1-464 is a series of residential buildings in the USSR, developed by the Giprostroyindustry Institute in the late 1950s. An all-Union series of Khrushchev panel buildings were built throughout the USSR from the late 1950s to the mid-1960s. In the 70s, modifications of this project appeared, which were built until the end of the 1990s. As part of the modified series, four-room apartments appeared, bathrooms began to be more often separated, and houses from 9 to 16 floors with an elevator and garbage chute appeared.
Khrushchev buildings of the 1-464 series are externally recognizable by the windows on the interfloor area in the entrances, identical to the double-leaf windows in the apartments.
History of creation
Standard design houses were built en masse between 1970 and the late 1990s. Individual houses have been built since 1965. Typical series are represented by projects with the number of floors from 5 to 12; the most common are 9-story houses. Some houses are designed in such a way that shops, pharmacies and other important infrastructure facilities are located on the ground floors.
There are several series of houses that are most often found in Minsk
1. Series M-335. Houses of this series were built in Minsk from 1970 to 1975. These are 9-story buildings with 4 apartments per floor. Number of rooms from 1 to 4. The apartment has built-in wardrobes, mezzanines, storage rooms. Kitchen area 7.5 and 10 m2. The ceiling height is 2.5 m. There is 1 passenger elevator and a garbage chute between floors.
Series M-335. st. Zhudro, 17. 1975
2. Series M-464. The construction of houses in this series took place from 1968 to 2000. The number of floors in the building can be 9 or 12, with 4 or 6 apartments on the site. The number of rooms in the apartments is from 1 to 4. Their area is from 30 to 80 m2, the ceilings are 2.5 m high. The kitchen area is 7 m2, and the area of the rooms is from 7.3 to 17 m2. There is 1 passenger elevator and a garbage chute in a 9-story building.
One of the first houses of the M-464 series. Partizansky Avenue, 30/2. 1968
There is a modification in this series - M-464 (towers), these are houses of 12-14 floors. There are few such houses in Minsk, but among them there are some that are known to most Minsk residents. For example, the towers along Partizansky Avenue, on the left side towards the city center. These are houses 28/1, 30/1, 32/1 and 34/1 on Partizansky Avenue, their architect is V. Afanasyev.
Partizansky Avenue 30/1, 1975
3. MK-9. Houses of this series were built in Minsk from 1965 to 1977. These are 9-story brick houses. There are 4 or 6 apartments on the landing. Layouts of apartments with 1-4 rooms, ceiling height 2.5 m. There are built-in wardrobes and mezzanines. Kitchen area 7.3 m2. One passenger elevator at the entrance and a garbage chute between floors.
One of the first houses of the MK-9 series. Boulevard Shevchenko, 17. 1965
4. 3-OPB. This series is represented mainly by 9-story buildings. The series was developed by the BSSR and was approved in 1968. During construction, technology was used based on load-bearing volumetric blocks or block rooms. It was supposed to reduce the cost of construction and speed it up. The total construction period was reduced by 2-2.5 times compared to large-panel construction, labor costs were reduced by 15%. For their production, they even opened DSK-3 in Minsk, designed for 100 thousand square meters. meters of living space per year.
Series 3-OPB. st. Judro 29. 1974
The famous house on Belsky, 17 was also built from load-bearing volumetric blocks. The house, of course, is not a typical one, built in 1976, its architect is Temnov.
The houses of this project were built from 1972 to 1977. The number of rooms in the apartments of these projects is from 1 to 4. The area is from 35 to 81 m2. Ceiling height 2.46-2.5 m. Kitchen area 6.9-7.6 m2. Built-in wardrobes and mezzanines are provided. 9-story buildings have one elevator at the entrance and a garbage chute between floors. Houses in this series have received complaints about poor sound insulation and rounded wall corners due to the specific technology of block rooms. It is difficult to tile the kitchen and bathroom; you cannot place furniture close to the corner.
Advantages and disadvantages
Although at that time the buildings of the standard series 1–464 were the most comfortable housing, they had positive and negative sides. We must pay tribute that there were still more shortcomings.
Advantages
- The structural design of houses 1–464 with longitudinal and transverse load-bearing walls makes it possible to obtain stronger and more durable structures. It is much more reliable than the “incomplete frame” used in Khrushchev buildings1–335.
- In buildings of the 1–464 series, each apartment, except the first floor, has balconies.
- Compared to series 1–447 of the same period, houses 1–464 have a larger number of three-room housing.
- Residential buildings of a standard layout were used to build the central areas of cities.
Flaws
- Inability to change the layout of apartments. Due to the fact that almost all the walls are load-bearing, they cannot be dismantled or partially destroyed.
- The thermal insulation properties of external walls are low.
- Poor sound insulation of apartment and interior partitions.
- Rolled bitumen roofing has a service life of up to 15 years. In summer, the roof becomes very hot from direct sunlight.
- Two and three-room apartments, according to the layout, have walk-through rooms.
- There is little free space in the hallway.
- The bathroom and toilet in all apartments are combined.
- Small kitchen dimensions.
- The landings are smaller than in other series of similar housing.
- All apartments, with the exception of corner ones, are oriented in the same direction.
Main characteristics
The main material used for standard design houses is reinforced concrete panels. Houses were also built from block rooms and bricks.
The number of entrances is usually 3 or more. Houses of a standard design are among the top ones with multiple entrances in Minsk. For example, a residential building on 2nd lane. Bagration has 24 entrances, Odintsova, 36/1 - 25 entrances, and Yesenina, 6/1 - 26.
Many standard-design houses have vestibules, usually for 2 apartments. Many citizens use vestibules as places to store strollers or bicycles. Previously, most of them had special boxes - storage for vegetables.
The design of the houses provides for a garbage chute. Despite the fact that they are currently being preserved in Minsk, at the time when construction began, they were considered a luxury.
Elevators
The era of standard-design houses has made elevators an integral part of the life of millions of Belarusians. SNiP 1971 provided for the mandatory presence of an elevator in houses with more than 5 floors.
- For houses up to 9 floors inclusive - 1 passenger elevator with a load capacity of 320 kg.
- For houses with 10-12 floors - 2 passenger elevators.
- For houses with 13-16 storeys - 1 passenger and 1 cargo (up to 500 kg), or 2 passenger and 1 cargo, depending on the number of apartments on the floor.
Nowadays, many buildings have replaced elevators with modern ones.
Article on the topic
Improved project houses in Minsk: history, layout features, advantages and disadvantages
Links
- Typical series of residential buildings in Novosibirsk: options for redevelopment, layouts
- N.P. Rozanov, Large-panel housing construction, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1982, 224 pp. with illustration.
- V.A. Kossakovsky, Pioneer of industrial housing construction, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1980, 80 pp. with illustrations.
| Residential buildings | Since 1957, after the adoption of a law that provided for the elimination of excesses in the design of houses, buildings of a new type began to be erected in the USSR. Popularly, such houses were called “Khrushchevka” (derived from the name of the General Secretary of the CPSU Central Committee N.S. Khrushchev). Such houses received a second name - Khrushcheby, mainly because of the inconvenient and disproportionate layout of the rooms, narrow corridors and landings, thin walls and, as a result, terrible sound insulation. In this article we will talk about what the typical Khrushchev series are, and we will try to highlight the main pros and cons of these buildings. We will provide the planning features in the form of descriptions and photos. |
Layouts
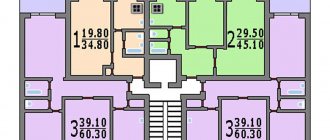
In houses of this period the number of living rooms is from 1 to 4. In most layouts they are separate. The exception is some projects of three- and four-room apartments, where there are walk-through rooms. Ceiling height is 2.48-2.52 meters.
The kitchen area is from 6.9-7.5 m2, which allows you to place not only a kitchen set and a refrigerator, but also a full-fledged table with a bench or chairs.
The bathroom in most layouts is separate. The bathroom already has space for a washing machine.
The hallways and corridors are equipped with built-in wardrobes and mezzanines. In 4-room apartments you can find storage rooms.
The project includes both balconies and loggias. The exit is usually from a larger room.
Total area of common layouts:
- 1-room apartments – 32-35 m2;
- 2-room apartments – 46-49 m2;
- 3-room apartments – 61-67 m2;
- 4-room apartments – 70-85 m2.
pros
- Increased kitchen size compared to previous types of projects.
- Regularly shaped corridors provide space for a built-in wardrobe. Today, deep sliding wardrobes are perfectly built in there.
- The bathroom is separate, and the bathroom has enough space to install a washing machine and washbasin.
- Most layouts have a loggia with an area of about 4 m2. Many buyers convert it into an office or children's playroom.
- Apartments on the ground floors of standard-design buildings are in greater demand than similar options for “Khrushchev” or “Brezhnevka” buildings, since these floors are usually high. Also, apartments on the 1st floor with loggias often have a cellar.
- The widespread presence of elevators has made it comfortable to live on high floors, which suffer less from the noise of the local area, can have a panoramic view, and are better ventilated.
Minuses
- In some houses, radiators are built into the walls, which can affect the temperature in the apartment during the heating season. You will have to dry things without using batteries.
- Relatively poor sound insulation. This parameter varies significantly depending on the design of the house and the quality of its construction. It is worth interviewing your neighbors when choosing an apartment.
- In some projects, a technical floor is not provided on the top floors. If it is not there, then it can be hot and stuffy in the summer, and cold in the winter.
- In older houses of a standard design, major repairs have not yet been carried out en masse. The condition of the entrance can be upsetting.
- The first projects of 3-room apartments have a walk-through room, as do many 4-room apartments.
Apartments in standard-design buildings are in stable demand on the Minsk real estate market. Often, 1-room apartments in such houses are purchased for children as a start to independent living in the capital. According to our statistics, most 1-room apartments in standard-design houses do not stay in the same hands for long, and within 4-5 years of life they are sold to purchase a two- or three-room apartment.
We recommend that you approach the purchase process responsibly and check the legal history of the apartment. You can order ]real estate inspections[/anchor] from us, at Avangard Real Estate.
Did you like the article? Share it with your friends!
1-464d-83.
Series I-464 (1-464) - a series of large-panel residential buildings, developed by the Giprostroyindustry Institute in 1958, developed and improved by TsNIIEP housing (project authors N.P. Rozanov, V.G. Kocheshkov, A.G. Rosenfeld, Polozov I.P.) The series is based on a structural scheme with transverse (steps of 2.6 and 3.2 meters) and longitudinal (spans of 5.76 meters) load-bearing walls. Houses of the I-464 series are available in every district of Novosibirsk. Houses of the I-464 series were produced by the Sibakademstroy trust and the House-Building Plant No. 1 (DSK-1) of Glavnovosibirskstroy.
I-464 is the most popular Novosibirsk series. From the details of this series, four-, five- and nine-story residential buildings, which became the most widespread, were built, residential buildings with a height of 12 floors, residential buildings with a height of 2-3 floors and even public buildings (for example, building 63 on Mira Street, in which Clinic No. 21 is located).
The first houses of the I-464 series were built in 1961 in the “B” microdistrict of Akademgorodok and on Gogol Street, the first nine-story house DSK-1 was installed in 1967 on the Zatulinsky residential area. In 1972, DSK-1 became the general contractor for the construction of all houses of the I-464 series, produced until the mid-1990s.
Nine-story buildings
Nine-story buildings of the I-464D series are the most common high-rise buildings in Novosibirsk. DSK-1 Glavnovosibirskstroy mastered the production of the widest range of houses and block sections: ordinary, end, corner and rotary (at different angles) block sections, houses with passages and driveways, houses with built-in and attached shops.