Being in a room, everyone can understand by their feelings whether they are comfortable or not. But few people know how such conditions were created. Many people don’t even think about which direction the air moves in the room where they are, if they feel comfortable there. To create these conditions, you need to choose the right air distribution scheme. But it’s not at all easy! It is necessary to take into account that dust in the workshop should not get on people’s faces, that contaminated areas should not pollute “clean areas”, that heat from food rises along with warm air, that drafts must be avoided and many other aspects. First of all, the efficiency of the ventilation system depends on the type of air supply devices and their placement. In this article we will try to consider existing air exchange schemes and in which rooms they are best used.
Basic schemes for organizing air exchange
The indoor microclimate is created by air distribution systems. In other words, these are the ventilation systems we are familiar with. Conditioned air enters inside in the form of a turbulent stream with a higher or lower temperature than in the room. However, jets can be compact (their velocity vectors are parallel) and fan-shaped (the vectors are directed at an angle). The main task of air distribution is to ensure standardized flow speed and temperature at the boundary of the working area. Therefore, the development of the supply air jet is calculated.
Air distribution is selected in accordance with SNiP 4 1 -0 1 -2 0 0 3, Recommendations for the calculation of air distribution 1988 or Manual 1.91 to SNiP 2.04.05-91. There are also more modern manuals for specific buildings. You can also use programs specially created for this.
There are four main schemes for organizing air exchange. They are supplemented in connection with standardized requirements. First of all, the air exchange scheme is selected in accordance with SNiPs and SN for the design of structures for various purposes.
Air exchange scheme “bottom up”
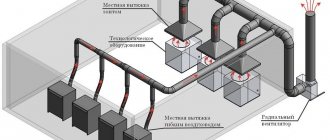
This method is classified as repressive. From the name it follows that the supply grilles are located in the lower part of the room. Air masses can be supplied in a compact jet directly to the work area (in rooms with excess heat generation of more than 23 W/m3). The intake of air masses is provided from above. Therefore, the scheme can be used, for example, from a thermal workshop to offices and cafes.
Its main advantage is that air enters the breathing area uncontaminated. The disadvantages of this scheme include regulatory requirements for the microclimate in the work area. All parameters must be met and fed at a speed of 0.1 m/s.
Air intake elements must be placed in the ceiling part when there is a large excess heat, harmful and flammable gases, and vapors. When the height of the room is up to 6 m, at least one air exchange should be removed. If above 6 m - no less than 6 m3/h per 1 m2 of floor.
It is possible to have air flow outside the workplace from under the floor, for example, this is often done in welding shops and theaters. Underfloor air distribution is now popularized because the air ducts are placed in the underground space. This allows the designer to organize the workspace without considering the placement of air ducts.
Top-to-top air distribution pattern
Naturally, here both the supply and exhaust air distributors are located in the upper part of the room. It is often used when designing ventilation for homes, public and administrative buildings. Rarely, but still used, this scheme is used in industrial ventilation, for example, in a spinning hall. It is also called mixing.
The incoming air cannot avoid mixing with the internal air. Therefore, it is disadvantageous when removing excess heat. After all, some of the excess heat cannot be removed by exhaust systems. The temperature gradient is 0, but not always. Therefore, in calculations it is customary to take Δtcalc. = 5-10 °C.
Air exchange scheme “from top to bottom”
Another preemptive scheme. For example, it can be like a compact jet that is supplied horizontally under the ceiling and laid on it (often for rooms up to 4 m high). And just a compact jet, fed vertically, fan or combined flow.
Such air distribution schemes are used for commercial, administrative, and industrial buildings. Exhaust grilles should be placed in places that are not intersected by the supply flow, with the highest temperature and concentration of harmful substances.
This is the most common ventilation system. Can be used, for example, in theater halls with balconies, concert halls. In addition, it is also appropriate in “clean” rooms, painting booths and buildings with a toxic density greater than that of air.
Air distribution pattern “bottom to bottom”
This scheme is suitable in the absence of excess heat. Air is supplied and discharged from the lower part of the room, that is, fresh air is supplied directly to the breathing zone. But, on the other hand, air is also removed from the lower part, and the flows are mixed. Moreover, with this scheme, not all air is replaced. Some of the old is mixed with the supply and remains in the room. Therefore, when releasing toxic elements, such a scheme cannot be used.
There are requirements in regulatory documents that complement them. In this regard, four more schemes for organizing air exchange are being created, called “combined”:
- "top and bottom up." For example, galvanizing shops and other rooms with moisture.
- "from below and from above to below." For example, in cinema halls.
- "from top to bottom and top." For example, in a welding shop, where it is necessary to remove 2/3 of the air from the bottom of the shop and 1/3 from the top; as well as in concert halls without balconies.
- "bottom to bottom and top." For example, in paint shops and battery shops, where gases are not allowed to accumulate in the upper part due to the risk of explosion.
First of all, based on the selected air exchange scheme, the type of air distributor is selected. Of course, the determination of the distance to the entrance of the air stream into the working area and its parameters at this point depend on this. As a result, according to reference books, formulas are selected that determine the temperature and speed of air flow at the exit from the zone.
Checking the functionality of the ventilation shaft
The flow of fresh air into the room can come from various places, and its removal only through one or two ventilation shafts.
To check the strength of the flow that leaves the apartment, you need to place a sheet of paper on the exhaust grille, completely closing it. With normal air flow, the paper should stick to the grill.
If the paper is stuck, then the ventilation is working.
Testing ventilation using an open flame is considered an unsafe method. If the exhaust shaft malfunctions, flammable gas may accumulate.
If this does not happen, then we can talk about weak air flow. Low flow can be caused by two reasons: lack of normal inflow and problems in the exhaust shaft. It is very easy to find out which reason affects ventilation. It is enough to open the windows in the room. If the paper then sticks to the exhaust hole, then the problem is insufficient air flow, which means you need to organize additional air flow. This can be done by installing a supply valve.
If the paper does not stick when the windows are open, then you need to check the exhaust shaft. For owners of apartments in apartment buildings, they should contact the management company to check the exhaust shaft.
Air distribution calculation
Before starting calculations, you need to understand the parameters of the air stream. First of all, it is assumed that there may be workplaces under a direct stream, because the boundaries of the zone can only be known after calculating the air distribution.
Moreover, in summer the temperature on the jet axis will be lower than the ambient air temperature, and in winter it will be higher. Thus, knowing the air exchange patterns, you need to determine which initial data to pay special attention to. Subsequently, based on them, choose one of the options for arranging air distributors.
Video description
For more information about recuperators, see the following video:
It is important! Including a recuperator in the supply and exhaust system allows you to save up to 70-90% of the heat of the exhausted room air.
Phases of operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust ventilation mode in the house Source moydomik.net
Initial calculation data
The basis is taken from the data obtained from air exchange calculations, as well as the requirements of building codes.
Basic initial data for calculating air distribution:
- firstly, the selected air exchange scheme, and the air exchange determined for it Lin;
- secondly, the length, width and height of the room in meters;
- thirdly, the amount of air inflow L0 = Lin in m3/s;
- supply air temperature t0 = tin, °C;
- normalized air temperature twz of the blown zone, °C;
- normalized air speed Vwz in the ventilated area, m/s.
However, there are times when additional data is needed:
- concentration of harmful substances in the supply air in mg/m3;
- maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of a harmful substance in the work area Swz in mg/m3;
- amount of air removed by local suction, m3/s.
The calculation of air distribution occurs in the following sequence:
- The first step is to determine the scheme. When choosing, the size of the room, architectural features and regulatory requirements are taken into account.
- Finding the normalized difference in temperature and air speed.
- Determining the number of air distributors and their type.
- The pitch of the air distributors is determined.
- Determination of the excess temperature and air speed in the supply jet at the point at which the jet enters the work area.
- Comparison of calculated and standardized values.
- Acoustics check.
We provide a calculated example below.
In conclusion, we can only advise when choosing an air exchange scheme to take into account all possible factors. Using regulatory documents will only make your work easier. In addition, the design guidelines for certain rooms indicate recommended air distribution patterns. These data are obtained as a result of tests and detailed study.
Recuperator
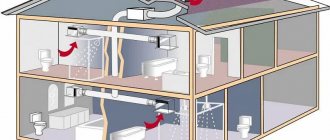
When arranging supply and exhaust ventilation in private homes, significant savings come from the use of systems with heated supply air, called “supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery.”
Scheme of operation of ventilation with recuperation Source airclimat.ru
Recovery means the process of recycling heat from internal exhaust air with a temperature tb, which is emitted into the street during a cold period with a high temperature, to heat the supply external air. The process of heat recovery occurs in special heat recuperators: plate recuperators, rotating regenerators, as well as in heat exchangers installed separately in air flows with different temperatures (in exhaust and supply units) and connected by an intermediate coolant (glycol, ethylene glycol).
The last option is most relevant in the case when the supply and exhaust are spaced along the height of the building, for example, the supply unit is in the basement, and the exhaust unit is in the attic, however, the recovery efficiency of such systems will be significantly less (from 30 to 50% compared to the PPV in one building.
Video description
For a clear overview of ventilation in a private house, watch the video:
Usually, the doors from the staircase to the floor must be closed for the normal functioning of natural ventilation
In the attic it is always necessary to install forced ventilation, since the standard natural draft is not provided due to the low height of the ventilation ducts.
Kitchen ventilation
To ventilate the kitchen, builders of a private house must provide a separate ventilation duct into which the exhaust air flow will be sucked.
The channel is mounted from galvanized steel sheets or other stainless materials. The surface of the channel should be smooth so that greasy fumes from the kitchen and soot from the stove do not settle on it. The inlet and outlet openings of the channel are protected by grilles.
As in the whole house, air circulation in the kitchen is carried out by natural and forced methods. Those. vents and windows are opened, or a hood is purchased. The latter option is clearly preferable, since the inability of natural ventilation to cope with the odors that appear during cooking is beyond doubt.
Why is ventilation needed?
It is thanks to ventilation that a healthy and comfortable microclimate is created in the room, namely:
1. Carbon dioxide levels are normalized
Carbon dioxide is always present indoors: after all, we exhale it! The only question is how much it is. When carbon dioxide accumulates excessively, it has a negative effect on the human body. It interferes with the full supply of oxygen to the blood and organs. The brain begins to become “lazy,” and we feel tired, lethargic, and become inattentive. A high concentration of carbon dioxide is also associated with a feeling of stuffiness.
Good ventilation ensures constant air renewal. The air coming from the street replaces the air in the room along with the carbon dioxide accumulated in it. It is not stuffy and comfortable to be in such a room.
2. Humidity is normalized
Proper ventilation implies that excessively humid air from the premises is promptly released into the exhaust hood. This eliminates the formation of eternally damp areas in corners and on walls where mold actively grows.
The ventilation system may also have additional functions. For example, air filtration allows you to remove contaminants from the air at the entrance to the room and make the air healthy and safe. And the heating function in the ventilation prevents the risk of catching a cold from cold air from the street.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
The installation of ventilation of this type does not differ from the standard placement of similar household appliances, but their autonomy is much higher. They are not tied to the ventilation system, so the designers have developed a number of compact retractable hoods that use recirculation. They are called telescopic hoods. During operation, they carry out filtration by creating a strong lateral draft, sucking in all contaminants along with the air flow. After switching off, the system is recessed into the tabletop, very convenient and original.
Advantages
This type of device has slightly less performance and power, but this has allowed manufacturers to reduce their cost, which only pleases users. All components of the systems experience less load, so they can operate without accidents for much longer.
When such a system operates, there is no room for reverse thrust. The autonomous location allows for free installation of the stove - users place it where it is most convenient for them, regardless of the location of the entrance to the ventilation shaft. Recirculating hood Recirculating hood in the kitchen interior
What is better - natural or forced air movement?
The choice of air exchange device concept is determined by the specific operating conditions of the room. The merits of each system should be taken into account. In particular, the advantages of natural ventilation include:
- Inexpensive infrastructure available to build for private homeowners.
- The absence of mechanics eliminates the need for regular maintenance and installation of power supply lines.
- There are no maintenance costs. It is enough to periodically clean the channels, which requires minimal investment and effort.
- No noise due to a running fan.
The result is a simple system that is easy to use, but at the same time it gives a modest effect in terms of ventilation.
Now you can consider the advantages of a forced air circulation system:
- Regardless of external conditions, it can provide sufficient ventilation.
- In addition to circulation as such, it allows you to perform the functions of cooling, heating and filtering air masses.
- The possibility of organizing a heat exchange system involves practically free heating of the incoming masses.
The disadvantages of forced air exchange are due to the difficulties in installing and maintaining ventilation equipment, which will also require additional space for installation.
Buy a ventilation system
Get rid of stuffiness, establish proper air circulation in rooms, breathe clean air - all these issues can be easily resolved by purchasing a ventilation system with the functions of air supply, cleaning and heating.
Breezer is one of the most popular devices on the supply ventilation market. It supplies air to 4-5 people, cleans the supply air from dust, dirt, car exhaust, and allergens. The climate-controlled heater eliminates drafts. And you can control it from your smartphone manually or by setting the automatic mode.
There are different models of breathers. Functions, characteristics, design, price - Tion ventilation meets any requirement.
Ventilation with additional functions
Ventilation with heating
If sub-zero temperatures outside the window are not uncommon, then supply ventilation with air heating is needed. Otherwise, cold air will blow into the room, and this can easily result in a cold.
Heated ventilation can be climate controlled and automatically heat the air to a user-selected temperature.
Ventilation with filtration
Clean air is an important condition for a healthy lifestyle.
Ventilation with filtration contains air filters for various purposes. These can be simple filters with a mesh structure, highly efficient filters with a complex interweaving of the finest fibers, or carbon filters that trap harmful gases and odors.
Tips, recommendations, nuances
Often, owners of private houses are lenient when it comes to ventilation requirements for their own home, especially if they may entail additional costs. Here are some misconceptions regarding the use of technical means in residential premises.
- Installing an air conditioner will solve all ventilation problems.
The air conditioner is able to change air parameters, cool or heat the air, and dry it. But it does not create an air cycle. In a house with a working air conditioner, a comfortable temperature will be established, but after a couple of hours the body will feel a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide.
Ventilation is always installed along with air conditioners Source anantaircon.podbean.com
- If you install an exhaust fan, this will be enough for good ventilation of the house..
If plastic sealed double-glazed windows and doors are installed, there is no air flow, which means there will be no exhaust/removal of air masses. After a few minutes of operation of the hood, a pressure will be established in the room that simply will not push air to the fan blades.
- Periodic ventilation or an open window for micro-ventilation will solve all problems.
The issue of ventilation will not be fully resolved, since there remain fairly large periods of time during which it will not be possible to ventilate the house, for example, at night. If in the summer this is a solvable issue, then micro-ventilation in the winter is fraught with drafts that will quickly cool the room, preventing it from being ventilated.
- Using equipment with a heater will allow it to be operated at the lowest temperatures
As a rule, equipment with recovery has restrictions on the minimum outdoor air temperature. This is due to the capabilities of the recuperator and the limit is -25…-30 oC. If the temperature drops, the condensate from the exhaust air will freeze on the recuperator, so at ultra-low temperatures an electric preheater or a water preheater with antifreeze liquid is used. (The range of these installations is presented on our website)
Video description
An example of combining natural ventilation with a hood in the kitchen in the video:
Since a kitchen stove is a constant source of fairly strong odors, the area above the stove needs ventilation most of all, and it is above it that the natural ventilation outlet channel or an electromechanical hood is placed.
When installing ventilation in the gas stove area, first of all, it is necessary to compare the number of burners with the volume of kitchen air space. The standards require:
- for a kitchen space with a volume of more than 8 m³, it is allowed to install a stove with two burners;
- for a kitchen with a volume of 12 cubic meters - no more than three burners;
- for a kitchen of 15 cubic meters - 4 burners.
If this standard is observed, for high-quality air exchange in the kitchen with a gas stove, an air exchange rate of 140 m³/hour is sufficient, and with an electric stove – 110 m³/hour.
Bath ventilation
The air in the bathhouse has its own specific specifics - during bathing procedures the humidity reaches 100%, and when the bathhouse is not in use, everything depends on the quality of air exchange in the room. To comprehensively solve these issues, mixed ventilation is used.
An example of air movement in a bath Source elektroservis-rostov.ru
But since the mechanical part is needed only during the operation of the bathhouse, then, in fact, the most effective natural ventilation is made and fans are added to it. Thus, during operation, the power of the ventilated installation allows you to comfortably steam in the bathhouse, and during its downtime, natural ventilation ventilates the room.
Technically, this is expressed in the arrangement of one or two supply channels and an outlet on which a fan is installed (preferably with an adjustable number of blade revolutions).
It is important! When arranging a bathhouse, one should not forget about floor ventilation. To do this, the floor covering is assembled from boards with a gap of 5 mm between them.
Ventilation principle
This is a type of microventilation system that involves removing air along the shortest paths. For example, this could be a direct air exhaust from the kitchen or bathroom. Moreover, unlike windows or other points of natural circulation, the modern principle of ventilation assumes the possibility of regulating flows. These manipulations can be carried out either manually or automatically. The second option turns out to be more preferable, as it contributes to the formation of a microclimate close to natural. For example, in an apartment, air circulation based on the principle of automatic ventilation can be based on changes in pressure. The system takes into account wind speed, directing optimal air flow into the room. This eliminates hypothermia and generally establishes a comfortable temperature and humidity balance.