Designing the foundation of a private house, the walls of which are made of foam blocks, begins with determining the depth of the supporting part. A competent choice will ensure the strength and reliability of the base, the absence of cracks and other damage on the walls. The value depends on many factors, of which not a single one should be overlooked.
Types of foundations for foam blocks.
A heavy foundation for the construction of a building made of foam blocks will lead to unnecessary expenses that will not justify themselves.
Therefore, already at the initial stage of building a house from such material, the benefits are quite obvious. Three types of foundations are considered the most suitable for foam blocks: strip, columnar and slab. Each type is used depending on the structure of the soil, the value of its heaving, and the depth of groundwater. For example, if groundwater is located at a depth of three meters or more, a shallow strip foundation is suitable for a house made of foam blocks. Its difference is that the trenches for such a foundation go deep into the ground to a distance of 50 cm, so one person can dig such holes.
What properties does this building material have?
More and more people who own suburban areas give preference to foam blocks. Naturally, it’s not just a matter of price; the fact that the material has many advantages is also of great importance:
- unique structure - foam concrete is a breathable material, due to which we can say with confidence that fogging of the walls (as a consequence - the formation of fungus) is excluded;
- in summer it provides coolness, and in winter, on the contrary, it retains heat;
- it is economical - due to the fact that it retains heat well, you can save on heating;
- has excellent soundproofing properties;
- is environmentally friendly – safe for the environment and people;
- easy to process.
Strip foundation.
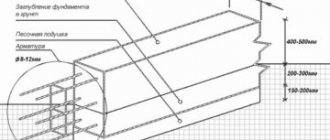
Trenches 50 cm deep are located around the entire perimeter of the house and under the planned load-bearing walls. The base of the foundation must be made wider than the walls themselves by 100 mm; a cushion of sand and crushed stone should be laid at the bottom in 2 layers, the thickness of each of which is approximately 10 cm. Then the formwork is installed and a two-layer reinforcement frame is laid. Metal rods with a diameter of 10 mm are suitable for it. Concrete is poured into all trenches at once. To prevent concrete from drying out quickly in summer, its surface is watered and covered with film after it begins to set. The hardening of the foundation continues for a month from the date of pouring. When building on a site with a high level of groundwater, the foundation is protected with waterproofing material.
Final stages of work
The cast tape is aged for 28 days. The first 3 days it is necessary to water it with water every 4 hours, then for a week watering is done every 8 hours. This allows you to equalize the stress and humidity of the outer and inner layers of the tape.
The formwork is removed 10 days after pouring.
NOTE!
Despite the long curing period, you should not try to shorten it, even if you feel that the concrete is already quite hard. The foundation is a critical element of the building, which does not allow for a free approach to technology.
Columnar foundation.
A columnar foundation for a foam block house is used on soft soil, mainly consisting of peat, clay or loam. Also, this type of foundation for a house is used on heaving soil with a freezing depth of 1.5 m. The pillars for this type of foundation are made of reinforced concrete. They must be located under load-bearing walls, corners of facades and other places with heavy loads.
The depth of reinforced concrete pillars is equal to the depth of soil freezing, but it cannot be less than 1 meter. The distance between the pillars varies from 1.5 to 2 m. If the planned house consists of three floors, this type of foundation for foam blocks is usually reinforced with a reinforced concrete grillage. Formwork in a columnar base has a bottom supported by special supports that are installed in the ground. The reinforcement frame is attached to the mounting loops of the posts using a special knitting wire. Concrete grade M200 and rods with a diameter of 8 mm are used.
Pile installation technology
After marking the construction site, pile elements are placed in the corners, under load-bearing walls in increments of 1.5-2 meters.
After marking the construction site, pile elements are placed in the corners, under load-bearing walls in increments of 1.5-2 meters. A properly installed pile-screw foundation can withstand a load of up to 25 tons per element. But installation is not difficult, and we can do it with our own hands:
- The head of the finished element is equipped with a metal heel firmly welded to the rod. The nickel has holes for attaching equipment, where the gate is secured;
- Rotation of the gate deepens the pile into the ground, and during the screwing process, soil compaction occurs;
- The foundation requires the installation of a metal frame structure, attached to the pile heads by welding. This is a lattice base, made either from rods or from channel scraps.
Before starting tying, it is worth checking the level of the piles above the ground - an indicator of 15 cm is considered the norm. If the landscape has slopes, the height of the piles will vary. In places where load-bearing wall panels are supposed to be installed, a profile is placed, the width of the shelf of which is identical to the width of the block element.
Construction and concreting of bored piles
The arrangement of the basement also requires attention. Piles are constantly exposed to aggressive environments, so all elements need to be protected
It is especially important to prevent deformation of the structure in the cold season, otherwise damage to the frame will increase the risk of destruction of the structure
Facing piles does not take much time: the house is covered around the perimeter with panel sheets, then insulated with any available material and waterproofed with film
The entire structure can be covered with siding, but it is important to leave small expansion joints between the fence and the bottom of the house; they will protect the structure from temperature deformations
Slab foundation.
A slab foundation for the construction of a foam block foundation is installed on any type of soil with the exception of clay. This type of foundation is called floating because of its ability to move along with the soil, preventing the walls of the house from collapsing. When constructing a floating base for foam blocks, a 60 cm pit is dug under the entire surface of the house. Of the entire depth of the pit, 40 cm is allocated for a cushion of sand and crushed stone, the thickness of the layers is 25 and 15 cm, respectively. After this, waterproofing is carried out and the frame is installed. It contains two layers of reinforcement with a diameter of 8 mm and a pitch of 25 cm between the rods. Such a foundation has great strength due to rigid reinforcement.
The information presented above about the types of foundations gives a brief idea of their characteristics, which allows you to make the optimal choice of the type of foundation, taking into account the structure of the local soil, the number of floors and the size of the foam block house itself.
There are other types of bases, but they are used for heavier materials. As a rule, in private construction it is considered optimal to build a strip shallow foundation for a foam block house. One of its advantages is the ability to build a basement.
Soil and geological features of the site
The degree of soil heaving has a direct impact on the integrity of the concrete base . This characteristic is directly related to the soil's ability to hold water.
During the cold season, the moistened soil increases in volume and “displaces” the concrete floor from its mass. As a result, cracks appear on the walls of the sole, and the bearing capacity of the base no longer corresponds to the required value.
The table below gives an idea of the degree of soil heaving depending on its chemical composition:
| Heaving degree | Soil type |
| absent | rock, cemented and welded rocks |
| mild | coarse rocks with low clay content |
| average | refractory soils, silty and coarse clastic soils with a clay and sand content of more than 30% |
| strong | soft plastic, highly moistened rocks, clay |
Soil formation factors can change under the influence of climate change . But for most Russian regions, soil characteristics remain largely unchanged. This gives the developer the right to refer to reference information to determine the type of soil for his site.
Without recess
A variant of a strip foundation, which is used for the construction of lightweight structures on rocky, high-density soils. Due to the fact that the depth of the base is practically absent, the concrete strip poorly performs its supporting function.
Shallow
When the concrete base is deepened into the soil 0.3 - 0.6 m to the frost line, this type of base is called shallow. It is used in the construction of structures that do not place a heavy load on the ground.
A shallow depth of the tape is chosen for conditions with unstable soils so that the structure can move when the ground moves.
Recessed
A deep-lying tape is a load-bearing structure whose base goes into the ground below the freezing level. Typically, a trench for a strip monolith of this type is dug at a depth of up to 2 m.
The massiveness of the foundation must be sufficient to prevent heaving of the soil under the building from having a destructive effect on the structure.
The recessed version is suitable for construction:
- multi-storey buildings with walls made of brick or wood;
- large buildings with basement floors and underground rooms.
Deep laying will cost the developer a lot. Therefore, it makes sense to understand the calculation of the depth of the sole in order to eliminate the overuse of building materials.
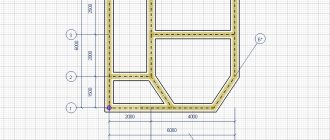
Checking the soil and depth for laying the foundation of a one-story and two-story house made of foam blocks.
The construction of a private house begins by checking the soil, and only then laying the foundation. First, the type of load-bearing surface is determined, the depth of the foundation itself is calculated, and only then the walls are erected. There is no point in saving on such events.
With the advent of durable, lightweight, and most importantly warm materials for quick construction of walls, the cost of constructing foundations has decreased significantly. These include: aerated concrete, gas silicate, foam concrete and expanded clay concrete blocks. A good choice if there is a need to lighten the structure of the house, make it warm, and there is an opportunity to save on work. It is much more expensive to build a brick house than a house made of foam blocks.
Determination of magnitude
It’s enough to just figure out the type of foundation and the presence of a basement. All options for supporting structures that are suitable for a building made of foam blocks can be of three types of laying:
- not recessed (applicable only to slabs);
- shallow;
- recessed
If we start from the presence of a basement in the house, then, if necessary, its devices choose the latter option. In this case, a columnar base is automatically excluded from the types under consideration, since it cannot be used in a building with an underground floor. Next, it is worth considering more complex criteria for determining the depth of foundation support for a building made of foam blocks.
Dependence on soil freezing
Soil prone to heaving is one that contains a large amount of water. When exposed to low temperatures, liquid turns into ice. From the physics course, you may recall that water? the only substance on our planet that has the unique ability to expand when frozen. In this situation, this property is dangerous for the foundation, since it leads to its uneven rise and the appearance of inclined shrinkage cracks on the walls of the building.
When designing the foundation of a building made of foam blocks, it is important to take into account the characteristics of the foundation soil, since they influence the likelihood of frost heaving forces occurring. Coarse foundations and sands of medium and coarse fractions are classified as conditionally non-heaving. For such foundations it is possible to use non-buried foundations. When building on clay, loam or sandy loam, the laying depth must be no less than the freezing thickness.
How to check the soil under the foundation yourself.
Checking the depth of the foundation for a foam block house.
Checking the soil by color.
Drilling test wells. By drilling a small shaft 1-2 meters deep, you can visually determine some of the qualities of the soil. You can also dig a small pit, thereby determining the location of the load-bearing layer of soil, loam or clay. But this is all relative; if analysis is impossible, a reinforced foundation is laid on piles or concrete pillars.
Direct factors, such as the presence of water, sand particles and stones, will prompt the choice and direction. But they do not cancel the need to do an analysis.
Of course, in most cases of construction of country houses, few people conduct such an analysis. Then it is recommended to develop the trench to a dense load-bearing layer. Here we will analyze more precisely all the stages, both for a one-story house and for a two-story one.
Need for a basement
Actually, we are not talking about the depth as such, but about the height of the foundation, that is, about the base of the building. But this is at the discretion of the owner. We have already discussed the ground floor in more detail.
You can come across opinions that the depth of the foundation is influenced by the quality and pattern of its reinforcement. It is quite difficult to agree with this, since when the soil moves, it does not matter whether it is pushed to the surface - pure artificial stone or reinforced with a metal frame.
But some other parameters should also be taken into account:
- what are the floors made of?
- dimensions of foam blocks;
- roof structure and roofing and “pie” materials.
Backfill depth for a one-story building.
Having set up several mines, we check after 24 hours whether there is any water in it. If it’s dry, you can look at the depth of the dense soil. When drilling with a change in soil layer (determined visually), measure the depth with a tape measure. It is better to make holes along the entire perimeter of the site, drawing up a map of the occurrence of load-bearing soil.
When checking, use a drill diameter of 200−250 mm. By drawing a preliminary sketch, you will have an idea of where and how much to dig. You will have to take into account several more important factors, the level of freezing and the depth of the bearing layer of the earth. This is also relevant for one-story and two-story houses made of any material, not just foam blocks.
Features of the building material
Foam block (PF) is a porous masonry product obtained by cutting a hardened mass of cellular concrete or casting in special molds. The bubble structure of the building material is obtained by adding a foaming agent to a traditional cement mortar. When it hardens, a process occurs that is reminiscent of rising yeast dough.
Foam blocks should not be confused with gas blocks. Foam concrete is produced by mechanical mixing of specially prepared foam with cement mortar, and aerated concrete is the result of a chemical reaction of reagents in the concrete mortar environment.
Varieties
Masonry material is made in three types:
- non-autoclave foam blocks (TU 5741-014-30414934-2014);
- tongue-and-groove reinforced PB (TU 5741-001-12346028-2005);
- especially strong blocks M 600.
Properties
Depending on the density, the building materials industry produces the following brands:
- D 300, 400, 500 - heat-insulating PB;
- D 500, 600. 700, 800, 900 – structural and thermal insulation blocks;
- D 1000, 1100, 1200 – structural foam blocks.
For the construction of load-bearing walls of one-story and two-story houses, the first two types of foam blocks are used.
Base load
When calculating the total load on the base of a building, the weight and height of the walls play an important role. To do this, you need to know the dimensions of the foam blocks, the length of the foundation perimeter and its width. The dimensions and weight of one block depend on its brand.
For example, the length of the perimeter of the walls is 20 meters, the height of the walls is 6 m (two-story house), the width of the strip foundation is 400 mm. In this case, foam block D 300 is used for laying the walls, where height/depth/width = 200/300/600 mm. The cubic capacity of 1 unit of masonry is 0.036 m3. To determine the required number of blocks, you need to multiply the length of the perimeter by the width and height of the walls and divide by the volume of one foam block, that is: (0.3 x 6 x 20)/0.036 = 36/0.036 = 1000 pcs.
Based on the data in the above table, the weight of one block D 300 = 11.7 kg, and the wall load will be 1000 x 11.7 = 11700 kg = 11.7 tons. This is much less if the masonry were brick or cinder block. Therefore, the load on the foundation from a house made of foam blocks will be much less than from a building made from other types of wall fencing.
Freezing level.
In the middle zone, ground freezing is not so deep, about 1.5 meters. In the northern regions, the level of freezing is always taken into account; development is carried out taking into account the average temperature over 3-4 years. Everything can be calculated using the formula. We will proceed from it.
Let's look at the notation. The M value shows the average monthly temperature taken in the desired climate zone. The D1 indicator is the depth figure, and D0 is the coefficient of the soil itself. Its limits can vary, from loam and clay 0.23 to rock and clastic rock 0.34. Having finished with the miscalculations, let's begin the process itself.
Dependence of the value on the material of construction
The amount to which the foundation will be buried also depends on what material the 1-story house will be built from.
Brick
- If the site has normal soil conditions, then a strip foundation for a brick house with 1 tier would be an excellent option.
This requires much less materials than when choosing a slab base. The width of the tape itself is determined by the thickness of the walls; it can protrude by 10-15 cm or be level with the walls. The depth of the laying will depend on the degree of heaving of the soil. If the soil is not heaving, then it can be buried 50-70 cm. If the soil is prone to heaving, then it can be buried 1.5 meters. - When choosing a slab base for a brick house, the depth is 50 cm. The slab can also be laid on the bottom of the pit, thereby creating a basement floor. If the groundwater level in the area is high, then do not forget about the drainage system. It will help preserve the strip or slab base. Drainage pipes are located around the perimeter of the house, placing them 10-20 cm below the supporting heel of the base.
Foam and gas block
Foam blocks and aerated concrete are materials made from cellular concrete that are lightweight. Because of this, the foundation depth will be small , especially if a private one-story house is being built.
The static load on the base of the house will be several times less than when using brick or standard concrete slabs.
Despite the ease of construction itself, when choosing the depth of depth, it is worth relying on detailed soil indicators, the possibility of variable loads, and the budget.
The porous structure of the house will be light compared to brick, but heavy compared to wood. At the design stage, all the nuances are taken into account:
- The most optimal foundation option in heaving soil conditions would be a pile foundation.
If the load is more substantial, then it is better to use a shallow shallow foundation.This option is relevant for soil freezing depths of 1 meter and for non-heaving soil.
- The shallow-depth tape is placed at a level of 60 cm, while not forgetting to arrange a sand-crushed stone cushion and to reinforce the base well. If the soil is heaving or clayey, use a buried tape, laying it 1 meter deep.
- When choosing pillars for the base, they are buried at least 1 meter, taking into account the level of soil freezing.
- If groundwater lies at a level of 50 cm or more, it is recommended to use a slab base.
timber
Houses made of timber are much lighter than structures made of foam concrete, but this also has its own nuances. For this type of house, a pile-driven or pile-screw foundation is often used. The structure consists of supports installed at certain points along the perimeter.
The supports are tied on top with metal channels or timber. The piles are screwed in to a certain depth. For a one-story timber house, this is approximately 1700-1800 mm. The depth of placement is determined based on the movement of the soil and the level of its freezing.
Frame
Buildings built using frame technology are also lightweight:
- If the house has only 1 floor, then a strip base will do. It is recommended to deepen it by at least 50 cm. If the screw pile option is chosen, the depth will be from 1500 mm.
- A slab foundation will not be very relevant here, since it is designed to withstand heavier loads, for houses of 2 floors or more. But if it is this one that is chosen, then it is recommended to deepen it by at least 40 cm.
Excavation and compaction.
What is the depth of a strip foundation for a one-story house.
Foundation arrangement option.
At a short distance from the city, soil development is carried out using a tractor. A house made of foam blocks weighs little, so a trench is dug to a depth of 1.3-1.4 meters, taking into account the crushed stone cushion. The width for a one-story house is 800 mm, leaving space for insulating the base. The standard foundation for a small building made of foam blocks is 600 mm in width. The cross-section of the monolith will be 1200×600 mm, reinforcement with fittings is mandatory, the optimal thickness of the rod is 12 mm, for both transverse and longitudinal strapping.
Compaction of the bottom of the trench is carried out with vibrating plates or gasoline rammers weighing from 100 kg. The coefficient must comply with the regulatory framework SNiP (building codes and regulations). Usually it is adjusted to 1.85−2.15 in relation to non-compacted soil. In muddy, silty or clayey soils, when tamping is carried out, a cushion of sand 200-250 mm thick is arranged, compacting it in stages.
Advice: If the bearing capacity of the soil is weak, piles are driven along the bottom of the trench at a distance of 3 meters from each other. The diameter of the pipes is chosen to be no less than 89 mm, with a length of 2.5–3.0 meters. These measures will prevent the foundation from sagging under the load of a one-story house.
General installation diagram
Procedure for constructing a shallow strip foundation:
- Removing the top layer of soil, leveling and marking the site.
- Digging a trench to a certain depth and width.
- Creating a sand cushion.
- Assembly and installation of formwork.
- Arm belt knitting.
- Pouring concrete, holding until the desired degree of hardening.
- Completion of work.
Without exception, all steps must be completed in the correct sequence.
IMPORTANT!
The depth of the trench should be increased by the thickness of the sand backfill layer, about 20 cm.
Pillow under the foundation
A layer of sand backfill is necessary to level the bottom of the trench and create a drainage effect
Screened river sand is used (ideally), without clay admixtures (this is important!). Backfilling is carried out to a thickness of 20 cm
The pillow is checked for horizontalness and compacted thoroughly. The possibility of tape subsidence depends on the quality of the seal. therefore it is necessary to achieve maximum density. The quality is checked by walking over the cushion - if no traces remain, then the tamper is of high quality.
Brand of concrete and reinforcement
For pouring strip foundations, M200 concrete is mainly used. This material has sufficient strength to support heavier buildings, but using concrete of a lower density is not recommended.
The quality of the material varies, but a certain margin of safety in this case will not hurt.
The thickness of the working reinforcement rods for the foam concrete tape is 12 mm, and for vertical (smooth) reinforcement, 8 mm rods can be used. This is quite enough, given the relatively small size of the tape.
When using composite (fiberglass) reinforcement, you should adhere to the same dimensions, since reducing the diameter of the rods can lead to deformations when pouring concrete.
Installation of formwork
To create formwork, you need to stock up on wooden edged boards.
The dimensions of the tape are small, so 25 mm thick lumber is suitable, but if the foundation parameters are large enough, you can use boards 30 or 40 mm thick.
The formwork is assembled in stages:
- Next to the trench, shields are assembled with a width of no more than 10-15 cm than the height of the tape.
- The shields are lowered into the trench, aligned along their axes and connected with crossbars. Their size determines the width of the tape.
- From the outside, the shields are fixed with inclined stops and vertical support bars.
When assembling the panels, it is necessary to monitor the tightness of the connection. There should be no gaps larger than 3 mm, as this will cause concrete to leak out. If gaps are found, they must be plugged with tow or hammered with wooden slats.
Reinforcement and knitting
The assembly of the reinforcement frame is carried out according to the standard scheme. It is necessary to form a spatial lattice of four working rods (two at the top and two at the bottom), with a depth of immersion in concrete of 2-5 cm. Vertical elements (clamps) are installed in increments of about 40 cm.
The corners are carefully designed, at which additional rods are installed to strengthen the joints.
The rods can be connected using electric welding, but for reinforcement of this size, annealed steel wire (1-1.5 mm) is usually used. A piece of wire about 25-30 cm long is bent in half, then the connection of the rods is grasped from below in a diagonal direction.
The ends rise up, grab the loop with a special hook and twist it 4-6 turns, tightly pulling the rods towards each other. The connection is strong, and the skill of operation is acquired very quickly.
Fill
Filling must be done at one time
This is important, since the connection of concrete that has begun to set with fresh pouring cannot be strong enough; if a break occurs for more than a day, you will have to stop pouring and wait until the concrete has completely hardened
At the same time, it will no longer be possible to create a full-fledged monolith, so it is necessary to organize the work in such a way as to fill it in one go.
It is recommended to order ready-made concrete, which will be delivered directly to the site. This will free up labor and help obtain material of guaranteed and uniform quality.
Pouring is done from different points so that the concrete spreads evenly along the entire length of the formwork. To remove air bubbles, use vibrating machines or ordinary pitchforks.
After pouring is completed, the surface of the tape is smoothed, then the formwork is covered with polyethylene to protect it from sunlight or rain.
Bookmark depth for a two-story building.
What is the depth of a strip foundation for a two-story house.
Sketch of optimal depth.
Such construction of a house made of foam blocks requires a reinforced foundation and careful preparation of the pillow.
The development of a pit with a depth of at least 2 meters is inevitable, since the weight of one block is 24 kg, and at least 800 blocks will be needed to build an average house with an area of 100 m², one floor.
Plus the weight of floors, floor slabs, roofing, windows, finishing inside and outside the building. It is necessary to prepare concrete for the foundation by distributing the load evenly over the entire area of contact between the foundation and the load-bearing surface of the earth.
Loads taken into account when calculating the civil protection
- weight of the foundation structure;
- walls, partitions, floor structures, ceilings and coverings, filling of openings, roofs;
- interior furniture, communications and equipment, people;
- snow and wind load.
To select a specific foundation design for a two-story house made of foam concrete blocks and its civil protection, it is necessary to take into account all of the above, because an error or considerations of saving money can cause irreversible consequences.
vote
Article rating
Preparing a foundation pit and load-bearing cushion for a two-story house.
Strip foundation depth for the house.
Preparing a pit for a two-story building.
Having developed a foundation pit, the bottom is measured using a level and the edge and area are cleared of crumbling soil. Then markings are made for the load-bearing concrete pad. The width of such concrete preparation is 100−1200 mm, with a thickness of 150−250 mm. It can be used to mount both a monolithic foundation and a block one. The formwork is prepared according to the diagram, installed around the perimeter, using reinforcement as stops, simply driving them into the ground.
Reinforcement is done in one tier, with class A 1-3 reinforcement. The mesh cell has a size of 200×200 mm, the joints are knitted with wire. The laying depth of the load-bearing belt is at least 1.8−2.2 meters for medium heaving soils of type 2. What is important when laying is to make a cushion of crushed stone under the base. The thickness of the pillow for a two-story house must be at least 120 mm. Crushed stone is laid on compacted soil. Then water drainage measures are installed or waterproofing material is laid. If construction is frozen for the winter, a pit is dug at the lowest point of the pit to collect water. The size of the sump (storm pit) must be at least 6 cubic meters.
Issues of waterproofing and insulation
The tape is waterproofed on all surfaces. Horizontal ones are insulated using a double layer of roofing felt, with an intermediate application of bitumen mastic . The bottom layer is installed under the formwork before the tape is poured, and the top layer is laid after reaching technological hardness.
The side surfaces are covered with bitumen mastic, hot tar or other means. Modern impregnations that cut off moisture from concrete at the capillary level have performed well. You can use roofing felt by gluing it to the walls with tape on a layer of bitumen mastic.
The insulation of the tape must also be done both from the outside and from the inside. For this purpose, polystyrene foam or liquid polyurethane foam is used. The choice of material is made based on the availability and financial capabilities of the owner.
Laying the foundation.
Strip foundation depth for a house.
The depth of laying the concrete foundation for a house made of foam blocks plays an important role. The entire system of load-bearing concrete structures has considerable weight. Monolithic casting (frame) of the future house is made of class B-26 concrete.
The main weight of a two-story house falls on the monolith. The entire load falls on the monolithic frame and grillage. The walls are self-supporting structures; foam concrete is simply placed in the openings. Therefore, the optimal laying depth for a house made of foam blocks in normal soils will be minus 2200 mm from the zero level of the project. But this is for the middle zone. In each case, the depth will be different; when building a two-story building, you need support with the installation of special load-bearing pillars or pillows (glasses).
To accurately calculate and optimize the costs of constructing a monolithic house, it is advisable to invite specialists from a design bureau. Specialists will carry out thorough calculations for any house and not only those made of foam blocks, clearly organize designer’s supervision during construction, and put the facility into operation. Saving you from mistakes and unnecessary waste on rework.
Relationship between the indicator and the type of foundation
This value for a 1-story building can also be determined based on the type of foundation. A few examples:
- Tape. The depth of such a foundation depends on the type of soil and the type of building.
It can be shallow and lie down to 60 cm. This option is suitable for light buildings made of wood or cellular concrete. It is used on non-heaving soils. The buried belt is laid below the freezing point of the soil. For this option, a monolithic tape with preliminary reinforcement is made. - Pile and columnar. This type of foundation is often used for one-story houses. It is convenient to use on sloping terrain. The laying depth should be 10-15% below the freezing point of the soil. This will allow the piles to transfer compressive loads from the structure.
- Slab. These foundations are resistant to ground movement. The depth will be 40-50 cm for a one-story building.
Slab structures are not buried to the freezing level. This option is suitable for use on soils with high groundwater levels.