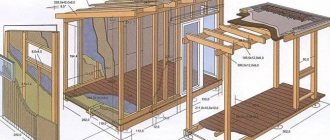
Timber is an ideal, universal construction material. It is environmentally friendly, warm, economical and easy to use. Thanks to these qualities, it is actively used in the construction of houses. The dimensions of the timber are different, but the most popular are 150mm by 150mm, they are much more convenient to work with. The technology for constructing such houses is not complicated, and is accessible even to a non-professional builder. It does not require the use of any special or heavy equipment; the main thing is to know the stages of building a house from timber and take into account some of the nuances.
Wooden house project
Building a house from timber always begins with the creation of a project. This work is interesting, you can realize all your imagination and create your dream house on paper. But at the same time, this stage is very important and responsible; it is better to contact a special office. There, together with professionals, you can develop a house plan with all the details, taking into account the soil on the site, and other nuances that are important for building a strong and durable house made of timber.
Construction stages
The technology for constructing a timber house from material with a cross-section of 15x15 cm is quite traditional. It includes the following stages:
- Selection of timber. The reliability and durability of a building depends to a large extent on the quality of the material. The best option today is profiled timber from reputable manufacturers.
- Selecting a project. It is allowed to use a standard project with mandatory reference to the conditions of a specific area or develop an individual set of documentation. The first option is simpler, faster and cheaper, and the second allows you to get housing that exactly matches the owner’s needs.
- Construction. The longest stage of work directly related to the construction of a building. Includes traditional stages, starting with the foundation and ending with interior decoration. In general, the technology for constructing a structure from 150x150 mm timber does not differ from the classical one.
Making the foundation
The next stage of building a log house with your own hands is to create a solid foundation, because the wooden house itself is not light in weight. There are three types of foundations that can be made for a log house:
- Tape.
- Columnar.
- Pile.
The choice of a certain type of foundation depends on the size of the house, the presence of a basement or cellar and the condition of the soil. Tape is suitable for most wooden houses; it can withstand heavy loads. A pile foundation is made if the soil is loose and the timber house is not small in size. A columnar foundation is the easiest to manufacture, but it is only necessary to build it for a small log house.
Choosing material for a frame house
The most suitable material for building a frame is considered to be well-dried pine. It has a natural resin content, which prolongs its service life and protects it from many insect pests. In addition, pine has an affordable price, and wood can always be purchased in sufficient quantities for construction.
A frame house can have dimensions that exceed the length of a standard beam made of natural wood. In addition, this building material may have natural flaws in the form of knots or bends. And it is not always possible to achieve uniform, high-quality processing over the entire surface. Another disadvantage of this type of material is its heavy weight.
These problems can be eliminated by purchasing laminated veneer lumber. It has no natural defects, is uniform throughout its entire length and can reach 12 m in length. But its main advantage is that this material has increased mechanical strength, which is achieved due to the different orientation of the fibers of the timber components. In addition, all the parts from which it is glued undergo pre-treatment, including drying and impregnation with special solutions that protect against insects, mold and fungi. Thanks to this, the design of houses of this type is more reliable and durable.
The disadvantage of laminated veneer lumber is its high price. But it is fully compensated by the reliability of the material.
Construction of timber walls
Before laying the walls, you need to take care of waterproofing the foundation. You need to lay roofing material on it in two layers, then lay the support board. The support board prevents unwanted contact of the foundation with the lower crown of the log house, thereby protecting the timber from excess moisture and other adverse influences. In addition, if the support board is damaged, it is much easier to replace than the lower crown. The actual assembly of log walls can be done in several ways:
1) Using dowels. The crowns of the log house are fastened together with wooden or metal spikes - dowels. For them, it is necessary to drill holes in the beams, taking into account that the distance between the dowels is at least 1 m.
2) Connecting the timber using a lock. This assembly option is mainly used for the construction of large houses, the walls of which are longer than the length of the beam, more than 6 m. To create a castle, it is necessary to make special holes along the edges of the beam, which will create a castle structure.
3) Assembling the frame using a root tenon. This method is carried out by cutting out a tenon on one beam and a corresponding groove on the other. When connecting the crowns, they should fit firmly into each other, creating a neat corner of the wooden house. In addition to creating tenons, it is also necessary to use dowels to fasten the beams to each other.
It is also very important to lay inter-crown insulation between the crowns of the log house. Even between perfectly even beams a small gap is formed, which will increase after the log house shrinks. To prevent heat from escaping through this gap, insulation is laid. It is better to purchase natural inter-crown material in the form of a ribbon, it can be jute, linen wool, flax. Such insulation is easy to install and birds will not pull them out over time.
Lower Level Mount
A layer of roofing material is laid on the mature and dried foundation, into which bolts for installing the timber are installed during the pouring process, and the bottom row of timber is placed on it, which is leveled using a level. If the master finds any irregularities, they need to be cut off and the recesses filled. If the holes are larger than 1 cm, it is better to lay wooden boards of the required thickness.
Holes are drilled at the junction of the timber with the anchor, after which the tree is laid on a layer of waterproofing on the foundation. When tightening the nuts with wide washers placed under them, you must ensure that the beam does not warp and that it remains horizontal along its entire length. It is recommended to choose a distance between bolts from 1 to 1.5 m, but not more than 2 m. If bolts were not installed in it when pouring the foundation, you can use anchors that are drilled into concrete.
Corner fastenings are made of two types: “in the paw” and “in the floor of the tree”. At least 4 nails are driven into each corner, so that the heads are no closer than 2 cm to the edge of the beam.
In the middle of the fastening you need to drill a hole for the dowel. This is a pin made of strong wood that holds two horizontal beams together. Its thickness must be at least 2 cm, and its length must be at least 25 cm. After it is driven into the bottom row, at least 15 cm of dowel must remain on the surface.
Having completed the fastening, be sure to check it again in relation to the horizon and remove all irregularities, due to which the frame house may subsequently look skewed.
Construction of a house roof from timber
After the walls of the wooden house are ready, it is necessary to begin the difficult construction of the roof. There are many design options for creating a roof. The most common is the gable roof, which consists of a roof and a rafter system.
The rafter system is the basis of the entire roof. It is made from rafters connected to each other with staples or nails. Afterwards, a vapor barrier film is laid on the rafters. It will protect the rafter system from overheating, moisture, and steam. Also, many films can suppress noise caused by rain or hail. A sheathing is installed on top of the laid film. And then the selected roofing material is laid.
How to make your cherished dream of owning your own home come true?
It's easy to do it yourself. It is easier to build a house with your own hands from wooden beams. Wood is a traditional material with time-tested quality.
The production of finished softwood timber in our time is represented by a wide number of options. If you have a ready-made project, it is possible to order material for the template.
Production will take a long time, but will be compensated for during installation.
7 steps to realizing your dream
After making a decision to build housing, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory measures.
The best time for this is considered to be late autumn and winter. It is necessary to spend a lot of time on all actions and it is advisable to time this period by the beginning of the construction season from mid-Vienna to early autumn:
- Decide on the choice of site.
- Order or buy a ready-made standard project for your home.
- Order and purchase basic material.
- Carry out preparatory work.
- Prepare consumables.
- Purchase a tool.
- Conclude agreements with contractors.
Manufacturing of floor and ceiling
The heat in a log house depends not only on the walls, but also on the floor and ceiling. The floor is most often made double to make the room much warmer. You can also lay a thermal insulation film between these two layers. It is best to use boards to cover the floor; among modern coatings, you can use laminate, which imitates various valuable types of wood. If the floor is covered with tiles, then the interior itself, the design of the wooden house, will be damaged by this material.
The ceiling must be created from:
- Beams that form the basis of the ceiling.
- A vapor barrier layer that will protect the rafter system from moisture.
- Then the beams must be hemmed with boards. After this, lay insulation on the boards between the beams, and thanks to it, heat will not escape from the house through the roof.
- And finally, decorate the boards with decorative material, this could be plasterboard, suspended ceiling, etc.
Fastening vertical bars
The corner beams are installed first. They have pre-drilled holes in the end (1 cm larger than the length of the protruding end) and are mounted on dowels. After this, they are attached to the lower level using metal corners. Having installed the corner posts, you need to additionally secure them with so-called slopes - these are boards that will prevent the beam from moving and disturbing the geometry of the frame.
After completing this stage, they proceed to fastening the remaining vertical beams. You can use two types of connections: with cutting or using a metal angle. The second method is simpler and more reliable and takes less time from the technician.
It is recommended to choose the average distance between the vertical posts within 50 cm. They also need to be leveled using a plumb line and temporarily secured with slopes.
Doors and windows of a timber house
Door and window openings in a log house are made in two ways:
- Directly during the construction of a house made of timber. Everything is calculated and bars of a certain size are installed in the required places to create windows and doors.
- After construction. First, a kind of box is erected from timber, then windows and doors are cut out of it. A chainsaw is used for this. The main thing during construction is to take into account the following: if there are two windows next to each other on one side of the log house, then the beams should be firmly fastened between them, otherwise they may fall apart after sawing.
Then, after construction or sawing, the ends of the timber in the places of future windows and doors are decorated with a frame, so that after the log house shrinks, the shape of the door and window opening should remain unchanged. Windows and doors cannot be installed immediately, otherwise they may become warped. For the first year after construction, the log house must remain uninhabited.
Step-by-step construction instructions with photos
There are several different technologies for frame house construction, but the classic method of construction is Canadian. It is also called the platform method, since first the floor of the frame house is assembled, and then the skeleton of the walls is assembled on it, like on a platform. We'll tell you how to build a house using this method. It won’t be difficult to figure out the rest: only the sequence of actions is different.
Step 1: Foundation for a frame house
Choosing a foundation is a separate complex and voluminous topic. The geological picture on the site, the height of the groundwater, the weight of the building and the seasonality of living in it, the region in which construction takes place, snow and wind loads are taken into account. But in general, foundations for frames are most often piled, piled-grillage or strip foundations.
In our country, the palm in do-it-yourself frame house construction belongs to the pile-grillage foundation. It is quickly built, requires small material investments, is correctly calculated and built, and is reliable. Combining the advantages of both pile and strip, it evenly transfers the load to all supports.
More reliable when constructing a pile or pile-grillage foundation are TISE piles. Due to the widened heel, they have a greater load-bearing capacity and better resist heaving forces.
Construction of a pile-grillage foundation with TISE piles
You can drill holes for piles using a hand drill or a motorized one. As formwork, use roofing material rolled into pipes of the required diameter (at least three layers must be rolled), secured with tape. Other options are asbestos-cement or PVC pipes of suitable diameter. Three or four reinforcement rods are installed inside the piles, connected to each other in the form of a triangle or square. The reinforcement rods are cut so that at least 0.7-0.8 meters protrude above the surface of the pile. Everything is filled with concrete of a grade no lower than M25 (read about concrete grades here).
After pouring the piles, the tape formwork (grillage) is installed, and the reinforcement is laid and tied into it. Longitudinal rods are connected to bent reinforcement outlets from the piles. At this stage, holes are left in the tape for supplying communications and ventilation (insert sections of plastic pipes across the tape).
The strapping beam will subsequently be attached to the foundation strip. To install it, studs are fixed in the tape. They are installed in increments of 1-2 meters. From each corner, 30 cm are retreated in both directions. Here, studs are required, the rest depending on the dimensions of the house, but at least every 2 meters. Please note that it is the studs that connect the frame of the house to the foundation. That’s why it’s better to deliver more often. And one more thing: no matter how short the wall is, there must be at least two studs.
When everything is ready, the concrete is poured.
Filled grillage. The foundation for a frame house with your own hands is ready
After pouring the concrete, so that it does not dry out, but gains strength, it is better to cover it with polyethylene (look at the photo). If the temperature after pouring the foundation remains within +20°C, construction can continue after about 3-5 days. During this time, under such conditions, concrete will gain more than 50% of its strength. You can work with it freely. When the temperature drops, the period increases significantly. So at +17°C you need to wait about 10 days.
Step 2: Bottom Rail and Floor
To prevent the wood of the frame from drawing moisture from the concrete, cut-off waterproofing of the foundation is necessary. The safest way to do this is with bitumen mastic. And it’s better - in two layers. You can also use roll waterproofing. Roofing felt is cheaper, but it breaks over time. Waterproofing or other similar modern material is more reliable.
You can coat the grillage once with mastic, and roll out waterproofing on top. Another option for cut-off waterproofing under a frame house is two layers of waterproofing coated with mastic: the closer the groundwater is, the more thorough the waterproofing should be.
The first layer is liquid waterproofing. While it is not dry, you can glue a layer of rolled waterproofing on it.
Then the beds are laid - boards measuring 150 * 50 mm. They must be dry, impregnated with bioprotective and fire-retardant compounds. The edge of the bed is aligned with the outer edge of the foundation. In the necessary places, holes are drilled for the studs (the diameter of the hole is 2-3 mm larger than the diameter of the stud). Then the second board is laid. It is placed so as to cover the joint of the first row. It turns out to be a castle.
The second board is laid so that the joints overlap
In general, you can lay one beam of 100-150 cm, but its price is much higher than two boards, which together give the same thickness, and properly fastened two boards have a greater load-bearing capacity, although their installation takes more time. To make them work as a single beam, they are knocked down with nails in 20 cm increments in a checkerboard pattern.
We install the harness and logs
Next, a strapping board is attached to the bed. Its dimensions are also 150-50 mm, but it is placed on the edge. Aligned along the outer edge of the foundation, nailed with long nails (9 cm) to the beam every 40 cm.
Installation of the piping: according to the instructions, the assembly of the frame house continues with the installation of the piping to which. the floor joists will rest
The next stage is installation and installation of the logs. These are the same 150*50 mm boards placed on edge. They are attached with two oblique nails (9 cm) at the end to the trim board, two nails on the right and left to the bed. So each lag is on both sides.
Example of installing floor joists
The photo shows that the first joist is installed close to the second - this way the load is better transferred to the foundation. It is installed along the second edge of the bed. The installation step is 40-60 cm. It depends on the length of the span and the cross-section of the lumber used: the longer the length, the smaller the step.
Layed and secured floor joists
If the logs are long and there is a cross beam, as in the photo above, to prevent the logs from “moving away,” jumpers are placed above the cross beam. Their length is equal to the step of installing the logs minus the double thickness of the board: if the step of the log is 55 cm, the thickness of the board is 5 cm, then the jumper will be 45 cm long.
Insulation and flooring
After the base for the flooring has been installed, it is time to insulate the floor. It can be done in different ways, with different materials. We will show you an economical option - with polystyrene foam boards with a density of 15 kg/m3 (more is possible, less is not possible). It is, of course, not environmentally friendly, but it is the only one that is not afraid of moisture and can be installed without a subfloor. The estimated thickness of the insulation is 150 mm, two layers are laid: one 10 cm, the second 5 cm. The seams of the second layer should not coincide with the seams of the first (they shift).
To begin with, a 50*50 mm cranial block is packed along the lower edge of the log. It will hold the foam.
At the bottom you get a frame made of a cranial block, which will prevent the polystyrene foam from falling out
The foam is cut with a regular hacksaw. The blade can be used on wood - it cuts faster, but you get a torn edge, or on metal - it goes slower, but the edge is smoother. The cut slabs are laid in two layers, the seams overlap. Then they seal the perimeter with sealant to ensure waterproofing.
Laying foam
Next, lay the subfloor from boards, level it and lay plywood on top (preferably FSF 5-6 mm). To prevent the rough flooring of boards from warping, lay the boards alternating the direction of the wave. If you look at the cross section of the board, the annual rings go in a semicircle. So, you need the arc to look up and down (see photo).
How to lay plank flooring correctly
You can do without plank flooring. Then the thickness of the plywood should be at least 15 mm. Consider what is more profitable in your region and choose.
In any case, the sheets should be laid in a spaced pattern - the seams should not match (as in brickwork). Also, do not forget to leave a gap of 3-5 mm between the sheets of plywood to compensate for changes in size when humidity changes.
The second stage of building a frame house has been completed: the floor has been laid
The plywood is attached with self-tapping screws 35 mm long (preferably white ones - less waste) around the perimeter in increments of 12 cm, inside in a checkerboard pattern in increments of 40 cm.
An example of using frame technology to build a wooden shed is described here.
Step 3: Frame Walls
There are two ways: the wall frame is assembled (all or part, depending on the size) on the floor, then raised, positioned and secured. Sometimes with this method, OSB, gypsum fiber board, or plywood are attached directly to the floor on the outside of the frame: the rigidity is greater. This technology is called frame-panel or “platform”. Factories generally operate according to this principle: they build ready-made panels according to the design in the workshop, bring them to the site and only install them there. But frame-panel house construction is possible with your own hands.
One of the options for assembling a frame wall, names of elements
The second method: everything is assembled gradually, locally. The beam of the bottom frame is nailed, the corner posts are set, then the intermediate posts, the top frame, etc. This is the technology called “frame house construction” or “balloon”.
Assembling the wall frame with your own hands can be done gradually (balloon technology) or in block-boards (platform technology)
Which one is more convenient? It depends on how many people work and whether it is possible, at least periodically, to attract help. Working on the floor is faster and more convenient than jumping up/down a stepladder countless times. But if the section is assembled large, then it will be difficult even for two people to lift it. The solution is either to call help or to break the wall frame into small segments.
Installation step and cross-section of racks
Corner posts should be 150*150 mm or 100*100 mm, depending on the load and the required width of the insulation. For a one-story frame house, 100 mm is enough, for a two-story frame house - at least 150 mm. The intermediate posts are the same in depth as the corner posts, and their thickness is at least 50 mm.
The installation step of the racks is selected taking into account the load, but in reality it is more often selected based on the width of the insulation. If you will be insulating with mineral wool in rolls or mats, first find out the actual width of the material. The gap between the posts should be 2-3 cm less than the width of the insulation. Then there will be almost no waste, no gaps and cracks through which heat will escape. The density of installation of insulation in frames is the main point, because only it will serve as protection from the cold. The slightest violation will lead to the fact that the house will be cold. Therefore, the selection of insulation and its installation must be treated with full attention.
An option for gradually assembling the frame of a house: corner posts are placed and secured, the top frame is immediately mounted on them, then the vertical posts are installed at a selected step
Fastening the racks is possible in several ways: with wooden dowels, with a notch or on corners. The cut into the board of the bottom trim should be no more than 50% of its depth. The corners are attached on both sides. Fastening with dowels is an old technology, but difficult to implement: long dowels are planed, a hole is drilled obliquely through the stand and beam of the lower trim, a wooden tenon is driven into it, the excess of which is cut off. It works well if the wood used is dry. If not, drying out and loss of fastening rigidity is possible. Installation on reinforced corners is much easier.
According to Canadian technology, the beams to which windows and doors are attached are made double. There is more load here, therefore the support must be more powerful.
Reinforced counters near windows and doors are a must. This is the only way a frame house built with your own hands will be reliable
Read how to make a gazebo out of wood (also using frame technology) here.
Bevels or braces
If the outer cladding is planned to be made of high-strength slab material - OSB, gypsum fiber board, gypsum fiber board, plywood - temporary slopes are installed from the inside of the room. They are needed to level and maintain geometry until the outer skin is attached. The strength of this material is sufficient to create the required structural rigidity.
If the cladding is planned to be made up of linings, etc. installation of permanent jibs is required. Moreover, the best option is not those that are placed on several racks, but four small pieces for each: two on top and two on the bottom (as in the photo below).
Such braces will give sufficient rigidity to the walls of a frame house.
Please note that in the photo above the racks are prefabricated: two boards are nailed together along the entire length in a checkerboard pattern. Such racks have even greater load-bearing capacity than solid ones and cost less. This is a real way to reduce construction costs without losing quality. But construction time increases: you have to hammer in a lot of nails.
Corners of a frame house
The most questions arise when constructing corners. If you place a beam in a corner, then there seem to be no difficulties, except that the corner turns out to be cold. In regions with short and mild winters this is not a problem, but in central Russia it requires some kind of solution.
Even with this option, the corner will be colder
There are several ways to make the corner of a frame house warm. All of them are shown in the diagrams, so it’s clearer.
When building a one-story frame house, you can do this
For a residential second floor, corners are made in one of these ways
After assembling the frame, it is most often sheathed on the outside with OSB, plywood or other similar material.
The construction of the woodshed is described in this article.
Step 4: Covering
The floor beams rest on the beam of the upper frame. There are several mounting methods:
- on supporting steel brackets;
- on the corners;
- with insert;
Notching - the depth of the cut should not exceed 50% of the thickness of the top frame timber. It is hammered on top with two nails, which should go into the harness at least 10 cm
Corners are a common method. You can use reinforced ones, but not necessarily
Perforated staples - shape may vary
Fastening the ceiling beam using metal brackets
The dimensions of the beams and the pitch of their installation depend on what will be on top. If there is a second residential floor or attic, the cross-section is taken larger, the step is made smaller: so that the floor does not sag. If only the roof and attic on top are assumed to be non-residential, these are completely different calculations and dimensions.
In this one-story frame house, the floor beams also support the rafters. Therefore, they are extended 30 cm beyond the perimeter of the walls
If a second floor is being built, the ceiling is sheathed with the subfloor of the second floor. This will make it easier to work on creating the second floor of a frame house. Its assembly is no different from the construction of the first one. The only reason is that all the lumber has to be hauled to the second floor.
Step 5: Rafter system and roofing material
When developing a house project using frame technology, the most popular are a gable or mansard roof. Their device is no different. All the same principles and calculations. The only limitation concerns the weight of the roofing: it must be a light material, the load from which wooden beams and ceilings can withstand.
This is what the frame looks like before the sheathing. If the walls are not sheathed, slight vibrations are felt when working on the rafter system. The outer skin makes the frame much stiffer
A gable roof with a raised puff was chosen
For ease of fastening the rafter legs, a 50*50 mm block was nailed along the edge of the floor beams. There was a groove made under it in the rafters. During installation, they first simply rested against the block, then fastened
To fix the rafters in a given position before the sheathing was filled, temporary jibs were used
Another relatively inexpensive technology for building a house from aerated concrete is described here.
Step 6: Insulation
A frame house can be insulated with any of the materials available on the market with the appropriate characteristics. All of them are imperfect, but all problems have standard solutions.
The most popular insulation for frame walls is basalt wool. It is available in the form of rolls or mats of different densities. It is more convenient to install mats in walls: they are denser and hold themselves well due to the pushing force. To do this, as mentioned above, their dimensions should be 2-3 cm larger than the distance between the frame posts. The mats, of course, are additionally fixed with special fasteners, but it is more convenient to work with than with a soft roll.
The most common type of frame wall insulation
Mineral wool has high thermal insulation characteristics and good sound insulation. But there is also a serious drawback: it is afraid of getting wet and it must be protected on all sides not only from moisture (rain), but also from the penetration of steam. Therefore, from the side of the room it is covered with a layer of vapor barrier membrane, which prevents vapors from penetrating inside.
On the street side, the thermal insulation made of mineral wool is covered with another membrane, but of a different type with different characteristics: a hydro-wind-protective vapor-permeable membrane. It is not blown through, it does not allow moisture in liquid or gaseous states to pass through from the street side, and vapors can escape from the insulation: the vapor permeability is one-sided. After installing the insulation, only finishing work remains. Actually, that's it, construction is over.
This is what a basalt mat looks like installed between the posts
Now you know how to build a frame house. The detail of some processes is far from complete, but you have a general assembly sequence.
Video “Turnkey frame construction in 2 months.”
Perhaps another video from a professional carpenter who has been building frame houses for decades will help you (see below).
Finishing a timber house
The 150x150 timber itself has a beautiful, even structure and the best option for finishing a house is its natural beauty, i.e. the log house can be left untouched. You can only apply a colorless varnish or other protective impregnation to it to protect it from the effects of atmospheric phenomena and other biological pests. You can also cover a wooden house with siding, block house and other finishing materials, but in such cases the texture of the timber will be hidden.
Conclusion
Contrary to popular belief, frame construction is not a way to spend the minimum and get the maximum. If high-quality materials are used and technology and design are followed, the house can be even more expensive than a brick/stone one. But it will not be inferior in terms of characteristics, and will serve more than one generation. But when the goal in itself is budget reduction, and due to damp wood, poor insulation, and neglect of standards, it turns out that the Russian frame is terrible. As with everything, everyone chooses for themselves.
One of the previous thematic materials is about classical technologies of frame house construction. About a small but very interesting frame structure - the article “Budget and beautiful house with a mezzanine and second light: photo report.” The video is about a frame house in pastel colors on a hill.
Subscribe to our Telegram channelExclusive posts every week