Greetings to you, my Readers and Viewers of the construction Blog “The Way Home”. Today we will be engaged in design and I will answer questions from subscribers on such a topic as a monolithic slab on a strip foundation with backfill as permanent formwork.
Many years ago I made a video called “An alternative to ground floors. Lopatino” I named it for a reason, because everything is learned by comparison. The technology I talked about is, in some situations, even more economical in price than floors on the ground.
Over the years I have answered questions regarding this topic many times. But still, let's return to this topic again to refresh this information in our memory. Moreover, at that time I had a slightly different task - I had to select a technology in order to compare the price and choose the most rational option.
Full question: Nikolay / Monolithic slab on a strip foundation, with internal backfill as permanent formwork. With releases of strip foundation reinforcement for connection with slab reinforcement. Viability and feasibility of such a design.
Where did my phrase “soil like permanent formwork” come from?
In general, permanent formwork is formwork that remains part of the structure. that is, it is not removed, buried, or becomes a finishing layer. How can this be applied to soil, you ask?
Different life situations lead to reflection with very unexpected conclusions. We have had cases where floors that were built on the ground collapsed at sites. The floor fell 10-15 cm.
This is a consequence of a poorly compacted base. In my videos about ground floors, I constantly emphasize that the base should be compacted very well! But it is quite difficult to control this. This can be done, but at a small thickness.
At one of our sites, geology showed one and a half meters of black soil. Black soil is considered a poor base for ground floors because it is the area where the garden used to grow; the ground is full of roots that will rot.
In fact, it turns out that this one and a half meters of soil needs to be pulled out, a foundation made, resting on normal soil, and the one and a half meters of soil must be filled back in. At the same time, compact all this in layers of 20-30 cm. Since my task is to offer the client a rational solution, I calculated the estimate with the expectation of leaving this soil.
Yes, it's bad because it's black soil. But from the point of view of protecting the client’s finances, it turned out that even if the black soil is sold, the client still finds it cheaper to bury the black soil in this massif. And make a monolithic slab on the strip foundation.
2:00 What is “soil as permanent formwork”? 3:00 Floor failure 4:40 Chernozem 7:55 Connecting a slab with a strip foundation 11:40 Grid 13:15 Calculation 14:05 Intermediate wall 15:45 Errors 17:34 Sequence of work 28:09 Cold bridges
30:50 Is a 150 mm slab realistic?
A monolithic strip foundation is an integral structure made of steel reinforcement and concrete strip. It is located under all load-bearing walls. If you follow all the rules for constructing a foundation, the structure will be very strong and reliable.
A monolithic slab on a strip foundation can support not only private cottages, but also multi-story buildings. This type of foundation is best used when the groundwater level is low, if it is below the depth of the structure. Otherwise, you will have to arrange drainage, and this will entail considerable additional costs.
The strip foundation can be deep or shallow depending on its depth. The second type is built on slightly heaving soils for light buildings made of wood or using frame technology. This type of foundation must be at least 0.6 m.
Deep strip foundations are used for massive buildings. They are lowered below the soil freezing level by 12-15 cm.
The base of the foundation must rest on a dense layer of soil. If this condition is not met at a given depth, you will have to make a recess lower. For example, if the soil freezes to a depth of 1 m, and the fertile layer is at an area of 1.2 m, then the foundation must be laid to a depth of more than 1.2 m.
Is formwork necessary?
The construction of a strip monolithic foundation involves the installation of formwork.
It is assembled from panels that serve as a form for concrete and prevent it from spreading. Of course, the construction of formwork entails additional costs, as well as time. Sometimes they save on it and make a pit for the foundation exactly according to the markings so that its walls are perfectly straight.
But such technology does not guarantee a high degree of reliability, and it is impossible to predict how durable such a foundation will be. To gain a certain strength, you need water, and without formwork the moisture is partially absorbed into the surrounding soil. This will affect the quality of the structure, and in the worst case, it will crumble.
With stable soils, such foundations last for many years.
But over time, cracks may appear or the concrete will begin to crumble. Another disadvantage of a foundation made without formwork is its uneven geometry. To reduce heat loss, it is insulated with polystyrene foam boards or polystyrene foam, but the uneven surface makes insulation much more difficult.
The situation is similar with waterproofing; the film is very difficult to attach to uneven porous concrete.
Important! From the point of view of a specialist, a foundation without formwork is only suitable for a shed or garage.
Selection of materials
Backfill for filling the foundation cavities:
- sand;
- crushed stone-sand or gravel-sand mixture;
- clay;
- soil extracted when digging a pit.
The easiest way is to fill the sinuses with soil removed earlier. But this is not an ideal option for arranging a reliable foundation for a house. Therefore, it is better to replace the soil with clay or sand, which provides reliable support for building structures and improves the drainage of water from underground structures.
Base requirements
The backfill material is selected so that it optimally meets the requirements for the load-bearing soil at the base of the house:
- was dense and durable;
- it should not retain high water and fallen water;
- do not lose their strength properties due to repeated wetting, swelling, drying;
- have slight heaving and, if possible, do not change volume when freezing;
- do not have uneven shrinkage - this leads to damage to the blind area, and in difficult cases, to the foundation structures;
- do not contain organic residues.
Land works
Before starting earthworks, the soil is examined and the levels of freezing and location of fertile soil, the depth of groundwater, soil heaving, etc. are measured.
Important! If the soil allows and the house is planned to be one-story, then you can limit yourself to the construction of a shallow strip foundation with a monolithic slab.
The amount of excavation work depends on whether there will be a basement in the house or not. If not, then the soil will need to be excavated only to the depth of the tape, and in width - with a margin for the thickness of the formwork. Wooden planks need spacers to support them and prevent them from falling.
If you plan to build a basement, then all the soil should be removed. The size of the pit is usually 2-5 m larger than the dimensions of the foundation, since a reserve is needed for the formwork panels.
To organize a large pit, it is better to hire special equipment, since this solution will be optimal in terms of cost and speed of work.
The fertile layer is laid out separately in the garden or vegetable garden. The rest of the soil needs to be piled up, since some of it will later be useful for backfilling, and the excess will need to be removed.
Dependence on soil type
The type of soil also greatly influences the choice of strip or slab foundation. The tape is suitable for slightly heaving or non-heaving soils. This means that if the soils are prone to movement during seasonal freezing and thawing, then the foundation on them will quickly collapse, as it will not withstand the load.
If the soil is complex, for example, clayey, sandy, dusty, or heavily saturated with water, then only a monolithic slab is suitable. It will be necessary to carefully level the area under it and make good reinforcement, and then the slab will support a house of any weight on any soil.
Compaction and tamping
The bottom of the pit must be leveled and compacted. Since the excavator cannot provide the same depth over the entire surface of the pit, all uneven places must be leveled by adding earth and compacting the surface with a vibrating plate. This is necessary so that the foundation can withstand the load at any point, otherwise, due to uneven soil support, cracks may appear on it.
To quickly and efficiently level the bottom of the pit, you can sprinkle it with sand, moisten it and compact it with a vibrating plate. It is able to compact sand to a depth of 14-20 cm; this is the layer that can be poured and compacted in one go.
If the project requires a sand-crushed stone cushion, then crushed stone with a fraction of 25-55 mm is poured on top of the compacted sand.
It is compacted in the same way. Thus, the soil is not only leveled, but also compacted. The plate drives stones into the soil to a depth of 0.5 m.
Filling communication recesses
Before starting work, it is important to familiarize yourself with the following nuances:
- Before laying pipes, crushed stone is poured into the bottom of the recess (layer 10 cm). Next, pour 30-40 cm of sand.
- Next, the pipeline is laid and the work is checked. If everything is in order, backfill is done.
First, the sand is laid 30 cm thick and then compacted using additional tools. Next, layers of soil are applied. The thickness of each should not be less than half a meter.
It is important to note that the process of backfilling the foundation inside to the floor level is an important undertaking that does not tolerate even the slightest mistakes. It can only be carried out after completion of the basement work and waterproofing.
In order to competently complete the task, it is advisable to get advice from a competent specialist before starting work, and also check that the basic requirements for backfilling are met, and use only high-quality material so as not to reduce the strength of the structure.
Reinforcement
Due to its large length and small width, the strip foundation is subject to forces that can break it across. To avoid this, use ribbed reinforcement measuring 1 cm in diameter. If a basement is not planned, then two reinforcing layers are usually sufficient: upper and lower.
At each connection point of the reinforcement, it is tied with wire.
This is done manually or using knitting guns. Sometimes the reinforcement is connected by welding, as this significantly speeds up the process, but then the adhesion becomes rigid. Wire binding provides the reinforcement with some freedom of movement and thereby compensates for actions that deform the foundation.
If, when reinforcing a monolithic slab of a strip foundation, a bunch of rods is made by welding, then these places are the first to be destroyed.
During the reinforcement process, openings are made for the future building through which communications will pass. If you don’t remember this in time, you will subsequently have to destroy the monolith, which will reduce its quality.
How to best compact the soil when backfilling
Manual tamping is the least preferred option. Undesirable due to low quality. Hands are used in small niches and openings where equipment does not fit.
Device
Use technology wisely. No device purchase required. Nowadays it is possible to rent the necessary equipment.
Using tamping equipment, carefully check the layer. For sand the maximum thickness is 70 centimeters, for clay and soil – 50 centimeters. A mixture of sand and soil - 60 centimeters.
Tamping by hand involves layers of a maximum of 30 centimeters; double coating is prohibited, as it disrupts the structure.
Tamping is done outwards from the base, carefully. Afterwards, formwork is installed - a barrier to water.
Backfilling is an important construction operation necessary to compact the foundation and clearly “position” it in position. The foundation is the basis of the house; the durability of the building and operational capabilities depend on it. Any nuance of working with the foundation part is treated carefully, instructions are followed step by step.
Average score of ratings is more than 0
Share link
Comments There are no comments yet, but you could be the first...
Pouring the foundation
When building a foundation for a house, it is better to buy ready-made concrete, then pouring work will take only a day. If you still want to make the mixture yourself, then you will need a concrete mixer.
After pouring, the concrete mass is subjected to vibration using special vibrators. This is necessary in order to remove all voids from the concrete and make it more uniform. Then its strength will increase and its frost-resistant characteristics will improve.
Important! When pouring concrete mass from a machine, it is necessary to install additional gutters, since the height of the fall should not be more than 1.5 m. Otherwise, falling from a height, the concrete will delaminate.
Reinforced concrete foundations as a leading technology in suburban housing construction
If developers have an eternal debate regarding the choice of materials for walls and roofs: what is better and what is worse, then as soon as the question concerns the foundation of the building, there is no disagreement. In this area, the absolute leader today is concrete.
Although, until recently, in the last century, foundations were sometimes built from brick or dense shell rock, now no one would even think of putting their house on a foundation made of these materials.
Reinforced concrete (reinforced concrete) is currently used for these purposes. By all characteristics, this is the cheapest, most durable, and most durable material, and there is simply no other choice.
Curing
Different temperature conditions have a corresponding effect on concrete:
- if work is carried out in hot weather, it is better to cover the tape with a film so that the moisture does not evaporate too quickly and the upper part of the foundation does not dry out; if the ambient temperature is about 19 ° C, then after three days the concrete will strengthen by 50%; and after another day, the formwork can be removed and the next stage of work can begin; at temperatures below 19°C, it will take longer to wait for the concrete to harden; and if the temperature is 5°C or lower, then the concrete will no longer set, then it will have to be heated.
Requirements for work performance
When handing over an object, private organizations are required to provide a certificate of completion of work with a detailed description of each stage of work, backfill technology, and composition of the material. The regulated SP for earthworks includes clause 45.13330 with technical information.
Organizations should focus on ENIR, and also use SNIP 3.02.01-87 and SNIP 2.02.01-83 4. The PPR is compiled by the chief engineer or foreman responsible for the quality and timing of the work. The estimator or chief accountant calculates the GESN. The technical map is drawn up taking into account the coefficients on the day of drawing up the contract between the customer and the contractor.
It is not recommended to backfill in winter, as the soil tends to deform under the influence of low temperatures.
A concrete foundation properly filled with sand will last for decades and will provide reliable support for your home!
Waterproofing
If you want to protect the foundation from moisture, you need to additionally lay a waterproofing layer.
This is often a film, preferably without seams, since this is where it tears most quickly. If you are waterproofing an already finished foundation, in this case it is coated with bitumen and a film is glued. To protect against moisture, clay or a polymer composition is also used.
Thus, the monolithic strip foundation is very strong and has a long service life. After all, the foundation of the house in construction is of key importance.
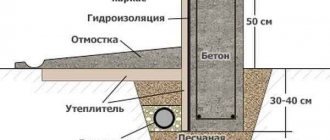
The advantage of this type of foundation is that it does not have any restrictions on shape and is suitable for any shaped structure. A monolithic strip foundation has a high load-bearing capacity, so it is possible to build houses on it from any heavy building materials with several floors. Scheme of a strip foundation with a monolithic slabThe construction of any building begins with the choice of the type of foundation. The main factors in this case are the characteristics of the soil at the construction site and economic costs.
The foundation must be strong and reliable so that the constructed structure can be used for a long time. If construction is planned on sandy, floating or peat soils, then you should pay attention to a strip foundation with a monolithic slab. This option is highly reliable. This type of foundation can withstand significant loads from heavy buildings and from the ground.
When to backfill
Necessary conditions for backfilling a slab or strip foundation:
- set of concrete of a certain strength;
- insulation device;
- performing waterproofing.
The optimal time for backfilling is when the concrete has gained sufficient strength. In hot weather, the ripening time for concrete is at least 10 days, at 20°C - two weeks, in cooler weather - at least 20 days. Although during this period the concrete will not gain maximum strength, it will already become quite hard, and lateral pressure during the process of adding soil and compacting it will not harm the structures.
It is advisable to carry out all work at above-zero temperatures so that the backfill material does not freeze into lumps that interfere with compaction. But the presence of a little rain is not of fundamental importance, but it interferes with the workers. In heavy rain, it is better not to work; cover the clay or sand with a film to prevent it from getting too wet.
It is better to backfill the foundation in positive weather, it will be easier to compact
Features of a strip foundation with a monolithic slab
A reinforced concrete slab on a strip foundation is a monolithic structure of a combined type, combining the features of two types of foundations. The load from the building is distributed along the perimeter over the entire belt.
Moreover, both parts complement each other well. In practice, the slab can rest either on the soil with the tape, or only on the tape base. The last option is similar to the use of floor slabs.
Combined base design
This option for constructing a foundation is almost similar to a slab foundation with stiffeners. The latter are protrusions located on top or bottom of the slab, or on both sides.
The combined foundation allows the construction of buildings with or without an underground garage (ground floor). Both options involve securely connecting the slab with the tape into a solid structure.
The combination of foundations is used in the following cases:
- when buildings are built on unstable types of soil, and it is impractical to erect other types of foundations; if it is planned to create a basement under the entire structure, then the internal partitions located above the floor will rest on a monolithic slab; when erecting a heavy building, for example, from reinforced concrete, cinder block, brick, natural stone and other materials.
Base option with a basement Without supports, it is permissible for the slab span to be no more than 6 m. This must be taken into account during planning before carrying out construction work.
Process Features
The pit must be filled with material removed during digging. Another construction mixture can ruin the foundation: the clay will swell over time and “tear” the concrete wall, the sand will be unevenly distributed around the perimeter and will overload one of the sides, until cracks form.
Particular attention should be paid to the density coefficients of the building material. If you still decide to use sand, then its condition should be close to natural. To select the optimal consistency, tests must be carried out. The density indicator should be about 0.94. And the moisture content of the material is expressed as a percentage.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
If you combine a strip foundation with a monolithic slab, this allows you to achieve a number of advantages that are characteristic of both types of foundations.
All the pros and cons of this combination are presented in the table below. No. Advantages of the foundation Disadvantages of the foundation 1 is a very reliable, durable and strong support for the building (estimated service life is more than 100 years) construction is accompanied by large labor costs 2 the combined foundation can withstand heavy loads, which allows the construction of heavy buildings for it the structure requires a large amount of building materials, which is accompanied by significant financial costs3 the relative simplicity of the installation technology, which allows you to do all the work yourself; if according to the plan there is no basement under the building or a basement room, then after erecting the foundation, laying communications that were forgotten to be taken into account is problematic4 allows you to erect buildings on various types of soils construction requires quite complex calculations
Reliability, durability and strength are the main factors favoring the use of a combined base. They outweigh all labor and financial costs when carrying out construction on soil types with low bearing capacity.
Stages of filling the base
Backfilling of the foundation cavities is carried out after the site around the foundation has been prepared.
It is necessary to achieve optimal moisture content of the material and fill in the base. When the foundation has completely hardened, clay soil is gradually poured into the dug pit. The cavities are filled in small portions, and the layer height should not exceed 30 cm level.
Next, it is necessary to compact the soil so that it forms a monolithic, even slab. It is best to do this manually or with a special tool that runs on mains power (make sure you have access to energy sources in advance) or a gasoline generator.
The depth of the foundation, as well as its area, determine the number of layers and the volume of material used.
ADVICE. Backfilling of any type of foundation with sand should be carried out after checking the building material for the presence of foreign objects: construction debris, stones. Organic structures in the process of decay leave empty cavities, which create pressure differences in individual areas. This can cause cracks to form. Moreover, tying the internal foundation with reinforcement, pouring a new one on top of the old one, or performing any restoration work will not work - the foundation of the house will burst and heave.
Construction technology
Combined type foundations are built with or without a basement floor. In the first case, the monolithic slab is supported by the perimeter of the foundation strip, and in the second, by the entire surface of the soil underneath it, which increases the stability and reliability of the structure being built.
Installation of formwork and reinforcement cage
To build a strip foundation combined with a monolithic slab, without a basement, perform the following steps:
- conduct geodetic research at the construction site to determine the type of soil and the location of groundwater; dig trenches under the tape 0.4 m wide and 20% deeper than the freezing level of the soil in the region; a sand and gravel cushion is formed in them, which is compacted , while pouring water; they build a pit for the slab according to the project; its bottom is covered with geotextile and covered with a layer of sand-crushed stone mixture 40 cm thick, leveling the surface; a heat insulator is laid; utilities are installed: water supply, sewerage and others; formwork is installed ;create a frame from reinforcement, which is placed in two rows (the distance between them is taken from 10 to 15 cm), while connecting the slab with tape; fill the installed structure with a solution; after the concrete has reached the required strength (this period takes up to a month, depending on climatic conditions) dismantle the formwork and carry out waterproofing.
The work uses reinforcing rods with a cross-section of 12-14 mm.
On top of the tape along its entire perimeter, after 0.5 m (on average), their vertical ends are left sticking out for connection with the slab frame. When reinforcing, leave a gap of about 20 cm between the rods in one row. The distance from the bottom layer of the frame to the insulation is approximately 5 cm.
It is recommended to make and install external formwork 25 cm above the monolithic base.
If groundwater lies close to the surface, then a rolled waterproofing coating is laid in the pit and trenches on the cushion.
Concreting is carried out so that the solution covers the reinforcement from above by more than 5 cm.
Pouring a foundation with a basement is somewhat more difficult than without it. According to the technology, work is carried out in the following order:
- a strip foundation is poured; a deck is installed on top of it, covering it with plastic film; holes are made in the formwork for various communications and a door (hatch) to the basement; a frame made of reinforcement is mounted and filled with concrete.
Finished subfloor The foundation tape acts as a stiffening rib, which strengthens the entire structure and reduces material consumption, reducing the required slab thickness. Reinforced concrete can withstand heavy loads and acts as a reliable, uniform support for the building.
Types of strip base
At the first stage of construction, a strip foundation is erected. A trench is dug under it, and a layer of sand is laid along its bottom. Waterproofing is installed on top of the pillow and only after that can you begin to arrange the base itself. Strip foundations can be of two types:
- Monolithic, that is, made of concrete mortar;
- Prefabricated, that is, assembled from reinforced concrete products.
The second option is not used as often, since it requires the use of special equipment. The foundation can also be divided according to the type of burial:
- Shallow - such structures are suitable for one-story buildings or light cottages (frame, timber, foam block). The depth in this case is 0.5-0.7 meters. The soil acidity indicator is also important; it should be low or medium.
- Recessed - this type of foundation is used for the construction of high-rise buildings or when using heavy materials, for example, in the construction of monolithic cottages. In this case, the foundation goes deep 0.2-0.3 m below the soil freezing level.
Bottom line: which is better?
It remains only to determine which foundation is better to use than a slab or a strip foundation. And here only one answer can be given: it depends on the construction conditions. If the soil is sufficiently stable and the structure of the building is simple, then a strip base is suitable. But if the soils are difficult, and the building is heavy and difficult to construct, then the choice should be made in favor of a monolithic slab. Rely on the advantages and disadvantages outlined in this material, as well as the conditions of each specific construction, to choose which is best.
Backfill under the slab
For backfilling, a homogeneous material is used, optimally river sand . It is important to prevent the presence of clay inclusions in it that retain water . Different sources offer their own backfill options - either sand is used entirely, or layer-by-layer backfilling is done with sand and small crushed stone.
The presence of crushed stone allows the bottom layer to be compacted more densely - the sharp edges of small stones compact the sand layer more effectively. A leveling sand layer of 5 cm is again poured on top of the crushed stone.
IMPORTANT!
No general consensus has been reached on this matter. The subsidence of the cushion, noted in practice, occurs in both homogeneous and multilayer backfill options, which is explained by a greater load on the internal load-bearing walls than on the external ones.
General method for calculating thickness
Before starting the calculation, a geological analysis of the soil is carried out and the value of the specific pressure on the ground for the selected type of foundation is selected from the reference information. Taking into account the degree of soil heaving, the depth of the sole is calculated.
At the stage of determining the weight loads, all structural features of the building are taken into account (wall material, size of openings, weight of the roof, etc.). To the resulting value add the operating load for all floors and the average snow load for its roof type.
Knowing the area of the base of the monolithic slab and the magnitude of the specific load per square meter of the site, find the estimated volume of the foundation and the preliminary thickness of the base .
After this, the calculation must be repeated, but taking into account the weight of the foundation pit, adding it to the building loads. The resulting number is compared with the permissible pressure for the selected area. The calculated parameters will be useful when choosing the grade of concrete for the solution and the reinforcement scheme.
Flooring options
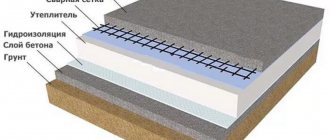
There are many options for creating a floor on a monolithic slab. The main task is to insulate the slab and ensure a high-quality microclimate inside the house.
Most experts consider the optimal composition of the floor pie to consist of the following layers:
- Layer of sand.
- “Skinny” screed 5 cm.
- A layer of insulation (penoplex 5 cm).
- Concrete screed giving strength (5-7 cm).
- Leveling screed (2-3 cm, ready-made compounds).
- Final (finish) coating.
At the same time, if the slab is sufficiently insulated from below, simpler methods can be used. For example, a “floating” floor consisting of a layer of sand backfill (as an option, you can use fine expanded clay, which provides additional insulation) and sheet materials installed on top (chipboard, plywood, MDF, etc.).
The backfill layer is carefully leveled flat and horizontal, a subfloor made of sheet materials is laid on it, then the finishing coating is installed.
There are other options for arranging the floor, but they all represent different combinations of laying layers of backfill, insulation, and leveling screed. They have no fundamental difference or significant advantage, having approximately equal performance qualities.