Having a well on a personal plot is a vital necessity. Even if you have a car, it is extremely inconvenient to deliver water to your dacha in cans and bottles. Digging a well is quite a feasible task, but here you need to arm yourself with knowledge, since you will have to master methods for determining where exactly to look for water and how to correctly position the well shaft in terms of sanitary norms and rules.
Where to begin?
It is recommended to start searching for water in a well site by examining the area for the presence of springs and springs. Do your neighbors on the property have a well? The presence of both of these signs indicates that aquifers can be found on your site. You can also study where aquatic indicator plants grow. For example, the abundance of woodlice indicates the close occurrence of groundwater. Mark the proposed search area in accordance with sanitary standards for distance from the septic tank.
ATTENTION! In areas with a slope, you need to look for water for the well in its lowest part.
How often should you test your water?
The first check is carried out 3-4 weeks after drilling the well. During this period, sand and particles of hard rock raised during excavation have time to settle. The optimal time for laboratory research is the off-season, because... It is in autumn and spring that surface waters are most polluted.
In the future, water quality analysis is recommended to be carried out once a year. The following cases are exceptions:
- the water source is located in an industrial zone: testing is carried out once a quarter or at least every six months;
- water is used for drinking: testing is carried out 2-3 times a year.
An unscheduled inspection is carried out after repair work in a well/well or after installation of filtration and purification equipment.
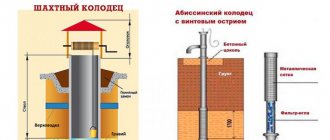
What horizons are suitable for a well?
When searching for water for a well, they stop at either high water or groundwater aquifers.
- Soil water or perched water is suitable for technical and agricultural needs, but is completely unsuitable for drinking. They can be found at a shallow depth of a meter and a half, especially if the area is low-lying or is located in close proximity to a river or stream.
- Groundwater begins after one and a half meters. While soil waters are not filtered, spilling between loose-grained layers of the earth, groundwater is held between layers of water-resistant loam and clay, rocks, limestone, and layers of sand. These multi-level layers are good natural filters, purify water and make it suitable for drinking, and do not allow harmful pollutants to enter the aquifer.
If you decide to make a well not only for domestic needs, but also to provide your family with drinking water, you should take groundwater no higher than 10 meters; the ideal option is a well fifteen meters deep.
Layers of soil, sand, stones, and clay form an internal structure with gaps and cavities of different sizes, in some places the voids are very narrow, and in other places bends are created like lenses or gaps that are filled with groundwater. These places have an abundance of water, and in narrow interlayer cavities the volume of water is minimal.
Groundwater and soil waters have no pressure; only in rare places, groundwater aquifers, sandwiched by impermeable layers, can be characterized by small pressure values.
FACT! Groundwater has an undeniable advantage. They are not only clean, but also access to them is stable, unlike perennial water, the volume and presence of which directly depend on the amount of precipitation and time of year. Also, the perched water is easily contaminated by the leaching of fertilizers from agricultural land during periods of snow melting or heavy rains.
Placement of aquifers in the ground
The water is located between layers of underground soil that cannot be eroded. It is either rock or clay. Underground layers of clay alternate with deposits of sand, gravel or pebbles, where clean water is located.
To develop an autonomous water source, it is precisely this underground layer that needs to be reached. Both the final result and the final cost of the work depend on the successful choice of the location for drilling a well.
The layer of underground water has not only different depths, but also location configurations. In some places the layer is wider and deeper, in others it is much thinner. The layer can be vertical, horizontal or have a curved shape.
What are the sanitary requirements for the location?
The water intake point should be located at least fifty meters away from toilets and cesspools upstream of the groundwater flow. Otherwise, there is a high possibility of mixing harmful substances into the water and contaminating it with pathogenic bacteria.
This is the optimal distance. If the personal plot of an ordinary summer resident is four hundred square meters, densely planted and built up, then such a norm is difficult to achieve. In this regard, there is an opinion that it is quite enough to make a well at a distance of about 8-10 meters from the toilet and cesspool.
INTERESTING! If the soil on the site is clayey, then such distance should not bother you at all. Especially provided that you take all possible measures to insulate the walls of the well, also constructing an upper protective well ring that protects the water from possible contamination during rains and spring melting, when water flows can flow into the well from the surface of the earth.
According to regulations, when looking for a place for a well, you should avoid:
- Frequently flooded areas.
- Wetlands.
- Close proximity (less than 30 meters) to public roads and highways.
Is water alive or dead?
Remember the fairy tale about living and dead water? Tap bleach is bad. Whether it’s a well or a borehole, the water from which undergoes multi-stage natural filtration in the layers of the earth, therefore, it is an order of magnitude better, cleaner and healthier. However, this is not quite true. And the first thing you need to understand is the difference in the chemical composition of waters lying at different depths.
- Surface , replenished by precipitation. This water is suitable for irrigation, but it cannot be called drinking water. It is usually very turbid, because, coming from the soil surface and passing through the clay and sandy layers, it retains a lot of suspended solid particles.
- Groundwater , also replenished by rain and melt water. An additional risk factor is pollution from industrial and livestock waste. It is these waters, together with surface waters, that fall into wells up to 20 m deep.
- Interstratal , surrounded by waterproof soil layers. They are the ones who most often go to the owners of their own well in the country. Water from a depth of 20-30 m, as a rule, contains a lot of chlorides, nitrogenous compounds and sulfates. At a depth of 30-70 m, the temperature is lower and the pressure is higher. As a result, carbonate and bicarbonate ions of calcium and magnesium are formed here, which increases water hardness. Another problem with waters at this depth is an excess of ferrous compounds.
- Artesian ones lie at a depth of more than 100 m and are the most environmentally friendly. However, they may also contain impurities that are hazardous to health. Typically, artesian water suffers from increased mineralization and a high percentage of manganese. Also, at great depths, optimal conditions are created for the development and activity of hydrogen sulfide bacteria.
Thus, “living” water extracted directly from the ground is much more dangerous than purified (even chemically) “dead” tap water. But this does not mean that wells have become obsolete. Not at all. It’s just important to evaluate the quality of the water before you start using them.
Traditional methods
These are the simplest methods of finding water, based on centuries of experience.
Observations of natural phenomena
In the warm season, in the early morning hours or in the evening, observe where the fog is thickest. The thicker the fog cloud, the closer the groundwater. This observation is justified by the fact that fogs are formed from earthly moisture, and in places where subsurface water accumulates, the fog is usually thicker; it literally swirls from the soil in such areas and spreads along the ground.
Observation of animals and insects
Dog owners may notice that their pets, in the heat, dig holes and lie down there to cool down. Animals sense where the coolest, and therefore wetter, places are. This temperature feature is also caused by the proximity of aquifers.
Midges and various midges also sense such places; they gather in flocks and swarm in the late afternoon where there is increased soil moisture.
Plant observation
Plants, as well as natural phenomena, and animals and insects can help in finding water for digging a well. The presence and proximity of aquifers can be judged by the following grasses, shrubs and trees.
- Hemlock, an abundance of nettles, thickets of sorrel and coltsfoot can be found precisely on consistently moist soil fed by groundwater.
- Birches, willow bushes, and alder love moisture and grow well only in places rich in water.
- But apple or cherry trees do not like wet soils, and their presence indicates that water cannot be found nearby. Of course, we are talking about healthy and abundantly growing trees. If the trees are sick and frail, the possibility of finding water-bearing veins is higher.
- find the aquifer veins above.
The depth of the water layer is determined by plants:
- Sandstone reeds, for example, can tell you that the water is a meter or three from the surface.
- The reed suggests an aquifer at a depth of one and a half to five meters.
- Wormwood from three meters to seven meters deep.
- Licorice from one and a half meters to ten.
- Alfalfa is from one and a half to two, but sometimes up to 15 meters.
Dowsing method
They are trying to link this method to the scientific field, which is fundamentally wrong. From this point of view, the previous information is much more useful than this method. However, he has his fans and for good reason. The emphasis is on the presence of energy information fields of various types in the surrounding reality and a person’s ability to sense these fields.
In the old days, the method had no competition and no alternative, now the possibilities of science are very high, and this entertaining method is still firmly one of the first in the popularity ratings. It would not be true if we said that the dowsing method is ineffective at all, but its infallibility does not correspond to reality either.
Since it is not always possible to use expensive services for searching for water resources in the soil, you can try it. It is better if you make an initial determination of the search location using tests with plants and animal behavior. Analyze the area from the point of view of geologically expected aquifer zones (the presence of lowlands, ravines, proximity to water intake points and springs).
Dowsing technique using aluminum frames
Manufacturing:
- The total length of the aluminum rod is about 90 cm, its diameter must be at least 3 mm.
- Having measured 15 cm from the edge, you need to bend the rod at a right angle.
- Insert the short ends into the tubes; any option will do for this.
- The diameter of the tube should be such that the rods rotate freely and move, but not at an angle.
- Take tubes 0.5 mm wider than the diameter of the aluminum wire.
- You need to make two such bent rods and insert them into the tubes.
Using frames to find water
Aluminum frames are held in both hands.
At the same time, it is very important to tune in to the search process. Let go of everything and wonder about the location of the water, completely shifting your attention to the frame.
Your hands should not be too tense; too much relaxation will also ruin the process. It is necessary to reach some golden mean.
The frames should become an extension of the person, a part of his attention, his being. It's like a kind of meditation with concentration on a specific task.
When the desired feeling of immersion and concentration occurs, a person should begin to slowly move around the site, snake-like across its entire area, testing the territory.
At the stage of finding the aquifer zone, a marking stick is driven into the area of land indicated by the frame.
It is believed that in places where there is water, the frames come into active motion.
Using a framework to determine the depth of a water resource
- From the marking peg, the footage is laid out using a tape measure in a straight line on the surface of the earth.
- Next, they begin to determine the depth of the aquifer. To do this, they slowly walk along the laid out building meter with frames, testing at what depth the water lies.
- The mark at which the frames become active and begin to spin and sway from side to side is considered a measure of depth.
Nuances that are forgotten
The well should be in a place that can be approached from any direction and from where it will be easy to draw water. It cannot be located next to the house or other buildings on the site; shrubs and trees should not grow near it. Without electricity, the pump and related equipment will not work, so the energy source must be as close as possible.
Distance between objects on the site Source permexpertiza.ru
There should be no communications at the site of the proposed well, and a trench can be dug for the water supply system.
But even if these conditions are met, the choice of point may be incorrect if, as a result, the drilling machine cannot approach it.
Alternative methods
In this case, a number of methods are used, aimed at measuring the level of humidity at different points of the site. Where there are aquifers, the humidity is significantly higher. To do this, use silica gel, brick, salt, earthenware or glass jars.
Method using desiccants
- Take a moisture-absorbing substance, for example table salt, silica gel.
- The substance is dried in an oven, poured into a dried, unvarnished clay container, wrapped in a piece of natural fabric.
- All this is weighed on precise scales.
- Usually about a dozen such testing “devices” are prepared. Each one should be signed so as not to make a mistake when re-weighing.
- Next, the containers are buried at a depth of half a meter to a meter in the ground.
- After 24 hours, the weight is re-determined.
IMPORTANT! The more the weight of the indicator increases, the higher the probability of the presence of water at a given point.
Manipulations with brick, lime and salt are done exactly according to the same principle.
Glass jar method
- Dry glass jars without lids are placed upside down throughout the water search area.
- After a few hours, the jars are inspected.
- Where the inner surface of the jar has become heavily moistened and a high percentage of condensation has accumulated, water is expected to be found.
How does depth affect the purity of the result?
The upper part of the layer can be only 1.5-2 meters under the ground. But it is necessary to remember that this will be dirty water; sewage runoff, sediment, and dirt can easily get into it. It is advisable to use the source exclusively for irrigation or domestic needs.
This layer is usually called "upper water". It is not stable, and during periods of drought or frost, all moisture can easily leave it. During the spring rains, on the contrary, it fills up. Sometimes even neighboring areas are drowned.
According to most studies, drinking springs lie at a depth of about 15 meters. In some cases, this figure increases to 25-40 m. There is a layer of continental sands, saturated and filtered. And such an amount of soil above it ensures reliable cleaning of pollutants.
The sand filter is of sufficient quality to allow drinking moisture to pass through and remove any remaining unnecessary dirt from it.
Scientific ways
The most reliable methods for exploring water in a personal plot are scientific methods. They are all based on physical principles.
Spectral seismic exploration
An impact influence on the earth's surface is organized and a special seismic-sensitive device records response impulses and oscillatory signals.
This information is entered into a computer and, using a specially created program, calculations are made about the probable location of the water. Seismic instruments allow you to scan the bowels of the earth, identifying their structure, bends, layers, the presence of voids, as well as the level of occurrence of aquifers.
The method is very expensive and is only suitable for search activities in large-scale projects.
There is also a set of existing geophysical data about certain areas; these inquiries can be made with the help of specialists in the field of hydrogeology and geophysics, they can also help in finding water.
Manual drilling
They use a hand-held garden drill with a diameter of thirty centimeters. Test wells are made from five to ten meters deep. After inserting the drill into the soil, deepening the auger, remove the soil every 15-20 cm and inspect it in order to protect the drill from breakage and check the moisture level as an indicator of the proximity of the aquifer.
The method is effective and, unlike seismic exploration, accessible to private individuals. The percentage of accuracy and efficiency here largely depends on the professionalism of the driller.
Laboratory research
The most accurate way to determine water quality is to send a sample for examination. In each federal district there are organizations that have the authority to conduct relevant research:
- sanitary and epidemiological stations,
- laboratories at the research institute,
- geological laboratories,
- accredited laboratories of Rospotrebnadzor,
- laboratories in regional water utility departments,
- laboratories in organizations whose activities are related to geological exploration.
The cost of services depends on whether you contact a private or public organization, as well as on the type of research. For example, you can conduct not a full, but a partial test aimed at identifying a separate group of substances.
The comprehensive analysis consists of two parts. The scan parameters are listed in the table.
| Chemical testing of water (analysis for compliance with SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01) | Microbiological examination of water (determination of bacteriological and parasitological indicators) |
|
|
Upon inspection, you will receive a document with detailed characteristics of the water. This will allow us to conclude whether the existing well can be used for specific purposes. Also, a report from the laboratory will help you choose the optimal cleaning system that will solve existing problems.
Video description
All stages of drilling are shown in this video.
Drilling is best left to professionals. It is difficult to do this on your own, especially if the soil is rocky. In addition, people experienced in this matter can easily determine the presence or absence of water.
Drilling is best done by a professional team Source burenie177.ru
Downhole depth gauge
The operation of the IUGS device is based on the principle of a reflected echo signal sent by a special emitter. After reflection from the bottom, the data is processed internally. In this way, depths of up to 80 m can be determined with an accuracy of 150 mm. The recommended casing diameter is from 60 to 150 mm.
Measuring the depth of the well with a depth gauge
The IUGS depth gauge consists of an electronic unit, an acoustic probe and an angular adapter. The latter device allows you to determine whether there are deviations from the vertical line. It is very convenient that a battery is used for power: this makes it possible to carry out work away from power lines.
Downhole depth gauge
Acoustic depth gauges are also very popular in the mining industry. The only drawback of devices of this type is their high cost. Purchasing such a device for domestic use is not very profitable. A more practical option is to rent a depth gauge.
Read also
How to calculate the volume of a septic tank and not make a mistake
The principle of operation of the local sewerage system. Regulations and regulatory requirements for the volume of septic tanks. What is required to calculate the volume of a septic tank? Calculation of the volume of a septic tank for a private house. Determining the number of chambers in a septic tank.
Technological process of well construction: understanding the nuances
2 options for well construction. Equipment for well construction. Stages of the technological process of well development. Arrangement of well drainage. Protection of the well from atmospheric phenomena. Recommendations on well construction technology.
Well pump for water supply: types, design, recommendations for selection
Types of pumps for water supply. Necessary information for choosing a well pump. Criteria for choosing a well pump for water supply. 4 popular models of well pumps for water supply.