, 200 grams of powdered citric acid is required.
Before cleaning a floor-standing gas boiler, turn off the gas and water supply taps, drain the water from the heating and hot water circuits. Next you need to get to the heat exchanger. Remove the door, disconnect the wires connected to the piezoelectric element, remove the thermocouple and nozzle, dismantle the ignition system and burner.
Unscrew the nuts securing the top cover and remove it. You have gained access to the heat exchanger and can clean it of soot with a brush and brush.
Connect the leads of the booster to the heat exchanger pipes, which will pump a citric acid solution into the pipe under pressure. Circulating along the circuit for 4-6 hours, it will dissolve the scale. The rinsing time depends on the level of contamination.
To keep the process under control, use a pH meter. This device will show the change in acid concentration in the solution, which occurs as a result of the ongoing chemical reaction of dissolving carbonate deposits.
If the acid has neutralized and the meter displays a pH value of 1, you may have to repeat the process all over again. A stable pH level between 2 and 4 indicates descaling.
Finally, the pipes are washed with a baking soda solution to neutralize residual traces of the reagent. Next, it remains to install the parts in their places, check the unit for leaks by washing and visually inspecting the detachable connections, or using crimping. If there are no gas or water leaks, the boiler operates as usual.
Cleanable nodes
Gas boiler installation. (Click to enlarge)
This type of equipment contains the following components that need to be cleaned periodically:
- igniter;
- burner with nozzles;
- gas filter;
- heat exchanger;
- firebox;
- chimney.
It is worth noting that cleaning each component of a gas boiler has its own specifics, which we will dwell on in more detail.
Igniter
The cleaning procedure occurs in the following sequence:
- shut off the gas supply to the boiler;
- unscrew the igniter;
- Clean thoroughly using a wire brush;
- perform purging;
- Reinstall the cleaned igniter.
Burner with nozzles
The sequence for cleaning the burner with nozzles is as follows:
the gas supply valve closes; the burner is removed from its installation location; the location of the nozzle is noted, and then it is carefully unscrewed; You need to carefully clean the nozzle with a brush; the burner is cleaned with a brush, and its hole is purged using available pumping equipment; the nozzle is inserted into the burner according to the mark; the burner is installed in place.
Expert advice: cleaning the burner with nozzles should be done once a year, preferably before the heating season.
Therefore, it is very important to regularly clean the filter from accumulated clogging.
Heat exchanger
It is also necessary to understand that this element of the boiler unit can become clogged both inside and outside.
The outer part of the heat exchanger becomes contaminated with soot, which negatively affects its functioning. This boiler unit can be cleaned of soot mechanically, in other words, cleaning is done with your own hands.
To do this you will need the following set of tools:
- scrapers;
- metal brush;
- various shapes of brushes;
- power tool with cleaning attachments.
The cleaning procedure is as follows:
- gas supply and power supply from the boiler is turned off;
- the heat exchanger is carefully removed;
- cleaning is carried out using convenient tools;
- the device is installed again in its place.
An important point: try to use a tool for cleaning that does not have sharp edges. Otherwise, you may cause damage to the heat exchanger, which may cause corrosion of the product in the future.
Here
As a result, the throughput of the heat exchanger decreases, which generally affects the functioning of the entire gas boiler. The most optimal way to clean the inside is to flush the gas boiler heat exchanger using chemicals.
Among the reagents that are used to clean the internal walls, the following products can be distinguished:
- adipic acid;
- sulfamic acid solution;
- special gel.
Specialist's note: the choice of reagent for flushing should depend only on the degree of contamination of the heat exchanger.
The booster consists of the following elements:
- circulation pump;
- reagent container;
- electric heater.
The principle of cleaning the heat exchanger using a flushing device such as a booster is as follows:
- to improve cleaning properties, the reagent is heated in a container;
- Using a pump, the solution is supplied under pressure directly to the heat exchanger.
As a result of the circulation of the chemical, the scale lags behind the internal walls and comes out along with the waste solution.
Experts advise: using a booster, you can clean not only the circuit of hot water boilers, but also the pipes of the entire heating system.
Firebox and chimney
Therefore, it is recommended to carefully monitor the formation of soot and regularly clean the chimney and firebox. We hope that the information presented in the article will be useful to you when cleaning your gas boiler.
Watch the video, which shows in detail how to properly clean a gas boiler at home:
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The heat exchanger of a gas boiler can be easily washed at home without the use of professional equipment:
How to descale the secondary heat exchanger of a double-circuit boiler and what is needed for this:
Modern methods and means help to effectively combat scale and prevent its formation. The main thing is not to forget to periodically flush the heat exchanger so that the real characteristics of the gas boiler correspond to the passport indicators throughout its entire service life.
Tell us about how you washed the heat exchanger of your own gas boiler. Share the effective methods of removing mineral plaque that you know. Please leave comments in the form below, ask questions and post photos on the topic of the article.
Frequency of cleansing
Typically, maintenance periods are reflected in the passport of each model. However, these are indicative values. And they mean that the device will work in comfortable conditions. In practice, the heat exchanger needs to be washed more often.
The need for these operations arises when:
- There is a big difference in the calculated parameters of the unit from the values in its passport. Efficiency decreases and thermal energy consumption increases.
- According to the plan, the rubber seals of the heat exchanger are being changed.
- Very dense deposits appeared on its plates.