Strengthening foundations with cementation is a common, effective method of strengthening them. The technology is used to improve the load-bearing characteristics of the soil before construction and to repair the existing foundation. In the latter case, not only the foundation is strengthened, but also the soil under its sole. Under the influence of various factors, the support under the building may become deformed. This is often accompanied by the appearance of cracks on the walls of the building. To stop the process of destruction and extend the life of the structure, it is imperative to carry out strengthening. A preliminary inspection of the structure is carried out to identify the cause of the process.
When the need for reinforcement arises
Subsidence or initially weak soil is strengthened under an already constructed building or before the start of construction on a site with poor engineering and geological conditions. As a rule, strengthening the soil under an existing structure is combined with repairing and strengthening the foundation.
The need to strengthen the foundation under the foundation of an existing building arises for the following reasons:
- design miscalculations due to the lack of or unreliable information about the geology of the site, poor quality construction work;
- increased load on the foundation during reconstruction, addition of additional floors, installation of new equipment;
- displacement of layers during construction and installation work nearby;
- erosion of the foundation due to rising groundwater levels, disturbances in the drainage of melt and rainwater, and failures of water supply and sewerage systems;
- swelling of the soil due to an increase in the depth of freezing in winter under the influence of climate changes.
The choice of a specific technology when strengthening the foundation under a constructed structure is linked to the corresponding objective restrictions. During new construction, the method of strengthening soils is chosen based on the results of a feasibility study.
Recent technologies make it possible to use in construction, after additional preparation, sites with the most difficult engineering and geological conditions.
Diagnosis of the problem
Diagnostics is a set of measures aimed at obtaining complete information about the condition of the supporting structure, the presence of mechanical damage, cracks or deformations.
The condition of the underlying soil, sand cushion and other elements that bear the load from the weight of the house is examined.
The procedure is carried out in stages:
- External inspection of visible parts of the tape . Visual detection of tape damage is carried out from the outside, from the basement (if possible). Looks for visible signs of problems with adjacent layers of soil - subsidence, gullies, etc.
- Underground inspection . The tape is dug around the perimeter, the condition of the trench is checked, the surface of the tape is inspected and any damage that has occurred is detected. The immersion depth of the tape and the base material are assessed.
A defect report is drawn up, which includes all detected damage. A foundation plan is drawn up , on which points of damage, cracks, and deformed areas are noted.
Based on the documentation compiled, a decision is made on measures to solve the problems that have arisen.
During these works, a monthly check of the belt immobility is carried out . Special control beacons are installed on the surface and their condition is recorded.
After a month, their position is checked. If there are no changes, it means that the tape has completed settling.
To perform complex work, unloading of the foundation is required . Its purpose is to transfer the weight of the house to an auxiliary support system, allowing the soil under the tape to be removed for replacement or waterproofing.
Measures to prevent soil erosion
Strengthening the foundation is inextricably linked with work to protect against erosion and remove excess moisture.
Ways to protect against erosion:
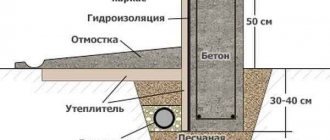
- installation of a blind area - concreting or asphalting along the perimeter of a building with a slope to drain melt and rainwater from the foundation;
- drainage - the formation of a network of pipes, trays and other drainage paths around the building, the installation of a storm system if necessary;
- pumping - discharging water into storage pits, wells or pits with subsequent pumping into drainage ditches;
- vacuum installation with ejector wellpoints - lowering the groundwater level by pumping it under vacuum through a wellpoint installed in the ground;
- electroosmotic dehumidification - compaction of wet silty soils through which a direct electric current is passed; when electroosmotic dehumidification is combined with vacuum dewatering, efficiency increases.
Taking measures to prevent erosion of the foundation, in addition to the stability of the building, has a positive effect on the waterproofing of building structures.
How to strengthen the foundation of an old house
Let's consider the most reliable and almost universal method of reinforcement - a reinforced concrete jacket. Procedure:
- Dig out the base. The concrete strip should be dug out and reinforced in small sections of two to three meters.
- Clean and degrease the surface.
- Make notches on the concrete tape to improve adhesion to the concrete.
- Drive horizontally through the anchor.
- Install formwork for the future belt.
- Install the reinforcement cage and weld it to the anchors.
- Pour concrete and wait until it hardens.
- Carry out waterproofing.
- Fill the ditch, compacting the backfill layer by layer.
When installing a brick frame, the base is covered with brick around the perimeter, connecting the new belt with the old anchors.
Sometimes you can observe subsidence in the corners of a house (for example, a wooden one). In such cases, the corner is raised and the corresponding section of the base is refilled. To perform this procedure:
- Place a jack approximately 40 cm from the emergency corner.
- Thick boards are placed above and below it.
- They slowly lift it, inserting first boards and then concrete blocks into the gaps.
- Remove and replace rotten logs.
The remains of the former foundation are dismantled and a new one is poured.
Injection of the base
Strengthening the soil under the foundation by injection involves drilling wells and pumping a strengthening repair composition through injection devices. Under a strip or columnar foundation, wells are drilled obliquely from the surface of the earth; a slab foundation is drilled through from above.
The repair composition under pressure penetrates into all voids adjacent to the well. Constant monitoring of the process is necessary to ensure that the injected material does not go deep. The choice of a specific injection technology is influenced by the type of soil, on which the type of composition depends.
Methods of soil injection:
- Silication . Liquid glass is used for injection. The method is used to consolidate sandy or loess soils and quicksand.
- Smolization . Synthetic fast-curing resins are pumped into wells. The technology is used to strengthen water-saturated or dry sands, loess, sandy loam, and loam.
- Cementation . Wells are filled with a cement-based mortar mixture mixed with clay, loam or sand. Hot bitumen is additionally pumped into large voids. The consistency of the solution is selected taking into account the density of the soil or the size of cracks in the rock. The technology is difficult to implement in fine-grained sands and is completely unsuitable for sandy loam, loam, clayey or silty soils.
- Ammoniation . The method is intended to protect against subsidence of loess soils. Ammonia gas is injected into the soil beneath the foundation, which reacts chemically with the rock.
The injection process occurs without the use of large-sized equipment and does not require partial disassembly or suspension of operation of the building. An additional advantage of injection technology is the ability to lift and return the settled foundation to its original position. In addition to strengthening the foundation, an impervious curtain is created under the foundation for rising groundwater.
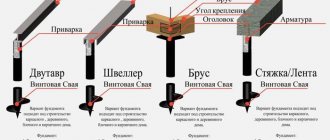
Application of profiled pipes
To strengthen the pile foundation, profiled pipes measuring 3x6 cm are used. The work is carried out using the following technology: using pipes of the required size, piles are connected in series under the entire building. This option is applicable when the supports rise above the surface by at least 0.7-0.8 m.
The pipes must be welded from the inside of the supports - in the future they will not interfere with finishing work or installation of protective panels. If the piles protrude more than 0.7 m above the ground, the pipes are welded crosswise. The middle of the joint is secured using a special metal plate. This is the name of a square plate measuring 20x20 cm.
Jet grouting of the base
Jet grouting technology, or jet grouting, consists of eroding soil while simultaneously filling the resulting cavity with a solution pure or mixed with the soil mass. This method of strengthening the soil under the foundation can be considered in two ways - as strengthening the soil base with the installation of an impervious curtain and as the formation of a new pile foundation under the old one.
Unlike injection, jet grouting is suitable for almost all types of soil, the result of strengthening is determined with high accuracy. The structure and composition of the soil, as well as the percentage of cement, affect the strength of hardened soil concrete.
Jet cementation is carried out in two stages - first, washout is carried out and a well is formed, and during the reverse stroke of the drill string, a solution is supplied. The diameter of a column made of hardened mortar depends on the type of soil, the force of the applied pressure, the duration of erosion, and the technology used.
Technology options:
- One-component . For erosion, only cement mortar is used, the diameter of the columns is the smallest.
- Two-component . Additionally, compressed air is supplied, the diameter of the columns is approximately twice as large as in the previous case.
- Three-component . Erosion is carried out with a water-air jet, and cement mortar without impurities is pumped into the resulting cavity. The diameter of the columns is the largest, but the strengthening technology is the most complex and requires large-sized equipment.
Many foreign companies have now begun to use high-power compressors for jet cementation. The use of such equipment made it possible to increase the diameter of the columns to 5 meters.
Step-by-step work order
Timely reinforcement of foundations with cementation helps prevent subsidence of corners and collapse of buildings and structures. The work has strict regulations.
- Sanding. The perimeter of the foundation is exposed in the part where drilling is to be done, at a depth slightly less than the level of the base. It is advisable to place them in a checkerboard pattern, from the inside and outside of the base of the house. Approximate dimensions 1x1 m.
- Inspection of supporting structures. It is necessary to identify weakened areas of the surface. After digging pits, a visual assessment of the depth and size of the failures is carried out, and, if necessary, supports are installed to ensure the safety of the work.
- Drilling of the wells. They are placed at a distance of 25-50 cm, at an angle, directly in the body of the building support. The drill should have a diameter of 40-110 mm, its immersion depth is calculated so that about 300 mm or more remains to the base.
- Preparation of the solution. Most often, a cement mixture with fine sand is used, liquid enough to easily pass through the hose used. The exact selection of the composition is determined by the type of building foundation. The solution must match it in proportions.
- Connecting pumping equipment. It will deliver the solution from the concrete mixer to the base of the object. It is important that all connecting elements are sealed. This is necessary to prevent leakage of the cement-sand mixture as it moves under pressure.
- Primary supply of solution. First, it is made very liquid, with a ratio of dry ingredients to water in the range of 0.9-1 to 1. This mixture is fed to the sole for 10 minutes at a pressure of 0.2 MPa. Pumping is stopped when the absorption of the solution decreases to 3.5 l/min.
- Secondary and subsequent cementation. For each such stage, the density of the mixture increases. The solution is pumped until the flow rate drops to 5 l/min. The optimal pressure for thick mixtures will be 0.3 MPa.
- Excerpt. The strengthened areas are left for 48 hours for the solution to harden. As soon as it sets, you can proceed to backfilling the soil. The sole will be considered reinforced.
Following the instructions, you can strengthen the foundations by pouring cement mortar under it as a binding element.
Thermal method
This method is used mainly for strengthening subsidence soils. The technology for strengthening soil by thermochemical firing is based on treating the base with combustion products of liquid or gaseous fuel. If necessary, the burned material is enriched with additives.
The fuel burns in a sealed well located vertically, horizontally or at an angle. As a result, strong thermal soil pillars are formed.
More modern electrothermal firing is carried out using nichrome electric heaters. The ability to fluctuate the heater power along the well height allows you to adjust the shape and size of the columns formed during firing in accordance with the heterogeneity of the layers.
Strengthening the foundation with your own hands
Requirements for restoration and reconstruction of foundations are set out in SP clause 13.9.
The method of strengthening the base itself depends on its type and the nature of the cracks. Options:
- concrete strip, small horizontal or hairline cracks. A suitable method is shotcrete: applying an additional layer of concrete to the surface;
- tape, vertical and inclined cracks. Widening the base of the foundation due to an additional layer of reinforced concrete or ready-made reinforced concrete slabs;
- a shallow tape with the same cracks can be repaired by deepening the sole. The technology is similar to the previous one;
- the same thing, the third method is a reinforced concrete or brick frame (shirt);
- fourth option - a beam is installed between the wall and the foundation, supported by additional piles. Fastening of elements - with anchors;
- fifth - I-beams or channels are mounted in specially made grooves in the tape. Transverse beams are installed under the longitudinal beams and supported on piles;
- in case of minor damage, a bored or columnar foundation can be strengthened by gunite;
- for serious cases - four options. The first is to combine the supports into a single strip;
- widening the soles of the pillars;
- deepening;
- brick or reinforced concrete frame.
Deep compaction
The soil base is compacted mechanically, using sand or soil-lime piles. When lime is slaked due to contact with water, it increases in volume many times over and presses on the walls of the well, greatly compacting the soil. Other compaction options are the installation of rigid elements or vibratory ramming.
Deep compaction of foundations under already constructed buildings is carried out through inclined wells. Previously, such wells were drilled with drilling equipment, followed by the removal of crushed mass or punched with cores. The imperfection of drilling consists in insufficient compaction, and when punching, a strong dynamic effect occurs and there are difficulties in removing the core from the well.
Now, due to these shortcomings, they are trying to use more advanced technologies for strengthening soils by deep compaction - screw punching or the already mentioned jet cementation.
General recommendations
There are many ways to strengthen an incorrectly calculated and constructed foundation, however, there are 3 golden rules of restoration:
- Revision and recalculation of the project is mandatory. If the piles were placed without calculation and it was not possible to guess the location of the supports and their load-bearing capacity, is it worth the risk again?
- Taking action quickly is half the battle. It is difficult to predict how quickly the deformation will develop, and this is fraught with cracking of the supporting structures, which entails the risk of destruction of the house.
- A professional approach is very important. Only experienced builders with the necessary equipment will really help restore the foundation, because in this matter accuracy is very important, from lifting the house to installing a new grillage.
Do not ignore signs of deformation and general recommendations, because the most valuable thing is at stake - your life and health.
- Foundation
Replacing piles
Sometimes the supports under a home are so damaged that they need to be replaced. How to dismantle a pile foundation, if, for example, it is necessary to remove piles under wooden houses and replace them with new ones, then there is no need to dismantle the buildings. So, if shrinkage has occurred and the pillars have completely failed, to strengthen the foundation of a wooden house, you can increase the head of each support. The ends of the support are called the end of the support, which is located on top, directly under the house. You can build up the supports by exposing the reinforcement. Elements of the required height are welded to it, the sheathing is installed and poured with concrete. Repairing the heads using this method after inspection can be done independently, as it is not difficult. If the pillars are squeezed out, the heads are removed, for which the excess part is carefully destroyed to the required height, and then the reinforcement is cut off.
If this happens in a strip foundation, you will have to take radical measures - the foundation will need to be replaced. This must be done by conducting a preliminary examination.
Using an angle and channel
The technology for using a reinforcing corner is similar to how a stiffening belt is created when reinforcing pipes. To do this, the prepared elements are welded between the piles so that they intersect near the supports. To do this, when marking, mark the places where the corners will be located. The elements are welded on the outside and inside of the pile base. Thanks to this, it will be possible to increase the strength of the foundation under the house and prevent further shrinkage. If there are sagging supports, the reconstruction will strengthen them and the foundation will not fail.
There is another way to strengthen piles in foundations. If it is necessary to strengthen the foundations of wooden houses whose piles have subsided in moisture-saturated soils, channels ranging in size from 16 to 20 mm are used. The channel is welded on piles along the upper chord. In other words, such a reconstruction is the creation of a kind of additional heads connected into a solid frame. The design does not allow the piles to deflect, which preserves the strength of the strip or pile base. Of course, the cost of such protection is quite high, but it will prolong the operation of the old foundation and protect it from subsidence. Builders claim that an old foundation reinforced with channels can surpass strip foundations in strength. They will soon not be in danger of shrinkage and subsidence of individual supports.
Grillage installation methods
The following methods are used to strengthen grillages::
- Shotcrete . This is a procedure for spraying concrete under pressure, allowing you to create an additional layer of the required thickness. The specificity of the application ensures a high density of the newly formed concrete jacket, helps fill potholes, heals cracks and other defects.
- Installation of a concrete frame . The problem area of the grillage is prepared, through holes are drilled through which reinforcing bars are passed. Then, along the entire length of the area intended for reinforcement, a reinforcement frame is assembled, rigidly connected to through rods. Formwork is built around the armored belt, ensuring the specified thickness and width of the frame, after which concrete is pumped into the cavity. Sometimes special structures are used as formwork, which are tightly pressed around the grillage tape and filled with concrete.
- In difficult cases, before installing the concrete frame, a “wall in the ground” is installed . This technique involves installing a mechanical shutoff between the walls of the trench and the side surfaces of the grillage. This method allows you to work without fear of rising groundwater, crumbling trench walls, etc.
NOTE!
The strengthening of the grillage must be calculated in advance so that the procedure does not have to be repeated the next year. The main quantities that must be clarified are the thickness and extent of the reinforcement layer. Sometimes you have to increase the thickness of the tape around the entire perimeter.
What materials are needed?
When selecting building materials, you should determine in advance what technology will be used to strengthen the piles. If the strengthening is carried out by creating additional drilled or bored piles, reinforced concrete frames or shotcrete, a sufficient amount of concrete mixture will be required for the work.
To prepare it you need:
- cement;
- sand;
- gravel;
- water.
In most cases, metal reinforcing mesh and steel reinforcement are required. These materials are used to increase the strength of reinforced concrete structures intended to strengthen weakened or damaged foundations.
Also, before starting repair work, it is necessary to purchase the required amount of waterproofing products. Depending on the restoration method, compositions based on bitumen, extruded polystyrene foam, liquid rubber or other materials can be used.