Air ducts are the transport networks of the ventilation system. Their design and installation are regulated by strict regulations and technological maps. Compliance with regulatory requirements during construction is a guarantee of flawless operation of the network, ensuring stable air exchange.
We will tell you how to install ventilation pipes in accordance with building requirements. Every developer must know the basic rules for laying and fastening air ducts. The information will also be useful for owners to understand the cause of the problem and decide how to fix it.
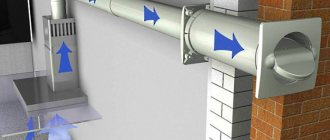
Unit 1.15 Attaching the air duct to the wall
Description
Fastening round non-insulated air ducts of medium diameter to the wall with a clamp hung on a console with a stud. This installation method helps to distribute the load evenly along the length of the beam, preventing it from bending into an unacceptable position. It is suitable for air ducts with a circular cross-section, through which air of low humidity and temperature, free of dust, contaminants, and caustic compounds, flows at low speed. They are used to install ventilation or air conditioning systems in production workshops, warehouses and commercial facilities, and somewhat less commonly in everyday life.
Two FAZ anchor bolts secure the console to the wall, a stud is screwed into it and secured, and a clamp is placed on its opposite end. An air duct is placed inside it and fixed there by clamping the screws.
Accessories
Made of steel with galvanized galvanized surface. For use in structures subject to vibration, destructive loads and constant humidity.
- Mounting console made of C-profile. The pin has perforated grooves to select the desired position. An air duct is hung on it.
- Round clamp for air duct. Connects it to the traverse and serves to evenly distribute the load. Reliable fixation with long service life.
- Traverse plug. Protects against injury during installation. Covers the end of the console.
- Expandable anchor bolt. Securely attaches the console support plate to the wall, evenly transferring force from the duct mounting assembly to it.
- Nut for the traverse bar. Fixes the position of the stud on the console using a bolt with the required thread.
- Hex nut. Used as a fastener that locks a stud with a clamp in a tire nut.
- Threaded stud. Firmly connects the clamp to the console into a rigid structure.
Variety of installation types
Bandages can be used to secure parts of the structure. The technology is quite simple. To do this, it is enough to draw up a statement in which all enlarged fragments without exception will be taken into account. Fasteners and lifting mechanisms are installed. If the air duct is round, then it must be assembled from large blocks.
The first part is freed from the bandage. Its ends must be separated and inserted into the next part. All ends are tightened with a bolt. All parts are assembled and mounted one by one.
There are also fastening methods that use slats and tires. This option is perfect for installing a structure with a rectangular cross-section. The whole process comes down to several stages. It is necessary to install all fasteners and lifting mechanisms. Raise part of the structure and secure it where necessary. If installation is carried out in a horizontal position, then traverses will also be needed. Vertically, it would be better to use a grip, which is intended for this same purpose. All joints should be connected using busbars. Where this is not possible, ordinary planks will do.
Unit 1.16 Attaching the air duct to the wall
Description
Installation of a circular air duct of small diameters (without insulation) on the wall of a room is done using a clamp secured with a pin on a cross-arm. This installation reduces the force on the console and eliminates its deflection or separation from the base. The fastening unit completely preserves the geometric shape of the air duct and prevents damage to its walls during installation, because the ventilation duct is suspended and comes into contact only with the half-clamps. It is used in domestic conditions for supply and exhaust ventilation of individual houses, as well as small car services, car washes, catering units of cafes and restaurants.
The traverse is attached to the wall through the base plate with driven anchors. A pin with a clamp is installed in its cantilever part. To secure it, the round air duct is inserted into the clamp and crimped with captive screws.
Accessories
Made of high-quality heat-resistant steel, protected from corrosion by galvanization. Used in fastening units exposed to humid air, high temperatures and aggressive compounds.
- Perforated mounting crossbar. An air duct is hung onto it through a clamp.
- Round clamp. Covers the air duct, uniformly transferring the force from its mass to the stud and, further, to the console. Durable fastener with a long service life.
- Crosspiece end cap. Improves appearance and prevents moisture from appearing in its hidden cavity. Eliminates injuries to performers during installation or maintenance work.
- Drive-in anchors with bolts and flat washers. The console is fixed, thereby redistributing the load from the air duct fastening unit onto the wall.
- Console nut. Reliably determines the location of the stud on the traverse and is clamped with a bolt.
- Hex nut. Protects the pin with a clamp, fixed in the tire, from spontaneous unscrewing during operation.
- Threaded rod. The main element that ensures the strength of the fastening unit, as well as the connection of the console with the clamp and the air duct.
How many fasteners are required?
The type of fasteners and their quantity are determined at the design stage, taking into account the weight, dimensions, location of different types of air ducts, materials of manufacture, type of ventilation system, etc. If you plan to tackle these issues yourself, you will need to do the calculations and use reference data.
The consumption rates for fastenings are calculated based on the surface area of the air ducts. Before you begin calculating the surface area, you need to determine the length of the duct. It is measured between two points where the center lines of the highways intersect.
If the duct has a round cross-section, its diameter is multiplied by the previously obtained length. The surface area of a rectangular duct is equal to the product of its height, width and length.
All calculations are made at the preliminary stage, the obtained data is used during installation, marking helps to observe the calculated distances without allowing errors.
Then you can use reference data, for example, standard indicators of material consumption (NPRM, collection 20) approved by the Ministry of Construction of the Russian Federation. Today this document has an inactive status, but the data contained in it for the most part remains relevant and is used by builders.
The consumption of fastenings in the directory is indicated in kg per 100 sq. m. m. surface area. For example, for round seam air ducts of class H, made of sheet steel, 0.5 mm thick and having a diameter of up to 20 cm, 60.6 kg of fasteners per 100 sq. m. will be required. m.
A properly designed and installed air duct system not only functions flawlessly, but also organically complements the interior of a modern home.
When installing air ducts, straight sections of air ducts along with bends, tees and other shaped elements are assembled into blocks up to 30 meters long. Next, fastenings are installed in accordance with the standards. The prepared air duct blocks are installed in the places designated for them.
The following article will familiarize you with the regulatory requirements for organizing ventilation in a private house, which all owners of country property should read.
Unit 1.17 Attaching the air duct to the wall
Description
Round air ducts, in addition to ventilation, are used to remove air with excess moisture, contaminated with dust, or to move bulk cargo. The load on the air ducts and their mounting points increases, and vibration and noise may occur. For such situations, it is better to use a more reliable fixation of the air duct on the wall at two points along its height, without using a stud. And the clamp must be equipped with a vibration-sound-insulating insert. Such fasteners are used almost exclusively in industrial conditions for smoke removal systems, pneumatic transport and aspiration.
Two consoles are placed on the wall so that one supports the air duct from below, and the other presses it from above. To fix each traverse to the wall, use a pair of FAZ anchor bolts. The FAF corners are fixed in the grooves of the consoles with a bolt and nut. And a clamp with an air duct is attached directly to them.
Accessories
Made from galvanized steel. They work excellently in loaded ventilation systems, with significant exposure to noise, vibration and elevated temperature of the moving environment.
- Installation crossbar (C-section profile) to support the air duct from above and below. The clamp is mounted with a gap from the wall, the size of which is determined by the project. The bolts in the tire are perforated.
- Clamp for fastening air ducts, designed for long-term operation. It is rigidly attached to the console using an angle, simultaneously fixing the position of the round air duct.
- End plug for traverse. Covers the sharp edges of the tire, thereby eliminating cuts and injuries to installers.
- Expanding anchor bolt. Serves to fasten the supporting surface of the console to the wall and balances the loads arising in the fastening unit and the air duct.
- Metric bolt with T-shaped head (for perforation). You need to secure the corner with a clamp to the traverse.
- Hex nut. Fastener for tightening captive screws that clamp the duct with a clamp.
- Corner with two holes. A universal part that connects the console and clamp to the air duct into a strong and durable fastening unit.
Methods for fixing air ducts
Fasteners are selected depending on the cross-section of the hole and the location where it needs to be fastened.
- corner bracket. Parts of the air duct are secured to the bracket using screws and screws;
- z-shaped holder. Used for rectangular sections. Attached to each other with screws and bolts;
- profile with studs. To ensure sound insulation, it is permissible to use a rubber profile;
- fastening with punched tape. Best suited for fixing the air exchanger in a circle. To make such a fastener, you need to make a loop and attach it to the bolt where the ventilation elements have connections. Among the advantages of this fastening method is the relatively low cost. The disadvantage is that the type of fastening allows vibration due to loose fixation;
- The clamp is ideal as an addition to fixation with punched tape. It helps reduce noise levels. Use only for pipes that have a diameter of less than 20 cm;
- clamps are used in addition to a hairpin;
- fastening with anchors. To make such a fastener, you need to make a hole and attach it with a pin;
- traverses with studs. The method is suitable for fastening pipes with rectangular sections and large dimensions. The air exchanger rests on a traverse in this type of mounting;
- a metal beam with a clamp and a pin that is attached to it.
Methods for mounting air exchangers vertically
First of all, mark the places that are intended for fastening elements. The next step is to install the parts. The air exchanger elements are brought to the location where installation is to be carried out. Next, attach the bracket, lift, console, and block system to the outer wall. The structure with braces is assembled using single parts. The umbrella is being installed and the part of the air duct that has already been assembled is being lifted. The structure should be leveled using guy wires and secured in a suitable position. The vertical air duct is extended using:
- lower construction extension;
- upper extension of the air channel;
- use the extrusion method.
When there is a need to increase the air duct on the wall outside, the first technology is used. To do this, they use a winch with a cable that is lowered into the shaft or along the wall. Fastening is done using lifting mechanisms. Next, the air exchanger is installed in stages. The link is lifted by a rope to the junction and secured. The remaining elements of the ventilation structure are installed in order. Upon completion of installation, the winch is removed and the remaining parts with the umbrella are strengthened.
When the structure slightly exceeds the weight for which the mechanisms are designed, the following method is used. All the necessary blocks are assembled, and large-sized elements are combined with an upper extension. Initially, all parts are fixed to the supports separately, then the next part is installed in the place indicated in the project. And from it the winch rope is lowered to the first element.
Using a winch, the cable is tensioned, and the fastenings are removed from the first structural element and transferred to the next one. There the lifting assembly is secured with supports and removed. Such actions are carried out until the required level of growth is reached.
The extrusion method is used to install vertical air exchangers in hard-to-reach places. Initially, 2 winches with blocks are installed, and fasteners are screwed into the walls. Part of the structure is assembled from elements, and the slab is attached to the lower flange with lugs. They are needed to pull cables through them. The assembled air exchanger is raised until the top flange is visible above the building. Next, elements with an umbrella are attached, they are then connected with cables to the roof of the building.
General rules
When installing cables hidden or open, indoors or outdoors, there are several general rules:
- The optimal distance between fasteners is 40-50 cm.
- If self-tapping screws, screws, or dowels are used, they are tightened all the way so that the protruding cap does not damage the insulation.
- The cable is laid evenly, without humps. If a reserve is needed, it is placed in the least visible place.
Basically, that's all the recommendations. They are versatile and uncomplicated. The distance can be reduced if necessary. For example, at turns of the route, the fasteners are installed at a short distance from the bend point - 5-10 cm. The task is to ensure reliable fixation and prevent sagging.
Standard distances in relation to building structures and utilities
Along with the rules for installing ventilation, there are restrictions related to the distance from engineering and construction buildings. With them, fastening ventilation ducts is not allowed:
- between the ceiling and round-type ventilation communication - 100 mm, between walls - 50 mm;
- the structure of rectangular air ducts and reinforced concrete columns should be at a distance of:
— 100 mm with ventilation side 400 mm;
— 200 mm on the side of the ventilation system from 400 to 800 mm;
- 400 mm with ventilation side from 800 to 1500 mm.
- the distance between communications and ventilation should be at least 250 mm;
- the distance between electricity cables and ventilation should be 300 mm;
- building elements and joints of ventilation systems must pass at a distance of at least one meter.
How to fix a horizontal ventilation system?
To secure the horizontal air exchange system, you will need metal brackets in the form of corners. They will need to be secured to the wall using a backing. How deep the bracket needs to be mounted into the wall depends on the size of the pipe.
If you need to fasten equipment parts to a reinforced concrete column, then gussets made of metal sheets, corners, and struts are used for this purpose. First, using dowels, the gusset is strengthened on the column, and a brace and corner are attached to it.
To attach the equipment to a concrete slab, you will need special brackets; if the column is made of metal, then traverses and clamps. Metal brackets will be required to attach the structure to the beam.
Air duct mounting methods
The mounting of vertical air ducts is naturally installed in different ways. Horizontal round systems can be mounted in three ways. The methods for attaching them look like this:
- using a clamp and a pin, the air ducts are secured to the wall;
- thanks to the punched tape, there is no need for a clamp here;
- using a clamp for fastening air ducts and punched tape.
Rectangular systems are mounted using air duct fastening parts:
- z-shaped profile and studs;
- L-shaped profile and studs;
- traverse and pin. This is how the air ducts are attached to the ceiling.
Air duct fasteners can be fixed using a clamp, anchor and R, V-shaped bracket.
When installing hood mounts, it is necessary to maintain the distance due to regulatory, generally accepted standards.
Recommendations for calculating fastenings
- The placement of the duct axis relative to the plane of the building structure is only allowed in parallel.
- The maximum length of the distance from the axes of the air ducts to the building structures is calculated using the formula:
- for round ducts
where Dmax is the maximum diameter of the air duct together with the insulating coating, mm;
- for rectangular air ducts
where bmax is the maximum width of the air duct, mm;
x - distance between the outer surface of the air duct and the wall (not less than 50 mm), mm.
3. From the outer surface of the electrical wires, the shortest distance to the axis of the air duct can be determined by the formula:
- for round ducts
- for rectangular ducts
- The pipelines are laid so that the minimum distance from the outside of the pipeline to the axis of the air duct is:
- for round ducts
- for rectangular ducts
- The minimum distance between the axes of the air ducts, when they are laid parallel to the same level, is calculated using the formula:
- for round ducts
- for rectangular ducts
where Dmax and D'max are the diameters of the air ducts, mm; b'max and bmax are the dimensions of the sides of rectangular air ducts, mm.
- The axis of the air duct relative to the ceiling is placed at the minimum distance, which is found using the formula:
- for round ducts
- for rectangular ducts
- If air ducts pass through building structures, then the distance from the flange connections to the surface of these structures must be more than 100 mm.
- Installation in a horizontal position of metal air ducts on a wafer connection is carried out at the distances between the fasteners:
- no more than 4 m if the diameter of the round duct or the larger side of the rectangular duct is less than 400 mm;
- less than 3 m if the diameter of a round duct or the larger side of a rectangular duct is 400 mm or more.
- When installing metal air ducts on a flange connection in a horizontal position, the distance between the fasteners is assumed to be:
- for non-insulated air ducts no more than 6 m, if the diameter of a round air duct or the larger side of a rectangular air duct is up to 2000 mm;
- for insulated air ducts, if the diameter of a round duct or the larger side of a rectangular duct is more than 2000 mm, they are accepted as working documentation.
Installation of a rigid rectangular duct
To connect ventilation pipes to each other and to fittings, various connecting devices are used. The flange method is considered the most popular in this matter. Here, metal corners and tire rails are used as flanges for grooves of various profiles. They are sealed in the form of a square.
In practice, there are several ways:
- An object of the required cross-section is first manufactured and then secured by welding.
- A common option is to connect the parts of the channel using anti-corrosion rivets. They look like special clamps. On the metal structure, in the groove of the bus bar, stiffening angles with technological holes for connection with bolts are installed. Connections between metal structures are sealed with a rubber seal of six to eight millimeters. You can use silicone sealant. If there is warm air in the ventilation system, then asbestos cardboard is used in its design.
Not everywhere, thanks to bolts, studs and nuts, sufficient tightness of the system is achieved.
If the pressure in the structural ventilation device is not more than 1000 Pa, but the dimensions of the sides of the structure are large, clamps in the form of a bracket are used:
- bracket more than 900 mm with twenty mm flanges;
- bracket more than 1100mm at thirty millimeters.
At a pressure of more than 1000 Pa in the system, the need to use staples is as follows:
- for 20 mm joints, from 700 mm is used;
- for 30 mm joints it is used for widths greater than 900 mm.
On straight sections of the structure, fewer clamps are required at joints than on curved and conical surfaces. After any installation, be sure to check it.
Design features and dimensions
Remember that when purchasing PVC air ducts, you need to stock up on adapters that will be needed to connect the plastic pipe and the hood. Adapters are also used for air duct bends and connection to general house ventilation. If a corrugated product is used for exhaust, then you can save money on adapters for bending the pipe.
Any bending also negatively affects the functionality of the hood. When installing air duct in the kitchen, try to avoid 90-degree angles. This will cause overload of the hood, which will significantly reduce the service life of the product.
The diameter of the plastic pipe is selected according to the cross-section of the ventilation hole. The sizes of rectangular and square PVC kitchen air ducts are standard. The most commonly used values are: 110 × 55, 120 × 60 and 204 × 60 mm. The sizes of round plastic pipes vary from 110 to 150 mm in diameter.
You can purchase these products at almost every hardware store. It is worth noting that the price of flexible air ducts is slightly higher than that of flat PVC ducts.
Installation of flexible air duct
Flexible systems are much easier to install than rigid systems. A hood over a gas stove is an example of installation. There are three types of system installation:
- Sealing. With this type, the connecting joint of the system is sealed with sealant, and is not the only method in horizontal installation.
- Cutting. According to this installation option, the flexible ventilation pipe is stretched. Measure the required length, and cut off the required part along the turn.
- Compound. In this case, the air duct is placed on the connector. At a minimum, the connectors must have a five-centimeter presence of part of the system on one side.
The flexible air outlet installation is installed taking into account the air movement in the system. Properly installed ventilation reduces noise. This can be achieved by installing excellent ventilation, with an arrow indicating the air flow.
Hood installation
Preparation
Before proceeding with installation, choose the correct location for the equipment - gas stove + hood. The photo shows an electric stove - the recommendations are also relevant for gas objects.
Before installing a hood over a gas stove, you need to first prepare the room.
- Mark on the kitchen plan the location of all communications, as well as installed appliances, if the installation is carried out in an already used room.
- The energy dependence of the hood requires the presence of an outlet (but not above the stove!) with 220 V connected. A model with an automatic switch is preferable: it will always turn off in time if a short circuit or fire occurs. If the kitchen is not equipped with a grounded socket, the rules for installing a hood over a gas stove require that a separate RCD (16 A) be provided in the electrical panel. Connect to the network a line of three wires “zero”, “phase”, “ground” in yellow insulation with a green stripe running along it.
- The value between the exhaust device (lower edge) and the surface of the stove (burner) is measured.
- The completeness of the package is checked for the presence of the necessary fasteners, hooks, dowels, etc.
- The location for attaching the structure is marked.
Installation
- the air duct is assembled. It can be with a square or round cross-section. Standard option - size 130x130 mm It is better to choose a plastic design with smooth internal surfaces. Its diameter should be the same along its entire length, correspond to the cross-section of the ventilation hole and, preferably, have a check valve.
- Using a hammer drill, holes are drilled for the hood clamps.
- The screws are screwed in.
- Using a level, check the horizontal installation.
- The hood is hung (without a box).
- Connects to the exhaust pipe connected to the duct.
- The hood is connected to an electrical outlet. If the cord is missing or short, an autonomous line is drawn from the panel or diverted from the outlet closest to the hood. Making twists insulated with insulating tape in places where the missing part of the cord is added is strictly prohibited.
- A test run of the technical device is carried out in all modes.
- During normal operation, the final stage is to secure the box.
Exhaust equipment installation options
Comparative illustration: gas stove and electric
According to installation design, exhaust devices are:
- built-in type - the entire installation is hidden in a hanging cabinet;
- fireplace and dome type - the structures are fixed on the wall;
- island model - mounted on the ceiling;
- corner hood - placed in the corner;
- flat model - involves two planes of fixation: from the back - to the wall, from above - in the hanging cabinet.
Any of the models provides a certain type of filter elements that absorb strong odors, grease and other secretions.
Used as filters
- Grease traps are installed only in kitchens with a ventilation shaft.
- Carbon filters are elements of modern treatment systems with recirculation mode of operation.
Even if you follow the rules for installing the exhaust system and operating it, the efficiency will be reduced if preventive maintenance is not carried out in a timely manner: clean surfaces, change filters. Thus, creating the conditions necessary for a safe and comfortable stay in the kitchen is not difficult at all. Various methods are used for this. But it is the forced system with local exhaust above the stove that is considered the most optimal and common option.
Installation of insulated air duct
Due to its affordable price, a flexible ventilation system with thermal insulation is in demand. When installing this type of system, several points need to be taken into account:
- When connecting two parts of a system or connecting to equipment, accurate measurements are required. It will be used to cut and adjust parts of the system.
- When putting the pipe on the connector, the insulating material is pressed out for convenient work with the internal component of the ventilation material.
- The joint of the internal parts of the system is connected with aluminum adhesive tape.
- After sealing the internal parts, the insulation is returned to its place and also connected with an aluminum adhesive strip. Then it is secured with a nylon or metal clamp.
Recommendations for selection
Experienced specialists give a number of tips to make it easier for owners to choose products for arranging a ventilation system. Some of them:
It is best to buy products in branded stores or specialized retail outlets. In addition to the product, the kit should include instructions for use, as well as a warranty card.
If such documentation is missing, it is better to refuse the purchase. It is necessary to take into account the design of the products so that they fit organically into the interior of the room. The manufacturer is of no small importance. It is advisable to choose high-quality branded models. No need to focus on low prices
Of course, a high-quality and reliable ventilation system will be quite expensive, especially if good materials are used. However, you need to understand that high-quality models will serve for many years without complaints. Products must have sufficient performance. If the ventilation system is weak, the hood will not be able to cope well with its main task, so the exhaust air masses will remain in the room.
In addition, when choosing the components of the ventilation system, you need to take into account the main functions of the kitchen hood. The latter must meet the following characteristics:
- An attractive appearance is important so that the device fits organically into the interior, complementing it.
- Low noise level during operation.
- The ability to quickly and to the required extent remove foreign odors.
Safety precautions when installing an air duct
Each installation in construction must be guided by regulatory documents. When installing ventilation, equipment installers are guided by OST 36-108-83, which is interpreted as “Installation of air conditioning and ventilation systems.” Safety requirements". This act describes the “dogmas” of safety precautions. Indicators of hygiene and sanitation are reflected. Environmental requirements are also covered.
This document ensures the safety of all team members performing their proper duties during installation. The act contains a large list of important notes for carrying out labor activities at the work site:
- providing the employee with special clothing, footwear and personal protective equipment;
- the working day schedule and rest time are prescribed;
- lighting conditions at the work site;
- preventing onlookers from entering the installation area.
Safety precautions cannot do without fire extinguishing equipment at the equipment installation site. There must be essential medicines at the installation site to provide assistance to the injured.
According to this document, each member of the installation team must have access to the site. Admission is permitted after instruction regarding a particular object. Issues of safety and first aid are covered.
Before the installation of ventilation equipment begins, the installation plan and the availability of all components and components necessary for installation must be agreed upon.
Along with this regulatory document, installation specialists must also be guided by the air duct installation flow chart. Along with the above aspects of on-site work, installers can be given additional instructions if required by production needs - working at heights, with winches and hydraulic lifts. After this briefing, the employee is given a document certifying the acquired knowledge regarding work in special conditions.
thermal ducts in the floor against the ceiling
Floor ducts are less noticeable.
Heating channels should never be an afterthought. Your climate, the size of your home, the number of floors and the height of your ceilings should influence your decision to place duct openings in the floor or ceiling. Choosing the right location can reduce your home heating costs.
Floor ducts
Warm air is less dense than cold air. This is why heat rises. Floor ducts are efficient because they deliver heated air at floor level. The heat then rises and continues to warm the rest of the room. Floor vents are typically used in homes where the furnace is in the basement or ductwork (pipes from the furnace) run through an underground crawl space. Heat should spread over a shorter distance and penetrate the room faster and more efficiently.
Ceiling ducts
Holes in ceiling ducts are commonly found in homes that do not have a basement. The furnace may be in the garage, attic, laundry room, or in an interior closet for access. Ducts typically run through walls, behind drywall, and out through openings in the ceiling at first floor levels. It then moves along the floor joists to any upper levels. Holes in ceiling ducts work against the general law of physics, which states: "Increase in temperature." For this reason, some homeowners use ceiling fans that rotate in a reverse, slow motion to help dissipate heat downward to warm the room.
similarities
As part of an HVAC system, floor and ceiling ducts supply warm, cool, or simply moving air. Homeowners can also combine the two types to produce better efficiency. For example, owners of multi-story buildings may use a combination of in-floor ducts for heating and ceiling ducts for cooling.
Differences
Ceiling ducts cannot be used with radiant heating systems that generate heat from the floor. Floor ducts are not as visible as ceiling ducts. They can be disguised with decorative vent covers that match carpet, tile or hardwood floors. Ceiling ducts are more visible than floor ducts and are more difficult to disguise. Because heat dissipated from ceiling ducts first reaches the upper level of the air, the HVAC system must work harder to dissipate heat into the room. Floor channels located under the window give better results; warm air compensates for any cold air entering around the window and reduces condensation or freezing on the window. The opposite is true for ceiling ducts, which should be located as far away from windows as possible so that the heat warms the room, not the window.
, Introduction to interior design ceilings and their functions
Introduction to ceilings and their purpose in the interior
The ceiling trim or product is attached to the ceiling strips underneath the roof frame and is typically some form of drywall. We usually see ceilings as a flat plane above us that hides the roof or floor frame.
They are usually made of plasterboard on a lightweight wood frame attached to the roof or floor frame. However, ceilings can be made from a variety of materials and perform a number of functions, as listed below.
Ceiling aesthetics
We usually see the ceiling as a flat white plane that sits above us. However, the ceiling can be made from different materials such as timber or PVC, suspended within a grid with different panels imparting different properties, painted, textured, vaulted, have recessed elements or have a suspended bulkhead.
All of these different treatments can add another dynamic or element to the space. We can create a much more interesting effect and/or evoke a different mood by matching the trim or shape to the ceiling.
The ceiling trim or product is attached to the ceiling strips underneath the roof frame and is typically some form of drywall.
Sound
Ceilings
are one of the main areas that reflect pure sound. That is, the ceiling is often a large, flat, rigid plane that is ideal for reflecting sound. Often this is desirable, but sometimes it is not. Different properties of sound reflection and absorption can be achieved by using different shapes and materials to either enhance or reduce the reflective properties.
For example, allowing sound to be absorbed or transmitted through the ceiling can be achieved by using softer materials such as soft slabs of soft fabric, or by leaving perforations or holes in the ceiling. (Please note that acoustic design is a very complex topic, and for serious projects it should be left to the audio engineer, who can measure and design the room for specific acoustic properties.)
Of course, the most obvious way to reduce sound reflection in a room is to stop the reflection at another level, such as the floor and walls, using soft floor coverings such as carpet and furniture, and drapery to absorb or at least distort or disrupt sound. wave.
The ceiling can also be used to stop sound transmission from the floor above. In this case, serious and professional advice should be taken as this can be a very complex issue. The key is to stop or reduce the penetration of sound waves into the room below.
Ceiling space
This area is often not considered because the off-site area is out of sight, however the ceiling space often acts as one of the main areas through which services are carried out. Therefore, when designing a ceiling, it is necessary to pay special attention to the services that can be transmitted through it. These may include ventilation and heating ducts, electrical and data cables, recessed lighting, as well as locations for mounting pendant lighting, plumbing and, in to some extent, drainage from the bathroom or kitchen upstairs, which may be in the ceiling, and in these cases sufficient heat and noise insulation or sound insulation must be used. This can take the form of lagging or fiberglass blankets. In all cases, services must be attached to the supporting structure and not to the ceiling itself. Do not allow wiring, ductwork or plumbing to rest on the surface of the ceiling. It is good practice to have all services mechanically secured to a suitable frame and then carried either through the ceiling or in the case of wiring for fixtures or vents, so that they can be was dropped and attached to the fitting or penetrated the surface.
Ceiling insulation and ceiling types
The ceiling is one of the main areas where thermal insulation is required as this is the area where heat will rise and in the case of the ceiling under the roof and not the floor also where the heat from the sun is and therefore the roof space is the area that will allow the heat to penetrate into the living space. Highly undesirable in the middle of summer or if the air conditioning system is running. There are several methods that can be used when insulating, the most common being fiberglass wool blankets or bales stretched across the ceiling to create an insulating barrier.
This is achieved by creating an air barrier in the insulation, stopping or reducing heat transfer.
Heat will naturally rise or "gravitate" and dissipate into the cold area. There are other systems that use granulated and treated paper and items such as expanded vermiculite.
However, the key is that most systems reduce heat transfer by creating an air barrier.
Other types of ceilings and ceiling finishes
Suspended ceiling system
There are other systems that use overhead wires to support the ceiling. Commonly known as Donna system or suspended ceiling system. The ceiling is either mounted to a ceiling screw or attached to a metal grid, which may or may not be exposed.
The panels, which typically measure 1200mm x 600mm or 4ft x 2ft, made from a variety of materials from styrene to plasterboard or painted or vinyl softboard, are inserted or lowered into the ceiling grid to form a panel and suspended ceiling system. This system can also be used to form recessed or suspended ceilings and is very common in commercial applications.
T and G (or tongue and groove) Ceiling
This is another common ceiling shape that was traditionally used in many older homes. Today it is an expensive finish, but is aesthetically pleasing and can create a feature. Although it is attached to a wooden frame, it may require special frame construction due to its increased weight.
Bend and Ceiling Floor
Ply and batten is similar to a wooden ceiling and its own ceiling panels.
Other considerations that may need to be made when selecting a ceiling system may include:
- Moisture resistance
- Fire resistance
- Production of smoke when heated or burned
- Reflective qualities
- Impact resistance (eg gyms)
,
Types and types of air ducts
Conventional ventilation systems are used to move air. In other words, these are ordinary pipes. They are distinguished by the material of production, rigidity and the presented shape.
The material from which the metal channel sheet is made. They are distinguished by characteristics and are applicable in different situations:
- Thin sheets 05-1.0 mm are suitable for air directions with a relatively cold flow of up to 80 degrees and no more than 60% humidity. In this case, cold-rolled galvanized steel is suitable.
- Sheets in the range of 1.5-2.0 mm are suitable for high temperature flows and humidity levels. Sheets made of carbon steel and stainless steel are applicable here.
- In buildings where there is the presence of gases and vapors, ventilation systems made of metal plastic and aluminum compounds are used. The protective layer of the structure will provide the necessary protection.
- In everyday life, ventilation systems made of polypropylene and fiberglass are used.
Stiffness is an indicator by which all air ducts are distinguished into:
- Flexible, which in turn can be framed or frameless. They are a corrugated sleeve. They are used for short air systems. Excellent replacement for corner bends. They stretch and contract many times. The steel spiral is covered with synthetic material and aluminum tape. They do not lose their properties.
- Semi-rigid ones are a little denser. They are based on a double-sided aluminum coating with a layer of mineral wool on the inside. There is also a wire frame. Semi-rigid systems include a pipe made of aluminum strip. It can only be stretched once. It is perfect for smoke exhaust systems and can withstand temperatures of 700 degrees.
- Rigid ventilation ducts are suitable for industrial premises. They are durable and reliable. There are both spiral-wound and straight-seam. The tightness of the joints is ensured at the highest level.
Ventilation shapes are mainly mounted in round and square types. In other cases, flat systems are installed. They are applicable only due to the peculiarities of the premises in the house. In practice, you can find rectangular and oval canals. A round system is less expensive than a square one. It is much lighter and is distinguished by its flexibility. Easy installation, quiet operation and sealing are the choice of most customers. Rectangular pipes are used to save space; in small rooms they are a good option.
Some nuances and points of SNiP
Effective sound insulation of air ducts.
Today, it is SNiP that regulates the correct execution of work on the installation of air ducts. Manual 7.91 to SNiP 2.0 allows you to create systems based on the data specified in it. Only in accordance with them will all the work be carried out correctly, and in the end the expected result will be obtained. This manual is intended for specialists who work with ventilation, air conditioning and heating systems. Of course, the manual can also be used by amateurs who decide to build similar structures in the house themselves. It is worth talking about the main points of this annex to SNiP in more detail.
Here, appropriate measures must be taken to protect the building from the penetration of fire. All this is included in the technical documentation of the project.
Measures and means of protection against the spread of fire include:
- placement of all air ducts and related systems within one fire-proof area of the building;
- restrictions on connecting into a common air duct systems that have varying degrees of fire safety and explosion hazard;
- the use of fire-resistant materials in the design of air conditioning, heating and ventilation systems;
- the use of a special system of valves, which, if necessary, can be closed to limit the spread of fire through the air ducts.
There are several basic systems for placing air ducts and related equipment. If the air valves on the branches are located behind the collector, then they have a reduced degree of fire safety. However, this does not mean that they cannot be used in practice. They are quite widespread due to their simplicity.