Everyone involved in housing construction studies the connections between the level of housing, the technical and operational properties of building materials and their economic feasibility. POROTHERM blocks, made from clay, water and sawdust that burn out during firing to create a porous structure, are environmentally friendly, have a high heat capacity and are capable of allowing evaporation to pass through. This is an economical large-format wall material that can be used for the construction of even multi-story buildings.
Masonry is a system of masonry elements that are laid in a certain sequence and fastened with mortar. The complex POROTHERM masonry system allows the construction of buildings of any layout, using a variety of architectural forms. In addition to the porous blocks themselves, which have a vertical tongue-and-groove connection, it includes ceramic lintels, beams, floor slabs, facing bricks and dry mixtures for mortar and plaster.
Masonry mortars
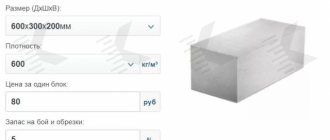
Cement-sand or lime-cement mortar, usually used for brickwork, is not recommended for laying large-format POROTHERM blocks, due to the large difference in thermal properties. Otherwise, mortar joints, which are “cold bridges,” will negate the remarkable thermal insulation characteristics of porous blocks. It is advisable to use “light” (thermal insulating) masonry mortars - more expensive, but with a higher bonding ability. From 20 kg of dry mixture, if the instructions are strictly followed, you get 30-32 liters of the finished solution. The consistency should be such that the solution does not flow into the vertical holes of the bricks.
What does installation of ceramic blocks mean?
The concept of “laying walls from a ceramic block” means a set of works associated with laying stone from warm ceramics for the construction of a wall.
During masonry work, a special heat-insulating solution is used to prevent cold bridges from occurring during the operation of the house. Warm ceramic masonry is used not only in the construction of residential private houses; this material can easily be used for :
- construction of a bathhouse;
- garage;
- barn;
- utility premises.
Ceramic blocks have non-standard sizes and large formats. They are lightweight, but at the same time durable. That is why, according to standards, it is allowed to build multi-storey buildings from this material up to 12 tiers.
When working with warm ceramics, it is important to adhere to construction technology and use reinforcing materials where necessary. It is also worth considering that the material itself is considered fragile and if handled carelessly, the stone can crack.
Is it suitable for walls?
It is allowed to build walls from such a hollow block, and there are even several advantages when working with warm ceramics.
For example, this raw material has a low thermal conductivity coefficient. This means that a house made of ceramic blocks will always be warm inside .
If construction takes place in the southern region, then insulation of the ceramic block wall will not be required.
Ceramic blocks with mineral wool in the holes are also available for sale. Raw materials act as additional insulation, so insulation with finishing materials is out of the question.
Bed stitch
The thickness of the bed seam for POROTHERM blocks should be, on average, 12 mm - this is enough to equalize permissible deviations in the dimensions of the blocks. If the bed seam is thicker, the strength of the masonry will decrease. The solution must be applied so that the entire block lies on an even layer of the solution. When laying all load-bearing walls, external and internal, which are under static tension, the solution is applied to the entire surface of the bed joint. When laying walls and partitions that do not experience static loads, it is possible to use an intermittent bed seam.
Vertical seam
Traditional masonry, with vertical joints filled with mortar, is used for load-bearing (external and internal) walls. The consumption of solution and working time in this option is very significant. Tying vertical seams into a tongue-and-groove pattern is more technologically advanced, does not require mortar, and is used for constructing external thermal insulation walls in one row. The blocks are laid end to end in a horizontal direction. The humidity of the entire masonry is less than with traditional masonry, so the walls dry quickly, acquiring the appropriate strength characteristics and level of thermal resistance. The optimal thickness of external walls is achieved when laying in one row of POROTHERM blocks with a thickness of 510 mm. A more economical solution is possible if you use 380 mm thick blocks.
Features and characteristics of the material
The product is an improved version of conventional brick. This is a large-format building material with voids inside and grooved edges on the sides. Its light weight and large dimensions make the construction of housing practical and reduce the time required for the work.
The high energy efficiency of the block is achieved due to the porous structure and components included in its composition. During the production process, wood shavings are added to the clay batch, which are burned out during subsequent firing, and microscopic pores appear in their place. They increase the thermal insulation qualities of the material.
Inside, the ceramic block is a hollow multi-slot structure. Due to air-filled voids and micropores, the material has low thermal conductivity.
Laying the first row
POROTHERM blocks require reliable waterproofing between the wall and the base. To do this, a waterproof solution is applied to the base and a waterproofing membrane is laid on top (2-3 cm wider than the intended wall). A layer of masonry mortar is applied to the waterproofing, thicker than the bedding mortar, and carefully leveled, starting from the highest place. And on top there is a thin layer of cement to prevent the blocks from immersing in the solution. First, place the blocks in the corners of the walls and connect them with a mooring cord on the outside of the masonry. Next, lay the blocks one after another, end to end along the cord, inserting them from above, along the tongue-and-groove direction. No horizontal displacements are allowed! The blocks are cut to the required size using a tabletop circular or chain hand electric saw. Ceramic blocks should not protrude beyond the foundation by more than 25 mm. After laying the full perimeter, give the first row time to dry, at least 12 hours.
Pros and cons of using ceramic blocks
Ceramic blocks are becoming increasingly in demand in the construction of budget homes and commercial buildings due to their cost-effectiveness and performance characteristics.
The material has the following advantages:
- high thermal insulation;
- environmental cleanliness;
- low thermal conductivity;
- increased sound insulation;
- frost resistance;
- the material is non-flammable and has good vapor permeability.
The material retains its characteristics for a long time. Its service life reaches up to 150 years.
The material is fireproof because it is produced by high-temperature firing. It is non-flammable and belongs to fireproof products.
Ceramic blocks have the ability to maintain the required humidity in the room. Walls made of them perfectly retain heat and create a healthy microclimate in the room.
As for the disadvantages, the main ones are fragility and increased moisture absorption. The material should be transported carefully and stored in closed areas.
Dressing of masonry
Bonding is the most important static characteristic of masonry. The wall, if properly bandaged, will work as a single structural element. Vertical seams between individual blocks in two adjacent rows must be shifted by at least 0.4 h (h is the height of the brick). Thus, for POROTHERM brick blocks with a height of 219 mm, the minimum dressing pitch is 87 mm. The recommended horizontal module of 250x250mm POROTHERM blocks provides a dressing pitch of 125 mm. To bandage masonry obtuse and sharp corners, POROTHERM blocks must be sawed.
Wall masonry
Before applying the solution, wet the top surface of the laid row of blocks with water. Apply the bedding mortar over the entire surface of the wall, up to its outer edges, but if it protrudes outward, collect it with a spatula. Start each row by installing corner bricks and continue as described above. Make sure that the distance between the vertical seams of adjacent rows along the wall is 125 mm. Using a level and a plumb line, check the horizontal and vertical alignment of the stacked blocks, knocking them down with a rubber mallet if necessary.
Types of building ceramics
Building ceramics are made by firing clay concentrate containing various improving additives.
Due to their strength, durability and remarkable decorative qualities, ceramic elements have found the widest application in various fields of construction.
The availability and low cost of industrial raw materials made it possible to establish the production of this material in almost all regions of the country.
Dense material does not absorb moisture as well as porous material
Ceramic building materials are divided into several types according to their technical properties and purpose. According to their density they are:
- dense;
- porous.
Dense ceramic products have a low moisture absorption rate, amounting to about 5% of their own weight. Porous materials have many interconnected cavities inside, so they can absorb a very large amount of moisture - up to 20% of their own weight. Accordingly, dense materials are more durable and weather resistant.
But at the same time, porous products have better thermal insulation properties, which allows significant savings on additional insulation.
According to their purpose, ceramic building materials are:
- Roofing. These include various types of tiles.
- Floor coverings - tiles, porcelain tiles, etc.
- Special purpose - fire-resistant lining, pipes for laying communications (sewerage, electrical and fiber-optic cables), thermal insulation protection (expanded clay).
- Facing – tiles for decorative wall finishing, facing bricks.
- Wall materials – intended for the construction of load-bearing structures, primarily the walls of buildings. These include ceramic bricks and wall blocks.
Let's consider the last type of building ceramics in more detail.
Working conditions
Porous POROTHERM blocks, under construction conditions, should be protected from moisture. The temperature during masonry production should not fall below +5°C. Do not use bricks covered with ice or snow. It is necessary to protect the finished wall from getting wet, otherwise water will accumulate in the vertical holes of the blocks, which will take a long time to dry. It is especially important to reliably cover the upper surface of walls and window sills with plastic film or tarpaulin to prevent, in the event of rain, the leaching of fast-soluble mortar substances from the seams.
Differences in construction technology
There are several differences in the construction of walls made of ceramic blocks for a home and for a bathhouse.
House
Depending on how many floors there will be in the house, it is necessary to calculate the number of dressing rows with reinforcement.
In addition, when designing a house, you need to take into account the calculated load on the foundation. To create external walls, you can use ceramic blocks with insulation inside - this will not only keep the room warm, but will eliminate the need to additionally insulate the house from the outside.
You can learn more about building a house from ceramic blocks here.
Bath
When building a bathhouse, you should also not forget about waterproofing after the foundation. Another important point is the arrangement of ventilation ducts at the bottom of the wall. Since moisture will accumulate inside the bathhouse, professionals recommend not only waterproofing, but also vapor barrier of the walls, as well as additionally finishing the walls with protective building material from the inside.
It is not recommended to build a bathhouse entirely from porous ceramics; it is better to combine several materials. For example, a washing room and steam room are considered wet rooms, so it is better to build them from a different material.
Read more about the construction of the bathhouse here.