A well in a dacha is one of the most acceptable water supply options, used by many owners. If it is properly arranged, it will properly perform its functions for many years. But some homeowners are trying to solve the problem of supplying their property with water at the lowest cost, saving on the work of professionals.
As a rule, the result of such work is disastrous: in the spring, groundwater enters the well, which makes it unsuitable for use from March to mid-June. Often, groundwater in a well becomes a source of harmful impurities, salts, pesticides and herbicides, which are used to treat fields.
In what cases is a drainage system necessary?
Drainage is a technology for collecting and discharging groundwater, melt and storm water from a site, technical and residential buildings.
The drainage system prevents leaching, heaving and waterlogging of the soil, which occurs due to oversaturation with moisture. Arrangement of a drainage system is not necessary at every site. In order to determine how much your area needs drainage, you will need to conduct a visual inspection.
Pay attention to whether the area is flooded after the snow melts, how quickly water is absorbed after watering the plants, whether there are puddles after heavy rain and downpour. If you have observed these signs more than once, then drainage is required.
The drainage system helps remove stagnant water from the site
If visual confirmation is not enough, then you can conduct a simple experiment - using a hand drill or an ordinary shovel, you should dig a hole 70–100 cm deep. It is better to do this in several places on the site. If after 24–36 hours water accumulates at the bottom of the hole and does not leave, then this is direct evidence of oversaturation of the soil with moisture.
Soil drainage is carried out under the following conditions:
- high groundwater table;
- the site is located in an area with clay soil;
- the site is located in a lowland or vice versa - on a slope;
- The location of the site receives a large amount of precipitation.
The presence of drainage helps preserve the finishing and facing materials used for laying garden paths, finishing the basement and façade of the building.
How to get rid
The functioning of the old source can be restored by properly cleaning the shaft. For this, a special steel shield is used to protect water from the penetration of sandstone particles. It is installed at the joints of well rings.
The rings are mounted using stainless anchors, and the gap between them and the concrete is sealed with bitumen sealants. The method prevents large pieces of sand from entering the well shaft, although it does not protect water from microparticles. Thanks to this method, the well does not become shallow and retains the volume necessary for operation.
Surface
Surface drainage of the site is carried out using various rainwater inlets and trays. This type of drainage got its name because the entire system is located on the surface. Trays can successfully cope with flows of rainwater, as well as moisture that forms as a result of melting snow.
There are two types of surface drainage: point and linear.
- Spot. Such a system consists of water collectors, which, in turn, are connected to the sewerage system. Water collection devices are usually installed under drains, in low spots and under taps.
- Linear. The system resembles a canal that slopes towards a well. This is where moisture from rainfall comes in.
It cannot be said that one type of drainage is better than another. Often both varieties are used together for greater effectiveness. All devices in the system require regular cleaning, otherwise they will no longer function properly. A well-organized drain serves well and does its job.
Installing a bottom filter
To get rid of quicksand in a well, you need to tongue and groove and lay the bottom with aspen logs with a diameter of 20 cm. You need to make a shield from moisture-resistant wood and cut holes in it for water. The wood should extend beyond the sheathing on all sides.
To install the bottom filter, you must follow the steps:
- remove accumulated sand;
- cover the bottom with gravel up to 1 m thick;
- lower the filter and fix it at the top;
- attach the filter to the bottom ring;
- the space between the filter and the walls of the well is filled with brick and concrete mixture.
The filter should be replaced once every 5 years, as the wood is subject to rot.
How to determine the need for a drainage system
The surest sign of increased soil moisture is the massive growth of plants, typical of swampy areas. These include weeping willow, sedge, and reed.
In addition to plants, evidence of the close occurrence of groundwater will be puddles that remain after rain or spring melting of snow. If they do not go away for a long time, then there is enough other moisture in the ground.
It doesn’t always rain, so it’s much easier to use a long-proven method of checking the soil moisture level. To do this, you need to dig a hole about half a meter deep at the highest point of the site. If water collects at the bottom within 24 hours, it means that the area needs drainage.
How to walk correctly when digging
In some cases, it is enough to simply deepen the bottom, bypassing the dangerous area.
This method provides for the accelerated completion of work on digging a mine, every minute counts. Long interruptions in operation are detrimental to the source, since it will receive a large volume of water contaminated with sand. A sump pump should be used continuously to remove this sediment.
An effective method is to use steel formwork in laying the well, which is slightly smaller in diameter than standard concrete rings. It is lowered directly into the soft mass, where it hermetically blocks the flow of liquefied sand into the well shaft. Then concrete rings are installed, which, when covering the connecting seams with sealed material, do not ensure the integrity of the well structure.
It is much easier to resolve the issue at the very beginning of work.
Advice! It is better to do it in winter, when the water level is minimal, and install 3 staples per connection.
Digging one ring of quicksand is comparable to five regular soil, so few people want to take on such work!
On clay soils
Not all types of soil drain water well. These include clayey ones. Clay soil is characterized by an excess of moisture. Because of this, the required amount of oxygen does not reach the roots. As a result, the plants die. Dense turf also leads to oxygen starvation of plants.
When arranging a drainage system for a small area, it is not necessary to make calculations during the design process. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the parameters regarding drains:
- slope;
- location according to plan;
- depth;
- distance between rows;
- arrangement of wellhead and inspection wells.
It is better to use the natural terrain of the site with a slope when constructing a drainage system.
Using terrain
Laying in clay soil
It is easier to work with a sloping area than with a flat one. This is due at least to a reduction in labor costs. All you need is to correctly combine open and closed drainage.
How to detect a leak?
The water enters the source through the joints of several upper rings. If melt water penetrates to depth, it is filtered. Therefore, you need to look for leaks in the upper tiers. During the snowmelt season, you need to carefully inspect the walls inside. If they are dry, restoration work may not be carried out this year.
Violation of the tightness of the joints is first manifested by the appearance of condensation, the accumulation of moisture at the places of the locking joints of the rings. Sometimes trickles are visible that appear from the joints. If such undesirable signs of waterproofing destruction are detected in the spring, protective actions are urgently taken.
What water is removed by drainage?
Drainage of a site is a costly and labor-intensive undertaking that requires a large amount of excavation work. The best time for construction is the process of planning and arrangement of the site. Late deadlines lead to a lot of chaos, which doesn't make everyone happy. However, if there is water on the site, you have to do this too.
There are several types of water on the site that bother us and that need to be drained. They are of different nature and require different measures.
Surface water
They are formed during snowmelt and heavy rainfall, during work on the site (watering, washing paths), discharge of water from a reservoir, etc. What all phenomena have in common is their one-time nature: surface water appears after certain events. A more reasonable way to drain them is to install a storm drain. She copes with the task “excellently”, and the costs of arrangement are much lower.
Storm sewers are responsible for the removal of surface water.
To drain surface water, mostly open channels are installed; water intake is point-wise under storm pipes or linear along the entire roof overhang. From these receivers, water is carried through solid plastic (asbestos-cement) pipes into a drainage ditch or discharged into a river or lake into a ravine. Sometimes we allow output to the ground.
Groundwater
Those groundwaters that have a seasonal level (higher in the spring after a flood, lower in the winter), have a recharge zone (where they come from) and an outflow zone (where they go) are called groundwater. Typically, groundwater is present on sandy, sandy loam soils, less often in loams with a small amount of clay.
The presence of groundwater can be determined using self-dug pits or several wells drilled with a hand drill. When drilling, a dynamic level is noted (when water appeared during drilling) and a steady one (some time after its appearance, its level stabilizes).
When the groundwater level is high, strip foundations are also made, but the waterproofing must be high
If we talk about draining water from a building, then a drainage system is installed if the groundwater level (GWL) is only 0.5 m below the foundation. If the groundwater level is high - above the freezing depth - then a monolithic slab foundation with measures taken to drain water is recommended. At a lower level, other options are possible, but careful and multi-layer waterproofing is required. The need for foundation drainage should be assessed by specialists.
If high groundwater (groundwater level above 2.5 meters) prevents plants from growing, drainage of the area is required. This is a system of channels or special drainage pipes laid in the ground at a certain level (20-30 cm below the GW level). The depth of laying pipes or ditches is below the ground level so that water flows to lower places. In this way, the adjacent areas of the soil are drained.
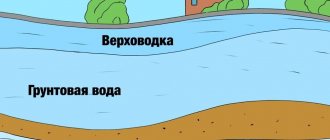
Verkhovodka
This groundwater occurs on soils in highly located impermeable layers, but its appearance is often a consequence of construction errors. Usually this is water that, being absorbed into the soil, encounters on its way layers with a low ability to absorb moisture. Most often this is clay.
If after a rain there are puddles in the area and do not go away for a long time, this is perched water. If water accumulates in dug ditches, this is also perched water. If, a few years after building a house on clay soils or loams, the walls in the basement begin to “cry”, this is also high water. Water has accumulated in crushed stone pockets under the foundation, in blind areas, etc.
To avoid this situation, site drainage is required.
The easiest way to drain high water is with the help of ditches, but it is better to prevent its occurrence - backfill the foundation not with crushed stone and sand, but with clay or native soil, carefully compacting it in layers. The main task is to eliminate the presence of pockets in which water will accumulate. After such backfilling, it is necessary to make a blind area that is wider in width than the backfill and an obligatory touch is the drainage of storm water.
If the site has a slope, consider installing terraces and retaining walls, with the obligatory installation of drainage ditches along the retaining wall. It is most difficult to deal with perched water in low areas, which are located at a level lower than neighboring ones. A reasonable solution here is to add soil, since there is usually nowhere to dump water. Another possible option is to drain the drain through neighboring areas or along the road to the point of possible discharge. You have to decide on the spot, based on the existing conditions.
Raising the area
If the site is located in a swampy area, then you can use soil backfill. The disadvantage of the method is its high labor intensity. It is used in difficult cases when other methods do not achieve positive results.
Setting up a full-fledged drainage system is unprofitable for economic reasons. The method of draining the soil by backfilling depends on the degree of waterlogging. It is recommended to raise the problem area by 300 cm. For this purpose, imported fertile soil is used. After filling the soil, it is recommended to plant moisture-loving shrubs and plants.
To raise the soil level, the following work must be done:
- First, the top fertile layer is removed.
- After this, the lowland is leveled using inexpensive drainage materials. For this purpose, crushed stone, crushed brick or sand are used.
- At the final stage, the soil is returned to its place.
If the area is very swampy, then it is necessary to equip a deep drainage system. To increase the efficiency of the method, other techniques are also used.
Why is drainage needed in a garden plot?
Any builder or landscape designer should know where to start arranging a suburban area. There is only one answer - from drainage, if required. And, as practice shows, such a need is almost always present.
And we need to start with it only because creating a drainage system involves a huge amount of excavation work. Almost the entire dacha plot will have to be dug up with ditches. And if some buildings have already been erected on the site, they will simply interfere with the drainage construction.
It must be added that the construction of a drainage system is an expensive process. Therefore, many private developers refuse it, citing the fact that just recently everyone somehow managed without it. The argument, to put it bluntly, is weak. After all, life has gotten better in recent years. Small dachas made from boards have long gone into oblivion. They were replaced by houses built of stone or wood, in extreme cases using frame technology, but sheathed with modern materials.
The consequences of the lack of a drainage system are sagging foundations and cracks on the walls of the house. Source pinterest.comThat is, everyone wants to live comfortably and beautifully. Why do some people refuse to improve their garden plots and create a beautiful landscape design in which drainage plays an important role? But its absence can lead to serious problems, where puddles after rain, dirt on garden paths, poorly growing plants are just “flowers”. The consequences can be much more serious, for example, a sagging foundation, hence cracks in the walls.
Drying without drainage
This is an environmentally friendly method that is harmless to the environment and humans. The only drawback is that it takes quite a long time.
The process is simple and easy. It is necessary to plant plants that drain the area. This:
- willow;
- maple;
- birch:
- ate.
Poplar and alder absorb excess moisture well, but it is not recommended to plant them in a suburban area - their fluff can cause allergic reactions.
A pleasant additional bonus of this drainage method will be the decoration of the garden with beautiful plantings.
In addition to trees, you can opt for shrubs, such as:
- rose hip;
- hawthorn;
- irga.
By planting these species around the perimeter of your estate, you will get a spectacular hedge.
Some types of flowers can also be used for drying:
- perennial asters;
- aquilegia;
- swamp iris
Flowers such as hydrangea, Amur lilac, and mock orange are also effective natural dehumidifiers. True, they can help if the level of swampiness in the area is not very high.
Construction of artificial reservoirs
If the size and geological features of the site allow, then one of the ways to drain the site can be considered the creation of an artificial pond. This can be done when the lowest and wettest place is located on the periphery of the site. And although this method is called drainage without drainage, surface drains here can be present in the form of ditches designed as decorative or “dry” streams.
The advantage is the construction of an artificial reservoir as an element of landscape design. The disadvantage of this type of drainage is the need to regularly clean the reservoir and pump out water - the water is not flowing, accumulates, and can itself serve as a source of waterlogging. In addition, over time it begins to bloom.
Waterproofing measures
There are two types of waterproofing - external and internal. Work to complete them:
- will prevent deformation and destruction of hydraulic structures;
- protect from temperature changes;
- will increase the service life of the source;
- protects against leaks.
External waterproofing of the well from groundwater prevents it from entering the source and cuts off the layer of perched water. Most often it is used during the construction stage. Also, to increase the tightness, the well rings are simultaneously fastened together.
But external waterproofing can also be done during renovation work. When repairing, foundation preparation is required. To do this, the shaft of the hydraulic structure is dug up several meters, the destroyed concrete is beaten off, the surfaces are cleaned, and the visible parts of the reinforcement are treated with a corrosion-preventing agent. Then they begin the main work, using special materials (polyurea, rolled materials, polymer-cement compositions).
Waterproofing a well from the inside from groundwater is carried out using materials for waterproofing concrete surfaces. They are durable, practical and easy to use.
If the source is located on quicksand, in addition to waterproofing, you will need to install a bottom filter in the well. Otherwise, the water will enter the house cloudy and unsuitable for consumption. If necessary, we will help you choose a filter and install it. We improve the quality of water in the well, and we know how to do it correctly.
Why do you need to drain soil and storm water from the site?
The close occurrence of soil water leads to wet foundations, basements and basements. Water may accumulate in the basement or ground floor when the snow melts or after a long period of heavy rainfall, which must be removed and the room dried; the rest of the year it will be damp, moisture will settle on the structures, fungus and mold will grow, and the air will smell of mold and rot.
In winter frosts, soil saturated with moisture will freeze, compress the foundation, swell and push the building upward. In this case, cracks appear in the foundation and structures of the building; in severe cases, the structure of the house will begin to collapse.
If the area is swampy or groundwater is located very close, then plants grow very poorly on it, mosquitoes hatch, and an unpleasant odor appears. You can forget about beautiful well-groomed flower beds, beds and berry gardens.
If the soil is clayey, then after rain or snow melts, water stagnates on the surface, saturates the ground near buildings, and damages green spaces.
Choosing a site for construction
If the well has not yet been built, the project is just being developed, there is time to pay more attention to the correct choice of location. To prevent melt water from entering the mine, it is better to build on a hill, taking into account the distance standards from objects that may be pollutants.
If the well is located in a lowland, then in the spring, when the snow melts, puddles will stand near the source of drinking water. This can quickly destroy the waterproofing. Over time, you will have to clean and replace the protective layer. It will be important to send the water for analysis to ensure that it is safe and suitable for drinking and domestic use.
Selection of materials and components
Table of components for surface modification drainage
| Name | Description and purpose |
| Drainage tray made of concrete with a galvanized stamped grid. | Removes moisture from the soil. Suitable for installation on sites and along paths. Depending on its dimensions, it has different throughput. Transfers weight up to one and a half tons. |
| Drainage tray with cast iron grate. | Designed for the same thing as in the above case. Load capacity up to twenty-five tons. Can be installed on roads. |
| A rainwater inlet made of plastic, including siphon partitions and a trash can. | Collects water. They are located in the place where water drains from the roofs of houses, garages, bathhouses, and sheds. Transfers weight up to one and a half tons. |
| Sand trap made of plastic and steel grate. | Included in the linear modification drainage system, it is used to collect sand and small mechanical particles. Sand traps are required for installation at the junction of drainage systems if the surface system is connected to the deep one. Carry loads up to one and a half tons. |
Trays and storm water inlets are the most important parts of the drainage system. They are made of steel, plastic, concrete, polymer concrete and reinforced concrete. They carry a load of up to twenty-five tons, depending on the dimensions they have different throughput. To carry out, for example, drainage of a site on clay soils with your own hands, you need to correctly calculate how much water flow will be per unit area of the site.
Table of components for deep drainage
| Name | Purpose and description |
| Corrugated pipe in a geotextile filter made of HDPE. Diameter value – up to 200 mm. | Designed for deep collection and drainage of water from the site and from under the foundation of the building. It is laid to a depth of up to four meters. The filter material prevents clogging and filling of the drainage pipe from the inside. |
| Corrugated HDPE drainage pipes coated with coconut coir. Diameter value – up to 200 mm. | Installed at a depth of up to four meters. Unlike geotextiles, coir has better durability and reclamation properties. |
| Shafts for wells made of HDPE. The diameter is up to 923 mm. | For creating all types of drainage wells. Maximum depth six meters. |
| Geotextiles. Polyester based filter fabric. | Used for all types of drainage. Filters out sand, silt, and small fractions of soil. Not affected by fungi, mold, microbes, insects and rodents. |
In addition to the main components (presented in the table), various couplings, rings, cuffs, bends, plugs and other consumables are used in drainage. The complete set depends on the individual characteristics of the drainage system for a particular location and is selected based on the characteristics of the topography, volume and depth of water in the ground.
When is site drainage required?
There is high groundwater in the area, what should I do? Desperate developers often come to us with this question. Of course, it is better to take care of the problem in advance, rather than looking for additional funds after the work has begun. Remember, during construction, drainage of the site is required in the following cases:
- the lower groundwater line will be located half a meter above or below the foundation;
- the basement is planned to be placed at a depth of 1.5 m in loamy soil;
- the area is quite frozen, for example, in the Far North;
- the pressure of groundwater washes out the foundation (or, according to calculations, will wash away);
- Construction is taking place in a swampy area.
Sometimes drainage becomes necessary after construction is completed. Thus, owners of private houses, dachas and cottages should think about draining water from the site when alarm signals appear:
- cracks in the walls, warped door and window openings;
- damp smell and mold growth;
- water in the basement;
- a lot of mosquitoes and frogs on the site;
- The flora is dominated by nettle, wormwood and reeds.
In the private sector, you can drain a small area yourself, however, when dealing with capital construction, the contractor is faced with a completely different scope of work, where it is impossible to do without specialists and equipment.
How to properly make deep drainage?
To correctly install deep drainage on a personal plot of land, first of all, a clear project of all work is formed, establishing the types of soil available on the territory, the features of the relief and the level of groundwater.
This type of research is entrusted to engineering and geological organizations. They will conduct a full study of the area, and then provide the customer with a topographic survey that describes in detail the relief, hydrogeological features and geological structure of the site. With this information at hand, installing an effective drainage system is easy.
The construction of the system is carried out in the following order:
The main elements of a deep drainage system are drains (pipes of a specific design). They are located below the foundation pad of the building that they plan to protect, or along the entire perimeter of the land at a depth of 80 centimeters to one and a half meters.
The required slope of the pipe is made towards the collector, drain well or any other natural or artificial reservoir located outside the site.
In this way, moisture collected as a result of precipitation is collected and the general level of nearby groundwater is reduced to a non-critical state. In the center of the site and along the edges, drains are located at a distance of 10-20 meters from each other. The structures are given a herringbone shape, where the outermost channels redirect all the water into the main trench leading to the main water intake.
To enhance the efficiency of the deep drainage system, it is worth using pipes equipped with a two-layer geotextile filter and a circular perforated layer. This communication option is suitable for all types of soils and has the ability to drain larger amounts of water.
On absolutely flat areas, the required slope is achieved by lowering it when digging the bottom of the trench. For loamy and clayey soils, the optimal slope level is 2 centimeters per meter of pipe, for sandy soils – 3 centimeters. If the site has a large area, several inspection wells are installed to avoid too extensive excavation work.
Communication pipes are equipped with rotary and water intake wells. If necessary and if it is impossible to remove excess water outside the site, an absorption (filter) well is added to the remaining elements, designed to drain the main volume of water.
Under the base of the absorption well, a bulk layer of crushed stone or broken brick must be made. This is necessary so that the collected liquid goes evenly into the soil and does not erode the lower layers, causing subsidence.
Immediately before laying the pipes, a 10-centimeter layer of coarse sand and the same layer of crushed stone are poured into the trenches.
The resulting shock-absorbing cushion prevents communications from breaking under the weight of the soil. To avoid silting of pipes, the channels are lined with geotextiles.
It is advisable to carry out the laying of deep drainage on the site after all heavy construction work, so that the communications do not sag or crack as a result of intense operational load
On top of the laid out pipes, another layer of sand and crushed stone is made, and the remaining voids are filled with earth, making mounds on the surface. When the system finally “sits” in the trenches, the poured earth itself will drop to its natural level.
A correctly and clearly installed system ensures timely and rapid removal of moisture from the site and reliably protects buildings from flooding and subsequent destruction.
Prevention measures
To extend the service life of the well and prevent the appearance of quicksand, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not allow the water level to decrease by less than half (if the pressure created by the water decreases, the mine will collapse);
- monitor the bottom filter and change it after its service life has expired;
- clean the well at least once every 5 years;
- remove accumulated sand from the bottom of the well;
- use specialized equipment for cleaning.
It is prohibited to use any electrical appliances in the mine.
General information
The principle of operation of drainage on the site
The presence of a drainage system on the land plot of a country house increases the level of comfort while living in the house. Drainage protects the basement floors from dampness, the formation of cracks on the building, and paved paths, which guarantees the preservation of the landscape design on the site unchanged. It is possible not to lay drainage in rare situations.
What determines the need for drainage:
1. drainage is laid to drain water from the base of buildings. If water comes very close to the foundation, then the soil can shift and the house can “float.” This phenomenon can be found in clayey areas. If you add soil freezing to this, frost heaving may occur, as a result the house may be squeezed out of the ground.
2.drainage protects basements from flooding. With better installation of waterproofing layers, moisture will still penetrate into the house if there is a lot of it. Mold and mildew grow quickly in damp basements. Rain and snow, combining with salt solutions from the soil, are aggressive substances that corrode the structure of the foundation and walls.
3. If there is drainage and high groundwater levels, the septic tank is not in danger of being squeezed out of the soil.
4. Drainage and storm sewer together will quickly remove water from the building, preventing it from seeping underground to the foundation.
5.Drainage maintains the soil at optimal moisture; puddles will not form on the ground.
6.Abundance of water in the soil will lead to rotting of tree roots.
7. If the site is inclined, then with heavy rainfall and floods the upper fertile soil can be washed away. The water will go deep through the drainage and the soil will not be washed away.
In what situations does drainage require construction?
There are cases when the need for drainage construction is not questioned. Under what circumstances is the drainage structure shown:
1. When the site is located without a slope, drainage is required. If there is a lot of precipitation or a lot of snow melts, the water will not flow down the slope, it will stagnate in the form of puddles.
2. When the site is located in a lowland, drainage is required, because all the water will accumulate on the site, running down the slopes.
3. If the site has a strong slope, drainage is required, because water, quickly flowing down, will take with it the upper black soil layer. This flow of water should be directed deep into the drainage system.
4.If there is a clay type of soil, drainage is required because soils have low drainage capacity. Water will stagnate on the surface without penetrating into the deeper layers.
5. When water occurs underground above one meter, drainage is needed.
6. If the foundation is located too deep, close to the flow of groundwater, then with a seasonal rise in water, the base may flood.
Attention! The drainage system should be planned at the design stage. 7. When covering a large part of the area with concrete, tiles, or a lawn that has an irrigation system, drainage is required
7. When covering a large part of the area with concrete, tiles, or a lawn that has an irrigation system, drainage is required.
In most cases, a drainage system is vital. Before its construction, you should study the properties of the soil on the site.
Useful tips and tricks on how to remove it
If there is no other source near your site, it is better to carry out test drilling by hand to identify quicksand.
The work is carried out with a hand drill, reaching a depth of 15-20 m. By carefully studying the soil being removed, it is determined when the drill entered the float. After that:
- Based on the number of installed shafts, they determine the level at which the floater is located, the size of its body, and the depth of the aquifer. Based on this data, they decide what type of well will be built;
- if a small amount of impurities is found, and under them there is an aquifer no more than ten meters from the ground, they choose the option of constructing a tube well. In case of deeper water, a well should be drilled.
If you started constructing a mine without exploratory drilling and found quicksand, in this case it is difficult to determine the thickness of its body and make some kind of informed decision. Another situation may arise - water began to disappear from a long-used well. Its quality began to deteriorate, and the source began to become shallow over time.
The solution to these problems is to drill deep into the well. The cost of the work will be lower, since it is not carried out from the surface. Pumping equipment will then be installed in the mine.
Storm drainage elements
The surface drainage scheme for the site includes:
- water intake trays covered with gratings on top. Depending on the location, they can be made of steel, cast iron, ceramics, plastic, concrete, polymer cement. They are usually installed along paths, roads, houses, blind areas, sidewalks, etc.;
- fittings and connecting elements;
- point water inlets with a connected pipe or tray are usually installed at the point where water drains from the building’s drainage system. The water intakes are covered with gratings on top;
- rainwater is collected in wells and discharged to drainage points in the same way as water from deep drainage.
In large wetlands, drainage is found using ditches filled with crushed stone and diverting water towards a natural drainage area. In compact summer cottages, such a scheme is not applicable - it requires a lot of space.
A photo of the drainage systems on the site will help you understand all the structural elements.
Rules for operating a well on quicksand
In order not to render the well with quicksand inoperative, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- The quicksand constantly strives to fill the well, so under no circumstances should you pump out the water completely. The recommended minimum level is 40-50 cm.
- You cannot fill the bottom of the well with quintals of pebbles and crushed stone in the hope of crushing the quicksand. It will successfully swallow and drown them, and the cost of the next cleaning will increase.
- To prevent turbidity of water when taking it to the bottom with a bucket or pump, it is advisable to install a bottom filter made of wooden boards or stainless metal mesh wrapped in geotextile.
- Filters are installed to protect the pump and household appliances.
- Vibrating pumps activate quicksand, so they cannot be used in a well with quicksand.
When cleaning a well, you need to choose the soil carefully and moderately. Quicksand is characterized by height and pressure. You can draw until you lose your pulse, but the level will not decrease, and may even increase.
Amateur well cleaning can not only lead to a deterioration in the quality of water in the well, but can also cause its irreversible failure. Only professional maintenance will ensure a long life for a quicksand well
The optimal time for cleaning and repairing a quicksand well is a frosty winter or dry summer. Its level decreases and allows you to work more comfortably. The water from the well is partially pumped out, and cleaning is carried out in the usual way. A wooden shield is well preserved in water, but at first it will give the water a specific taste.
What problems does a drainage system solve?
Correct drainage of excess water from the base of the foundation of residential buildings and outbuildings protects buildings from settlement, the appearance of unsightly damp spots, darkening of corners and the formation of mold, and basements from annual seasonal flooding.
The soil does not “float”, and at low temperatures the consequences of frost heaving do not occur, “squeezing” buildings out of the ground. Layers, paths and sidewalks placed on the territory do not crack and are kept in perfect condition.
In well-drained areas, treatment communications and structures operate for a long time and reliably. Even with an increase in the seasonal level, groundwater receives a path to outflow and does not provoke the release of septic tanks and sewage from cesspools to the outside.
Moisture from precipitation, which leaves in a timely manner through drainage channels, does not react with salts contained in the soil and does not form aggressive compounds that decompose building materials.
High-quality drainage does not allow puddles that form after rain to stagnate and waterlog the soil in the garden, thereby causing water erosion.
In areas with a pronounced slope, the drainage system redirects water flows into drainage channels during heavy rainfall, thereby preventing soil erosion and maintaining the attractive appearance of the overall soil surface.
In combination with roof storm drainage communications, the drainage system quickly removes excess water from the perimeter of the land, prevents it from seeping into the basement and basement rooms and prevents flooding of both buildings and the entire site.
Water erosion negatively affects the condition of land cover and significantly reduces the yield of garden and vegetable crops
Sealing joints
A hydraulic seal must be installed at the junction of the concrete rings. If there is a leak from which water flows under pressure, a special emergency composition is used. The filling is prepared according to the manufacturer's instructions. The joint is sealed with the prepared material. Some compounds set in literally 30 seconds.
If water does not flow under pressure, non-emergency compounds are used to treat well seams. The material will hold better if you cut out a dovetail-shaped recess when creating the groove. The expansion should be directed deep into the base.
The material is mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions and applied to the prepared hole. You will have to wait until the composition hardens. The curing time does not match between different manufacturers; it is usually indicated on the packaging of the material.
What are drains and what are they for?
Complex of pipes and wells
Drains or drainage pipes are used to drain the area from excess moisture, groundwater or soil water. The drainage system forms drainage - a set of pipes that help maintain soil quality and the stability of technical and residential buildings.
Water in the surface layers of the soil or under the foundation of a building on a summer cottage must be drained in order to:
- The garden building did not “lean”, its foundation did not sag
- There were no puddles left on the playgrounds and paths due to stagnant water
- There was no flooding of basements and ground floors
- Avoid the appearance of fungi on the walls of buildings due to excessive dampness
- Prevent destruction of load-bearing parts of the building or individual structural elements under the influence of salts and aggressive chemical compounds contained in water
- Prevent waterlogging and freezing of the soil in winter, which will negatively affect the germination, flowering and fruiting of garden crops
- Avoid washing away the fertile soil layer in garden plots with a slope
Veranda attached to the house - expanding the living space: projects, tips on how to create it yourself (200 original photo ideas)
Preparing surfaces for interior finishing
To create a reliable protective layer, several sequential actions are performed using sealing compounds. This procedure applies to new and old wells.
At the initial stage, it is planned to prepare the walls of the well for further processing. Surfaces are thoroughly cleaned with a metal brush. There should be no dirt, moss, fungus, plaster or other mortar residues left on the base. At the joints, grooves are made approximately 2.5 cm wide and 2.5 cm deep. If there is a leak, the joint is expanded even further in this place (up to 50x50 mm). It is advisable to treat the walls with a special primer or simply moisten them with plenty of water.
Backfilling an area with waterlogged soil
Before starting work on the site, the highest point is determined, at which leveling of the entire territory begins, with the exception of the area under utility and main buildings.
A separate drainage system is made along their perimeter. Pour the soil in two layers. The lower one is made of sand, the upper one is made of fertile soil. All types of crops and trees can be grown on a leveled area.
Getting rid of the swamp
An unpleasant smell from fumes, clouds of blood-sucking mosquitoes - these are the delights that await the owners of country cottages located in swampy areas.
You can get rid of the scourge only by completely removing moisture from the swamp. One of the possible options - planting plants that absorb moisture, has already been discussed in this article. Let's look at other methods.
Moisture-loving plants
Before you drain an area of water with your own hands, it is worth knowing that there is a way without installing engineering structures on the site. This is planting moisture-loving plants that will “work like natural sponges.” Their root system will actively absorb a large amount of liquid, and the vegetative part will evaporate it. However, this method will be effective in low swamp conditions. By using perennials and shrubs that need a lot of water, you can speed up the drying of the soil after rainfall or flooding. You can plant:
- maple;
- poplar;
- birch;
- dell;
- viburnum;
- swimsuit;
- day-lily;
- iris;
- aquilegia;
- Volzhanka;
- blueberries
The advantage of this method is that you can get rid of excess moisture from the area and create a carpet of beautifully flowering plants. However, using the method, the acidity of the soil increases. Therefore, to restore normal PH, you need to systematically add alkali to the soil.
Progress
The work steps should be carried out in this order:
- Prepare a plan with precise locations of trenches. Please note that they must be at least two and a half meters away from trees.
- Dig ditches.
- Place a ten or fifteen centimeter layer of sand at the bottom of the prepared trenches.
- Lay waterproof material – geotextiles.
- Place the pipes.
- Fill the remaining space in the ditches with gravel, so that about twenty centimeters remain to the ground.
- Cover the surface with geotextile and fill it with small stones and soil.
By following these instructions for draining the area, you will forever forget about excess moisture in groundwater.
Versailles variant
The residence of the French kings, which still amazes visitors with its beauty, was located on a marshy area. The famous Cross Canal was dug in order to drain excess moisture into it. We don’t suggest digging an imitation of the Versailles canal, but any summer resident can easily create a decorative swamp.
In summer, moisture will evaporate and the water level will drop significantly. During the rainy season there will be more moisture in the swamp.
One very significant advantage of such a reservoir is that there is no need to do the waterproofing necessary when designing other decorative water surfaces on the site.