Types of windows
Walking along a city street and looking at the houses standing on it, you will notice that the roofs of the buildings are equipped with small windows. The question arises as to why they settle in houses where there is nothing under the roof except the attic. Such window openings are not always glazed. This article talks about why and why such simple roofing structures are erected.
Classic
What it is?
Parameters needed to determine:
- There is no need to confuse dormer and dormer windows. The latter are solidly glazed window openings in living quarters located in the attic of the house. Auditoriums are special convection structures that are needed for proper air circulation throughout the building.
The window is made without sealing. It is called auditory because you can hear well through it. The absence of convection puts it into the rank of ordinary ones.
- A lucarne is a window made to ventilate and maintain a balance of temperature inside and outside the attic. The difference in indicators should be no more than 10 °C. The design is made in the form of a convection grille with or without double-glazed windows. A large temperature difference contributes to the formation of condensation, and this entails the appearance of dampness and mold throughout the building. At the same time, wooden roofing structures begin to rot and require replacement.
- The window is not intended for ventilation; this function is performed by ventilation ducts. It is necessary to ensure that there is natural light in the attic, which prevents the development of fungus. Its level should be sufficient, so up to several windows can be formed over large areas. For example, on the roofs of typical four-story buildings you can count from 6 pieces. and more. They are located along the entire perimeter of the roof. In private houses, where such a quantity is not required, but one or two such devices are enough, architects and designers advise placing them on the sunny side of the house.
- Technical - the need for free access to the roof of the house, this is especially true in multi-storey buildings, to which it is not always convenient to attach a high ladder.
- As a decorative element. Even in the Middle Ages, palaces and houses of noble persons were equipped with dormer windows of various designs. Fashion in construction is constantly changing: today massive options are popular, and tomorrow inconspicuous ones, made only from lamella strips, will be in demand.
gratings
are decorative convection elements of the roof structure that create favorable conditions for the operation and maintenance of the roof.
Calculation of attic ventilation
For those who decide to make a ventilation system in the attic of a private house on their own, before starting the installation procedures, you need to familiarize yourself with the calculation method and perform it. Only a professional can guarantee the maximum level of quality of the created project. However, there are several rules that, if followed, will allow you to ensure that your attic is well ventilated.
For every 1000 square meters, there should be two square meters of ventilation holes. In special cases, you can use a ratio of 1 to 300. It is important to understand that in the calculation process it is necessary to use values that do not take into account the width of the grilles and the length of the fins, even though they disrupt the natural movement of air flows.
Naturally, exceeding the size of the vents made will also negatively affect the quality of the ventilation system, as will their lack. Large openings may allow snow, water, etc. to enter.
Existing standards
The following requirements are imposed on hearing blocks: product strength, required convection and illumination. The number and their sizes are strictly regulated by SNiPs. For example, the minimum quantity is determined depending on the total area of the roof of the house in horizontal projection (1:300). With a cottage area of 8x8 m (64 m²), the window area will be 0.21 m² - this is a square window of 45x45 cm.
They cannot be installed on all roofs. This is allowed if the angle of inclination of the roof covering is more than 35 °. They should not be installed above the contact points between the slope and the roof support beams.
Ignoring these standards, as well as unauthorized changes to the standard, will lead to the adverse consequences that were indicated above.
Windows can be formed on the pediment or roof slopes.
Recently, variations of glazing in the roof have become widespread, and are increasingly used for attic buildings. They are original and very effective, but will not be discussed in this article, since they relate to residential attics, not attics.
The traditional installation method is vertical installation of the convection unit. The following technologies are used:
- side walls located within the contour of the building are used;
- side walls extending beyond the contour of the building are involved;
- are equipped without the use of walls inside the contour of the house.
Combined option
Dormer windows
In general, there is complete confusion with attic windows. Some people believe that auditory structures installed in an attic roof can also be considered attic. Someone denies this and claims that this category includes window structures that are installed in the plane of the roof slope. All others are auditory type.
Therefore, ordinary people are confused about the names, often calling one variety another. There is nothing wrong with this, because it does not affect the attic window itself in any way. But to be honest, they started talking about attic window models as a separate group only when they began to be built into the planes of roof slopes. So, we will assume that this is the attic variety.
Now about the window itself. There are strict rules for the window area that must be present on the roof. Its value should not exceed 10% of the area of the entire pitched structure. For example, if the roof area is 100 m², then the window area should not exceed 10 m². With such a difference, natural light inside the attic will be normal, and heat losses will not exceed acceptable standards.
Dormer windows in the plane of the roof slope Source trade-point.co.uk
This was rule number one for attic windows. Now the second rule. It goes like this: it is better to have several small windows than one large one. Therefore, there is an unspoken rule that shows the ratio of the glazing area to the number of windows:
- glazing area 1 m² – 2 windows;
- 2 m² – 3 windows;
- 3 m² – 4;
- and so on ascending.
Device
Dormer windows have different shapes. A gable or single-pitch roof is installed over such a structure.
The single-pitched variety is the most common. Snow falls from it towards the glass unit, which can cause its destruction. Therefore, the roof slope must be made larger than in other options. Sometimes it looks ridiculous, since her “hat” stands out significantly from the general background.
It is more difficult to assemble gable roofs, because it is necessary for the ridge to be of increased strength. But they cope with the function of drainage much better, and they look neater than single slopes.
With the modern level of technology and variety of materials, every owner can afford other geometric shapes.
Device classification
They differ in the number of slopes and general shape:
- single-slope, double-slope, four-slope (hip);
- flat (French), as well as arched;
- triangular and trapezoidal.
Glazing can be done partially; ventilation grilles can be installed as an addition. Designs can be made without glass at all; it is completely replaced by convection blinds.
Architectural features
Triangular roof options are especially popular; in terms of vertical projection parameters, they are close to equilateral triangles with slope angles approaching 30°. Typically, their gable is flush with the gable of the building.
For your information! They are located symmetrically to the main window openings of the building. This allows the triangular shape to harmonize with the ensemble of the entire structure.
The main advantage of this option is that the triangular design completely solves the issue of sealing the entire element: the ridge is reliably protected, and there are no insulation joints at the base. Water immediately enters the drainage gutters because the window is formed flush with the common gable.
Design and installation
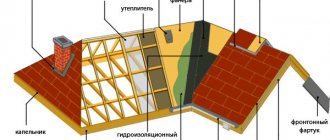
The construction scheme is simple; for a beginner, only the names of the structural elements of the roof can cause difficulty. The structures have their own frame and are sewn to the frame of the main roof.
Gable frame
It is designed in such a way that the window is located between the rafters of the roof of the house. In places of contact they are strengthened: double rafters are formed.
Construction is regulated by the rules of GOST 1250681:
- Load-bearing rafters should not extend beyond the plane of the building.
- When installing and fastening, it is unacceptable to cut into the base of the roof, i.e. cutting is prohibited as this reduces the strength of the main structure. Fastening is carried out using nails or self-tapping screws of the required length.
- The pediment of the windows must be strictly vertical, in one common plane.
- In accordance with the dimensions, two rafters are selected to form a gable triangle, which are attached to the ridge.
- The resulting frame is covered with moisture-resistant plywood or sheathing, after which the finishing coating is laid.
Common Misconceptions
There are quite a lot of stereotypical misconceptions about the design and installation of attic ventilation systems. Oddly enough, most people actually believe these myths to be true. The main ones are as follows.
- There is an opinion that in the winter season, when air temperatures are below freezing, heat escapes from the house through the ducts of the ventilation system. In fact, heat will only escape from the house through ducts if the system is designed incorrectly or poorly. The real source of this problem is poor insulation material that allows moist air currents into the attic space. Consequently, this leads to the formation of condensation, which in turn affects the integrity of the roof.
- Some people are sure that the ventilation system is only relevant in hot weather. In fact, it works at any time of the year. In hot weather, the system promotes air circulation, which prevents stuffiness from forming. In winter, with high relative humidity, it prevents the formation of fungus and icicles.
- Very often, when designing an attic ventilation system, people do not pay due attention to the size of the ventilation openings. As already mentioned, it is possible to create a high-quality, high-quality project only if the correct calculations are carried out. With a chaotic choice of the size and location of the holes, most likely, the ventilation efficiency will be zero. The average ratio of vents to ceilings should be 1 to 500.
Expanding the space
The hatch was installed, the attic became light and fresh. An attic with such a window is not suitable for winter living, but it will cope well with the role of a summer room.
Attic room
In an average house, you can carve out at least half of the entire attic area with a height of about 220 cm, and this is a noticeable increase in usable space. A creative owner is able to equip a rectangular room where the window will be the central element.
For winter use, you cannot do without modifying the window. It needs to be insulated, i.e. remove the ventilation (move it to another place) and insulate the room.
Ventilation of a warm attic
Modern heating systems very rarely use a natural air circulation system. Therefore, when converting an attic space into an attic, it is necessary to ensure absolute ventilation.
For a roof made of sheet metal and flexible tiles, it is necessary to sew counter battens, rafters and sheathing. Ventilation of a warm attic, the roof of which is made only of metal, is carried out using specialized windproof films - geosynthetics.
For roofs covered with slate, the use of counter battens is not necessary, since the attic will be ventilated in the same way as in other rooms.
Accommodation options
Roof options are divided into 2 types.
Single-pitch
The simplest solution is a flat roof with a slight slope and a slightly larger canopy.
Regarding the requirements for the device, the following can be noted: since its angle of inclination is small, the smaller the degree, the more slippery the coating should be.
Gable
This is a hybrid of a single slope and a triangle, i.e. triangular cap and the presence of side walls. Such options are erected mainly for the sake of creating a certain architectural style, since they are more complex than triangles in execution, and are less functional than single slopes.
Construction stages
- cutting into the roof rafters is unacceptable;
- the foundation must be strengthened;
- the frame is assembled after preparing the elements according to the template;
- the bottom of the window should be at an appropriate distance from the “clean” floor.
Finished frame
After construction, the frame is sheathed and the roof is laid.
A short excursion into history
For the first time, dormer windows began to be used in the architecture of medieval Europe, becoming especially widespread during the Renaissance (XV-XVI centuries). In Gothic buildings they were traditionally decorated with rich stucco or carvings, turrets, side pilasters and false columns. Structurally, they were a continuation of the wall of the building’s facade, and were located parallel to it. Visible from afar, such structures in an exquisite decorative frame became a real calling card of the entire building.
The construction term “dormer window” is used only in Russian, having no analogues in other countries. Thus, in Europe, windows in the roofs of buildings, since the Middle Ages, have traditionally been called “lucarnes” in the French manner.
Dormer windows - lucarnes
In England and the USA, the name dormer or skylight is more common - attic, skylight. Where did this rather strange name come from in our language? There are two versions of the origin of this name. One is given in V. Dahl’s Russian language dictionary, and the other is associated with the legend about the construction of the Moscow Manege.
The great Russian ethnographer Dal in his dictionary gives the following interpretation of this architectural term. “A hearing window made in the roof.” The word “rumor” previously in colloquial Russian also had the meaning of “vent”, “ventilation hole”. Dahl is inclined towards this interpretation, because “there is nothing to listen to in the attic through this window.” The legendary version associated with the construction of an arena in Moscow is also widespread. This building, now located on Manezhnaya Square of the same name, was erected in honor of the five-year anniversary of the expulsion of Napoleonic hordes from Russia.
As you can see, the playpen has many dormers
Initially, the Manege was called Exertsirgauz, and was intended for drill training of troops, as well as for reviews and parades during bad weather. The construction was initiated by the victorious Emperor Alexander I personally. The construction of the building was completed in a year, and the autocrat had to personally accept the building. But by the time Alexander visited the Manege, a big problem had occurred: the suspended ceilings, richly decorated with plaster stucco, were noticeably deformed for some reason. This did not escape the meticulous gaze of the emperor, who ordered the cause of the defect to be identified and eliminated.
The reason turned out to be simple: deformation of the rafters made of larch. The metal roof of the Manege heated up in the summer sun, and after it, the attic space, made without vents, also heated up. The civil engineer Slukhov was entrusted with correcting the situation, who found a way out in the device along the entire roof of two rows of ventilation windows. Since then, roof windows have become an integral part of the structures of all large buildings, especially those roofed with metal. And in Russian architecture, they are named after the engineer Slukhov, and the name “auditory” is supposedly assigned to them.
More information about the history of dormer windows:
What to consider?
The main thing is the total area of the lucaren, which is necessary for proper ventilation and lighting. It is a ratio of 1:300.
The remaining points relate to the shape of the structure and other architectural issues.
Steepness of the slope
This issue must be resolved for single-pitch models. The minimum value for “single slopes” is 15 °. However, in the case of installing such windows on flat vaults, this parameter must be increased to 25-30 °.
The angle depends on the roofing material: the smoother it is, the smaller the angle is needed for normal snow and moisture shedding.
Form
This parameter is important if the homeowner needs to allocate usable space, which is larger for simple lean-to variations.
Triangular shapes are more convenient and reliable than others in terms of waterproofing, so they are often chosen when modeling dormer windows.
The remaining options are purely architectural solutions.
Location
Any element in the design of the house must be in harmony with the overall appearance of the building. Recommendation from experts: place dormer windows at least 1 m in vertical projection between structures if they are made in a checkerboard pattern.
Tips for arranging a utility system
To determine the level of complexity of work when installing the system, we will consider the ventilation features of an insulated residential and unequipped cold attic space. Let's figure out what the differences are in organizing air exchange with different types of room insulation and temperature conditions.
Attic ventilation devices perform the function of thermoregulation of the entire building. With proper installation, vents and attic windows will reduce heating costs and provide the necessary level of cooling in summer
Air exchange helps extend the service life of the roof, rafter frame, equipped and unfurnished rooms under the slopes. The system also prevents snow accumulation, roof icing, and moisture formation.
Ventilation of non-residential attic space
A cold attic, not equipped for living, is a space under the roof without insulation and finishing of the walls and floor, which serves as a technical floor. However, it also needs to be equipped with a ventilation system.
It is optimal to deal with this issue at the stage of project development and construction. Rafters and gratings should be left partially open to allow air flow to circulate.
To organize the movement of air, various devices are used. For inflow - soffits with small holes that cover the overhangs from below right up to the wall of the house. The special design prevents debris and insects from entering the room, but allows air masses to flow freely.
If it is not possible to equip the eaves overhangs with soffits, they are covered with corrugated sheets with perforated elements or a regular board, leaving ventilation gaps between the elements
The panels are produced in several modifications. The most common types of products:
- solid – used for installation on gazebos, verandas, terraces;
- perforated in the center - placed on the fronts, eaves of roofs;
- fully perforated - designed for roofs covered with bitumen shingles.
When covering the roof with slate, ondulin, without the use of insulation materials, natural air exchange will occur. Therefore, there is no need to organize a special ventilation system in the attic.
The end of metal and tiled roofing, corrugated sheeting, and ondulin is not covered along the eaves. In the ridge area, before laying the covering, a porous polymer tape is installed that freely allows air flow to pass through.
Gable roofs are most often equipped with ventilation ducts, which are placed in the fronts. If there are small gaps on the overhangs, air circulation will occur correctly.
If the lining fits tightly to the eaves overhangs, you will need to make several holes, in accordance with the standards for organizing ventilation, or install special grilles with mesh with a pitch of 80 cm along the entire overhang.
Ventilation of the attic space of a pitched roof is provided by windows or openings located in the pediment or gable of a gable structure. If they are equipped with glazed sashes, burst ventilation should be carried out periodically
When arranging an air exchange system, it is necessary to take into account the design features and shape. For a certain type of roof, various ventilation elements are used.
For the efficient operation of an engineering system, devices are needed not only for inflow, but also elements that will remove exhaust air masses. In practice, various options are used - deflectors, making the ridge ventilated, leaving a gap around the perimeter of the roof, others.
Warm attic: is air exchange necessary?
The attic space is an integral part of the house, which can be used as additional space for permanent residence. However, this will require not only insulating it, but also properly organizing the ventilation system.
For the attic, everything is designed and arranged in the same way as is usually done in organizing the ventilation of a two-story house. You should think through the design in detail and select the necessary air exchange elements, taking into account the area of the attic.
The space of the equipped attic is ventilated like a normal room. Windows are opened for ventilation. If they fail, supply and exhaust valves with fans are installed in the slopes
Let's consider the basic ventilation equipment schemes for various types of roofing:
- From sheet material, flexible tiles - a ventilated area is arranged by sewing a lath onto a continuous sheathing of plywood or OSB boards.
- From metal tiles - it is recommended to use lathing along the rafters.
- Made from slate or ondulin – you don’t need a counter-lattice for free air flow and exit. The material is attached to the sheathing, which will form a distance for the free entry of air flow at the eaves and exit through the ridge.
In modern homes, aerators are installed to remove waste air. The devices prevent the occurrence of condensation and also prevent precipitation from entering the room.
The living area should be ventilated no worse than other rooms. Air masses enter through attic windows and additional valves, and exit through overhead ventilation devices.
To properly ventilate a residential attic floor, use the following scheme:
- place pipes with a deflector on the roof;
- ventilation grilles are installed in the gables;
- A heat-insulated ventilation duct is located in the upper part of the roof or outer wall.
To install air exchange elements on the roof, you must use only durable products that are resistant to gusts of wind and precipitation.
Step-by-step instruction
Stages of work
Procedure:
- According to the drawing, the roof rafters are reinforced at the installation sites.
- The structure is built between two rafters, to which two transverse supports of the canopy are attached.
- The window frame is formed.
- The resulting workpiece is attached to the beam with crossbars.
- The frame is reinforced with metal brackets, anchors and bolts.
- When fastening, leveling is carried out.
- The sheathing is being done.
- The gables are covered with boards or plywood.
- The roof covering is laid.
Frame development
Having decided why there is a dormer window on the roof, and having figured out the project, you will need to create a drawing of the window structure, determine the size of the openings, and the location of each product. It is necessary to take into account which side the windows will be turned on, how many of them there will be, and what the under-roof space will be used for.
The width of the auditory opening is calculated taking into account the width of the attic floor: it should be more than half of this parameter.
Design diversity
It seems that the variety of design solutions knows no bounds; Each craftsman strives to give the dormer window individual features. However, all this splendor can be reduced to a small number of typical window designs, which include the following models:
- With a pitched (flat) roof. A window with side walls and a flat roof, the slope of which is less than the slope of the main roof. In this design there is enough space under the ceiling (unlike a gable one).
- With a gable . A classic and much-loved cuckoo, the structure of the rafter system repeats the traditional gable roof.
Forms for every taste Source pinterest.ca
- Triangular dormer . It is a simplified version of the previous version and gives the building a romantic, fairy-tale look. The difference is the absence of side walls, which makes the superstructure simple to implement. The main drawback is that there is not much light coming in.
- Dormer under a hip roof . The hip roof with dormer windows attracts the eye, and the building acquires a respectable and elegant appearance. To achieve harmony, the angle of the hip above the dormer follows the angle of the main roof.
Dormers under the hip Source proroofer.ru
- Arched dormer . Attractive in appearance, but troublesome to arrange and therefore a rare option. Such window openings are sometimes placed vertically, one above the other.
Arched dormers Source pinterest.com
- Bat . The window opening is elongated and pointed at the corners (in medieval architecture it was called a “bull’s eye”). A plastic form, the construction of which requires professional skills from the performer.
Bat Source makemone.ru
- Anti-aircraft lamp . The design, which gives the building an airy effect, can be in the shape of a pyramid, sphere, rectangle, or oval.
Standards and nuances when designing
SNiP 11.26-2010 contains instructions for installation, location, and organization of ventilation.
Installation technology is limited by the following rules:
- the rafters framing the window opening must be double, as they carry an additional load;
- auxiliary purlins should not cut into the body of the rafter legs; their ends are fixed with steel plates;
- the frame is protected with moisture-resistant plywood;
- The pediment of the window is made vertically, the correctness is checked with a level or plumb line.
According to the standards, window houses must have walls whose height starts from 1.2 m. The frames of the vertical side railings rest on the ceiling purlins located under the opening. A distance of 0.8 m is allowed between adjacent dormer boxes; narrower spaces contribute to the accumulation of snow in the gaps.