If you are building a country house or are seriously renovating an existing one, already at the planning stage you need to take care of how the premises will be heated during the cold season.
Correct design of heating systems in private residential construction is a guarantee of winter comfort, rational use of resources and efficient operation of equipment.
In this material we will look at heating systems for a private home, tell you how to choose the best option and show with an example how to properly design a heating system.
What does the heating system consist of?
The main element of the heating structure is the boiler. The choice of central unit is based on the required power. To find out, you need to divide the total area of the house by the specific power.
In this way, we will find out the minimum power of a heating boiler that can provide heat to all living spaces. 25% is usually added to the resulting number, thereby placing the optimal load on the unit and leaving a reserve of power in case of unexpected frosts.
Modern heating boilers are equipped with an electronic control system and other necessary elements. In addition to the heating boiler, the heating project includes a layout of pipes and radiators.
Such elements are widely represented on the construction market and can be made from various materials, differing in their properties, quality and, accordingly, price.
Boiler room arrangement
The design of a heating system must necessarily include an architectural part. It involves building or equipping a separate boiler room and calculating the chimney. When calculating, it is necessary to determine:
- pipe diameter;
- coolant volume;
- heating equipment power.
The boiler room in the house plays a very important role, because it will house the main heat generator. To prevent an accident from occurring during the operation of the heat generator, the room where it will be installed must have:
- total volume not less than 15 m³;
- height of at least 2.5 m;
- fences with a fire resistance limit of 0.75 hours;
- ventilation and natural light.
The boiler room must have certain dimensions and indicators.
A device with a power of up to 60 kW is allowed to be installed in the kitchen if it has an opening window. A device consuming 61-150 kW can be located on the second and subsequent floors of the house. Boilers whose power reaches 151−350 kW should be installed only in special boiler rooms, basements or on the first floors.
Once the location of the heat generator has been determined and equipped in accordance with all existing standards, you should think about another important part of the heating system - the chimney. It can be made of different materials:
The chimney is an extremely important part of the heating system.
- Brick. Such a chimney can be built into the wall during its construction or installed after the walls and roof are erected.
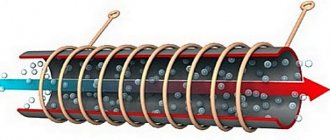
- Stainless steel. This metal is characterized by high strength and resistance to combustion products. A metal chimney is a structure of two pipes placed one inside the other. The space between the walls is filled with basalt wool for insulation.
- Ceramics. This type of chimney is used extremely rarely due to its fragility and heavy weight. The main advantage of ceramics is considered to be high heat resistance.
In order for a chimney to effectively cope with its function, it must have a certain diameter, height and degree of fire resistance. Only then will combustion products be completely removed outside without clogging the heating system.
Boiler selection
The type of boiler depends on the type of energy carrier on which it operates. The main element for heating a home should be selected taking into account the available type of fuel.
Gas
Due to their efficiency, gas units remain the most popular. An obstacle to their use may be the lack of gas mains in close proximity to the land plot. It is worth noting that equipment of this type requires constant maintenance and monitoring by special services.
Solid fuel
If the area has not been gasified, the design of heating systems can be carried out taking into account the use of a solid fuel boiler. This will make it possible not to depend on the centralized supply of energy, but will require additional sources of solid fuel and a dry place for its storage.
Liquid fuel
To install a heating system for a private home, you can purchase a boiler that runs on liquid energy. However, diesel is an expensive fuel, so the costs of its use will increase significantly. You will also need underground installation of a special tank in which it will be stored. You should also remember about the high degree of fire hazard of diesel.
Electricity
It is advisable to use an electric boiler in a joint system with electric radiators. Such a project involves converting electricity into heat without water resources - directly.
By analogy with liquid fuel, such an energy carrier will not be cheap. If funds allow, in such a situation it is better to opt for autonomous heating, which allows you to receive electricity from solar and wind converters or mini-hydro stations.
Choosing an energy carrier
The main selection criterion is the cost of energy, depending on the country and region of residence. If in the Russian Federation the undoubted leader is natural gas, then in the rest of the states of the former USSR the picture is different - firewood, briquettes and coal take the first place. Don't forget about electricity supplied at half the nightly rate.
When choosing the right type of fuel, it is worth considering five factors (in addition to price):
- efficiency (efficiency) of heating equipment using this energy carrier;
- ease of use;
- how often the units will have to be serviced, prices for calling a technician;
- storage requirements.
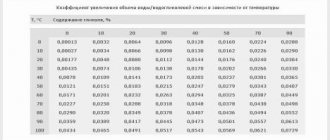
Below is a comparative table showing the prices of various energy sources and how much a kilowatt of heat produced in real conditions costs. Building area – 100 m², region – Moscow region.
Note. The calculation results and prices are given as of February 15, 2018. Over time, the data becomes irrelevant, but the difference in the cost of 1 kW remains.
Based on the numbers given in the table, it is much easier to find a suitable option (or several). Just make an adjustment for the cost of energy in your region. Based on other selection criteria, we will give 4 tips:
- It is most convenient to use gas and electric heating equipment. There is no need to store anything, constantly maintain and bother with cleaning water heating devices.
- Burning coal and wood is the most economical way to heat. Saving money will have to be paid for with labor - sawing, carrying, loading the firebox, cleaning the chimney. It is more comfortable to burn briquettes and pellets, but the price of the boiler installation and the fuel itself increases. Plus you will need storage for storage.
- Diesel fuel or liquefied gas is the best solution for providing autonomous and at the same time comfortable heating when other energy sources are not available. The downside is the decent cost of fuel and installation of the fuel tank.
- A proven option is the combination of 2-3 energy carriers. A common example: solid fuel + electricity at night tariff.
Which fuel is best to use in specific conditions is described in detail in a separate material. We also recommend watching the video and listening to useful expert advice:
Which system should you choose?
The design of the heating of a private house is carried out taking into account the energy carrier that will be used to heat the room. There are several most common systems through which heat is supplied to all interior spaces of a building:
- water;
- air;
- electric;
- open fire.
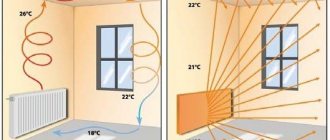
An “open fire” means a fireplace hearth or stove. Both of these heat sources are ineffective in providing full-fledged home heating, as they distribute hot air unevenly. They are most often included in a heating project as decorative elements. Let's look at other systems in more detail.
Providing circulation
The heating system of the house works due to the movement of the coolant along the main line. Water or other liquid poured inside can circulate naturally or using a pump.
Natural movement of water can only be ensured in large-diameter pipes installed at a slope. Changing temperature affects the physical properties of the liquid and causes it to circulate through the system. But natural circulation requires a large amount of water in the mains and large radiators.
The movement of coolant through the system is ensured by a circulation pump
The presence of a pump in the line provides certain advantages. Firstly, there is no need to observe an inclination when installing the heating structure; you can choose pipes and radiators of any size. Secondly, the pump requires a much smaller volume of water to operate.
Giving preference to forced circulation, it is important to determine the correct location for installing the pump. In heating systems of private houses, its role is most often played by a circulation pump.
It is best to place it on the return pipe in front of the heat generator: when pumping cold water it will wear out less.
Since the forced circulation heating system is a closed structure, it is important to take care of the safety of its operation. During heating, the circulating liquid tends to expand
To prevent the pressure inside the line from increasing to critical values, it is necessary to install an expansion tank into it. It will collect excess liquid and remove air, normalizing the pressure in the system.
Compliance with all design stages will allow you to create a heating system in a private home that will effectively perform the heating function. At the same time, it will be safe and convenient to use.
Water
A heating project based on the most common water system is the planning of a closed circuit through which hot water is continuously circulated. In this case, the function of a heater is performed by a boiler, from which pipes are distributed throughout the rooms and adjacent to radiators that give off the main amount of heat.
Having carried out heat transfer, the water flows back into the boiler, where it is heated again and repeats the technological cycle. Boilers operating on any fuel serve as heaters for water heating. The water heating system is divided into two types: natural and forced.
Natural circulation
In the first case, the coolant circulates through pipes and radiators without the influence of additional force. This effect is achieved by a certain method of installing heating main elements.
The design of heating with natural circulation of water provides for the necessary angle of inclination of the pipes, allowing the process to proceed under the influence of gravity.
Hot water is lighter than cold water, so it flows to the highest point of the riser. Having given up its heat to the radiators along the way, the cooled coolant is displaced by the hot one and drops to the lowest point of the system (into the boiler), where it heats up again.
Forced circulation
The forced movement of water through the system is achieved by the operation of a circulation pump integrated into the heating boiler. Unlike natural circulation, forced circulation requires a source of electricity from which the pump is powered.
Wiring
Natural and forced water circulation systems can be used for single-pipe, two-pipe and collector installations. In the first case, the design of heating systems involves the installation of one pipe, which performs the function of supplying and draining water simultaneously.
With this scheme, the temperature of the radiator farthest from the boiler will be lower than that of the one closest. In addition, if one battery fails, the others will also cease to function, since they cannot be turned off individually.
Two-pipe wiring allows for uniform heating of the batteries due to the fact that the supply pipe is connected in parallel to each of them. The second pipe carries the cooled coolant back to the boiler. If a tap is installed on each radiator, they can be turned off individually.
Manifold wiring is the most convenient, since after its installation you can regulate the temperature of the coolant in each individual room. This method of heating the room will require the installation of a collector cabinet.
Equipment, components and materials
The next step after developing the scheme is the selection of all heating elements:
- heat generator;
- radiators, underfloor heating collector;
- pipes;
- expansion tank, circulation pump, fittings and heater piping parts.
Clarification. Wall-mounted gas boilers and some floor-standing models are equipped with a pump and expansion tank located inside the unit. If you plan to purchase such a device, still make sure that the tank volume is sufficient for your system.
Let’s immediately make a reservation that we will consider a hot water boiler as a heating unit. You will not be able to install an air or geothermal heat pump without the help of specialists, and connecting the water circuit of the stove is carried out in the same way as connecting a solid fuel heat generator.
How to calculate the capacity of the expansion tank, choose the right pump and fittings:
- The useful volume of the tank must be at least 10% of the total amount of coolant circulating in the heating network. The water jacket of the boiler is also considered.
- If the building area does not exceed 150 m², then circulation will be provided by a pump with 25/40 or 32/40. The first number is the diameter of the threaded connection, the second is the developed pressure. The 25/40 unit is equipped with a 1” pipe thread and is capable of delivering a pressure of 0.4 Bar.
The most common model of pumping unit 25/40 from the Grundfos brand - For a large cottage and floor circuits, it is better to select a pump according to the algorithm.
- Shut-off ball valves are installed in front of the heat generator, expansion tank, pumping unit and on the make-up pipe. Additional equipment - a buffer tank, an indirect heating tank, a solar system - must also be cut off by taps.
- Each heating radiator is equipped with a thermostatic valve at the inlet and a balancing valve at the outlet. In the unregulated version, a ball valve is installed on the battery supply pipe.
The final list of components is compiled after selecting the main elements - a thermal power plant, batteries and a pump with a tank. Accordingly, we will next consider the issue...
Air
Such a system can be installed exclusively at the construction stage. It is not suitable for a finished private house. This is explained by the need to install metal, plastic or textile air ducts through which hot air heated by the heat generator is blown out.
A warm flow enters the room from under the ceiling and displaces cold air, which, in turn, returns through the air ducts to the heat generator.
Designing heating using the air heating method allows you to install a system for external intake of clean air, which is mixed with the flow. Circulation can be achieved by gravity or by force.
Natural air exchange occurs due to temperature differences, and forced air exchange is carried out using special ventilation equipment. The heat generator can burn diesel fuel, natural gas (mainline or bottled) and kerosene. Combustion products are discharged through the chimney.
Tips for installing a home heating system
The heating installation begins with the installation of radiators in pre-prepared places under windows or on corner external walls. The devices are hung on special hooks attached to the structure itself or the plasterboard finish. The unused lower outlet of the radiator is closed with a plug, and a Mayevsky valve is screwed in from above.
The pipeline network is installed according to the assembly technology of certain plastic pipes. To protect you from mistakes, here are some general recommendations:
- When installing polypropylene, take into account the thermal elongation of pipes. When turning, the knee should not rest against the wall, otherwise, after starting the heating, the line will bend like a saber.
- It is better to lay the wiring in an open way (excluding collector circuits). Try not to hide the joints behind the sheathing or embed them in the screed; use them to secure pipes.
- Mains and connections located inside the cement screed must be protected with a layer of thermal insulation.
- If for any reason a loop has formed in the pipeline, facing upward, install an automatic air vent on it.
- It is advisable to install horizontal sections with a slight slope (1-2 mm per linear meter) for better emptying and removal of air bubbles. Gravity flow schemes provide for slopes from 3 to 10 mm per 1 m.p.
- Place the membrane expansion tank on the return line near the boiler. Provide a valve to shut off the container in the event of a malfunction.
Installation trick. Do not fill the TP screed until you fill the circuits with water and warm up the system. The goal is to increase the pressure in plastic pipes and force them to lengthen, that is, to put them into operating mode. Then the material will not bend under the weight of the monolith and will not float up if the solution turns out to be liquid.
Electric
To heat your home, you can use electrical appliances: convectors, long-wave infrared heaters or “warm floor” systems. Also, to achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to combine several electrical appliances.
With any of these methods, large payments for energy consumption cannot be avoided, so it is recommended to install them in cases where there are no alternative heat sources.
Pipes for connecting radiators and heated floors
For homeowners without installation experience, we recommend the following options:
- If you want to save on materials, take reinforced polypropylene pipes (PP-R) with fittings. In addition, buy an inexpensive Chinese soldering iron - it will definitely be enough to assemble 1 system.
- Without special tools, you can install heating pipes from metal-plastic pipes on compression fittings, tightened with open-end wrenches. The disadvantage is the high cost of parts.
- The best solution is to assemble the system from cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic with press fittings. You will have to rent special pliers.
The structure of the polypropylene pipe - to prevent thermal elongation, aluminum reinforcement is laid between the layers of plastic
Important note. Polypropylene is not suitable for installing heated floors due to the thick walls and joints that fall inside the screed. Use metal-plastic or polyethylene PE-X, PE-RT.
Polypropylene pipelines are welded according to technology, the main thing is to accurately maintain the heating time. It is strictly not recommended to wall PP-R joints in floors and walls to avoid the consequences of leakage.
Beginners should not use copper, stainless or galvanized pipes. High-quality installation will require certain skills - welding, proper cutting, crimping. Metal is reliable, but inferior to plastic in price.
On the left in the photo are pipes made of metal-plastic, on the right - cross-linked polyethylene
What is included in the project?
Professionally drawn up project documentation should include the following items:
- company letterhead with seal;
- organization license;
- explanatory information about the project points;
- a detailed plan for routing highways (including high-rise ones);
- estimate;
- instructions for performing work;
- specification of materials and equipment;
- project sketch;
- drawing detailing all components of the heating main;
- plan for wiring communications and connecting nodes.
Pros and cons of an apartment with individual heating
Apartment heating has positive and negative sides, which appear depending on operating conditions.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| The ability to turn on the heating at any time of the year and turn it off when the temperature outside is high, reducing costs | Long design and approval times |
| Maintaining the required indoor air temperature regardless of external conditions | Significant financial investments at the stage of design and installation of equipment |
| Uninterrupted hot water supply even during maintenance periods | Costs for heating walls adjacent to neighbors when individual heating is turned on in the spring-summer period |
| Cost-effective, gas tariff is significantly lower than for centralized heating | The owner is obliged to pay for general house needs: Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 16-P of April 27, 2021. |
| Mandatory thermal insulation of risers remaining in the apartment, which spoils the appearance of the rooms | |
| Noise during boiler operation from burning fuel and circulation pump |
By choosing individual heating in an apartment, you can only save on monthly payments. When considering long-term operation, they take into account the cost of the purchased equipment, the cost of its installation and mandatory (for gas boilers) maintenance, as well as the cost of replacement after 6-15 years of operation.
Methods for laying heating pipelines
In the heating system of a cottage, pipes can be laid in two ways:
Open laying method
In this case, they are laid along the walls, parallel to the baseboards. Throughout their entire length they are within visibility range.
Advantages of this method:
- Access to pipes without dismantling structures
- Low heat loss
- Easy heating installation
Main disadvantages:
- The pipeline often spoils the appearance of the premises and does not fit into the design
- To avoid sagging and deformation, not all types of pipes can be used
Hidden laying method
The pipe is walled up in the wall, in the floor or decorated with external material.
The main advantages of hidden pipeline installation:
- Possibility to hide highways so they don’t spoil the interior
- Possibility to use pipes made from modern materials
The disadvantages include:
- Access to pipes is difficult in case of need for possible repairs, replacement of individual sections, or elimination of emergency situations
- Due to large heat losses, the lines must be thermally insulated
When performing hidden routing, you must use only reliable and proven pipes. The best option is pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Filling the coolant with this method must be performed only after a hydraulic test of the heating system.
Two-pipe scheme
Heating a house with a two-pipe circuit involves connecting radiators in series. The lines are common to all heating devices.
There are two options for implementing a two-pipe system:
Two-pipe associated (Tichelman loop)
The movement of the coolant in the forward and return circuits occurs in one direction. The return circuit starts from the first radiator, and the supply circuit ends last. The correct movement of the coolant is organized by selecting the diameter of the pipelines. Using a Tichelman loop, you can achieve uniform heating of rooms.
Double-pipe dead-end
It differs from the previous type in the multidirectional movement of the coolant in the forward and return circuits and consists of several branches (arms). The last radiator in each branch is a dead end. The return circuit begins from this radiator.
A two-pipe dead-end heating system scheme is more difficult to implement than a passing one. Careful calculation of the hydraulic component of the system is necessary. In addition, it is necessary to maintain equality of load on each shoulder. It is recommended to equip each arm with no more than five heating devices.
The advantages of two-pipe systems are low sales price and reliable operation (compared to single-pipe systems).
One of the disadvantages is the need for a large number of heating pipe connections. This significantly reduces the reliability of the system, and is especially critical when the installation is hidden.
In addition, there is no possibility of individually configuring each heating device separately, which often does not allow setting the required temperature in a particular room.
With a two-pipe distribution, the lines can be laid both openly and hidden. In the first case, pipes made of copper or polypropylene are usually used, in the second - from cross-linked polyethylene. Cross-linked polyethylene is used due to the increased reliability of the connection between the pipe and the fitting.