Individual design
On this page of the site you can familiarize yourself with the composition of the project of constructive solutions (CD) for a private country residential building - find out what it includes; the level of its elaboration, the composition of the drawings.
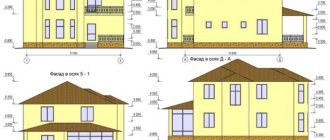
For clarity, an example of a structural design of a house in the Moscow region, Bely Bereg municipality, is shown. The facility is under construction. In order to monitor compliance with the design design, designer supervision is carried out. To control the quality of construction work, the developer can order a technical supervision service. The gallery above shows photographs of the phased implementation of the project.
Click on the QR code and scan it to read this page on your smartphone, or to share the link to the project with friends
Navigation
Why do you need a CD, initial data for design?- Why do you need a structural project?
- Initial data for the design of the RC
Composition of the design solutions project
- KP0 - foundation of the house
- KP1 - structures of the above-ground part of the house
- KR2 - roof structures
Example (sample) of a design design project
- KP0 - foundation of the house
- KP1 - structures of the above-ground part of the house
- KR2 - roof structures
How to order a constructive project
- If a design design is required
Composition of technical documentation for MKD
The list of documents that are part of the technical documentation of the MKD and must be with the MA is determined by clauses 24, 26 of the RF PP No. 491.
- technical passport of the house;
- documents for metering devices;
- documents on acceptance of work results, estimates, inventory of work;
- inspection reports, condition checks;
- inspection reports and issued certificates of readiness for the heating period;
- MKD operating instructions;
- cadastral plan of the land plot;
- extract from Rosreestr;
- urban planning plan of the land plot;
- documents on the validity of an easement or other encumbrance;
- design documentation;
- registers of owners and persons using common property on the basis of concluded agreements;
- agreements on the use of common property of apartment buildings;
- decisions and minutes of general meetings of owners;
- other documents.
Also, a list of technical documentation is contained in clause 1.5 of the resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation No. 170. It includes a site plan with buildings and other objects, design and estimate documentation, acts of acceptance of the house from the developer and the technical condition of the house, diagrams of intra-house networks, passports for each room in house and land plot, estimates of work for current and major repairs and technical inspection reports and other technical documents.
Why is it important for the management company to keep the technical documentation for MKD in order?
8812
1
How to order a constructive project
We are always open to dialogue and ready to help in resolving issues related to design and construction.
Send your applications to our email, or via Whatsapp, Viber, Telegram. All applications are reviewed by the chief designer personally, and based on the results of studying the assigned design tasks, a commercial proposal is formed, which includes a description of the composition of the project, its cost, deadlines, and a list of necessary initial data. Upon request, we can send you an example of a completed structural design for your reference. After agreeing on the commercial proposal, we proceed to drawing up the contract. Design begins only after it has been signed, an advance has been received and all the initial data necessary for the work have been received. Discuss the project with the designer
Obligation of the MA to store, restore and transfer technical documentation
The management organization is obliged to store and transfer all technical documentation and other documents to the house in accordance with clause 27 of the RF PP No. 491. The law establishes a presumption that the organization managing the house has the documents requested for transfer. That is, by default it is considered that the MA stores a complete package of technical documentation for the house.
If the owners of the OSS decided to change the management or management method, then the former management is obliged, after notification of this, to transfer technical and other documentation for the house to the new company or TSN within 3 days from the date of termination of the management agreement (clause 19 of the RF PP No. 416, Part 10 of Article 162 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
If the documentation is missing in whole or in part, then the MA has three months to restore and transfer it (clause 21 of the RF PP No. 416). If the MA does not comply with this requirement, it will be brought to administrative liability under Part 1 of Art. 7.23.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, and in case of repeated violation, he will lose his license (Part 5.2 of Article 198 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
It happens that the management organization cannot transfer technical documentation to the new MA or TSN, since it is completely or partially lost and was not transferred to the MA when signing the management agreement.
However, the absence or loss of documentation cannot be grounds for termination of the obligation to transfer it within the time limits specified in the legislation. In this case, the management authority must do everything in its power to find the missing documents or restore them at its own expense (decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated June 22, 2016 No. 307-ES16-6140, determination of the Supreme Court dated May 30, 2017 No. 307-AD17-5791).
Therefore, the management organization should check in advance the completeness of the documentation and, if necessary, take measures to find or restore missing documents. Some of them must be requested externally: from the developer, the former administrative authority, the RSO, the local self-government bodies and the State Housing Authority.
What reasons for the loss of house documentation are considered valid?
6843
1
Determining the technical condition of a residential building
Determining the technical condition of a residential building
Content
- Introduction
- Object characteristics
- Design solution and technical condition of building structures
- Foundations
- Wall construction
- Roof and roofing of the building
- Interfloor ceilings
- Stairs
- Building utilities
- Cold water supply
- Hot water supply
- Heating system
- Sewerage
- Electrical system
- conclusions
Deformation of the plinth masonry
Introduction
| 1. | Reason for conducting the survey. | Agreement No. 145-15 dated October 15, 2021 |
| 2. | Customer of the survey. | Individual entrepreneur … |
| 3. | Performers of the survey. | LLC "InRegionGroup" |
| 4. | Time of examination. | October 2021. |
| 5. | Object of examination. | House. |
| 6. | Elements to be examined. | - Foundations.
- Walls.
- Coating.
- Roof.
- Roof.
- Network engineering.
|
| 7. | Purpose of the survey. | Visual and instrumental examination of load-bearing structures of a residential building to determine their technical condition. |
| 8. | Survey objectives. | Measurement work of structures and dimensions of premises in a residential building. Determination of geometric dimensions of structural elements. Determining the technical condition of a residential building, determining the safety of living in a residential building, determining the safety of a residential building for others. Based on the tables of VSN 53(r), determine the physical deterioration of the building. |
| 9. | Completed set of works. | - Measurements of structures and dimensions of premises in a residential building were carried out. The geometric dimensions of the structural elements are determined.
- The technical condition of the residential building was determined. Based on the tables of VSN 53(r), the physical wear and tear of the building was determined.
- An analysis of the design features of the building was carried out. The actual strength characteristics of the materials have been determined. The compliance of the completed structures with the requirements of SNiP and GOST was determined.
- Based on the results of the survey, a report was compiled with conclusions and recommendations based on the survey results.
- An analysis was carried out of the presence of factors that pose a threat to the life and health of citizens from the erected structure (for compliance with the requirements of the Federal Law of December 30, 2009 N384-FZ “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures”).
|
| 10. | Instrumentation for examination, testing methodology. | The survey of geometric parameters and strength characteristics of structures was carried out using the following devices:- 5-meter metal measuring tape.
- Laser Rangefinder.
- Crack gauge template.
- Measuring ruler.
- Calipers.
- The object was photographed using a Canon EOS 550D digital camera.
- Ultrasonic concrete tester UKS-MG4
- Moisture meter Testo-606
|
| 11. | Design, executive, operational and other documentation used during the inspection. | The inspection work was carried out in accordance with the requirements and recommendations of SP 13-102-2003 “Rules for the inspection of load-bearing building structures of buildings and structures.” The classification of the technical condition of building structures is given in accordance with GOST R 31937-2011: Serviceable condition is a category of technical condition of a building structure or a building and structure as a whole, characterized by the absence of defects and damage that affect the reduction of load-bearing capacity and serviceability. Serviceable condition - a category of technical condition in which some of the numerically assessed controlled parameters do not meet the requirements of the design, norms and standards, but existing violations of the requirements, for example, for deformability, and in reinforced concrete and for crack resistance, under these specific operating conditions do not lead to a violation operability and load-bearing capacity of structures, taking into account the influence of existing defects and damage, is ensured. Limited operable condition is a category of technical condition of structures in which there are defects and damage that have led to some reduction in load-bearing capacity, but there is no danger of sudden destruction and the functioning of the structure is possible by monitoring its condition, duration and operating conditions. Emergency condition is a category of technical condition of a structure or building and structure as a whole, characterized by damage and deformations indicating the exhaustion of the load-bearing capacity and the danger of collapse (urgent emergency measures are necessary).
|
Deformation of the plinth masonry. Destruction of the blind area.
Object characteristics
| 1. | Location (address) of the object. | Moscow region, Ruzsky district, ... |
| 2. | Purpose of the building. | House. |
| 3. | Year of construction of the building. | 1993. |
| 4. | Number of floors. | 2 floors, with attic space. |
| 5. | Foundations | Strip foundation |
| Exterior walls | The building consists of a main volume of 6x8 m, with log walls and 2 frame-type extensions. |
| Presence of internal transverse walls | Frame type. |
| Interfloor ceilings | Wooden floor. |
| 6. | Spatial rigidity. | It is provided by a strip foundation, external walls, wooden floors, and the rafter system of the roof of the building. |
| 7. | External condition of the building: a) weathering of masonry and peeling of plaster mortar | Peeling of tiles, weathering of mortar joints, deformation of masonry. |
| 8. | b) state of jumpers | Due to deformation of the frame part of the building (extensions), window and door units cannot be opened. The technical condition is limited and operable. |
| 9. | c) deformation | During the inspection, deformations of the following structural elements of the building were recorded:- foundation subsidence;
- deformation of the frame of the extensions;
- deformation of the porches;
- deformation of the floor of the 1st and 2nd floors.
|
| 10. | Landscaping of the site (yard layout, presence of blind areas) | Blind areas around the perimeter of the building. The blind area has been destroyed in places. |
| 11. | Balconies, bay windows, cornices and other protruding elements of facades. | None. |
| 12. | Facades. | The facades are lined with siding. |
| 13. | Stairs. | Wooden internal single-flight staircase. At the entrance to the porch there is a single-flight staircase. |
| 14. | Partitions | Frame, covered with boards. |
| 15. | Window and door fillings | The window units are wooden with double glazing. Door blocks are metal and wood. |
| 16. | Roof, Rafter system | The roof of the building is metal. Wooden rafter system. |
| 17. | Classification of an existing building by capital | In accordance with Appendix No. 4 of the collection No. 28 “Enlarged indicators of replacement cost”, the existing building corresponds to capital capital group 4. Distribution of residential and public buildings by capital groups:
Technical condition of the pit
Design solution and technical condition of building structuresFoundations| 1. | Foundation design based on survey results. | The shallow foundation of the building is strip, made of FBS concrete blocks, monolithic concrete, and brickwork made of solid clay bricks with cement-sand mortar. The depth of the foundations is 1200 mm from the level of the soil level on the outside of the foundation and there is practically no penetration into the ground on the inside (from the side of the technical underground). There is no basement. | | 2. | Description of materials: class of concrete, type of brick, type and shape of stone, type of mortar, etc. | - Clay brick density p=1800kg/m3
- Cement-sand mortar p=1400kg/m3
- Heavy concrete p=2500 kg/m3
| | 3. | Horizontal and vertical waterproofing | Horizontal waterproofing was made from 1 layer of roofing material along the top of the foundation strip. | | 4. | Presence of dampness and capillary moisture. | The humidity of the lower crowns of the log house is 13.2-14%, the humidity of the floor boards is 9.8-12.4%. Increased humidity of wooden structures in the area of leaks due to leaks in the roof of the building. | | 5. | Information about the foundation soils located at the edge of the foundation. | Loams are moisture-saturated. The foundation soils are heaving. | | 6. | Defects identified during foundation inspection | Diagonal and vertical cracks of a sedimentary nature in the basement of the extension foundation.- Peeling of the plinth lining.
- Moistening the base masonry, defrosting the brickwork.
- Curvature of masonry rows in the basement of the extension foundation.
- Deformation of the furnace foundation.
- Insufficient foundation depth.
| | 7. | Technical condition and physical wear of the foundation | In accordance with SP 13-102-2003, the technical condition of the foundation under the main volume of the building (log walls) corresponds to a limited serviceable condition. The technical condition of the foundation under the extension corresponds to emergency conditions. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r) Table 3, the physical wear of the foundation under the extension is 60%. The physical wear of the foundation under the main building corresponds to 40%. | | 8. | Scope of work to eliminate defects | In accordance with Table 3 of VSN 53-86(r), with physical wear and tear of 60%, it is recommended to carry out the following types of work:- − strengthening the foundation of the veranda, replacing individual sections of brickwork, installing a 100mm thick reinforced concrete cage around the perimeter of the foundation, reinforced with a mesh of 10mm reinforcement.
- − restoration of horizontal waterproofing by injection into the horizontal joints of the plinth masonry.
- − installation of vents in the foundation of the building.
- − strengthening the furnace foundation with reinforced concrete casing, 100 mm thick.
- − from the technical underground side, make a soil embankment of sand, ensuring that the foundation is buried into the ground at least 1400 mm.
- − dismantling porch foundations and installing new ones.
- − install wall drainage along the perimeter of the building’s foundation with organized drainage of surface water.
Requirements for ventilation of technical underground In accordance with SNiP 31-01-2003 9.10. In the external walls of basements, technical undergrounds and cold attics that do not have exhaust ventilation, vents with a total area of at least 1/400 of the floor area of the technical underground or basement should be provided, evenly spaced along the perimeter of the external walls. The area of one vent must be at least 0.05 m2.
Calculation of the required number of vents The total floor area under the main volume of the building measuring 6x8m is 48m2. Required number of vents = 0.12m2. With a vent size of 250x250mm. Area of one vent = 0.0625m2, which corresponds to the recommended value of 0.05m2. The required number of vents will be 0.12/0.0625= 1.92 (2 pcs). |
Cracks in the base
Wall construction| 1. | Construction of walls and partitions based on survey results. | Walls of the main volume of the building at the 1st floor level Log house. The cladding of the external walls is made of plastic panels (siding). Attic walls and extension walls. Wooden walls. Structurally, the walls are framed and sheathed and consist of wooden crossbars and frame posts, which are sheathed on the inside with boards and on the outside with plastic panels (siding). Porch Frame structure made of racks and wooden crossbars. | | 2. | Description of materials | Wood with a density of 500 kg/m3 | | 3. | Defects identified during the inspection. | - Increased humidity and rotting of log walls and internal cladding due to leaks from the roof of the building.
- Deformation of the frame of extensions due to uneven settlement of the foundation.
- Deformation of the frame of the porch walls.
- Gaps between boards of interior cladding.
- Humidification of thermal insulation.
- The construction of the frame partition inside the building was made without taking into account the clearance for the settlement of the crowns of the frame walls of the building, as a result of which the ceiling above the 1st floor is deformed.
| | 4. | Partitions | Wooden frame-cladding partitions. | | 5. | Waterproofing | 1 layer of roofing felt along the top of the foundation strip. | | 6. | Presence of dampness and capillary moisture. | Traces of dampness and fungus formation on the crowns of the building's frame in places where there are leaks from the roof. | | 7. | Technical condition and physical wear of the walls. | In accordance with SP 13-102-2003, the technical condition of the log house walls corresponds to limited working condition, in areas of roof leaks - emergency condition. The technical condition of the extension frame corresponds to limited working condition. The technical condition of the porch walls corresponds emergency condition. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r) Table 8, the physical wear and tear of the walls of the log house (the main volume of the building) is 30%. In accordance with Table 7, the physical wear and tear of the extension walls is 60%. Physical wear and tear of the porch walls is 70%. | | 8. | Technical condition and physical wear of partitions. | In accordance with SP 13-102-2003, the technical condition of the partition corresponds to a limited working condition. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), the physical wear of partitions is 40%. | | 9. | Wall finishing | Sheathing with boards (lining). Facing with siding. | | 10. | Technical condition of finishing coatings | In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), the physical wear of plank cladding is 40%. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), when wear is 40%, it is necessary to reassemble the skin, in some places up to 50% of the area without adding materials. Exterior decoration made of plastic panels needs repairing up to 50% of the area. | | 11. | Window units Type Technical condition Physical wear | Wooden window units with double glazing. During the examination the following defects were recorded: - Small cracks in the places where the frames meet the walls, wear or cracks in the narthexes.
- Minor damage to tides.
Technical condition : limited operability . In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), the physical wear and tear of window units is 40%. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), when wear is 40%, repair of bindings is necessary, strengthening joints with overlays, restoring glazing. It is recommended to replace the window units with new ones. | | 12. | Door blocks Type Technical condition Physical wear | Internal doors are wooden. During the examination the following defects were recorded: - the door leaves have sagged or have a poor rebate around the perimeter of the frame, the door frames (blocks) are skewed.
Technical condition : limited operability . Physical wear and tear is 40%. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), when wear is 40%, repair of door leaves and frames is necessary. It is recommended to replace the door blocks with new ones. |
The seams between the FBS blocks are not sealed
Roof and roofing of the building| 1. | Type and design of the roof of the building. | The roof is of the attic type with an internal attic living space and an attic space. The load-bearing structures of the attic are wooden rafters with a cross-section of 150x50mm. The rafters are lathed with 200-250x20mm boards. | | 2. | Building covering and roof materials | The rafters and sheathing are made of pine with a density of 500 kg/m3. | | 3. | Filling. | Thermal insulation made of mineral board and vapor barrier made of black paper. | | 4. | Defects identified during the inspection. | Roof:- weakening of notches and connections due to deformation of the extension structure due to uneven settlement of the foundation.
Roof: - Destruction of the roof at the junction of the main volume of the building with the extension. Lack of fastening of roofing sheets. Leaks.
| | 5. | Technical condition of rafters, beams, coverings, sheathing. | The technical condition of the rafter system and sheathing corresponds to limited working condition. The technical condition of the thermal insulation and vapor barrier corresponds to an emergency condition , due to moisture in the thermal insulation and breaks in the vapor barrier, as well as exceeding the service life. Replacement required. Physical wear and tear of the roof in accordance with Table 38 is 20%. In accordance with VSN 53-86(r), when wear is 20%, repair of fasteners and joints of wooden parts is necessary. Due to the deformation of the rafter system, it is necessary to strengthen the joints by placing galvanized metal plates on the joints. | | 6. | Construction and technical condition of the building roof. | The roof of the building is made of ondulin type material. The technical condition of the roof corresponds emergency condition. Physical wear and tear of the roof in accordance with Table 44 VSN 53-86(r) is 80%. It is necessary to install a new roof from lightweight materials (metal tiles) with vapor and thermal insulation from mineral basalt slabs of the “NG” type. |
Floor filing. Extension foundation.
Interfloor ceilings| 1. | Type and design of building floors. | The ceiling above the technical basement is made with thermal insulation from expanded clay backfill with a thickness of 100-150mm, with a vapor barrier. Wooden flooring made of planks is made along the beams The ceiling decoration is made of planks. | | Floor materials | Beams and floor boards made of pine, volumetric weight 500 kg/m3. Backfill with a volumetric weight of 600-800kg/m3. | | Floor defects | On the 1st floor, due to leaks from the roof, the joists and floor boards have become rotten. On the 2nd floor, due to the lack of a technological gap between the partition and the floor beams, the joists and floor covering are deformed. On the 2nd floor, at the entrance to the 2nd floor, from the stairs, there is a breakdown in the connections between the beams and the walls. | | 2. | Technical condition of floors. | The technical condition of the interfloor ceilings, including the 1st and 2nd floors, corresponds limited working condition. On the 1st floor in the place of leaks from the roof - emergency condition. In accordance with VSN 53-96(r), the physical wear of floors is 40%. In accordance with Table 26 of VSN 53-86(r), it is necessary to eliminate cracks and gaps and strengthen the beams in places. In areas where roof leaks occur, physical wear is 80%. In places of leaks, it is necessary to completely replace the joists and floor boards above the technical underground, with the installation of new layers of vapor barrier and thermal insulation. It is recommended to replace the vapor barrier and thermal insulation above the technical underground over the entire floor area. Due to the deformation of the floor above the 1st floor, it is necessary to strengthen the beams in the place of deformation above the partition and to bulkhead the floors on the 2nd floor, leveling the floor level. It is necessary to install support posts under the floor joists at the entrance to the 2nd floor. It is recommended to install a layer of non-combustible basalt mineral slabs in the ceiling of the 2nd floor. | | 3. | Floor type Physical deterioration | The living areas have plank floors. Taking into account the presence of defects in the form of deflections and subsidence, and sometimes breaks (in quarters) of individual boards, in accordance with Table 51, the physical wear of the plank floor is 60%. In accordance with Table 51, when wear is 60%, it is necessary to carry out repair measures: re-flooring with the addition of new material up to 25% of the floor area, replacing joists in places. |
Sedimentary cracks. Destruction of masonry.
Stairs| 1. | Type and design of stairs. | Single-flight wooden staircase leading to the attic. | | 2. | Staircase materials. | Pine with a volumetric weight of 500 kg/m3. | | 3. | Technical condition of the stairs | The technical condition of the stairs corresponds to working condition . The physical wear and tear of a wooden staircase is 20%. |
Deformation of the concrete foundation
Building utilitiesCold water supply| 2. | Type and design of cold water supply system | Water is supplied to the system from an individual well. | | 3. | Piping system | Polypropylene pipes. | | 4. | Physical wear and tear of the cold water system | Physical wear and tear of the cold water system, in accordance with Table 65, is 20 %. It is recommended to repair the system at the entrance to the building, rebuild the pit with a device for entering the building without a pit, because The pit is a source of stagnation of surface water, which leads to premature wear of the foundation material. Thermal insulation must be installed on the pipelines at the entrance to the building and in the technical underground. |
Measuring the strength of concrete
Hot water supply| 1. | Type and design of the DHW system | Autonomous hot water supply system. | | 2. | Piping system | Polypropylene pipes. | | 3. | Physical wear and tear of the hot water supply system | Physical wear and tear of the hot water supply system is 20%. Partial renovation needed. |
Rot damage to the crowns of a log house in the area of roof leaks.
Heating system| 1. | Type and design of the heating system. | Autonomous heating system. The heating system equipment consists of 1 heating boiler using liquid fuel. The heating system of the building is made according to an open circuit, with overhead wiring. An expansion tank is installed in the attic. The heating system is introduced on the 1st floor of the building and consists of 2 pipelines - supply and return, on which shut-off valves are installed. The coolant flows to the heating devices through risers from the main pipelines. Steel radiators are used as heating devices. | | 2. | Pipelines of the system. | Pipelines made of black steel. | | 3. | Physical wear and tear of the heating system. | Physical wear and tear of the heating system does not exceed 20%. After a period of non-use of the building, it is necessary to check the functionality of the boiler and perform a pressure test of the heating system to check the functionality of the system. |
Emergency technical condition of the roof
Sewerage| 1. | Type and design of the sewerage system. | Gravity sewer system with septic tank. | | 2. | Pipelines. | Polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 100mm and 50mm. | | 3. | Physical wear and tear of the hot water supply system. | Physical wear and tear of the sewerage system is 20%. It is necessary to repair the fastening of sewerage system pipelines to building structures. |
Furnace foundation. Deformation.
Electrical system| 1. | Electrical system type and design | The building has hidden wiring in a metal corrugated pipe. Due to roof leaks, water may accumulate in the corrugations; in places where building structures are deformed, the wires experience additional tension; the wire sheath has lost its elasticity and is cracked. | | 2. | Network type | Wires with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 for lighting and 2.5 mm2 for sockets. | | 3. | Physical wear and tear of the electrical equipment system | Physical wear and tear of the electrical equipment system is 80 %. It is necessary to replace the power supply system with a new one with open installation in boxes. |
Condition of the house facade. Peeling of the plinth lining.
conclusionsBased on the examination of the technical condition and structures of an individual residential building at the address: Moscow region, Ruzsky district, ... the following conclusions can be drawn: 1. The existing residential building is a permanent structure and belongs to capital group 4 and responsibility class 2. The building structures are non-demountable, the building foundations are buried in the ground and are connected to the ground. The load-bearing structures of the building are: - The foundation is strip made of brickwork.
- Brick walls.
- Wooden roof.
- Wooden floors.
2. Based on the examination of the technical condition of the foundation, roof, roofing and brick walls, we can conclude that these structures need major repairs. 3. As a result of the visual and instrumental examination, signs of a decrease in the strength and stability of load-bearing building structures were recorded in the form of deformation sedimentary cracks in the walls and base of the building. 4. Based on the classification of defects, the load-bearing capacity of the plinth masonry was assessed. The reduction in the bearing capacity of the base, in places where cracks form, will be 75%. Fixed cracks of a sedimentary nature divide the foundation structure into separate volumes and, as a result, the spatial rigidity is disrupted and the stability of the building walls is reduced. 5. The reason for the appearance of cracks in the base is subsidence of the foundations, due to the presence of heaving soils and insufficient depth of the foundations. Currently, the above-ground part of the building is deformed at the junction of the main volume with the attached part. The depth of the foundations, in accordance with the verification calculation, must be at least 1200 mm. For further normal operation, it is necessary to add sandy soil to a height of 1400 mm from the technical underground. 6. To increase the load-bearing capacity and durability of the furnace foundation, the extension foundation and the foundation of the main volume of the building, it is necessary to reinforce the outer side of the foundation with a reinforced concrete frame 150 mm thick. The reinforcement of the cage is made from a mesh with a cell of 200x200mm, consisting of rods with a diameter of 10mm of class A500. Fix the reinforcing mesh in the existing foundation structure with horizontal rods with a diameter of 10 mm, with a pitch of 600 mm, in a checkerboard pattern using chemical anchors. The concrete grade of the cage should be class B25. Fill the joints between the FBS blocks with a mortar of NTs brand cement by injecting the mortar into the masonry. Replace areas with deformed brickwork of the basement with new ones (photos No. 1, No. 2). 7. To stabilize moisture in the foundation structure, it is recommended to install wall drainage from plastic pipes below the base of the foundation, with organized removal of surface water from the foundation through a drainage well. Drainage pipes (drains) should be laid below the edge of the monolithic grillage at a depth of at least 300 mm. The backfill should be made of medium-sized sand with layer-by-layer compaction up to Kp=0.95. 8. The building’s blind area and drainage system do not provide normal drainage from the building’s foundations. When performing major repairs, it is necessary to take the following measures to organize drainage from the foundations of the building: - Install drainpipes and eaves trays on the roof of the building.
- Combine drainpipes and blind areas into a single system by installing storm drainage.
Due to the exceeding of the service life of the horizontal waterproofing material, it is recommended that when carrying out major repairs of walls, install horizontal cut-off waterproofing under the walls of the main volume of the building. Waterproofing is carried out by injecting polymer waterproofing compounds such as “Lakhta penetrating” or “Penetron” into 2 rows of the brickwork of the base. 9. The wood of the lower crowns of the frame, lining and rough floor boards has an increased moisture content of the boards exceeding the standard value established in SP 28.13330.2012. 10. The reason for the increased humidity of the wall and ceiling materials above the technical underground is the following factors: - Insufficient ventilation of the technical underground.
- Capillary suction of moisture from the soil and insufficient number of layers of horizontal waterproofing.
- The emergency condition of the blind area and the unorganized vertical layout contribute to the penetration and accumulation of surface water and water of the “overwater” type in the technical underground.
- Roof leaks.
11. It is necessary to carry out additional treatment of the floor beams and the lining along the beams with bioprotective compounds. In accordance with SP 28.13330.2012, the following compositions must be used to protect wood: - Impregnating water-borne acrylic and acrylic-alkyd with a composition consumption of 120-150g/m2.
- Impregnating organic alkyd, with a composition consumption of 120-150g/m2.
- Film-forming compositions are water-soluble, with a composition consumption of 150-200 g/m2.
12. Treat the wood of the floor above the technical underground with fire retardant compounds. 13. Due to roof leaks, the wood of the floor joists of the 1st floor are susceptible to biological damage. It is necessary to replace the floor joists of the 1st floor in the area of leaks. Based on the results of verification calculations of the thermal insulation of the 1st floor floor, made of expanded clay gravel, it was established that the heat transfer resistance is insufficient for normal operation. To eliminate additional moisture build-up in the floor materials above the technical underground, it is recommended to replace the existing bulk thermal insulation and vapor barrier with a new one made of mineral wool basalt slabs with a thickness of at least 100 mm. The following materials can be used as a vapor barrier: waterproofing film ISOSPAN-AM in one layer along the sheathing and joists. For thermal insulation, vapor barrier film ISOSPAN - V. 14. The technical condition of the thermal insulation of the attic and extension is emergency, due to high humidity. During major repairs, it is recommended to install new thermal insulation from a mineral slab with a thickness of at least 100 mm and install a new vapor barrier. 15. The technical condition of the frame crowns in places of leaks from the roof corresponds to an emergency condition. Replacement is required. Due to uneven settlement of the foundation and deformations of building structures, the following structures must be strengthened: - veranda frame at the connection points of the elements;
- rafter system at connection points;
- floor beams above the 1st floor.
16. The technical condition of the roof corresponds to emergency conditions. The roof needs replacement. 17. The building is equipped with autonomous heating systems, hot water supply, a common cold water supply system and a sewerage system. 18. The building is also powered from the general electrical network; an ASU panel is installed at the entrance to the building. The building has hidden wiring in a metal corrugated pipe. Due to roof leaks, water may accumulate in the corrugations; in places where building structures are deformed, the wires experience additional tension; the wire sheath has lost its elasticity and is cracked. Physical wear and tear of the electrical equipment system is 80%. It is necessary to replace the power supply system with a new one with open installation in boxes. 19. The hot water and cold water system is made of polypropylene pipes. It is recommended to repair the system at the entrance to the building, rebuild the pit with a device for entering the building without a pit, because The pit is a source of stagnation of surface water, which leads to premature wear of the foundation material. Thermal insulation must be installed on the pipelines at the entrance to the building and in the technical underground. 20. Physical wear and tear of the heating system does not exceed 20%. After a period of non-use of the building, it is necessary to check the functionality of the boiler and perform a pressure test of the heating system to check the functionality of the system. 21. The technical condition of the porches is emergency. The structures need to be dismantled.
|
First, contact the former MA
The first step in restoring documents for a house created not by the management authority, but by third-party organizations, will be to contact the company that previously managed the apartment building. First of all, you need to request, if they are missing, the instructions for using the MKD, technical passport and technical plan, documents for ODPU and IPU installed in the house.
In this case, you must strictly follow the rules for such correspondence:
- Negotiations must be conducted in writing in order, if necessary, to confirm the actions taken to search for technical documentation at home.
- It is better to send all requests and requirements by registered mail with notification. This will eliminate the fact that letters were lost and the possibility that the addressee did not receive the application.
- In the letter of demand, indicate the deadline when the company is obliged to provide you with the missing documents for the apartment building.
If the company refuses to provide documents, contact the State Housing Authority or the prosecutor's office with a statement about violating licensing requirements and creating obstacles to the management of the house. Supervisory authorities must oblige the previous organization to hand over the missing documents, including this done in court.
How to update the data of the MKD technical passport
33536
0
What is included in the preliminary design
We should also talk about the composition of the preliminary design. What do you get by paying a decent amount of money to specialists?
- Explanatory note. It contains a copy of the technical specifications, a list and sequence of work performed at the site, optimal construction and finishing materials, as well as a list of information and software that was used in drawing up the sketch.
- Facade plan. Serious companies offer several facade options so that the client chooses the one that fully meets all his requirements.
- Floor plans, attic, basement layout options. The area and shape of each room, the thickness and location of the partitions - all this shapes the interior appearance of your future home.
- Illustrations. Image of the house from the inside and outside. To create illustrations, special programs are used to create 3D images of the cottage, which greatly simplify the perception and implementation of further work.
- Drawings of the cross-section and longitudinal section of the building. Their number depends on the client's requirements.
- Roof. All calculations for roofing using the material chosen by the customer.
- General plan of the site. General drawing of the land plot, top view. The location of both the house itself and all other buildings is shown here.
- Foundation. The location, shape and size of the foundation, as well as calculations confirming its necessity.
As you can see, a building sketch is a very complex set of information, without which you simply cannot begin building your dream home.
Searching for a copy of the home's operating instructions or information about its loss
If the previous management organization did not have instructions for operating an apartment building, then you should contact the developer and the municipality archives for it.
According to clauses 24, 25 of RF PP No. 491, the developer is obliged, within a month after receiving permission to put the house into operation, to transfer three copies of the instructions: one to the HOA, if one has been created in the house, the second to the first owner of the premises who applied for it in the house, and send the third to the municipality archives.
If the house does not have an HOA, and the owners have not applied for their copy of the operating instructions, then these copies are kept by the developer for three years. Similar requirements have been imposed on developers since July 1, 2007, when the order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated June 1, 2007 No. 45 came into force.
For three years, while the developer must keep the operating instructions for the house, the management organization can contact the company that built the house with a written request to provide it with a document by decision of the general meeting of owners (clauses 27–29, 31 of order No. 45) .
If the three-year period has expired or the developer responded that he does not have such instructions, the MA must contact the municipal archives for a copy of the third copy. If there is no such document in the archive, then the management organization must retain letters confirming the lack of instructions from the developer and in the archive. With their help, the MA will prove to the supervisory agency that it has taken all possible measures to restore this document.
Errors in USRN data about a house and steps necessary to correct them
19659
1
Facade style
Of course, the main requirement for a façade is its beauty. The house should be attractive, elegant, original and at the same time discreet. But experts pay attention not only to beauty, but also to functionality.
- How and where is it better to place doors, windows, terraces and balconies?
- What configuration should the gables have?
- Where should the roof drain be located?
- The optimal height of the floors, the slope of the roof - all this must be taken into account.
And if all these requirements are met, an experienced architect manages to make the building even more attractive. This is real art, which an amateur who is taking on such work for the first time will obviously not be able to achieve.
Restoration of documents for metering devices
Information about the ODPU and IPU installed in the house must be placed by the organization managing the house in the GIS Housing and Communal Services in accordance with clause 5 of section. 10 of order No. 74/114/pr. If these documents are not available, then the management company must restore them as soon as it has concluded a management agreement for the apartment building with the owners.
If the previous management authority did not provide such data, you can request it from the developer, if possible, or from the resource supply organization that supplies utilities to the house. The RSO must store certificates of approval for the operation of common house and individual resource metering devices.
The storage of such documents by the RSO and the developer is provided for in paragraphs 6, 7, part 3 of Art. 55 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 7, art. 11 No. 261-FZ, clause 4 of Rostechnadzor order No. 1128 dated December 26, 2006.
Data on the technical characteristics of installed metering devices can be obtained from the owners of the premises, who must keep meter passports, or requested from the manufacturer. True, the latter will most likely ask for a fee for the service.
The amount of information transmitted, which relates to the established DPPU and IPU, depends on whether the MA was the provider of public services or the owners entered into a direct agreement with the RSO.
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on the establishment of an easement on a land plot
21326
2
Location on the site
When locating housing on a plot of land, it is necessary to comply with a number of sanitary and fire safety requirements, as well as building standards. The distance from the house to the border of the neighboring plot must be no less than the established minimum. It is also necessary to correctly orient the house relative to the cardinal directions. Technical rooms are best located on the north side, while residential rooms should be placed on the south.
Of course, the house should fit gracefully into the surrounding landscape, and not stand out from it. When drawing up a master plan for a site, an experienced architect will successfully place on it not only the house itself, but also all the buildings that the owner of the site considers necessary. This could be a gazebo, garage, bathhouse, guest house and a number of other buildings.
Obtaining inspection reports and certificates of readiness for the heating season
Having lost the right to manage the house, the organization must transfer to the new MA or TSN, a person authorized by the meeting of owners, certificates of readiness of the house for operation in the autumn-winter period, a passport for the last heating period.
The passport is issued by the authorized body of the local self-government on the basis of an inspection report (clauses 9, 11 of section II of the order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation dated March 12, 2013 No. 103). Therefore, copies can be requested from the municipality or the heat supplier. Documents on the readiness of the house for operation in the autumn-winter period must be obtained from the heat energy supplier and from the local government in accordance with Section. III order No. 103.
If the legislation of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation provides for the sending of such documents to the State Housing Inspectorate, then the management authority should contact the State Housing Inspectorate with a request to provide it with copies of such documents.
We check whether the housing stock is ready for the heating season
13721
2
How much does design cost?
Making a good plan takes time. It can take a week to create it, and several specialists will be involved in the process. With a thorough approach, the customer will receive 20–30 detailed drawings developed for his future home. In them, all parameters will be calculated, dimensions will be perfectly verified, parts and assemblies will be properly displayed, the maximum load will be calculated, and a list of building materials will be drawn up.
How much the project will cost depends on the area of construction and the number of circuits.
An architectural section designed by a professional architect will cost at least 40–50 thousand rubles. Working on a constructive one will increase the amount by another fifty. The engineering part will also require from 30 to 60. In total, a set of technical documentation for the construction of a small private house will amount to 120 - 170 thousand rubles.
From the outside, these numbers seem too high, but don’t rush to jump to conclusions. Creating a competent plan helps you save significantly. Without it, the construction site will turn into a center of chaos and endless errors. Financial costs in this situation will increase several times.
Financing the process at the expense of the management company or owners
Restoring documentation is a difficult, lengthy and sometimes costly procedure. The management organization should provide its own funds for this or, at a general meeting of owners, approve the amount of payment for housing services, which will include the amount necessary to restore the technical documentation.
If the documents were lost or not transferred by the previous company, then the MA should document all expenses incurred in restoring the documents and then present the amount to the company that previously managed the house for reimbursement voluntarily or compulsorily.
We will continue to talk about the restoration of technical and other documentation for an apartment building, including the restoration of the technical passport and the documents that the management organization itself must create and maintain.
Floor plan
The development of a sketch of the building itself begins practically from scratch. First of all, the architect builds the axles. The elements of the building are built in relation to them: foundation, roof, walls, door and window openings, ceilings and partitions.
You need to know a surprising amount in order to competently draw up a preliminary technical design of a building.
It only takes a few minor mistakes to make being in a building uncomfortable, let alone living in it permanently.
Calculating the optimal distance between load-bearing structures allows not only to guarantee strength, but also to reduce the cost of pouring the foundation and building floors.
Example of calculated dimensions between load-bearing structures
Project of a house made of timber
Most often, economical, strong and durable wood is chosen as the main material for construction.
However, the project of a private house made of timber requires compliance with certain conditions:
- If timber more than 6 m is required for construction, then additional insulation of the joints of the logs will be required;
- The joints are placed in a checkerboard pattern;
- The number of corners must be even;
- Particular attention must be paid to proper load distribution;
- Log partitions are placed only above load-bearing walls or on additional pillars.
Third stage - work plan
The working version of the project serves as a guide for the construction team and involves a complete description of all the envisaged work for building a house: architectural, structural, engineering and design.
In an architectural project, the location of all premises, their area, the presence of balconies or terraces, the size of windows and doors, the slope of the roof, and the thickness of the walls are outlined and drawn.
Important! Glazing and finishing of balconies can be ordered at low prices on the website viploggias.ru. "Modern Balcony" is a company with many years of experience.
The constructive type of project involves a detailed consideration of each element of the house from the foundation, walls and ceilings to the chimney, stairs and rafters. For example, a complete description of the characteristics of the windows is attached, where the width of the profile, the type of lining, the number of layers of double-glazed windows, and the presence of a window sill are noted.
We recommend: How to properly lay linoleum on the floor
Engineering design is aimed at drawing up a detailed plan for the implementation of work to establish sewerage, water supply, ventilation, heating, electrical wiring, grounding and security systems.
The design project makes final adjustments to the construction of the house. At this stage, the color scheme of the facade, walls, roof and interior decoration of the room is finally determined.
Brick house project
The design of a brick house must necessarily include an assessment of financial capabilities, since this type of construction is expensive and requires the creation of a strong and costly foundation.
When building brick houses, other features of the material should be taken into account: the use of clay bricks on the lower floors, double waterproofing in the bathroom, wall reinforcement for greater strength, strict adherence to horizontal masonry, laying out window and door openings with a quarter.
We recommend: Inserting water supply into a private house - advice from experienced