Polycarbonate can also be used to glaze the walls of the veranda and lay its roof. From this article you will learn about the advantages of such designs, the main characteristics of the material regarding the topic discussed. Let's discuss how to properly sheathe walls and which roof to choose for a polycarbonate veranda attached to a house. We will also touch on the points of panel fastening and operating rules.
Advantages and disadvantages of a polycarbonate veranda for a house
A veranda for a polycarbonate house has a large number of characteristic features and has both disadvantages and advantages.
Main advantages:
- lightness: glass weighs several times more than polycarbonate;
- sound insulation: walls made of this material practically do not allow extraneous sounds to pass through;
- thermal insulation: heat retention when glazing the veranda with polycarbonate is guaranteed;
- pliability: the material bends easily, which allows you to experiment and create the most outlandish architectural designs;
- ease of processing and installation: this material is easy to work with;
- fire resistance: does not burn in fire, at a temperature of about 120C it only melts.
Of course, when installing a polycarbonate veranda with your own hands, you may encounter disadvantages. The material can hardly be called environmentally friendly, and its ability to retain heat does not always play into its hands in the summer heat. However, the low cost of construction and the attractive appearance of the veranda can somewhat mitigate these inconveniences.
Fire characteristics
Polycarbonate, when exposed to an open flame and exceeding a certain temperature, begins to melt and ignite. When the external influence ceases, this process spontaneously fades. Panels made of polymer material have the following features in terms of fire safety:
- resistance to high temperatures and open fire;
- During the combustion process, the formation of smoke is minimal;
- combustion products are not toxic;
- the oxygen index of the material is 28-30%.
Monolithic polycarbonate belongs to the category of self-extinguishing materials. This allows it to be categorized as V-1 (B1) for fire safety in accordance with the requirements of UL-94 and DIN 4102 standards. Moreover, no fire retardants or other additives are used in the production process of the material.
Walls and roof made of polycarbonate - cellular or monolithic?
It should be noted that there are two main types of polycarbonate for verandas - cellular and monolithic. Their chemical composition is identical. It is a common synthetic polymer that belongs to the plastic materials belonging to the engineering grade. Almost anything can be made from the material - it is used to build greenhouses, gazebos, and road stops.
Let's figure out which polycarbonate is better for a veranda, discuss its physical properties and select the optimal width depending on different regions.
Characteristic
It is worth paying attention to the fact that monolithic and cellular polycarbonate for verandas, all other things being equal, differ from each other in sheet structure. If a monolithic sheet is a simple sheet without voids, then a honeycomb sheet is a structural sheet, filled with jumpers and essentially representing a set of cells. Accordingly, cellular carbonate has lower impact resistance and durability than monolithic carbonate - which, however, beneficially reduces its monetary value.
An important factor is that cellular carbonate also retains heat better.
Choosing the optimal thickness
The thickness must be chosen taking into account the construction. For a polycarbonate veranda at the dacha, greater thickness will not be a predominant factor, but do not forget that the lighter the sheet weight and the thinner its walls, the greater the likelihood of damage and cracking. This is especially true for cellular polycarbonate, which has less material security. Monolithic sheets are twice as strong - this must be remembered.
As for the thickness of the sheets, both cellular and monolithic ones can be of very different thicknesses (for polycarbonate verandas attached to a house, it usually varies from 4 to 16 mm). The thickness will depend on the number of layers in the panel.
| Component part | Roof | Walls | Roof | Walls |
| Region | With a lot of snow, severe frosts and frequent precipitation | Sunny and warm southern regions, with little snow in winter | ||
| Determining factors | The roof must withstand loads (snow precipitation), including precipitation in the form of hail. | The walls of the veranda must withstand strong winds and the load that will act from the roof. | The roof will be exposed to sunlight in warm regions, but it is not required to withstand the load of tens of kilograms of snow. | Walls must be able to withstand wind loads, but will not require as much direct protection as in cold regions. |
| Optimal thickness of polycarbonate | 12 mm | 10 mm | 8 mm | 6 mm |
Video description
Tips for choosing polycarbonate in this video:
The problem with choosing a quality material is that it is not always possible to check all the parameters by inspection. For example, how to determine the degree of UV protection. This can only be done in laboratory conditions. Therefore, preference should be given to polycarbonate from well-known, time-tested brands. A low price may be a signal of a low-quality product. It is better to choose the “golden mean”.
High-quality material Source polidin.ru
Tips for glazing a veranda with polycarbonate
In order to properly glaze a veranda with polycarbonate, you must follow several rules.
- When cutting, be sure to leave 5mm on each edge – polycarbonate tends to both contract and expand, and this will help you get the exact fit.
- When cutting out sheets, take into account the fact that the surface of the material where the film is visible is the outer surface.
- If you use honeycomb panels for installation, then lay them vertically in cavities - this way they will be enriched with air.
- It is advisable to seal the joints between the plates so that wind does not blow between the gaps.
Environmental parameters
As mentioned above, monolithic polycarbonate is produced from raw granules using special equipment with a closed technological cycle. This method of manufacturing panels allows us to minimize negative impacts on the environment. The material itself is chemically inert and does not emit any harmful or dangerous substances for humans and animals.
Due to its environmental characteristics, monolithic polycarbonate is recommended for use inside residential premises. Special grades of panels are produced specifically for use in the medical and pharmaceutical industries. This material can be used in construction for exterior and interior decoration.
Polycarbonate options for verandas
Veranda roofs made of polycarbonate can be different - the plasticity of the material allows you to experiment with shapes. The most commonly considered options are:
- single-slope and double-slope;
- arched and turning into walls.
Sliding windows for a veranda in a country house
Single-pitch and double-pitch
The classic (and most recommended by builders) option is one plane located at an angle. The single-pitched model is very easy to install - it does not need to be bent, this significantly reduces labor costs.
The gable design is not much more complicated, and only requires a larger number of trusses and the creation of an angle of inclination with their help.
Advantages:
- ease of installation;
- saving materials;
- distribution of the load of the snow cap and the slope of water flows during rain;
The last point can easily be called the most important - a polycarbonate veranda roof attached to a house will last a very long time and will not collapse under the weight of precipitation if you choose the correct sheet thickness and sheathing pitch.
Arched and turning into walls
Despite the fact that the production of such a frame may take more time than a single-pitched one, and will also require significant financial investments, the appearance still wins in the fight against pragmatism - such roofs look much more interesting.
When installing an arched veranda with a transparent roof to the house, pay attention to:
- depending on the type and thickness of the panel, there is a dependence with the permissible bending radius. The distances between the stiffeners and the weight of the polycarbonate panel are also taken into account.
- All arched structures are divided into three types: polygonal, hipped, round.
- The smaller the pitch of the nodes in the spans of the trusses, the higher the weight of the roof, but the higher the strength. This means that in this case a stronger foundation and walls will be required.
- Study SNiP P-23-81 on steel structures (useful when designing trusses).
There is also a separate type of covering for the veranda - a roof that turns into walls. We can conditionally classify this building as arched. When installing a polycarbonate veranda in your country house in this way, you first need to pay attention to the permissible bending radius of your honeycomb panels.
Sheet thickness and specific gravity
The industry offers a wide range of transparent and opaque panels in a wide variety of colors. Monolithic polycarbonate characteristics, which are unique in many respects, have a density of 1200 kg/m3.
This is significantly lower than that of window glass, which has more than twice the specific gravity. This circumstance makes it possible to significantly lighten many building structures, provided that their mechanical strength is maintained at the appropriate level.
Knowledge of such an indicator as the weight of one square meter of monolithic polycarbonate is necessary to determine the mass of roofing material when carrying out design and calculation work.
The mass value of monolithic polycarbonate will depend on the thickness of the sheet of material:
The dependence of the weight of a standard sheet of monolithic polycarbonate, measuring 2050 x 3050 mm, on its thickness.
How to properly sheathe a veranda with polycarbonate sheathing
In order to cover the veranda with polycarbonate, it is first necessary to complete the work with the sheathing and frame. If the frame was painted, then only after the paint had dried.
It is advisable to refrain from walking over the sheets - they are not so strong.
When covering the veranda with polycarbonate, make sure that the sheets are attached with the protective layer facing outward. You can understand that the protective layer is by seeing the film with inscriptions. Before installation, the film must be torn off from the edges. It must be completely removed after the installation process.
The sheets are mounted in such a way that the ribs or canadas are positioned vertically (from top to bottom) - this will help remove condensate.
For fastenings, it is necessary to use connecting profiles that are bolted to the supporting structures, after which the sheets themselves can be mounted on them. When using an arched model, the sheet is twisted into an arch to an acceptable radius (of course, without damaging the sheet itself). If you overdo it, you can completely deform the surface - the sheet will either burst or break. Please note that such breakdowns are most often not covered by the warranty.
Lifetime
Monolithic polycarbonate panels are made from granules using extrusion or injection molding.
The service life of this material is determined by the following factors:
- quality of raw materials and compliance with technical manufacturing conditions;
- correct installation;
- climatic conditions and exposure to adverse environmental factors.
Different manufacturers declare their terms of use of the material, with the minimum indicator exceeding 10 years. Studies carried out in a specialized laboratory have shown long-term irradiation (more than 2000 hours) causes a decrease in the permeability of the panel by less than 10%. This corresponds to approximately 20 years of polycarbonate use in desert areas of Arizona or Israel.
Features of completely transparent verandas
The main feature of a veranda glazed with polycarbonate will be its excessive heat resistance. If you plan to create something like a greenhouse or greenhouse, or the construction is supposed to be in the form of a winter garden, where warmth is an inevitable companion, then this model will suit all the characteristics. If such a goal is not set, it is better to refrain from this kind of installation, because a veranda sheathed with polycarbonate will turn out to be too hot.
Polycarbonate is a very durable material, and any ideas regarding glazing are better carried out with it rather than with glass, because the likelihood of damage is reduced by almost 200 times.
Pay attention to the transparency of the veranda attached to the polycarbonate house. There are quite a few types of panels, and not all of them will be completely transparent. You can purchase colored sheets - and then the veranda will look quite bright and interesting.
Chemical resistance of the material
Monolithic polycarbonate is a polymer that can effectively withstand destructive environmental factors. The material is inert to many aggressive environments, and this ability depends on temperature and concentration of substances.
The panels are characterized by high chemical resistance to the following compounds:
- Organic and inorganic acids and solutions of their salts.
- Various types of reducing agents and oxidizing agents.
- Alcohols and synthetic detergents.
- Organic fats and fuels and lubricants.
At the same time, some chemical compounds are capable of reacting with the polymer, which leads to the gradual destruction of the panels.
For the convenience of the reader, information about the resistance of polycarbonate to certain liquids is presented in the form of a table:
| Acetic acid | + | Hexane | + |
| Salt | + | Hydrogen peroxide, concentration up to 30% | + |
| Butyl alcohol | + | Gasoline, diesel fuel and mineral oils | + |
| Ethanol | + | Ammonia | – |
| Hydrochloric acid, up to 20% | + | Butyl acetate | – |
| Propane | + | Diethyl alcohol | – |
| Boric acid | + | Methyl alcohol | – |
| Potassium permanganate, max. conc. 10% | + | Alkaline solutions | – |
| The “+” sign in the table means the resistance of the material to long-term exposure to the specified substance. | |||
Roofing pie device
The veranda belongs to the category of extensions that are built for such purposes as evening tea, barbecue, billiard room and setting up a summer kitchen in a country house. All this suggests that on the veranda there will always be water vapor from food and people, and, due to its closed nature, the temperature will always be higher than outside. This means that you cannot build a simple roof without the necessary insulation from vapors and condensation.
On the other hand, for pitched roofs the arsenal of roofing coatings is much more open, while for the same flat roofs one often has to limit oneself to rolled materials or liquid rubber. Therefore, if your veranda is open, like a terrace, and you don’t plan to cover it with the same as on the house, seriously consider modern rolled materials - these perfectly protect the interior space of the veranda from precipitation and do not require additional roofing layers:
In other cases, you will need reliable waterproofing. This film or the membrane does not allow moisture to enter the insulation, and we will definitely use insulation in the gable roof of the veranda.
Next, under the waterproofing film, if you look from top to bottom, the insulation itself should be located. This can be mineral wool, glass wool, ecowool and any other modern insulation. The main thing is only to protect it from rain moisture and melt water, for which a film or membrane is spread over it:
But on the ceiling side of the veranda, the insulation also needs to be protected from moisture. We are talking about a vapor barrier film. This insulation is designed to withstand, as far as possible, invisible water vapor rising upward, which can cause a lot of damage to the insulation.
As a vapor barrier, we do not recommend that you use unusual inexpensive films that protect the insulation by only 50-70%, but modern dense membranes. You don’t want to completely go through the rotten gable roof of the veranda in 2-3 years, do you?
In addition, if according to the plan there will be something like tea and coffee on your veranda, then take a waterproofing film that is anti-condensation and must be breathable, with special drainage holes. Such, if moisture does penetrate into the insulation (and it will, for example, a high-quality vapor barrier film can withstand water vapor up to 90%, and yet there is this 10% that penetrates the vapor barrier), then it will bring these droplets out through itself, where they will be picked up by the ventilation flow.
This is how we smoothly approached the issue of gable roof ventilation:
How to attach plastic to the sheathing
- If you buy self-tapping screws, their length should exceed the thickness of the coating by 20 mm. So, with a canopy cross-sectional size of 20 mm, it is better to purchase screws with a length of 40 mm or more. Experts put forward this requirement when installing wooden profiles, but for metal ones, 5 mm will be enough to engage the wall. The screws themselves are purchased with a press washer, and the best option would be to have an anti-corrosion coating on the screws.
- When preparing a carport, the panels need to be connected, and for this we need joining profiles. If the roof is single-pitched, then when installing polycarbonate, not all types of profiles will be useful, but only connecting (detachable/one-piece), as well as end ones - for capping edges with honeycombs.
- When installing the covering across the slope, one sheet of panel will not be enough (even with a maximum width of 2.1 m) for a pitched roof. In this case, the polycarbonate is placed along the slope and cut into pieces according to the size of the sheathing. After all, the connecting profile should not hang, but lie on the sheathing beam.
- When choosing the size of a polymer sheet for a canopy, it is better to immediately calculate the roof correctly so that there is little waste.
- If you need three-meter fragments, then six- and twelve-meter panels will be useful - the cutting will take place without any residue. And to organize a carport for parking, it is better to use a wide sheet of 2.1 m, then there will be fewer joints and installation will be easier.
We hope that our article answered your question: what polycarbonate is used for awnings and greatly simplified the process of installing panels at home.
Let's sum it up
Polycarbonate is a material that has revolutionized the construction of transparent roofs. This is the only real alternative to glass not only for small buildings, but also for critical objects. Polycarbonate comes in three types:
- Monolithic is the most durable, even bulletproof, and durable, but expensive, heavy and difficult to install.
- Profiled - lightweight, very easy to install and quite durable, but it withstands impacts less well and practically does not prevent heat loss.
- Cellular is extremely cheap, very light and can withstand light impacts well, but transmits less light, is a short-lived and often unaesthetic material.
Polycarbonate is mainly used to make flat, single-pitched, gable and arched roofs of gazebos, terraces, galleries, verandas, greenhouses, and canopies.
To install monolithic polycarbonate, it is better to hire specialists, while profiled and honeycomb sheets can be installed on the roof yourself. How is written in detailed instructions in this article.
Assembling a carport frame: example
After you decide what thickness of polycarbonate is needed for the canopy, you need to start making the sheathing. It is quite possible to obtain a bent metal profile using a pipe bending machine and using a welding machine. But not every home craftsman has such tools. It is much cheaper and faster to prepare a wooden sheathing from timber - there will certainly be no problems with carpentry tools!
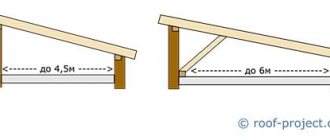
Then you should calculate the number of risers according to the area of the canopy. In this case, you need to make sure that there are no spans over 3 m, because the beams can bend under the weight of the snow. If you are making a canopy from polycarbonate, then you can use 100x100 mm timber as supports, then use a profile with the same cross-section to make the strapping (100x50 mm lumber is allowed).
To make the lathing, use a board with the same size of 100×50 mm - this is the most optimal option. If such material is not available, you can use other values - 70×40 mm, 70×30 mm. The width of the building is of great importance when choosing the size of lumber. Since the length of the parking area is no more than 2.5 m, you can use the smallest section of the board.
Wood sheathing under polycarbonate is placed on a pitched roof on top of the beams, i.e., taking into account the slope, the mating will be carried out only along the edges of the board or beam. How to connect them? Let's say right away - it's not easy.
You can use two options:
- cutting a groove on the board and, accordingly, weakening the profile;
- installation and reinforcement with corners on both sides.
The last method is the simplest, and the design with corners will be more rigid and stable.
The pitch of the sheathing for an overall polymer roof should not exceed 50-60 cm, and with frequent fastenings the pressure on the polycarbonate decreases. The size of the roof overhang depends on the wishes of the customer, but keeping in mind the loads of wind and snow, it is better not to increase it more than 40 cm. The thickness of polycarbonate for an canopy was discussed above.