In terms of composition and characteristics, diatomaceous earth brick is classified as a fire-resistant building material. It is successfully used for fire protection of reinforced concrete, wood, metal, concrete buildings and structures, thermal insulation of industrial structures and equipment. Diatomite brick is durable, affordable, and safe for human health and the environment.
Composition and production
Main components:
- diatomite;
- natural foaming agent;
- natural polymer lignin or wood shavings;
- clay;
- stabilizers - casein glue, lime.
Diatomite is the main element. Consists of shells of dead diatoms. Extraction is carried out in special quarries. Before use in production, it requires purification if there are impurities. Oxides of silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium and titanium are the main components of diatomite.
Diatomite brick is produced in a molding furnace by firing at a temperature of 700-900 degrees Celsius. The presence of clay in the composition improves refractory qualities, enhances hardness, gives shape, and stabilizes the mass of the product. The sawdust burns out during firing, forming a system of closed pores. This makes the structure of the product spongy. Foam diatomite brick (FB) differs in that instead of sawdust, the foam-forming substance saponin is added to the mixture. As a result, the finished product has improved qualities: lower volumetric mass and lower thermal conductivity.
Return to contents
Features of masonry walls made of large-format ceramic blocks
It should be noted that wall materials for single-layer walls have mediocre, both mechanical and thermal properties . We have to improve them with various design tweaks.
A large-format ceramic block is pressed against an already installed block and lowered vertically onto the mortar so that no gap is formed in the vertical seam between the blocks.
Hollow ceramic blocks are cut using special stone-cutting saws - hand-held or on a stone-cutting machine.
To lay communications in the masonry of the wall, you have to punch holes - fines. Horizontal and vertical fines along the entire length of the wall or the height of the floor are allowed to be made with a depth of no more than 3 cm. Short vertical fines located in the lower third of the floor height are allowed to be made up to 8 cm deep.
Deeper grooves weaken the wall's masonry. Therefore, their dimensions and location must be indicated in the project and confirmed by calculations. Deep and extended fines are especially dangerous for walls less than 30 cm thick.
After laying communications, the grooves in the external walls are filled with heat-saving mortar.
Connection of external and internal walls from large-format ceramic blocks
Internal walls can be load-bearing , taking the load from the structures lying above - floors, roofs, and self-supporting - partitions.
Internal load-bearing walls are erected simultaneously with the laying of external walls. Load-bearing walls must rest on the foundation. In turn, load-bearing walls serve as support for the floors and roof truss system.
1 - load-bearing internal wall, 38 or 25 cm; 2 - thermal insulation, 5 cm; 3 - outer wall
Internal load-bearing walls are connected to the outer wall using masonry bonding. To do this, insert a block of the inner wall, position 1 in the figure, into the outer wall, position 3, to a depth of 10-15 cm. The blocks are inserted not in each row, but every other row. In the second course of masonry, the inner wall block is simply adjacent to the outer wall masonry block.
Partitions in the house serve only to separate rooms. They do not bear the load from the overlying structures of the house. The laying of partitions can be done simultaneously with the construction of external walls, but it is more convenient to do this after the construction of the frame of the house.
In any case, the height of the partition should be 2-3 cm below the ceiling so that the ceiling cannot put pressure on the partition. The gap between the ceiling and the masonry of the partition is sealed, for example, with a strip of mineral wool.
Non-load-bearing internal walls and partitions can be connected to external walls using galvanized steel anchors, placing at least 3 of them in the masonry joints.
along the height of the partition. The basis for partitions made of masonry materials can be a ceiling or a concrete floor screed on the ground. The ceiling or other foundation must be designed to bear the load from the weight of the partition. If necessary, strengthen the base by installing a monolithic reinforced concrete beam under the partition.
The thickness of the masonry is chosen based on the need to provide the necessary sound insulation between rooms. Blind partitions without doorways that separate living rooms from other rooms in the house are recommended to be made from ceramic blocks with a masonry thickness of 25 cm.
Other partitions are made of ceramic blocks or bricks with a masonry thickness of 12 cm.
Products for construction and repair
⇆
To improve sound insulation, it is recommended to fill vertical joints in the masonry of partitions and internal walls with mortar.
Read: Soundproofing frame partitions made of plasterboard.
Foundation and basement of a house made of ceramic blocks
If the foundation of the house is made of prefabricated concrete blocks, then a monolithic reinforced concrete belt must be installed on top of the blocks. The masonry of walls made of large-format ceramic blocks should be supported by a continuous strip of reinforced concrete.
The thickness of the single-layer walls of a house made of large-format blocks is quite large: 38 - 51 cm. To reduce construction costs, the width of the foundation (basement) walls is made smaller than the load-bearing walls of the house. The wide wall of the house overhangs on one or both sides over the narrower wall of the basement. Vertically, the wall of the plinth falls behind the surface of the masonry walls of the house.
Without performing calculations, the width of the plinth wall can be made 20% narrower than the thickness of the masonry made of porous blocks. For example, with a block masonry thickness of 44 cm, the width of the plinth wall can be reduced to 35 cm. Reducing the width of the plinth wall by 30% is allowed, but must be confirmed by the designer’s calculations. The horizontal surface of the wall overhang above the plinth is plastered from below.
To protect the ceramic walls of the house from splashing water and moisture when the snow melts, it is recommended to choose a height of at least 30 cm above the level of the blind area.
Ceiling in the wall made of large-format ceramic blocks
1 - compensation tape; 2 — seam reinforcement (if necessary); 3 - reinforced concrete belt; 4 - thermal insulation 10 cm; 5 — additional ceramic block; 6 - wall made of ceramic blocks; 7 - a cushion of cement mortar no less than 2 cm. 8 - prefabricated monolithic, often ribbed ceiling; 9 - concrete screed 5 cm; 10 - thermal and sound insulation.
At the level of supporting the floors on load-bearing walls made of ceramic blocks, a continuous reinforced concrete belt is installed, pos. 3 in the picture. A continuous belt is installed on top of all load-bearing walls of the house. A monolithic reinforced concrete belt forms a rigid frame that absorbs the vertical and horizontal loads of the floors, as well as the upper floors, and evenly transfers them to the load-bearing walls of the house.
The installation of a monolithic belt is mandatory if the floor is made of monolithic or precast reinforced concrete. Reinforced concrete belt is also required in seismic hazard areas. The minimum dimensions of a monolithic reinforced concrete belt in section are 150x150 mm.
By the way, you can also use large-format ceramic blocks to install floors in your home.
Read: How to make a prefabricated monolithic frequently ribbed ceiling from large-format ceramic blocks.
The length of support of a prefabricated reinforced concrete, prefabricated monolithic or monolithic floor on a wall made of large-format porous ceramic blocks must be at least 125 mm.
Steel and wooden beams of prefabricated floors rest on a monolithic reinforced concrete belt with a width of 150 mm and a height of at least 100 mm. The belt is installed under the ceiling.
In one-story houses, wooden floor beams can be supported on a masonry of three rows of solid ceramic bricks. There is no need to make a monolithic belt in such houses.
Window in the wall made of porous ceramic blocks
1 - seam reinforcement (if necessary); 2 — additional ceramic block; 3 - thermal insulation 10 cm; 4 - window; 5 - masonry made of large-format ceramic blocks; 6 — reinforced concrete lintels; 7 - reinforced concrete belt; 8—frequently ribbed ceiling; 9 — heat and sound insulation slabs; 10 - concrete screed 5 cm; 11 - compensation tape.
As lintels over window and door openings, item 6 in the figure, it is recommended to use reinforced concrete products - crossbars, specially designed for walls made of large-format ceramic blocks. Such lintels have dimensions convenient for placement in the wall and do not require adjustment to adjacent wall elements.
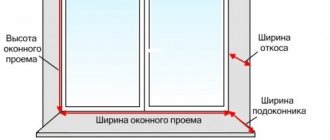
In a single-layer wall, it is recommended to place a window or door along the thickness of the wall, closer to its middle. In this position, heat loss in the slopes at the junction will be minimal.
Heat loss through windows can also be reduced by using modern designs. When making heat-saving windows, the number of chambers in a double-glazed window is increased, special glass with a selective heat-reflecting layer is used, and the thickness of the window frame is increased.
It is recommended to install roller shutters on the windows of a private house from the outside. Closed roller shutters not only protect windows from burglary, but in severe frosts they reduce heat loss through the windows, and in the summer heat they reduce overheating of the house from the sun's rays. It is better to foresee the installation of roller shutters on windows in advance, at the design stage of the house.
Connecting the roof to a wall made of ceramic blocks
1 - mauerlat beam; 2 - monolithic reinforced concrete belt; 3 — additional block made of porous ceramics; 4 - masonry of the wall from large-format blocks; 5 - insulation boards
The roof of the house rests on walls made of large-format ceramic blocks through a monolithic reinforced concrete belt, position 2 in the figure. A continuous belt is installed on top of all load-bearing walls of the house. A monolithic reinforced concrete belt forms a rigid frame that absorbs the vertical and horizontal loads of the roof and evenly transfers them to the load-bearing walls of the house.
Sizes and brands
Based on regulatory production documents, foam diatomite brick has dimensions (mm): length - 250 ± 5, width - 123 ± 3, thickness - 65 ± 3. Depending on the density, there are 4 efficiency grades (the number expresses the volumetric weight of one unit): 350; 400, 450, 500. The most commonly used efficiency is 400.
The specific gravity of foam diatomite brick is 450-500 kg/m3. Silicate white or clinker red per cubic meter requires from 1800 to 2200 kg. At the same time, the load-bearing capacity of the efficiency is not inferior.
Return to contents
The use of porous blocks in the construction of residential buildings
If you use the material described in the article, you can build a house that will be reliable and durable. The products can withstand a load of 150 kilograms per square centimeter. It is this characteristic that allows you to build buildings whose height is equivalent to 9 floors. Thanks to this strength, porous bricks can be used in any type of construction.
The manufacturer made sure that the blocks have the most convenient dimensions; they differ from ordinary bricks. On sale you can find products of various sizes, the thickness of the walls will be 250 millimeters. The speed of construction can be compared with the speed that can be achieved when using gas blocks. One team of builders, even without professional experience, will be able to build a building box using the described brick in one week.
Pros and cons
Foam diatomite brick has many advantages compared to other options:
The properties of the material are very similar to those of fireclay brick.
- Fire resistance. Withstands temperatures up to 900 degrees Celsius. It is similar in quality to fireclay, but due to its cellular structure and composition it has advantageous differences: savings in raw material costs during production;
- low volumetric weight;
- low load on the foundation;
- high strength due to the presence of silicon and clay compounds;
- possibility of using various mixtures in masonry work.
The complex production of the material determines its high price.
The disadvantages include:
- The price of diatomite foam block is more expensive than other thermal insulators due to the complex production process.
- The porous structure does not make it possible to use efficiency in external structures without a protective coating.
Return to contents
Disadvantages of houses made of ceramic blocks
The main disadvantage of ceramic blocks is their fragility.
- The outer walls of the blocks are thin, and the walls that define the voids are super thin. This material requires careful handling; it cannot be transported, loaded and unloaded at random.
- And the fastening capacity of the blocks is also low. On our portal you can find stories about how all the wall-mounted kitchen cabinets in the house from this material became floor-mounted. It’s true that block walls do not hold standard dowels, but this problem is easily solved with chemical anchors and fasteners for cellular concrete (which are more expensive than standard dowel fastenings). Although some of our users claim that if you drill blocks in a non-impact mode and with a Victory drill, avoiding excessive pressure, then any plastic dowels will hold on like a glove.
- Ideally, it is recommended to scrape walls for laying communications by hand, with a hammer and chisel. As a last resort, use wall cutters or angle grinders. The preforator in crushing mode can destroy blocks.
- Ceramic blocks absorb moisture perfectly, this must be taken into account. It is the high hygroscopicity that leads to cracks running through the blocks. Therefore: a mandatory layer of waterproofing between the foundation and the first row of masonry, protecting the wall from precipitation during construction and storing the material indoors.
- For a house made of ceramic blocks, the qualifications of the builders are very important. Not all masons know how to lay ceramic blocks; in some regions of our country it is impossible to find such specialists.
The installation technology is easy to break, and this leads to the formation of cold bridges and freezing of the walls. A house made of warm ceramics will be a damp and cold house. This is evidenced by reviews from people who have experience interacting with such builders.
GalenaForumHouse Member
Not all masons can lay large-format stones correctly. You need to use warm masonry mortar and carefully monitor how ceramic blocks are laid, especially in the corners of the house. Think in advance about how the stones will be cut so that you get even cuts and thus avoid cold bridges in the masonry.
Porizovka houses grow so quickly that builders sometimes do not meet the deadlines for the walls to gain the required strength and immediately install ceilings on them. Therefore, shrinkage of walls made of warm ceramics may also exceed permissible values.
Application of diatomite foam bricks
Used in industrial production:
- For thermal insulation of equipment, the surface of which heats up during operation, when organizing: pipelines;
- boilers for glass melting;
- coke oven batteries;
- blast furnaces;
- baths for electrolysis.
Fireplaces can be built from this material.
In construction:
- construction of non-load-bearing walls and partitions;
- laying ventilation ducts, pipes, fireplaces, stoves;
- roof thermal insulation;
- installation of barbecues;
Foam diatomite block has sufficient strength, so sometimes it replaces ordinary brick. In general, the scope of application of the efficiency factor completely coincides with the scale of use of hollow bricks. It can be used when constructing a foundation, but it is important to take into account that the heaviest brand of bricks is laid below, lighter ones are used above.
Return to contents
Disadvantages of hollow bricks
Despite all the above advantages, the building material also has some disadvantages, which we will discuss further.
Hollow brick is highly not recommended for the construction of building foundations; for such purposes it is recommended to use solid building material, since it has a large margin of safety. In addition, the presence of cavities, as well as the high porosity of the building material, mean that it is hydrophilic.
Yellow hollow brick
This is another reason why hollow brick is highly not recommended for use in foundation construction. The fact is that the material will eventually absorb moisture, which will fill the cavities inside the brick, and with the onset of winter, the liquid will freeze, which will lead to cracking of the brick.
Return to content
How and from what are efficiency factors made?
The raw material for this brick - diatomite - is mined in Russia, in the large Inzenskoe deposit. It is there that it has the least amount of impurities, which allows it to be used without preliminary purification (enrichment). Diatomite contains oxides:
- 85% silicon;
- 6% aluminum;
- 3% iron;
- 6% calcium, titanium, sodium, magnesium and potassium.
The block is produced by mixing with clay and firing the foam mixture in molding ovens. Clay is added to give strength during baking, increase fire-resistant properties and adjust volumetric weight. In general, the process resembles the production of foam concrete, but with the participation of firing in a press oven.
For the production of this building material, the standards TU 5764–001–87745488–2010 and TU 5764–002–25310144–99 apply.
Execution of channels and niches
Channels and niches should not reduce the stability of the wall and should not run over lintels or other structural parts built into the wall. The dimensions of vertical grooves and niches in the masonry, permissible without additional assessment by static calculation, are given in table. 5.
| Dimensions of horizontal channels and niches in masonry, permissible without calculations |
Horizontal and oblique canals are undesirable. If they cannot be avoided, then they must be located at a distance of at least 1/8 of the height of the room from the lower or upper surface of the ceiling. Their depth, permissible without additional assessment by static calculations, is indicated in table. 6. If one of the indicators exceeds the values indicated in the tables, then the wall’s compressive strength, bending strength and shear resistance must be checked by calculation.
| Dimensions of horizontal and diagonal channels in masonry, permissible without calculations |
The maximum depth of a channel or niche includes the depth of any opening made in constructing the channel or niche. As for additionally punched vertical channels that rise above the floor level by no more than 1/3 of the height of the room, a depth of up to 80 mm and a width of up to 120 mm are permissible if the wall thickness is greater than or equal to 225 mm. The horizontal distance between adjacent channels or a channel and a niche or opening must be at least 225 mm. The horizontal distance between two adjacent niches located on one or both sides of the wall should be twice the width of the larger niche. The total width of channels and niches should not exceed the length of the wall multiplied by 0.13. The maximum depth of a channel or niche includes the depth of any opening made in constructing the channel or niche. The horizontal distance between the end of the channel and the hole must be no less than 500 mm. The horizontal distance between adjacent channels of limited length, laid on one or both sides of the wall, must exceed twice the length of the channel. For walls more than 115 mm thick, a channel 10 mm thicker than usual is allowed if it is cut to the required depth using special equipment. If the channels are cut out using special equipment, then the channels on both sides of the wall can be deepened by 10 mm only if the wall thickness is at least 225 mm. The width of the channels should not be more than 1/2 the thickness of the remaining wall. Manually gouging out channels in masonry using a hammer and chisel is slow and labor-intensive. To reduce labor intensity and speed up work, we recommend using special electrical equipment for channel cutting, which can be purchased at specialized power tool stores.
Read the continuation in the article - Construction of a house from ceramic porous bricks (blocks), part 2
Difference between efficiency and similar materials in terms of properties
Fire resistance. This material was developed as an inexpensive and economical (in terms of raw materials) alternative to fireclay bricks (FRB). Everyone who has encountered it knows the disadvantages of CS:
- Large mass of block and masonry.
- Does not have adhesion to cement mortars; installation is only possible on clay or expensive special solutions.
- A weak block can break if dropped.
- High consumption of natural raw materials.
In the KPD, all these shortcomings were eliminated through the use of diatomite and a foam-porous structure, which provided the necessary adhesion. The volumetric mass of the block also decreased by 2–2.5 times due to foaming of the raw materials.
Load bearing capacity. As a load-bearing element, the closest “competitors” are red clinker and white sand-lime bricks. These honored participants in construction have undisputed strength and load-bearing capacity indicators that have become benchmarks. At the same time, there is one drawback for all - the large volumetric weight, which forced engineers to develop an alternative.
In practice, it turned out that rarefied (foamed) materials lose their load-bearing capacity - their crystal lattice changes. Here, diatomaceous earth again came to the fore, containing a huge amount of silicon, titanium, aluminum and iron. This balance allowed the foam block to maintain competitive load-bearing characteristics. At the same time, the volumetric weight was only 450–500 kg/m3 versus 1800–2200 kg/m3 for “competitors.” The load-bearing capacity of the efficiency repeats the capabilities of the red and silicate “brothers”, except with a higher starting threshold:
- Red from M75 (0.75 MPa) to M300 (3 MPa).
- Silicate M110 (1.1 MPa) to M150 (1.5 MPa).
- Diatomite foam - from KPD-400 (1.5 MPa) to KPD-500 (2.5 MPa).
Thermal insulation. Here, the closest competitor to efficiency is aerated concrete, which also serves as a structure, while possessing significant heat-insulating properties. Thermal conductivity of these materials:
- Aerated concrete - 0.12 W/m°C.
- Efficiency-400 (at t less than 100 °C) - 0.05 W/m °C.
As can be seen from the comparison, the efficiency is significantly higher than aerated concrete in terms of thermal insulation. At the same time, they have similar operational properties - vapor permeability, sound insulation. Compressive strength (bearing capacity) varies greatly - for aerated concrete it is 0.35–1.1 MPa.
Disadvantages of aerated concrete eliminated in the efficiency factor:
- Fragility. Foam diatomite is baked with silicates and clay, which makes it much stronger than material that hardens in a natural environment. This gave great advantages in terms of simplifying transportation conditions.
- Hygroscopicity. Any type of aerated concrete “pulls water” if it is not insulated. As a result, the material gradually deteriorates - a large percentage of lime affects it, which is easily washed away. Thermally strengthened efficiency does not have this problem due to a more durable (“sintered”) crystal lattice.
- High volumetric weight of high-strength grades. Strengthening of aerated concrete is achieved by introducing a larger percentage of quartz sand and compacting the structure. As a result, the volumetric weight reaches 1200 kg/m3. Efficiency has only three grades, the numerical values of which indicate the volumetric weight of the block:
- Efficiency-400 kg/m3
- Efficiency-450 kg/m3
- Efficiency-500 kg/m3
At the same time, aerated concrete remains an unsurpassed record holder for simplicity and accuracy of processing. Another advantage is the variety of sizes and shapes of the release (including jumpers).
Dimensions of ceramic blocks
Ceramic blocks are also used as insulation (their strength grade is M30-M50), and for the construction of load-bearing walls, blocks with a strength of M100 or higher are needed. They are made by adding special mineral additives to the clay.
Alexey Ektb FORUMHOUSE Member
If the blocks are standard, and not some test or discounted ones, then their safety margin is enough to allow you to lay floor slabs without any armored belt.
But such durable blocks have higher thermal conductivity, so walls made from them are lined with material with good heat-insulating properties.
UrailFORUMHOUSE Member
Any porous ceramic requires an external lining to protect the masonry from adverse weather conditions.
Very often, houses made of warm ceramics are built according to a combined scheme:
- the inner layer is made of durable ceramic blocks (this is about 60-70% of the wall thickness). Such blocks are selected based on the standard thickness of the supporting layer: 25, 38, 44 or 51 cm.
- The next layer is a layer of thermal insulation (20-30%),
- Then comes the outer cladding of half a brick made of low porosity brick (porosity is no more than 30%). The thickness of the cladding layer can be 8, 12 and 20 cm.
The strength of such a classic three-layer wall is equal to the strength of a pillar of 2.5 bricks of grade 100. And its thermal conductivity corresponds to the thermal conductivity of a 60-80 centimeter wall made of hollow brick.
Both masonry and facing blocks are laid only in a certain direction, connecting them with tongue and groove sides.
In practice, in Moscow and other cities and regions with a temperate climate, walls made of ceramic blocks 40 cm thick or more are not additionally insulated; only cladding and a plaster facade are used.
And this, judging by the reviews, is one of the main reasons for their popularity.
RomanF67FORUMHOUSE Member
I was building a house for a large family, three floors plus a garage complex. The house according to the project is large, has an impressive budget, and we spent a long time choosing materials with the customer. Ceramics are quite expensive, but we figured that if we spend more on materials now, we’ll definitely save on construction: ceramics don’t require so much mortar, and there’s no need for additional insulation with mineral wool. The cost of the house was within budget.
In Siberia, houses made of warm ceramics without insulation are built from blocks with a thickness of 51 cm. In the South, the best choice would be a 38th ceramic block.
Scope of application of efficiency
This material is used in all areas of industry and residential construction. It is absolutely environmentally friendly (just like its “competitors”), and at the same time has impressive load-bearing, heat-sound-insulating and fire-resistant properties. The maximum operating temperature of all three brands is 900 °C.
In industry. Using efficiency, they create furnaces for melting at a relatively low temperature - glass melting, firing and baking polymers, cooling chambers (cooling chambers). It is more widely used for thermal insulation of high-temperature furnaces. Here you can name any type of high-temperature equipment and diatomite will be appropriate as a heat insulator.
In construction and everyday life. The area of private use coincides with full and hollow red brick - there are practically no restrictions. In addition to the sufficient load-bearing capacity of the foundation, efficiency also benefits here due to its low weight. One more nuance: if the standards for bricklaying load-bearing walls are observed, it is necessary to use different brands of brick - on the first floors the strongest and heaviest, on the upper floors - in descending order of weight and strength. The efficiency has equally good properties throughout the entire height of the masonry.
Table of characteristics of wall blocks
| Name | Volumetric weight, kg/m3 | Block size, mm | Compressive strength, MPa | Thermal conductivity, W/m °C | Price 1 m3, USD e. |
| Red brick | 1800–2200 | 245x125x65 | from 0.75 to 3 | 0,34–0,43 | 85 |
| Sand-lime brick | 1200–1600 | 250x120x85 | from 1.1 to 1.5 | 0,28–0,42 | 80 |
| Aerated concrete | 300–1200 | different | from 0.35 to 1.1 | 0,12 | 60 |
| Efficiency | 400–500 | 246x122x64 | from 1.5 to 2.5 | 0,05 | 380 |
Of course, the issue of price is crucial for a private developer. The efficiency obtained its excellent properties thanks to a rather complex technological process, which is always paid for when purchasing the product. In this sense, it is difficult to compete with brick factories, of which many have been built, and the artisanal production of foam and aerated concrete. But at the same time, it is worth thinking about the costs of the foundation and insulation (for brick) and waterproofing (for aerated concrete), as well as the noise and heat insulation and fire safety that diatomite foam bricks provide.
rmnt.ru
10.10.18
www.rmnt.ru
Conscious need for poration
Mankind discovered houses made of warm ceramics thanks to the energy crisis of the 70s of the last century. Energy prices soared then that many people chose to turn off the heating altogether. Scientists were desperately trying to come up with a material for walls that would retain heat indoors, and engineers from Australia succeeded. They invented ceramic blocks for construction with a large number of voids inside. Air does not conduct heat well, and the more voids there were in the ceramic blocks, the warmer the walls made from them turned out.
The first blocks contained up to 53% air. How this was achieved: sawdust was added to the clay from which the blocks were made (then they were replaced with other porous additives). During the firing of the blocks, the sawdust burned out and voids formed in their place. The structure of the blocks ensured their low thermal conductivity, but this was not enough. To achieve the standard thickness of the outer walls of the blocks, engineers went beyond the standard brick dimensions and increased them several times. But here a new problem appeared: during construction, walls made of large ceramic blocks connected with mortar turned out to be less reliable than walls made of ordinary bricks. And then one side of the block began to be made in the form of tongue-and-groove joints.
Paveltmk FORUMHOUSE Member
We are building a house from blocks, very light, one weighs about 16 kilograms, they fit together clearly. The size of a block is approximately fourteen bricks - this speeds up the construction process significantly.
The first houses from such blocks were built in the early 80s, then the fashion for blocks spread throughout the planet, and in the late 90s the first manufacturing plant of this material appeared in our country. planet, and in the late 90s the first manufacturing plant of this material appeared in our country.
Composition of foam diatomite brick
The block is made from the following raw materials:
- diatomite;
- foaming agent – pine rosin;
- lignin or sawdust from wood;
- stabilizing additives – lime and casein glue;
The main component is diatomite. It is a fossilized algae, the rock from which is mined in quarries. Diatomite may contain various impurities that require additional purification of the raw material before use in production. The optimal composition for use would be with the following oxides:
- silicon – up to 85% of the total mass;
- aluminum – no more than 6%;
- iron – up to 3%;
- additional inclusions (magnesium, sodium, potassium, titanium, calcium) – up to 3%;
Weather
| Protecting the wall from getting wet |
Ceramic bricks (blocks) must be protected from moisture, and sufficient protection is provided by complete plastic packaging. The ambient temperature during laying, hardening and hardening of the mortar should not fall below 5 °C either day or night, since otherwise the chemical processes taking place in the mortar may be disrupted, and the solutions will not be able to acquire the properties that were declared manufacturer. When laying, you cannot use frozen bricks, i.e. bricks with snow or ice on the surface.
It is fundamentally necessary to protect the finished wall from getting wet (Fig. 8), since water accumulates in the vertical holes of perforated bricks, which takes a long time to dry. It is especially important to cover the upper surface of walls and window sills with moisture-proof coatings that protect against leaching of mortar and easily soluble substances, such as lime, from the joints, and also prevent the formation of plaque.
Specifications
dimensions
According to regulatory documents for production, the block dimensions should be as follows:
- length – 250 ± 5 mm;
- width 123 ± 3 mm;
- thickness 65 ±3 mm;
Brand
Diatomite foam brick is divided into four grades:
- Efficiency – 350.
- Efficiency – 400.
- Efficiency – 450.
- Efficiency – 500.
The difference between them lies in the density of the material; the number in the brand name indicates the volumetric weight of one unit. The most widely used is diatomite foam brick, efficiency 400.
Physico-chemical parameters
Technical conditions 5764-002-25310144-99 regulate the building material - diatomite foam brick. Its technical characteristics are presented in the table.
| Characteristics | Unit of measurement | KPD-350 | KPD-400 | KPD-450 | KPD-500 |
| volume weight | kg/m³ | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
| bending strength | MPa | 1,1 | 1,5 | 2,5 | |
| compressive strength | MPa | 0,6 | 0,7 | ||
| coefficient of thermal conductivity 200 ºС 400 ºС 600 ºС 800 ºС | W/(m*K) | 0,10 | 0,10 | ||
| 0,12 | 0,13 | ||||
| 0,13 | 0,15 | ||||
| 0,15 | 0,17 | ||||
| specific heat | kJ/(kg*K) | 0,84 | 0,98 | ||
| working temperature | ºС | 900 | 900 | 900 | 900 |
Application area
Due to its heat-insulating abilities, the product is used in both civil and industrial construction. In addition, it has good load-bearing characteristics and can withstand operating temperatures up to 1000 ºC. With all these qualities, it is inherently light in weight.
In civil engineering its application is quite wide:
- laying fireplaces and stoves;
- ventilation pipes and ducts;
- interior partitions;
- architectural elements;
Very often, such blocks are preferred if it is necessary to reduce the weight of any structure.
In industry it is common in the following areas:
- thermal insulation of melting furnaces;
- baking and firing of polymers;
- pipeline lining;
- glass melting;
Using diatomite foam brick Efficiency 400, the price of which corresponds to its qualities, the profitability when installing any equipment operating at high temperatures will be obvious.
Diatomite brick KPD-400 (GOST 2694-78)
LLC "Trading House PromStroyKomplekt" brings to your attention high-quality fireproof building materials produced at the facilities of the largest domestic enterprises. The company can order diatomite bricks from most commercially available series, including KPD-400. The products are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of GOST 2694-78 and have many advantages that guarantee a long service life even under the highest loads.
' m_image='assets/images/feed-product/diatomitovui.jpg' onclick=»attrib='Cost calculation Diatomite brick KPD-400 (GOST 2694-78)'; yaCounter24455516.reachGoal('zakaz-kat'); ga('send', 'pageview', '/zakaz-kat-ga/'); return true;">Cost calculation Diatomite brick
Information about brick KPD-400
The material is fire-resistant and is widely used in a wide variety of construction and industrial sectors. The raw material for brick production is diatomite, which is a sedimentary rock with a porous structure. Thanks to special processing, including firing in an oven at high temperatures, the amount of moisture in the material does not exceed 20%. Features of KPD-400 brand brick:
- non-toxic and complete absence of background radiation;
- low thermal conductivity, allowing protection of even the most heat-sensitive materials;
- absence of potentially flammable products, including organic substances and polymers;
- extremely low weight due to low density;
- ability to withstand temperatures over 900 °C for a long time.
Refractory brick has a bulk density of 400 kg/m³. The compressive strength is 1.5 MPa, and the bending strength is 0.7 MPa. The specific heat capacity of KPD-400 is 0.98 kJ. According to test results, refractory brick has a coefficient of 0.17 W / (m * K) when heated to a temperature of 800 °C. The chemical composition is standard for the efficiency series and includes silicon dioxides, oxides of aluminum, titanium, iron, magnesium, sodium, calcium and other elements. The brick has a characteristic orange tint.
Advantages of foam diatomite block
Carrying out a comparative analysis of brick with other building materials, a number of advantages are identified in terms of the following parameters:
- Thermal insulation. The closest analogue to a foam diatomite block is aerated concrete. Its thermal conductivity is 0.12 W/m*°C. As for the diatomite foam product, this value is lower – 0.05 W/m*°C. The thermal insulation properties of foam diatomite are much higher than aerated concrete. In addition, products made from diatomite are not susceptible to the following factors:
- hygroscopicity, the masonry does not absorb moisture from the solution, thereby the strength properties do not deteriorate;
- fragility, due to the combination with clay and silicates, the necessary hardness is created, this property significantly improves transportation;
- high volumetric weight, even for the most durable variety, KPD-500, it is 500 kg/m³, which is 1.5 times lower than the highest grade aerated concrete.
- Fire resistance. This product was developed as a replacement for the well-known fireclay, which is used for masonry of structures exposed to high temperatures. If we compare the pricing policy with the fireclay version of diatomite foam brick, its price will fluctuate in a higher range. This is due to the complex manufacturing process. Although their fire-resistant properties are similar, the diatomite analogue has a number of advantages due to its foam structure:
- saving on raw material consumption during the production process;
- reduced masonry mass;
- strength of the product due to the addition of clay;
- the use of various solutions during the masonry process.
- Load bearing capacity. This parameter can be compared with clinker or sand-lime brick. It is quite competitive, having a load-bearing capacity range of 1.1–2.5 MPa. The foam structure of most materials has a short service life due to loss of load-bearing capacity. The presence in diatomite foam brick of a sufficient volume of elements such as aluminum, silicon, iron, titanium allows it to maintain load-bearing characteristics for a long time.
- Environmental friendliness. Due to the fact that the rock has nanopores, this raw material is the most environmentally friendly of all heat-insulating materials. It does not emit toxic gases and is not subject to combustion and is absolutely safe in terms of radiation. All raw material components are natural and do not have chemical additives.
stroykirpich.com
Thermal conductivity of masonry
According to GOST 26254, λ is determined for brick and block masonry. To do this proceed as follows:
- During the observation period, the readings (arithmetic averages) for all thermocouples and tiplometers are determined.
- For masonry surfaces located inside and outside buildings and structures, the weighted average temperature is calculated based on test results. The area of the mortar joints in the horizontal and vertical sections, as well as the area of the bonded and tread sections are taken into account.
- Thermal resistance for masonry is determined.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of masonry is calculated from the value of thermal resistance.
Methods for reducing heat loss
There are 2 ways that you can use to reduce heat loss.
The instructions for action are as follows:
- use of insulation . In this case, when constructing buildings, they resort to materials such as mineral wool or various synthetic materials.
- the use of monolithic, porous, heat-insulating building products or blocks . In this case, when constructing buildings and structures, for example, blocks are used that have lower thermal conductivity than the same double sand-lime brick M 150.
What is important to know before purchasing material
Construction is a rather responsible process. In order for the work to be fast and of high quality, the volume of material must be correctly calculated. The thickness of the wall will affect the calculated figures. Thus, if you want to get a wall whose thickness is 120 millimeters, then you should lay half a brick. For a wall thickness of 250 millimeters, the products need to be laid out in one brick. 380 millimeters will be obtained if the blocks are laid in one and a half bricks. 510 millimeters can be obtained by laying 2 bricks. And for a thickness of 640 meters, two and a half bricks should be laid.
Types of thermal insulation bricks
Thermal insulating monolithic building materials will improve the heat efficiency of your home and will keep out the heat in summer and the cold in winter.
Thermal insulation brick includes 4 groups:
- cement-sand;
- foam diatomite;
- porous brick;
- heat-efficient (hollow brick).
Cement-sand
This type is obtained from cement sand, metallurgical slag, stone processing waste, carbonate sand. The price of this product is the lowest.
Note! Quite often, many of us chase cheapness when choosing a brick. Should not be doing that! It’s better to overpay a little now and save on heating and electricity bills permanently.
Foam diatomite
This type is obtained by foaming molten diatomaceous earth. Diatomite is fossilized diatomite algae. This building product has good thermal insulation properties and is often used in industry.
Porous
This type has good heat and sound insulation properties. High strength allows it to be used in facing works. Such bricks are produced by semi-dry pressing.
Thermally efficient
This product is lightweight and has low thermal conductivity. It has many voids filled with air. It is this building material that will save on home heating.
Let's take a closer look at the main parameters and properties of diatomite.
Characteristic features of porous brick
This simple production technology makes it possible to obtain a porous building material with unique properties.
This product combines the advantages of both red brick and aerated concrete, without the disadvantages that they have. This building material began to be produced not so long ago, but it has managed to gain its place in construction. It owes much of its popularity to its high thermal insulation properties. It is its energy-saving properties that are in demand in today’s society, which is aimed at saving energy resources. Externally, porous brick differs from the usual:
- its porous structure,
- sizes,
- less weight, even with large sizes,
- high thermal insulation qualities.
Various forms of porous bricks.
Advantages of porous brick:
There are many hollow cells inside the housing; they retain heat, that is, they reduce energy costs for heating the building. With the correct wall thickness, no additional insulation is required. Insulation, in this case, can reduce the thickness of the walls of the building, but the quality of the thermal insulation will not change
Whereas when using other bricks, insulation is necessary. No toxic substances are released during operation. Excellent sound insulation complies with the document SNiP 23-03-2003 on Noise Protection. Another important quality of this type: it does not overload the foundation. That is, to erect a building it is not necessary to build a reinforced foundation. The strength of masonry is confirmed by time. Natural materials are used for production: clay, and sawdust or peat are used as filler.
The formed products are fired. During the firing process, the organic filler burns out completely, forming pores inside the product. The resulting porous bricks are called breathable. The size of the bricks allows you to reduce construction time. The consumption of working solution is reduced. Foundation costs do not increase. The costs of maintaining buildings are reduced. Its thermal conductivity is characterized by a coefficient of 0.17-0.2. High frost resistance: from 25 to 100 freezing and defrosting. With such procedures, the brick does not crack, does not peel, and chips do not form on it. A high degree of fire resistance, which is ensured precisely by porosity. The material can withstand prolonged exposure to fire. When using double brick, you don’t have to spend money on the exterior decoration of the house, that is, you don’t have to paint it on the outside. Saving money on construction work.
Warm bricks are produced in 14 types of sizes, such a large assortment allows the construction of buildings with wall thicknesses, which can be from 25 cm to 50 cm. For example, just one block measuring 250x120x140 replaces two standard size bricks at once. This makes it possible, instead of laying out multi-layer walls, to make masonry from warm ceramic blocks of large sizes, using fewer of them, without using insulation.
Walls built from porous bricks:
- retains the resulting heat for a long time,
- do not absorb moisture or steam,
- are not affected by mold and mildew.
This type of brick significantly speeds up the construction process and has a positive effect on heat retention in the room.
When laying a ceramic warm block, only horizontal seams are connected using mortar. Fewer seams means less heat loss, and mortar consumption is saved. What actually happens:
- savings in foundation construction,
- savings in the construction of walls,
- saving cement mortar.
The properties of porous brick allow it to be used for the construction of residential buildings and enclosing structures. This new building material has good resistance to aggressive environments. It can be used either alone or in combination with other types of stones.
Porous blocks are used for:
- construction of residential buildings;
- internal partitions;
- construction of load-bearing structures.
Scope and properties of diatomite brick
Diatomite products are used in industry for thermal insulation:
- pipelines;
- boilers;
- electrolysis baths;
- melting furnaces.
In civil engineering it is used for thermal insulation:
- chimneys;
- ventilation pipes;
- stoves and fireplaces;
- when arranging partitions.
Note! It is allowed to build only interior partitions and non-load-bearing walls from diatomite bricks. This is due to its density and load capacity.
Depending on the density, diatomaceous earth bricks are produced in the following grades:
- Efficiency-350;
- KPD-400;
- KPD-450;
- Efficiency-500.
A special mention should be made of the product diatomite efficiency 400. It can withstand temperatures of about 10,000C and is often used for fire protection of various wooden structures.
Efficiency 400 is deciphered as follows:
- Efficiency – diatomite foam brick;
- 400 is a grade depending on the density of the material.
Diatomite brick has the following properties:
- ease;
- low thermal conductivity;
- heat resistance;
- environmental Safety.
Diatomaceous brick KPD-400I (TU 5761-00325310144-99)
- Acid-resistant brick
- Acid-resistant tiles Acid-resistant tiles PK-4 and PK-5
- Acid-resistant PS tiles
- Rashig's rings
- Fire-resistant lightweight brick ShL
- Fireclay clay PGA / PHB
Diatomaceous brick KPD-400I (TU 5761-00325310144-99)
Diatomaceous earth brick KPD-400I belongs to the group of non-combustible materials. It is used in the construction industry as a heat-insulating or sound-proofing material, and is added to some types of cement. It is used in conjunction with structural bricks to provide reliable thermal insulation.
- Description
- Characteristics
- Delivery
- Payment
- Reviews
Diatom products are suitable for creating thermal insulation for industrial equipment if the temperature of the insulated surface is no more than 900 °C. They can be used in melting furnaces, boiler equipment, electrolysis baths, pipelines.
Simple technology
Insulating brick walls from the inside does not require special technology. The method of applying polyurethane foam to walls is called spraying. When it is necessary to insulate large areas, this is usually entrusted to specialists. Indeed, in addition to the skill of working with such material, you will also need a large amount of polyurethane foam. But if you are planning to make foam insulation with your own hands, then I repeat, wear a protective suit, because the foam will stick to the body and will be difficult to clean.
The foam is a ready-to-use substance; it does not need to be diluted with anything. Also, no surface preparation is required before applying the foam. Using a gun and a foam canister attached to it, start spraying. All you need to do is apply the material evenly. After applying the insulation to the surface of a brick house, you will have to wait 3 hours for the foam to reach its full volume. And only after a day it will completely harden.
A simple technology for insulating a house from the outside