Everyone knows that water negatively affects any building structure, be it a multi-story building, a small country house or another structure. In this connection, during construction, much attention is paid to the issue of drainage and protection from groundwater and melt water. A highway is no exception; it also requires high-quality drainage to prevent destruction of the roadway structure. After all, major repairs of a highway are an expensive undertaking, which means that during construction it is necessary to comply with all the rules and, first of all, an effective drainage ditch must be installed along the road. It is through such a small trench (ditch) that water is drained from the roadway and thus does not destroy the road surface.
When is drainage ditches required?
The need to drain water from a site arises when water accumulates in large quantities on the surface of the earth and is poorly absorbed into the soil.
Water drainage from the site is also required in the following cases:
- the location of the territory in a lowland, where melt and rainwater flows from higher places;
- water seepage, damp smell or mold in the basement or subfloor;
- swampy area, wet ground even in the hot and dry season;
- puddles that do not dry out for a long time after snow or rain melt.
If the site is located on an elephant, to prevent erosion of the fertile soil layer, transverse drainages should be installed to intercept and drain water into storm drains, storage tanks and other suitable places.
The need for soil drainage can be determined after a hydrogeological study of the soil on the land plot.
If the site has a high level of groundwater, measures for water drainage must be provided at the stage of building a house.
Drainage ditches in an area with difficult terrain.
General information
Is drainage always necessary?
A drainage system is not required in every area. Drainage is required if:
1.groundwater is located high, above the level of the foundation, or the distance from the surface is less than a meter.
2. if the site is located on an area that runs along a slope or in a lowland.
3. if the soil is clayey and the foundation is slab or shallow.
4. if the area is partially or completely swamped.
5.if desired, prevent the formation of puddles and dirt in the area.
6.water often penetrates into the basement or basement floor where equipment is located, or the room is intended for other purposes.
7. If there is a clay-type soil on the site, surface drainage should be organized to drain water after rains and snow.
Attention! Sandstones and chernozems do not require mandatory drainage. A drainage system is not necessary if:
A drainage system is not necessary if:
1.groundwater rarely and briefly rises higher than the foundation is located.
2. if water rarely and in small quantities enters the basement.
3. the site is not of a swampy type, maintaining the appearance of the site without puddles is not required.
Signs when a drainage system is needed
The first step is to inspect the area. If the following signs are identified, then drainage is required:
1. cracked blind area, cracks appearing in the foundation and walls.
2. when water gets into the basement.
3.puddles stagnate after rains.
4.The water in the well is high, close to the surface.
Laying methods
Drainage ditches can be open or closed.
- Open drainage ditches are trenches located in areas of greatest accumulation of water. They are used to drain surface melt and rainwater and are especially effective for draining areas located on a slope.
To prevent the walls from collapsing, trays made of plastic, polymer concrete or reinforced concrete can be installed at the bottom of the trench. The trays are covered with decorative grilles on top for safety purposes and to protect them from leaves and debris.
The walls of the ditch can also be reinforced with metal meshes - gabions, natural or artificial stone, turf, special plastic geogrids and other materials.
- Closed drainage ditches are more complex in design.
Such structures are constructed by laying drainage pipes in trenches. Water enters the drains through the perforated walls and is removed by gravity outside the site or to specially designated areas. To prevent siltation, pipes are covered with drainage crushed stone and wrapped in geotextiles. From above, the drainage is filled with plant soil and sown with lawn grass.
The number of ditches depends on the height of the snow cover on the site, the degree of soil moisture during the rainy season and the depth of groundwater.
When installing open ditches, it is necessary to make the walls as airtight as possible so that the water, without being absorbed, goes into the storm drain.
Scheme of a closed drainage device.
Closed drainage system
This technology is a ditch, at the bottom of which water collects. This design can be made either temporary or permanent.
Temporary - does not require much knowledge or special technologies. The construction of trenches is the most common. The main thing is that they have a slight slope towards the drainage point.
This technique is based on connecting drainage pipes, a collector, wells, a water intake, and a drainage system. The water intake is a special ditch or sewer dug outside the site.
Classification of drainage ditches
The problem of soil waterlogging by storm drains, groundwater and flood waters is typical for country houses and summer cottages, highways and park areas.
The underground structures of houses suffer, roads and sidewalks are destroyed, the fertile layer is washed away and the soil structure deteriorates.
To solve waterlogging problems, drainage ditches are created, which are classified according to various factors:
By purpose
- drainage of water from the foundations of buildings and structures, cellars;
- redirection of water flows on slopes and areas with complex terrain;
- drainage of wetlands with high groundwater levels;
- protection of roads, sidewalks and access roads from destruction, arranged along roads in the form of ditches;
>At the installation location
Depending on the amount of wastewater discharged, drainage ditches are:
- main - in the form of a complex of trenches laid across the territory of the site;
- perimeter - made around the perimeter of a house or fence;
- auxiliary - receiving water from individual areas.
In case of minor watering, it is enough to arrange a ditch along the boundaries of the site. To fully protect an area with complex terrain, a complex drainage network will be required.
Figure 4. Open drainage tray.
Purpose and types of systems
Methods for organizing drainage systems on a site differ depending on the amount of precipitation, groundwater level, soil type characteristics, site topography, location of the house and other factors.
Based on the installation method, drainage can be divided into two types.
- A perfect drainage system is installed at the level of natural water flow. Moisture enters the drains through holes located on the sides, as well as through the top of the pipes.
- An imperfect drainage system is installed higher than the water level. Moisture penetrates into drains from below, above and on the sides. To strengthen the sides of this structure, a drainage cushion made of sand and crushed stone is used.
Based on the way drainage is arranged, it is divided into open and closed.
Open
Drainage is a system of gutters, trenches, gutters, and drainage trays. This system is organized without pipes. This drainage looks like a trench 0.5 meters wide and 0.5-0.6 meters deep, designed to drain melt and storm water from a house or site. The trench must have a slope towards the main water intake trench so that water is drained in the desired direction by gravity.
The main advantages of such a drainage system are its low cost and speed of creation. However, in order to drain large amounts of water due to precipitation, a deep drainage line will be required, which is unsafe. In addition, if the walls of the ditches are not equipped, they will quickly collapse. Another disadvantage of such a system is that it makes the area look less neat and aesthetically unattractive.
To increase safety and increase the service life of this drainage option, special concrete or plastic trays are used, closed on top with gratings. Open drainage is most often used in agriculture to drain water from already cultivated areas.
Closed
Underground drainage is a pipe system. It has a nicer appearance compared to the previous one, as it is equipped with a protective grille, but the receiving ditch is much narrower and smaller. Closed drainage schemes are used to protect foundations and basements from the effects of groundwater and increase their service life.
Particularly closed drainage is suitable for wetlands, as well as areas near which there are natural bodies of water or located in lowlands. In this case, closed drainage is best supplemented with storm drainage. Underground drainage is also called deep drainage.
Underground drainage is divided into two types:
- wall;
- trench.
If the house is already completely ready, then you should opt for a trench ring drainage system. But it is worth considering that it is only suitable for houses without a basement. In small areas where there is no need for open drainage, backfill drainage is used. The system of such backfill trenches cannot be maintained without dismantling after complete installation. This is its main drawback. The organization of backfill drainage is carried out in several stages.
Determining the direction of movement of wastewater on the site
The direction of movement of the drains and the slope of the drainage pipe depend on the following parameters:
- terrain and degree of elevation change;
- depth of groundwater;
- soil freezing level;
- geological features and soil type on the site.
The depth of groundwater can be determined by the water level in a well or river (if there are one nearby).
Otherwise, you will have to dig a well or order a hydrogeological survey of the site from a specialized company. The results of the survey will allow you to select the optimal option for drainage systems.
Drainage ditches will only work effectively if the correct slope of the turf is maintained, as regulated by established regulatory standards.
Table 1. Relationship between pipe diameter and trench slope.
| Diameter of drainage pipes (mm) | Trench slope per 1 m/p of pipe |
| 50 | 3 |
| 110 | 2 |
| 160 | 1 |
| 200 | 0,8 |
Drainage drainage trenches should be located in such a way that water flows through them by gravity
Insufficient pipe slope will lead to silting of the walls and blockages.
Too large a slope leads to significant loads and premature failure of communication nodes.
Errors in calculations will lead to ineffective drainage ditches or premature blockages. Experts will help you avoid technical errors.
Installation of drainage ditches on your own.
Drainage on a slope
An impeccably designed and well-calculated drainage will collect and drain groundwater from the site. It will protect the foundation from premature destruction and ensure normal growth of cultivated plants. In order to ensure spontaneous drainage of the water collected by the system, it is necessary to ensure the slope of the drainage pipe. And its device requires accurate information, right?
You will learn everything about the angle at which drainage pipes are laid and how to properly organize a drainage system from our article. By following the technical recommendations we provide, you will be able to design and accurately calculate your drainage network. The basis for the given data is building regulations.
To help independent craftsmen, the technology of constructing a water drainage system is described in detail, and the specifics of the calculation and installation of its components are thoroughly analyzed. Photos and videos are attached for visual perception of the information.
There are three types of drainage systems, each of which has its own design features:
- horizontal;
- vertical;
- combined.
The working elements of horizontal drainage can be:
- tubular drains;
- gallery drains;
- trays and trenches.
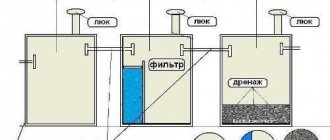
A system of drainage pipes in combination with a filter coating (multilayer) is a tubular drain.
Multi-layer filter coating, in this case, is done to prevent washed-out soils from entering the system. According to standards, the drainage circuit is always equipped with inspection wells.
To organize the drainage system of a construction site (site), different schemes can be used. The specific choice depends on the geological conditions of the area, the intensity of precipitation and other factors
Unlike tubular drains, gallery drains are made from pipes of a larger cross-section. There are holes on the walls of the pipes for collecting waste. The process of installing gallery drains also involves filling with additional filtration with geotextiles.
Tubular drain in section. It is on this principle that tubular and gallery drains are installed in modern house-building projects. Compliance with standards and accuracy of calculations guarantee high efficiency of drainage systems
A drainage system with trays and trenches is usually made in conditions where the groundwater level is allowed to reach 1.3-1.5 m. On stable soils, trenches are made with slopes; on unstable soils, the trenches are reinforced with reinforced concrete structures.
A vertical drainage system consists of a set of wells (wells) connected by a collector. Sewage is removed through the collector line using a pumping station. Also, drainage of wastewater on vertical drainage can be carried out by discharging into the lower layers of the soil.
The combined drainage system combines horizontal and vertical schemes. It is characterized by specialists as a complex drainage scheme and is usually installed in areas where highly efficient soil drainage is required.
Based on the calculated parameters of drainage depth, surface and deep drainage schemes are distinguished. The purpose of the surface scheme is to collect and drain atmospheric precipitation products, as well as nearby groundwater. The purpose of the deep scheme is to lower the groundwater level, collect it and drain it beyond the boundaries of the site where the construction site is located.
An example of a surface drainage system. Surface drainage is widespread in private housing construction. A system for collecting and discharging atmospheric precipitation products is necessary for every case of construction of residential buildings
The drainage water intake circuit supports point or linear design. In the first case, wastewater is removed from local sources (drains, sidewalk pits, entrance collections). The linear scheme ensures water drainage throughout the entire facility. As a rule, a combined solution with the implementation of both schemes is used on residential construction sites.
Deep drainage is required in almost all cases of private housing construction and landscaping of commercial plots. This is an effective protection of those elements of building structures that are located below the zero level (foundation, basements, plant root systems).
It is permissible to exclude the construction of deep drainage at elevations where the groundwater level does not exceed 1.5 m, where effective soil drainage is observed.
Fragment of the scheme for laying deep drains. Typically, such schemes provide for the placement of drainage wells - at least one for every 30 meters of the main line. On straight sections, installation intervals of 50 meters are allowed
Designing a deep drainage scheme requires high precision calculations. Even a minor error in calculations can cause low system efficiency. The practice of installing such schemes often indicates a common mistake - inaccurate calculation of the depth of drains. The result is uneven drainage of water from the territory of the facility or, even worse, flooding of fertile lands and basements.
The calculated values that will be required for the construction of a drainage system are usually:
- pipeline diameter size;
- pipeline laying level;
- pipe slope values;
- density of the geotextile filter.
And more details about each point.
From areas located on slopes, it is also necessary to drain excess water from the surface and from inside the soil. After all, large amounts of precipitation and water formed as a result of melting snow cause land erosion, contribute to landslides, and also erode the foundations of various buildings, paths, retaining walls and steps. For such areas it is necessary to combine open and deep types of drainage.
Read more: Technology for replacing heating batteries using gas welding
Actually, the installation of a deep drainage system in areas on a slope is not much different from that carried out in horizontal areas. But still, there are some points that should definitely be taken into account when performing these rather complex works. With this location of the site, it immediately becomes clear that the well for collecting water or sewerage should be located at the lowest point. The main or main trenches are dug, if possible, next to the fence.
Auxiliary trenches are directed to the main one at a certain angle. It turns out something like a Christmas tree. If the slope of the terrain is not enough for good drainage of water, then trenches are dug, gradually deepening so that the overall slope is from 2 to 4 cm per 1 linear meter of drainage.
If the area on the slope occupies a fairly large area, then it is worth dividing it with a transverse drainage trench, which will collect water from the area located above. The water from it will flow through buried drainage pipes into the lower water intake or sewer system.
It is worth remembering that the construction of a drainage system on a site located on a slope requires preparation, attention, careful execution and, of course, financial costs.
Don't be upset if you get an uneven piece of land. Thoughtful landscape design on a site with a slope and proper drainage will help turn the disadvantages of your garden into advantages.
Advantages and disadvantages
Properly executed drainage can lower the groundwater level, remove flood waters and heavy precipitation from the site, improve soil fertility, prevent the death of tree and shrub roots, and the formation of mold and mildew on building structures.
The main advantages of drainage ditches include:
- simplicity of design;
- high efficiency;
- minimal care;
- Possibility of installation on your own;
- rapid removal of rain and melt water outside the site;
- affordable price.
With a little effort and bringing to life design ideas and personal creative fantasies, you can decorate the trench so that it becomes a decoration of the land, harmoniously blending into the surrounding landscape and the architecture of nearby buildings.
Among the disadvantages of drainage ditches are:
- possibility of clogging and silting of the system;
- lower efficiency compared to storm sewer;
- the need for regular maintenance.
Diversion ditches can be arranged even in low-lying areas where other types of drainage are difficult to implement.
Storm water drainage
According to the classification, it is also classified as open drainage (but it has a significant difference - trays, grates and sand traps) and surface drainage. It is used for local collection and removal of water coming from above: rain, snow, car washing, watering paths with a hose. Therefore, such drainage is always done in the foundation area, on paths and paved areas, in garages and around garages, even on lawns - and is divided into two types: point and linear.
Most often, surface drainage of both types is required - point and linear.
Spot surface drainage
Small square, rectangular or round water collectors (rain inlets) are point-installed in the required places: under drainpipes, water taps, on platforms, paths, near garages, and so on. As a rule, they are connected to storm sewers. Catchment grates are usually made of plastic, but where special loads are expected, steel, aluminum, and cast iron are used.
Point surface drainage with cast iron grate under the drain - an effective design
The rain inlet has a fairly simple structure.
Storm water inlet device for point drainage: grate, sand trap, pipe
Point and linear storm inlets must be equipped with a sand trap to prevent the pipes from becoming clogged: then the drainage efficiency will drop to zero. In a point rainwater inlet, the sand trap is placed in the body itself. It is impossible to do without them.
Requirements for drainage ditches
The trenches of drainage ditches are arranged taking into account the slope, allowing water to move by gravity towards storm wells, reservoirs or special containers, from where water can subsequently be taken for irrigation or technical needs.
To effectively drain water, open ditches must meet the following dimensions:
width - 40-50 cm;
depth - 60-70 cm;
wall slopes are within 30-45 degrees.
The slope of the trench towards the drainage tank, storm well or reservoir must be at least two centimeters per linear meter of the ditch. To prevent blockages and ensure reliable drainage of water by gravity, it is better to arrange a slope of 3-5 mm per 1 meter of the trench.
The thickness of crushed stone drainage is selected depending on the water permeability of the soil.
For safety reasons, open ditches should be equipped with a low fence.
How to properly make drainage around the house. Step-by-step instruction
After completing the design work and purchasing everything you need, you can begin work.
- Clearing the area. Remove debris and anything that might interfere with work.
- Preparing the trench . Dig trenches while maintaining the slope. The minimum width is equal to the pipe diameter plus 30 cm. The slope is checked by level. Its size is 1-2 cm per 1 meter.
- Backfill. Fill the trenches with sand in a layer of at least 10 cm.
- The foundation is prepared for the wells . Make a platform of suitable size, filled with sand. If the groundwater level is high, the site for the well is concreted with a 10-centimeter layer on which the well is fixed.
- Cover the trenches with geotextiles . Its edges should extend beyond the top edges of the trenches.
- Laying drains . Crushed stone is poured onto the geotextile in a layer of 10-20 cm, leveled so that the thickness is the same and the angle of inclination does not change. Drains are laid, connecting them with fittings or sockets. Connect the pipes to the “inputs” of the well. For tightness, rubber O-rings are used.
- Backfilling of pipes . An even 20-centimeter layer of crushed stone is poured over the pipes and wrapped in geotextiles.
- Backfilling with sand . 20 cm of sand is poured on top of the geotextile, compacted, and covered with soil.
- Digging a well . The wells are buried and covered with lids.
If there is a large amount of precipitation in the region, especially in summer, storm drainage trays (storm drains) are located directly above the drains. They are laid on a sand cushion.
You can see an example of laying drainage around a house in this video.
Necessary materials
To make a drainage ditch yourself, you will need special materials:
- drainage perforated fiberglass pipes, 50-150 mm in diameter, for collecting and draining water from the site. Pipes must have perforations in the form of holes with a diameter of 1.5-5 mm located around the entire circumference of the pipe. May be encased in filter materials;
- bends, fittings and couplings for connecting pipes;
- geotextile fabric that protects the drainage system from silting;
- inspection wells for system maintenance;
- filtering or storage tanks for collecting wastewater from the site;
- river sand and crushed stone, for the construction of underlying and drainage layers.
In addition, you will need shovels for excavating soil, power tools for installing pipes and wells, and various tampers for compacting the bottom of the trench.
To protect drainage pipes when laid under the road, steel pipe sleeves will be required.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Several practical tips on laying drainage pipes will help you independently cope with the installation of drainage in a suburban area.
Protecting areas (territories) from moisture oversaturation is an urgent task that has to be solved in almost every construction case. Existing developments of drainage systems allow solving such problems .
The main point is to calculate and choose a drainage device option that would be ideal in each specific case.
Are you planning to arrange the drainage of the site yourself, but have encountered difficulties at the design stage? Ask your questions in the comments block - we will try to help you.
Or have you successfully built a drainage system and want to share your experience with other private homeowners? Write your recommendations, add photos under our article - many users will find your experience useful.
Stages of construction of drainage ditches
Before the start of construction work, they mark out the area and wait for heavy rain to determine where the most moisture accumulates - it is from there that the water should be drained first.
To construct open drainage ditches, soil is developed in trenches along the perimeter of the site, around buildings, or in the form of a branched network. The walls of the trays are reinforced with natural materials or plastic drainage trays are installed.
The technology for constructing closed drainage ditches involves performing the following operations:
- Manual or mechanized excavation of soil in trenches.
- Leveling and compaction of the ditch bottom.
- Construction of a sand cushion, 10-15 cm thick.
- Geotextile laying on sand preparation.
- Filling the bed with a layer of drainage crushed stone.
- Installation of perforated drainage pipes and connecting them to inspection wells and storage tanks.
- Filling the pipes with a second layer of crushed stone and wrapping the edges of the sheet. Geotextiles will prevent silting of crushed stone and drainage pipes.
- Backfilling of the drainage trench with soil and arrangement of the surface layer of the subgrade.
This design will allow surface and groundwater to filter through the crushed stone layer and be discharged through a drainage pipe into a storage tank or drainage well.
Storage tanks or filter wells are installed in the lowest part of the site. To clean pipes and monitor the condition of the system, inspection wells are installed at intersections.
The depth of the wells depends on the level of drainage pipes and methods of further drainage.
Water from storage tanks can be used for technical purposes or for irrigation of the site.
To protect the site from waterlogging, it is necessary to correctly draw up a diagram, calculate the slopes and arrange a system of drainage ditches.
Inspection well.
To guarantee the efficiency of the system, it is better to order turnkey installation of drainage ditches from specialized organizations.
Making deep drainage with your own hands
To know how to make drainage on a site, you need to know its construction technology. The drainage system for removing water from the ground surface is usually made of main or main trenches, which are often located along the perimeter of the site. They have a slope towards the sewer. There are also auxiliary trenches that run throughout the entire site from the places where the largest amount of water is formed to the main ones. Accordingly, the auxiliary trenches have a slope towards the main ones. Typically it ranges from 1 to 3 cm per meter.
Before you begin constructing the drainage, be sure to draw a plan of the site and drainage system. Mark trenches and monitor slope while excavating using tools. This will help avoid unpleasant surprises after all work is completed. Remember that the walls of surface drainage are located at an angle of about 30 degrees to the bottom. It is advisable to strengthen them. This can be filling with crushed stone or gravel, as well as finishing with large stones, concreting and planting various plants.
After digging trenches, be sure to check how the water will flow through the drainage system. To do this, run a sufficient amount of water over it and watch how it passes through it. If it stagnates in some area, it is better to eliminate this problem before the work is completed.
It is also worth noting that an open drainage system can become the center of the landscape composition of the site if it is decorated with beautiful combinations of stones of different shapes, sizes and colors.
A network of drainage trenches to remove water deep in the ground is dug according to a plan drawn up in advance and marked on the surface with the required slopes. The width of the trench at the bottom is usually at least 40 cm, and the depth is determined by the project. But usually it ranges from 0.8 to 1.5-2 meters. The slope varies from 2 to 5 cm per 1 linear meter of trench.
Read more: Grouting tile joints. How to choose the right grout for tile joints
A small layer of clean river sand (coarse-grained) about 10 cm high is poured onto the flat and compacted bottom of the trench, which is also carefully leveled and compacted.
Then the bottom and walls of the trench are covered with non-woven geotextile fabric, the density of which is about 200 grams per square meter. Moreover, the fabric is positioned so that it should completely cover the walls and still extend to its edges by 15-25 cm. A layer of washed crushed stone with a height of 15 to 25 cm is poured onto the fabric, which directly depends on the composition and water permeability of the soil. On lands with a large amount of sand, the layer height is about 15 cm, and where there is a lot of clay in the composition, the crushed stone layer is increased to 25 cm.
Crushed stone must also be compacted and leveled taking into account the required slope. You need to check the slope after each poured layer, its leveling and compaction. A perforated drainage pipe is laid out on it, which is then covered in layers with crushed stone or gravel. Moreover, each layer must be carefully compacted. The layer of crushed stone on top of the pipe is from 10 to 25 cm.
On top of the drainage pipe and the fill around it, the edges of the non-woven geotextile fabric are wrapped over each other with an overlap. Then a layer of sand 10 to 30 cm high is poured, after which the trench is filled with ordinary soil, which was removed during digging. Remember that river sand, crushed stone and gravel used in the construction of a deep drainage system must be free of soil, clay or other small particles. Drainage made in this way will drain water well and will last for many years.
Retaining wall in landscape design When we buy a building plot, the question arises: to choose a flat or sloping site. Frequently offered...
If you have received a building plot, studies of which have shown that groundwater lies very high to the ground surface, this does not mean that construction is canceled or hampered. You will simply have to increase the construction estimate for the installation of drainage and stormwater systems that will drain melt, rain and groundwater from the foundation of the house, ensuring the dryness of the structure and the duration of its operation.
It is more difficult to do site drainage on clay soils with your own hands, since clay does not absorb and allow water to pass through, but that is what the drainage system is for. On the other hand, clay soil keeps groundwater from penetrating into the upper layers of the soil from below, and you only have to protect the structure from moisture entering the soil from above - from rain and snow.
Drainage system on clay soil
Purpose of drainage
It is recommended to arrange drainage for a site on clay soils immediately after acquiring land for construction or development, and the first step to ensuring the safety of your home is geological and geodetic surveys, on the basis of which the project is drawn up. But if you have at least the slightest experience in construction, such research can be carried out independently, relying on information from neighbors and on your own observations.
Water passing close to the ground surface is dangerous in spring and autumn, as it is fed by precipitation, which quickly replenishes underground rivers. The weaker the soil, the faster the groundwater will be replenished by rain and meltwater. Therefore, the need for site drainage depends on the depth of groundwater, and when the water level is 0.5 m below the base of the foundation, it is necessary to drain water. The depth of the drainage pipes is 0.25-0.3 meters below the groundwater level.
Surface water (overwater) manifests itself if the site contains clay and loamy soil layers that practically do not allow water to pass through. In clay areas, immediately after rain, large puddles appear that do not sink into the soil for a long time, and this is the first sign of a large layer of clay in the soil. The remedy in this case is drainage and a storm system, which will immediately drain rain or melt water from the surface of the site.
Drainage and stormwater drainage system
In order to completely protect the house from surface water, in addition to drainage and storm drainage, layer-by-layer backfilling of the base with clay soil is done, with each layer being compacted separately. A blind area wider than the backfill layer is also required.
What and how to drain a site on clay soil? These are, first of all, the following events:
- Construction of a waterproofed blind area;
- Arrangement of storm drainage;
- Digging upland ditches is a depression in the ground on the upland side of the site for the purpose of draining rain and melt water;
- Protecting the foundation from moisture with waterproofing materials.
Storm drain
Drainage can be done general or local. The local drainage system is intended only for draining the basement and foundation; general drainage drains the entire area or its main part, which is at risk of waterlogging.
Existing site drainage schemes:
- The ring circuit is a closed loop of pipes around a residential building or site. The pipes are laid 0.25-0.35 m below the groundwater level. The scheme is quite complex and expensive, so it is used in exceptional cases;
- Wall drainage is used to drain the foundation walls, and is installed 1.5-2.5 m from the building. The depth of the pipes is 10 cm below the basement waterproofing level;
- Systematic drainage includes an extensive network of canals to drain water;
- A radial drainage scheme is a whole system of drainage pipes and drainage channels combined into one structure. It is mainly developed to protect the site from floods and flooding;
- Formative drainage protects against high water, and is installed together with wall drainage to protect the slab base. This scheme consists of several layers of non-metallic materials plus a layer of waterproofing, on which a reinforced slab foundation is built.
Read more: How to lay sewer pipes in a private house, diagrams, rules for laying pipes, installation stages
Ring drainage
Cost of drainage, approximate estimate
The first issue when planning drainage ditches on a site is their cost.
It depends on the following factors:
- ditch designs;
- length of the system;
- number of inspection, filter or storage wells;
- cost of materials;
- labor costs of workers.
The estimated cost can be calculated using electronic calculators on the websites of design and installation companies.
The final price is determined by estimates developed by specialists after examining the site and determining the drainage system layout.
Table 2. Approximate cost calculation for constructing a drainage ditch 55 meters long.
| Name of work and costs | Unit change | Qty | Unit price | Total cost (RUB) |
| ||||
| Development of soil in trenches | m3 | 70 | 300 | 21 000 |
| Sand preparation device with layer-by-layer compaction | m3 | 25 | 250 | 6 250 |
| Installation of perforated pipe | m/n | 55 | 180 | 9 900 |
| Filling the trench with gravel or crushed stone | m3 | 48 | 250 | 12 000 |
| Laying geotextiles | m2 | 250 | 20 | 5 000 |
| Filling the ditch with soil with compaction | m3 | 10 | 500 | 5 000 |
| Installation of a reinforced concrete drainage well | ||||
| Soil development | m3 | 5 | 300 | 1 500 |
| Installation of the bottom, rings and cover of the well | PC | 5 | 750 | 3 750 |
| Hatch installation | PC | 1 | 500 | 500 |
| Backfilling of soil | m3 | 2 | 500 | 1 000 |
| Total cost of work | 65 900 | |||
| ||||
| Crushed stone fraction 40-70 | m3 | 48 | 600 | 280800 |
| Quartz sand | m3 | 25 | 450 | 11 250 |
| Geotextiles | m2 | 50 | 300 | 15 000 |
| Perforated PVC pipe | m/n | 55 | 320 | 17 600 |
| Reinforced concrete drainage well rings | PC | 5 | 1 850 | 9 300 |
| Luke | PC | 1 | 2 500 | 2 500 |
| Total cost of materials | 84450 | |||
| 10 000 | |||
| Total cost of work and expenses | 160350 | |||
The cost of delivery of materials may vary depending on the remoteness of the facility.
The estimate provides for the construction of a drainage ditch with a slope of 0.6 to 1.5 meters.
Drainage systems in areas with complex terrain are complex engineering structures that require the development of design documentation.
You should not skimp on installing inspection wells to allow cleaning of drainage systems.
Installation work
An open system is easy to organize with your own hands. A closed system is more difficult to install; it requires knowledge and skills. If you follow the nuances, you can install the system yourself. The work will require assistants, at least three people.
How to prepare ditches
Ditches for the stormwater system are dug according to the size of the trays, adding up to thirty-five centimeters in depth. If you dig trenches on the surface of the earth, then the ditches should be up to a meter high, keeping the walls beveled to thirty degrees. If the drainage system is closed, then dig ditches more than one meter deep and more than three pipe circumferences wide. Thirty centimeters should be added to the required depth to lay a layer of crushed stone with sand. Drainage around the perimeter of the building requires ditches with a depth of over 1.2 meters, so that the system runs at a depth greater than the freezing level of the ground. The ditches run from the house at a distance of 1.2 m to 1.5 m, from the blind area at a distance of 90 - 120 centimeters.
How does a surface drainage system work?
The tray-based system is installed on an anti-heaving cushion, which is made of twenty centimeters of sand and fifteen centimeters of fine crushed stone. Each layer of the pillow should be wrapped in geofabric. When laying, an inclination of at least two millimeters per meter should be observed. Point storm drains are equipped with storm inlets with waste baskets.
How does a deep-type drainage system work?
To make a closed drainage, you must follow certain steps. The following stages are distinguished:
1.at the bottom of the ditch, lay geotextiles with wide strips to wrap up the crushed stone, and with narrow strips to wrap up the sand.
2.pour a layer of sand up to fifteen centimeters, compact it, and wrap the edges of the geotextile.
3.lay crushed stone with a grain size of sand from 16 to 32 millimeters in a layer of up to fifteen centimeters, it should be equal to the cross-section of the pipe. Level with a board that is nailed to the stick. Sprinkling the pipe with crushed stone is done so that groundwater undergoes first-level filtration. The crushed stone must be washed. It is raked into a pile to be rinsed under pressure of water for fifteen minutes, then packaged into bags. It does not need to be dried to avoid dust. The shelf life of the bags should not exceed a week. Crushed stone can be replaced with gravel.
4.Pipes are placed on the crushed stone. First, they need to be measured, cut to the required length, and then laid, starting at a collector-type well. Plugs are placed at the ends of the pipe rolls.
Attention! The pipes are laid maintaining a slope of at least 2 to a maximum of 10 millimeters per meter. 5. the remains of the washed crushed stone are poured to the height of one section of the pipe, wrapped in geotextiles
5. The remains of the washed crushed stone are poured to the height of one pipe section and wrapped in geotextiles.
6. A two-centimeter layer of coarse crushed stone with a diameter of 8 to 40 millimeters is poured on top.
7. backfill with earth.
How to build a well
A drainage well is a simple technical structure. The structure must be waterproof. From the outlets of the pipes to the bottom of the well, the distance should be over two hundred and fifty millimeters. Around the well, crushed stone is poured into the pit, and the layers are compacted. It is recommended to purchase ready-made well structures. They should be installed in places where pipes join and at all second turns of the pipeline.
How to install it yourself
If you can’t spend a lot of money on installation, you can do it yourself
It is important to follow the instructions, observing the technology. There is no need to buy advertised brands of pipes for the system
You can purchase rolled pipes at an affordable price that is not inferior in quality. The priority is pipes made of asbestos cement or plastic with large perforations.
How to Clean a Drain Pipe
The functionality of the drainage system may decrease as pipes become silted over time. Drainage elements must be cleaned through inspection or drainage wells. There are two ways to do this:
-mechanical.
-hydrodynamic.
Drains should be cleaned after an average of four years. For cleaning, pneumatic-type installations are used, equipped with a mechanism with which they pass through drains and crush deposits.
The hydrodynamic method is considered more effective. A special pump is connected to a pipe located in the well, and a compressor is turned on, pumping water with air to crush debris and sediment. Due to its effectiveness, this method allows cleaning to be carried out no more than once every ten to fifteen years.
Ways to strengthen drainage ditches
To prevent soil erosion in the ditch, the walls should be strengthened.
The most effective methods include:
- finishing the walls and bottom of the trench with natural stone;
- installation of gabions made of galvanized mesh filled with crushed stone or gravel;
- planting trees and shrubs along the edges of the ditch;
- attaching a geogrid to the walls and bottom of the ditch, followed by backfilling with soil, crushed stone or concrete;
- strengthening the embankment using special sods cut on loamy soils.
Drainage ditches in landscape design.
You can create a drainage ditch on your country property yourself, turning an ordinary ditch into an element of landscape design.
To avoid drainage
Installing a drainage system is an expensive undertaking. If it is possible to make do with other measures, it is worth doing so. Other measures include the following:
- Storm sewer installation.
- Construction of a blind area (for heaving soils, an insulated blind area is desirable).
- In areas with a slope, the installation of a mountain ditch is a ditch of sufficient depth, which is located on a slope higher than the house. From this ditch, water is diverted below the site, into a drainage ditch, and discharged into a ravine, river, lake, etc.
- Foundation waterproofing. To eliminate capillary suction of moisture, several layers of waterproofing material are laid on top of the finished foundation; to eliminate problems with damp walls in the basement, external waterproofing of the foundation is done (dug out to the full depth and treated with waterproofing materials). For greater reliability, treat the walls of the basement and/or ground floor from the inside with penetrating waterproofing of the “Penetron” type.
If after all these measures the situation does not suit you, it makes sense to make a drainage system.
Installation of ditches on a site with a slope
An excess of water can be observed not only in horizontal areas, but also in areas with complex terrain.
When snow melts or heavy, prolonged rainfall, streams of water can flow down the slopes, washing away the fertile layer of soil or causing landslides.
The technology for constructing ditches on slopes is practically no different from the construction of drainage structures on flat terrain.
The most effective drainage system is in the form of a herringbone, when the main trench is dug towards the lowest point of the site, and transverse channels enter it at an angle.
Water from the drained area can flow into storm drains, storage wells or nearby ravines, a pond or lake.
Discharge of water into existing reservoirs is permissible only after agreement with local administrative authorities.
Summarizing
The practice of users of our portal suggests that a way out of any situation, even the most hopeless one, can be found. If you lack experience or self-confidence, you can always seek advice from experienced FORUMHOUSE members, who will always tell you what and how to do correctly during construction. And even without a large budget, with the right approach you can make a reliable and inexpensive storm sewer and site drainage system with your own hands.
A thread on FORUMHOUSE explains how to drain and drain a wetland. We also advise you to study the topic, which gives advice on choosing geotextiles for the drainage system.
Useful articles about the features of the drainage system of the foundation and site, the choice and independent installation of a drainage well, and what to do if the basement floods.
The videos contain the nuances of site drainage and tips on choosing drainage pipes.
Description and principle of operation of drainage pipes
Drainage pipes can be made of asbestos cement, ceramics, metal, but they are rarely used due to their high cost, heavy weight and installation complexity.
Currently, corrugated perforated pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), high or low pressure polyethylene (LDPE or HDPE) are used to perform drainage systems.
Polymer pipes are lightweight, practical and durable. They are simple and easy to install, resistant to various fuels and chemicals.
Drainage pipes have a corrugated surface and perforation in the form of many holes with a diameter of one and a half to five millimeters located across the entire surface of the pipe.
Perforated pipes are available in various variations:
- single-layer;
- two-layer;
- with coconut fiber filter;
- in a geotextile shell.
Single-layer drainage pipes are used at a depth of no more than 1.5 meters. For greater trench depths, two-layer products are used.
Products with a filter and shell protect pipes from silting.
The diameter of the pipes is selected depending on the volume of water discharged.
Perforated drainage pipe.
Which pipes to choose?
It is easier, of course, to make the drainage open, but such a structure will not add an aesthetic appearance to the site. Therefore, most people prefer to build a drainage system that will last for decades and will not be noticeable on the territory. Quality work is done for the long term. When choosing materials for drainage, this must be taken into account.
They have a lot of advantages that will definitely make work and operation easier:
- Availability. This is one of the main points. Since the price of corrugated pipes is much lower than for similar products made from other raw materials.
- Strength. Such works can be laid at a shallow depth. They perfectly withstand soil pressure, subsidence and movement.
- Durability. Such products perform their functions perfectly for at least fifty years.
- Treatment. To cut a plastic pipe, you do not need to use special tools. They are easy to transport and convenient to connect.
Correct drainage slope
How to clear a clogged drain pipe?
Cleaning of drainage pipes can be done mechanically or hydrodynamically.
- Mechanical cleaning is carried out using various brushes, brushes or a sewer cable with a steel brush.
- Hydrodynamic cleaning is carried out using pumping equipment and a compressor. The blockage is cleared with a strong stream of water.
If you were unable to clear the blockage on your own, you should invite specialists who, using special equipment and pneumatic pumps, will clear the blockages and perform preventive maintenance of the entire drainage system.
Cleaning the drain.
The principle of the drainage system
Soil drainage on a site can be closed, immersed in the ground, or open, which is a network of open grooves.
In the first case, the system is designed to drain groundwater if it floods the area. In the second, drainage ensures a decrease in soil moisture during the flood and rainy season.
Both types of systems can be designed and installed in-house.
When purchasing a plot, owners often have no idea about the hydrogeological features of the area. If the soil is too wet and there is prolonged stagnation of water on the surface, you should select the correct drainage scheme (+)
Depending on whether it is necessary to collect moisture from the entire site or only from individual zones, drainages with linear and point water intakes are installed.
Systems of the first type require careful design; when installing them, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the laying technology and the slope angle of the drainage pipes.
Linear options become necessary if you need to drain areas around buildings, paths, entrances, improve the surrounding area, or remove excess moisture from the garden.
Such drains are shallow ditches into which water flows and then moves to special receiving tanks, storm drains, or to a discharge point off-site.
The choice and installation features of drainage elements depend on the expected load on the system: soil density, the amount of water that enters the drains. If the load is too great, you should choose structures made from the most durable materials
Point water collectors must also be accurately calculated and designed in advance. They serve to collect water locally, but are connected to a similar linear system of ditches or pipes.
Through the indicated drainage channels, the collected water is discharged in the same way into a collector well and then into an absorption well, drainage ditch or pond. Therefore, work on installing systems with point water intakes is not much different from systems with linear options.
Open systems are very simple to implement and cheap, but they spoil the landscape with an unaesthetic appearance. Another disadvantage is that the walls of the ditches have to be constantly adjusted, because they crumble under the influence of moisture, and the system ceases to perform its functions (water stagnates at the bottom of the trenches and does not move to the discharge point).
When planning drainage, you should decide on the type of system. You need to consider whether it will be open or closed. In the first case, ditches with slanted walls are dug to facilitate water drainage. The width of such a trench is usually 0.5 m, and it is dug to a depth of 0.7 m (+)
To solve the problem of crumbling ditch walls, you can use the crushed stone filling method: coarse material is placed on the bottom, and fine material is placed on top, after which the entire drainage pad is covered with turf.
This option allows you not to trim or strengthen the walls of the trenches, but it is suitable for areas with relatively low humidity, because The capacity of the ditch is greatly reduced.
The use of polymer and concrete trays in the construction of open drainage greatly facilitates and speeds up the work. In order to improve the landscape and protect systems from clogging, such open systems are covered with cast iron gratings.
To construct a closed system, special perforated pipes are used - drains, laid to the depth of the foundation. They are placed in pre-formed ditches and covered with material with excellent filtering properties, gravel, small crushed stone or GPS. To monitor the operation of the system and carry out periodic cleaning, inspection wells are installed in the corners of the building.
Closed drainage is a system of perforated pipes laid to the depth of the foundation. The task is to protect the underground part of the house from the effects of groundwater. If a closed system is installed to drain the site, then the pipes are located at a depth of 0.7 - 1.0 m
When determining how to properly lay a drainage pipe to protect plants from excess moisture, you can use average values. As a rule, the optimal depth is 0.6-1.5 m.
Decorating drainage ditches
The installation of drainage systems should be carried out before the start of landscaping work on the site.
Drainage ditches must fit harmoniously into the natural landscape.
When designing a trench, it is worth taking into account the general style of the site, the slope of the terrain, the location of green spaces and the architectural style of existing buildings.
To decorate drainage ditches, the following are used:
- natural stones laid with cement mortar or dry masonry;
- decorative grilles and hatches made of metal, plastic or sand concrete;
- gabions or Reno mattresses, which are metal mesh filled with stones.
Drainage ditches can be made in the form of a natural stream, supplemented with bridges or artificial ponds.
Aquatic and moisture-loving plants are planted along the edges of the ditch.
An interesting solution in garden design would be the “French ditch”. It is a trench 50-70 centimeters deep, filled with crushed stone or gravel. This option is convenient because garbage does not accumulate in such a ditch and water does not “bloom.”
Drainage ditches can be installed along paths, fences, or to zone different areas of the garden.
Decoratively designed drainage can become a real decoration of a suburban area.
"French Ditch"
The main types of drainage design
There are several types of drainage systems. Let's consider each type separately.
Wall design
The system is created around the base of the structure (foundation). Wall drainage must be installed if the building has a basement or ground floor. The installation of the wall structure must be carried out during the construction of the foundation of the building, when the foundation pit has not yet been backfilled. If installation is carried out later, you will have to perform additional work, which will require you to spend time, effort and money.
The system is laid along the foundation. Pipes must be routed from the corners of the building to the inspection wells. At the lowest point in the system, an outlet well is created. This well will drain water beyond the boundaries of the site.
Ring or trench structure
This structure is installed at a distance of two or three meters from the base of the structure. This type of drainage system is used for buildings that do not have basements or basements. Or the building must be located on a clay soil layer.
A clay castle is also created between the base of the structure and the drainage structure for additional protection. Drainage must be laid at a depth of 50 centimeters from the lowest point of the foundation. Drains should be laid on coarse crushed stone.
Filtration and storage wells
Drainage wells play an important role in the drainage system of the site.
There are tanks for various functional purposes, the main ones are:
Filtering
Designed for wastewater treatment. Wells are effective in areas where the volume of drainage does not exceed one or two cubic meters per day.
They are vertically installed cylindrical or cone-shaped containers, without a bottom, up to two meters deep.
Wells can be made of plastic or reinforced concrete rings.
At the base of the well, a filter layer of washed river sand, crushed stone, brick chips or coarse gravel, 20-30 cm thick, is poured and covered with geotextile.
The outside of the structure is also covered with crushed stone.
The wastewater enters through drainage pipes that enter the well at the top of the tank and goes through the drainage layer directly into the ground. Passing through a layer of sand and crushed stone, wastewater is purified from various contaminants.
Filter wells are installed at the lowest point of the site, no closer than 20 meters from the water intake well.
Filter wells are effective only on sandy and sandy loam soils that have good moisture absorption.
Installation of a filter well.
Cumulative
Wells are made of large-diameter plastic corrugated pipes, reinforced concrete or polymer-sand rings, steel or aluminum sealed tanks.
The bottom of the wells is concreted or the plastic bottom is sealed with bitumen.
Storage well made of reinforced concrete rings.
Drainage pipes cut into the installed tank. The joints are sealed hermetically.
Sand or crushed stone is poured between the tank and the walls of the pit.
The well is hermetically sealed with a metal, concrete or cast iron lid.
Water collected in a storage well can be used for technical purposes or for watering plants on the site.
Excess water is discharged into nearby ravines or reservoirs, in agreement with local authorities. To do this, a sewage conduit is installed through which the water can flow by gravity or be pumped out by a deep submersible pump.
The pump can be driven by a float sensor that responds to the fill level of the tank.
An effective and functional drainage ditch will ensure optimal humidity in the area.
Underground drainage equipment
To lay the drainage system, special pipes are used - drains made of PVC or polyethylene. They differ from other types of pipes by the presence of small holes located on the surface at the same distance from each other. The holes are used to allow groundwater to penetrate into the pipeline.
Drains are produced with a diameter of 50 to 200 mm, which allows you to select pipes for the required size of outlet openings and ensure the removal of the required volume of liquid
Wells are important elements of the drainage network. Typically, several types of wells are installed in the system. Inspection tanks are installed at all turning sections of the highway, as well as at joints.
Rotary wells are needed for periodic inspection of the system and, if necessary, carrying out cleaning work. Wells are plastic containers with a diameter of 315 or 400 mm. You can make them yourself using plastic pipes of the required diameter.
Through rotary wells it is easy to clean and flush the system when clogged. To do this, you simply need to direct a stream of water into the pipe under high pressure.
In areas where, due to the terrain or for technical reasons, it is impossible to drain water into natural reservoirs, water intake wells are installed.
They are designed to collect liquid, which can later be used for watering the site or other household needs. To prevent incoming water from flowing back into the pipes, a check valve is installed.
All pipes through which groundwater flows are diverted into one collector, which is often used to collect liquid coming from the surface drainage network
In soils with high absorption capacity, filtration wells are installed. In these structures, instead of a bottom, a special drainage backfill is provided, through which the liquid, after undergoing preliminary cleaning, goes into the ground.
The diameter of such a well is from one and a half to two meters. The design can serve drainage systems in which the volume of incoming liquid does not exceed 1.5 m2 per day.
Advice from the experts
Professional craftsmen have prepared several basic recommendations for installing drainage systems:
- It is necessary to plan work to drain water from the site after conducting geological surveys and examining the soil. If the area is waterlogged, drainage installation should be done before construction work begins.
- The design of drainage ditches should be selected taking into account the height of the snow cover, maximum precipitation level, freezing depth and groundwater level.
- It is better to use plastic perforated pipes to install drains. All connections must be made hermetically to protect the system from damage, leaks, and displacement as a result of frost heaving of the soil.
- When installing closed drainages, it is necessary to install inspection wells for cleaning and maintaining the system.
- Work on installing drainage ditches can be done independently, but it is better to entrust the geological survey of the site and drainage design to specialists.
For normal functioning of the drainage, the system should be cleaned and flushed from silt and sand at least once a year. Gutters and channels must be regularly cleared of leaves, branches, and large debris.
Turnkey installation of drainage around a private house
If you are not sure that you will be able to carry out proper drainage and storm drainage around the house with your own hands, you can order turnkey work. To do this, you need to choose a reliable contractor and find out the cost of the service in advance. You can buy all materials and components for installing a drainage system from a warehouse in Irkutsk.
How to choose a contractor
When choosing a contractor, you need to consider the following points.
- Famous name. The organization or team must have a certain reputation in a given locality/region.
- Positive feedback . It is necessary to find as many reviews and information about this contractor as possible.
- Official registration with tax and other authorities. Serious contractors have the status of individual entrepreneurs or legal entities. All information about them is transparent.
- Portfolio. The customer has the right to demand examples of work.
- Agreement. It is necessary to conclude an agreement. Before signing, the document is read carefully. All unclear points must be clarified immediately. If the conditions are not satisfactory, the customer must demand that they be changed, or refuse the services of this organization.
- Acceptance. Acceptance is made after inspection.
How much does high-quality turnkey drainage cost?
The cost of turnkey drainage depends on many factors. Before drawing up the project, no one will tell you the exact cost. The approximate price of a surface linear system is from 900 rubles/linear meter. Deep - from 1500 rubles/linear meter. Deep ring-shaped drainage costs from 3,000 rubles per linear meter. Storm drains – from 1200 rubles/linear meter.
Basics of storm drain design
The performance requirements for rainwater drainage take into account the average annual volume of surface runoff, which includes rain, melt, irrigation and washing water.
In the latter case, we mean washing facades, blind areas, paths and other hard-surfaced areas.
To determine the volume of rainwater, regional statistics of precipitation in the warm season are used; meltwater - statistical data on the thickness of the snow cover, taking into account snow removal outside the site area. For each type of surface, its area and runoff coefficients are taken into account:
- maximum - near the roof and asphalt;
- minimal - near the lawn, open areas of the fertile layer (vegetable gardens and flower beds), areas with crushed stone covering
The volume of water intake wells is calculated for peak loads, and knowing these parameters, the sizes of trays, gutters and pipe diameters of all linear sections of the network are determined. They also take into account: the permissible time of maximum concentration of water in storm water inlets and the time of passage (speed of movement) of water flows through the channels.
Stages of developing a storm sewer design scheme
Any construction begins with the development of a project. For a small area of a private house, there is no need to develop a project for the construction of a storm drain in the broad sense - it is enough to draw up a fairly simple diagram in the form of a sketch.
Development of a geodetic plan
The basis of the scheme is the geodetic plan of the site. But it must be done in compliance with the scale and proportions of objects - this way it’s easier not to make mistakes.
At the first stage, draw a regular plan on which they indicate:
- the boundaries of the site with the designation of red lines and adjacent areas of neighbors;
- direction of the natural slope (if there is one);
- contours of covered buildings (indicating the location of organized drainage pipes);
- contours of roofs, canopies and canopies without organized drainage (indicating the direction of the slopes and the location of the valleys);
- boundaries of paths, platforms and lawns and other surfaces where it is planned to arrange surface drainage (indicating surface materials, the planned location of points and drainage lines);
- underground communications routes;
- locations of septic tanks and underground fuel storage tanks;
- separate basements and cellars;
- water intake points;
- other objects that can affect the construction and operation of storm sewers.
At the second stage, the relief of the site is “transferred” to the plan, indicating the elevation marks:
- Divide the sketch into equal squares.
- Transfer the squares to the site, driving pegs of the same size in the corners.
- A conventional “zero mark” is found, and relative to it, using a laser level, a general horizontal level mark is made on each peg.
- Measure the height of the relief in each corner of the square - this is the distance from the general “horizon” to the top of the peg.
- Make appropriate marks on the plan.