Aerated concrete is a material that is becoming more popular every year. Most outbuildings, garages, bathhouses and low-rise buildings in Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and other CIS countries are already being built from aerated concrete blocks.
Now a new trend has emerged: construction companies use gas blocks as filler for walls in monolithic frame houses.
Such buildings are strong and stable due to the reinforced concrete frame, and at the same time quite easy to construct, since the blocks are easy to use.
Construction of monolithic frame houses: why aerated concrete?
The reasons for the high demand for the material are obvious; they lie in the characteristics of aerated concrete blocks.
Monolithic frame new buildings, which are being built by construction companies, are future homes for a large number of people who will live in close proximity to each other. So it is important to ensure a comfortable stay for residents.
Aerated concrete is a material that differs:
Fire resistance
The most important thing when building an apartment building is the safety of the residents. Aerated concrete does not burn at all; the material is classified as NG (non-flammable). So walls made of aerated concrete are the best option to protect yourself from possible fires.
Of course, this will not stop the spread of fire, since finishing materials catch fire quite quickly. But the blocks can delay the occurrence of a fire as much as possible in apartments adjacent to the fire source.
Aerated concrete heats up very slowly, so spontaneous combustion is excluded. All this makes life in a monolithic frame house using aerated concrete safer than in new buildings with other frame fillers.
- High noise insulation and sound insulation
Blocks can protect you from noise coming from the street. The metro, tram tracks near the house and noisy areas are no longer a reason to refuse an apartment, because aerated concrete blocks will provide you with peace and tranquility.
Also, neighbors stomping, knocking and always dropping everything on the floor are not scary. Filling with gas blocks ensures softening of all sounds from adjacent rooms.
In conditions of multi-apartment construction, aerated concrete blocks are an ideal option for maintaining silence for every family.
- Heat retention
Thanks to their porous structure, aerated blocks provide optimal temperatures in both summer and winter. During the warm season, they do not heat up, so they keep the room cool.
And in winter, due to the cells filled with air, aerated concrete gives residents warmth and comfort in the house. Heating bills in a house made of aerated concrete blocks will be significantly lower than in buildings made of other materials.
- Earthquake resistant
High-rise buildings made of aerated concrete are a good option for construction in places where seismological activity is frequent. Such houses perfectly withstand earth vibrations, storms, and storms.
Types of slab foundation
For frame houses, different types of slab foundations are used: “bowl”, “inverted bowl”, “slab with caisson”, USP. Foundations differ in load distribution, slab shape, presence of “ribs,” and method of installing reinforcement and formwork.
Solid slab
A solid monolithic slab is made without ribs, so constructing formwork and reinforcement is quite simple; this is the most suitable method for beginners. The reinforcement is knitted directly on site, the cell size can be easily “adjusted” to the location of engineering systems and walls. No special equipment is needed to excavate soil.
The main disadvantage is the increase in the budget due to the large volume of concrete work. When constructing yourself, it is necessary to take into account that it is impossible to mix so much concrete at one time.
The decision on the thickness of the slab foundation for a frame house is made after geological research. In most cases, for a standard 6x6 frame, a thickness of 200 mm is sufficient, for 8x8 - 250 mm, 10x10 - 300 mm. It is not recommended to locate the house below 200 mm so that the wooden parts of the structure do not suffer from capillary moisture.
Foundation - “inverted bowl”
For light houses, the “inverted bowl” slab, with the ribs down, is a popular and practical solution. Using ribs, they raise the floor level without creating a thick layer of concrete under the entire area of the house.
The main load, which in the case of a classic monolithic slab is distributed over the entire area, with an “inverted bowl” falls on the ribs. Permanent formwork is installed inside , the cavities are filled with sand, and the entire foundation is poured in one go. The advantage of the “inverted bowl” is the speed of construction and relative cheapness due to the saving of concrete.
Stove - “bowl”
In this type of foundation, the ribs are raised upward, playing the role of a base and giving the structure additional strength. It turns out to be a kind of “trough”, the load is distributed over the entire area.
The voids are filled with expanded clay and sand, and insulation and a floor are installed on top. The method is considered universal, suitable for different types of houses, but is expensive due to the need to raise the floor level with backfill and insulate it.
Slab with caisson
A slab with a caisson (recess) is convenient if you need a small cellar. When digging a pit under the main slab, a recess is made in the right place for the caisson. Rocky soil can be a problem as you need to dig to great depths.
Useful: Exterior decoration of a house from facade and basement panels
The advantage of slabs with a caisson is the organization of a place for storing crops, the disadvantage is the complex installation of fittings and the need for high-quality waterproofing. It is necessary to have an accurate design so that after the construction of the partitions it does not turn out that access to the storage is organized in an inconvenient place.
USHP is a new technology
USP, insulated Swedish plate, is a technology actively promoted by many developers. With this method, the contours of the heated floor are laid directly in the slab. The main advantage is energy efficiency and reduced heating costs. However, for a specific project of a frame house on USHP, you should compare the difference in budgets for different types of foundations and calculate when the resulting heat savings will pay off.
Flaws:
- high costs;
- complex construction technology;
- the possibility of damage to the insulation by rodents;
- all communications are carried out in the slab , so you need to be sure of the calculations and output coordinates;
- Typically, composite reinforcement is used for USP, for which sufficient statistics on service life and operation have not yet been accumulated.
Advantages of construction using aerated concrete
The work happens very quickly, because aerated blocks are lightweight and are 8 times larger in volume than bricks. If we compare filling walls with brick and aerated concrete, then the use of blocks speeds up construction by 3 times.
Of course, this makes it possible to complete construction faster, which means that residents will move into their apartments sooner, the house will be completed on time, and the company will be able to begin construction of the next building. Very profitable, right?
In total, the following benefits for construction companies can be identified:
- Cost-effective (the cost of aerated concrete is several times less than brick)
- Operation speed
- Ease of construction
Construction of a slab foundation
Before construction begins, it is necessary to conduct a site survey. The type of foundation, thickness of the pad and concrete slab are selected based on the composition of the soil, groundwater level and loads. Work begins with uprooting plants and clearing the soil at the building site to about the size of a spade. Each type of slab foundation has its own characteristics, but the main stages remain the same.
Work order
Construction stages:
- Excavation of soil for a foundation pit.
- Making a foundation cushion from compacted sand, crushed stone or a combination of layers of different materials. Before backfilling, geotextiles are laid on the dry bottom of the pit so that the backfill does not mix with the soil.
- Concrete preparation, footing, is a layer of lean concrete of at least 100 mm for additional waterproofing and leveling the bottom of the pit. There are different opinions among builders regarding the need for this stage. Sometimes they refuse it, but the decision depends primarily on the type of soil.
- Groundwater drainage. Pipes for draining groundwater are laid in a pit under the foundation cushion with the required slope (5 mm per linear meter).
- Waterproofing is necessary if groundwater comes close to the base of the foundation . In this case, concrete with its porous structure will absorb water, which will lead to corrosion of the reinforcement. If the groundwater level is low, waterproofing is not necessary.
- Insulation of the foundation under the slab. The first method is to lay insulation (expanded polystyrene) under the entire area of the slab. When laying a heated floor, use PPS with a thickness of at least 30 cm. The second method is to insulate the foundation walls, lowering the PPS below the base, and the blind area, slightly extending beyond the edges.
- Reinforcement. Depending on the specific gravity of the structure, the thickness of the concrete slab is calculated and the diameter of the reinforcement .
- Installation of formwork. The cheapest option is made from boards with natural humidity from 40 mm, usually 50x150. Thinner formwork may not be able to hold concrete, which will lead to violation of linear dimensions. If the formwork is removable, then after its removal the boards are reused for scaffolding or subfloors. Chipboard or polystyrene foam are also used as permanent formwork to immediately create a warm contour around the foundation.
- Pouring concrete.
- Removal of formwork, treatment with bitumen primer (primer).
- Filling the blind area - performed after completion of the exterior finishing.
Useful: We are building a foundation for a frame bathhouse or frame garage
All steps are clearly shown in the video:
Selection of base material
The decision on the choice of material for backfilling is made on the basis of SNiP and site analysis. The main criterion is the water saturation of the soil.
If the area is dry, use sand with a small layer of crushed stone . If the soil is saturated and there is water in the pit, then sand is abandoned in favor of crushed stone. The minimum thickness of sand backfill is 20 cm.
The ideal option is to order a soil study at the construction site, based on it, make a project, calculate the thickness of the pad and the height of the slab.
A special case is an artificial embankment with a difference in height
The main disadvantage of a slab foundation is its inability to be used in areas with large elevation differences. In some projects, in order to level out the difference in height, they build an embankment of crushed stone . If you make an elevation out of sand, there is a danger that the house will settle.
To prevent the embankment from spreading, you need to carry out additional actions: Expand the soil section by 3-4 meters compared to the foundation, dig a pit, fill it up and make an embankment of crushed stone. Crushed stone “does not spread”, unlike sand, and a stable base is obtained on which the foundation is built.
When building a frame house on a slab foundation, the budget is taken into account. To estimate the cost of the foundation, the cost of work and materials at each stage is calculated and summed up. The main cost items: digging a pit, compacting sand, waterproofing, insulation, reinforcement, construction of formwork and concreting. The estimate takes into account the costs of fasteners for formwork, costs of drainage and storm sewerage.
In frame house construction, different types of foundations are used: strip, columnar, pile. With heaving soil, there is a danger of the foundation being “pushed out” if it is buried above the freezing level. The slab foundation is called “floating” because of its ability to redistribute loads caused by heaving.
A slab lying on a sand cushion does not crack and the walls of the house do not deform. Such a foundation is reliable and does not limit the number of storeys, so cottages of 2-3 floors are built on it, reducing the building area and saving space on the site.
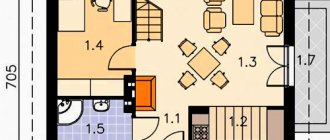
What does it represent?
A frame house is a building that is quickly built. The main type of construction is the construction of low-rise buildings. In such buildings, the layout can be changed. Such buildings are based on wooden or metal frames using sandwich panels coated with wood fibers. Such structures are insulated with mineral wool, ecowool and other insulation materials.
Such buildings are easy to plan; if changes need to be made to the design of concrete walls, this can be done without destroying the structure. Structures that are built on a reinforced concrete frame have walls without through construction joints.
Low-rise buildings are gradually being built using this technology (with frames). Such structures are built on any surface and in unfavorable territorial conditions. Concrete construction is convenient and affordable. One of the cheapest and most practical materials is concrete. It is used for the construction of both private houses and high-rise buildings.
DIY frame construction
To build a concrete foundation for a building, you need:
- carefully inspect the area for the presence of unnecessary materials that interfere with construction;
- mark where the structure will be;
- carry out excavation work;
- create reliable formwork;
- clearly arrange the reinforcing bars;
- pour the concrete mixture.
Before construction begins, the soil is examined, then the dimensions of the structure are indicated with signs and the thread is pulled. Then they dig trenches. You will need a shovel, hammer, and sledgehammer. The dimensions of the trench are 60 by 70 cm. This is influenced by the quality of the soil where the structure is being built.
When work with the trench is completed, it is compacted and laid with layers of crushed stone and sand. Then they begin to assemble the formwork. For this you need wooden blocks, a hammer, nails, a file, and a drill. Having folded the formwork, the reinforcement is prepared. You will need a grinder and welding. The reinforcement is laid in grids measuring 20-40 cm.
After installing the reinforcement frame, the preparation of the concrete mixture begins. Concrete is selected according to the size of the building being built. To create a concrete solution, cement, sand, water, and crushed stone are used. The grade of cement used is higher than the grade of the mixture. To prepare the mixture, use a concrete mixer. The finished concrete mixture must be poured gradually and evenly. There is no need to fill in parts, as joints will form and the structure will become fragile.
Cost and materials
When constructing monolithic type houses, the quality and cost of materials play a decisive role.
- The fittings must be free of rust and other damage.
- The concrete must correspond to the manufacturer's declared grade and the required strength limits. In the winter season, it is better to use special anti-frost additives in concrete. In severe frosts, it is better to stop work.
- Removable formwork must retain its shape. It is better to buy materials from trusted suppliers. And be sure to require quality certificates and hygienic certificates for all products.
The estimated cost of housing depends on many components. It includes the price of materials, delivery of materials, rental costs of formwork, construction machinery and mechanisms, and labor. All cost items are displayed in the project estimate.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of a slab foundation include:
- no need to deepen to the level of soil freezing;
- high resistance to temperature changes;
- Possibility of installation on any type of soil;
- increased service life;
- low probability of deformation and subsidence.
Negative points include:
- increased period of construction work due to laying the waterproofing layer;
- a perfectly smooth platform is needed for the foundation, which increases the requirements for construction conditions;
- relatively high costs for concrete mixture and construction reinforcement.
Varieties of monolith
If initially monolithic houses were only made of reinforced concrete, today there are variations on the theme - instead of DSP they use wood concrete or sawdust concrete, and instead of a reinforcement frame they use wooden racks.
But the essence remains the same - enclosing structures are not assembled or laid out from individual elements, but rather are poured. As a result, monolithic, seamless walls of almost any geometric shape are formed, which frees up the hands of architects. That is, if the abundance of bay windows and arches during construction from block/brick/wood significantly complicates the process, then no special effort will be required when pouring.
Since ordinary reinforced concrete turns out to be too cold, due to its high thermal conductivity and thin walls, foam concrete, polystyrene concrete or expanded clay concrete are used to do without additional insulation. In the first case, the thermal conductivity of the wall is reduced due to the formation of a large number of air pores in the concrete due to foam, in the second - due to the addition of polystyrene or expanded clay granules. But according to its varieties, the monolith is divided not by the type of concrete poured, but by the type of formwork - it can be removable or permanent.
Removable formwork
In the private sector, it is usually made of moisture-resistant or laminated plywood; boards, metal or plastic are less commonly used. The sheets are used whole or cut into pieces, depending on the scale of the fill. The elements are fastened together and, as they are poured, moved to a new location, since only specialized companies can afford to assemble the formwork for the entire house at once. And self-builders fill houses in stages, mainly horizontally. Plywood is deservedly popular, as it holds its shape well and allows you to get a smooth wall surface, and if it is also laminated, then the set can be enough for more than one construction site. As for fasteners, everything is individual.
Plywood 12 mm thick, increased moisture resistance, 2500 × 1200 mm, cut in half along the length (600 mm), four ties per sheet (sheets were drilled through, folded together, 100 mm from the bottom), the top was tied together with bars. Ties with two jammed nuts at one end, 250 mm long, 8 mm in diameter, were lowered into the spindle. Drive-in nuts are driven into the formwork from the outside; you only need to turn it (with a screwdriver) from inside the walls.
Rearranging removable formwork as it is poured is considered one of the most labor-intensive and time-consuming processes, and the fewer operations required, the better.
Turnkey slab foundation in Moscow and the Moscow region
Turnkey slab foundation in Moscow and the Moscow region! Best construction price and 3 years warranty!
The price will not increase after measuring, drawing up an estimate and signing the contract. If there is a shortage of materials, we will bring them at our own expense!
Measurements and cost calculations are carried out by our specialists. Then, a construction contract is concluded, with a guarantee stated in the contract that the price of the “foundation slab” will not increase during construction, and the work will be carried out in accordance with all the requirements of SNIP.
* Everything is included in the price: from the visit of a specialist and drawing up an estimate, to the acceptance of concrete and the work of construction equipment.
We have 2 concrete production facilities and work without intermediaries: and we are confident in the quality of the main material for the foundation. Monolithic workers with extensive experience and a professional foreman, we guarantee the best price for the construction of a monolithic slab in Moscow and the Moscow region.
Foundation cost calculator slab turnkey price
Submit your result. We will contact you to clarify details.
We provide a 3-year warranty on each work performed.
Load bearing calculation
A slab foundation will be considered reliable if its area satisfies the conditions of the formula: S > Kn × F / Kr × R, where:
- S – the base of the house, measured in square meters. cm.;
- Kn – support reliability coefficient (equal to 1.2);
- F – combined mass of all slabs on the foundation in kg;
- Kr – working conditions coefficient;
- R – conditional value of the calculated soil resistance in kg/sq.cm.
Kp starts from 1 (on plastic clay soils) and ends at 1.4 (on coarse sandy soil with easy construction conditions). The coefficient values are taken from special architectural reference books.
If, according to the formula, the area turns out to be smaller, it must be increased, or another parameter must be changed.
How to build a concrete frame of a house yourself
Build a concrete frame of the house, following the specified sequence of operations:
Prepare the construction site for the construction of a frame structure. Remove vegetation, remove debris and mark the area.
Carry out excavation activities aimed at constructing the foundation. Extract the soil for the future foundation to the level specified in the design documentation.
Level the soil and fill the prepared pit with a damping pad based on a crushed stone-sand mixture. Thoroughly compact the bedding and install the formwork structure.
Cut the steel reinforcement into pieces of the required sizes and tie the reinforcing lattice elements together using annealed wire. Assemble and fix the frame inside the panel formwork.
Pour the pre-prepared concrete mixture into the installed formwork. Compact the solution and allow the monolith to harden for four weeks.
Assemble a spatial lattice from steel reinforcement that matches the structure of the building being built. Assemble the formwork for pouring the columns.
Perform continuous pouring of concrete mixture into the formwork. Compact the concrete with vibrators and do not expose it to loads for a month.
Disassemble the formwork and build walls using various types of building materials. Insulate the walls, if necessary, using thermal insulators.
After installing the roof structure and completing external finishing activities, proceed to interior work.
Isoplat plate (ISOPLAAT) windproof
These are lightweight porous sheets produced only by thermal pressing of ground pine sawdust. Their direct purpose is to protect the walls of a frame house and external insulation from climatic influences. Throughout its entire thickness, Izoplat is impregnated with paraffin, which completely protects the plate from moisture. The dew point is outside the walls and water does not collect on the insulation. This allows, after completing the external insulation of a frame house with Izoplat, to take a long break before finishing the façade. Standard slab dimensions are 2700*1200*12 mm or 2700*1200*25 mm.
Insulation
Despite the fact that during monolithic construction of a private house, concrete walls are usually thinner than brick walls and have the same thermal conductivity, insulation will still be needed. When using permanent formwork, this stage can be neglected, but with traditional construction this is unacceptable.
Various insulation materials can be used as insulation materials, ranging from standard mineral wool to warm plaster. At the same time, you can separately finish the walls with decorative bricks.