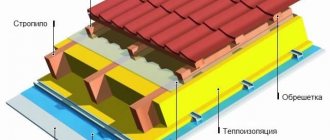
Typical wall design
Of course, the choice of wall thickness depends not only on the climate in the region, but also on the purpose of the structure: whether the house will be for permanent residence, or for temporary residence, as well as on the materials used in the construction of the internal and external parts of the wall, on the type of insulation used, presence of an air gap.
A classic wall consists of the following elements:
- External cladding . It can be from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters thick, depending on the materials used. Most often, cement-bonded particle boards or wood-based OSB boards are used; metal profiles or facing bricks are less often used. If there is no air gap, the outer part can simply consist of plastered insulation.
- Air gap . It is needed in order to prevent moisture from penetrating through the outer skin into the insulation, and it remains dry without losing its heat-insulating properties. Depending on the type of insulating materials used, it can range from 25 to 50 mm.
The order of layers in a frame house is standard Source sargorstroy.ru
- Frame . It may or may not be insulated. The minimum thickness of the load-bearing structure of a wall without insulation is 50 mm and increases depending on the type of insulation used: mineral fiber, ecowool, polystyrene foam, polyurethane spraying. The thickness of the insulation for the walls of a frame house can reach 400mm.
- Internal lining . It usually consists of more environmentally friendly materials than the external one, as it is connected to the living space. Most often they use plasterboard or materials based on natural wood (boards, timber), less often plywood, MDF or OSB. If the supporting structure of the frame is not insulated, then there may be no wall cladding.
From the structural features of the wall it is clear that the most difficult thing is to determine the thickness of the frame insulation.
It is the thickness of the insulation that will determine how warm the house will be Source otdelka-expert.ru
Protection from steam, moisture and wind
Windy weather destroys the effectiveness of even a thick wool sweater. But if you have a windbreaker made of thin, windproof steel, you immediately become comfortable and warm. The situation is the same with a frame house: the insulation, which is fiberglass, retains heat perfectly only if it is sheathed on the outside with a special windproof membrane. It will also protect against the influence of atmospheric moisture. On the inside, the insulation is protected by a vapor barrier, which prevents the penetration of warm, moist air into the space of the insulation and frame, as well as its condensation during cooling near the outside of the structure. A competent and professional approach to installing wind and vapor barriers is very important.
Insulation thickness
First of all, the thickness of the insulation in a frame house for permanent residence will depend on the geographical location of the future housing, its climatic zone, as well as on the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material.
Using the following formula, you can calculate the thickness of the heat insulator:
δ = R. k ,
where δ is the thickness,
R is the thermal resistance indicator for a specific region, and
k is the thermal conductivity coefficient.
The thermal resistance index R can be calculated independently, based on data from SNiP 23-01-99 Climatology, or can be taken from the following table:
Ready-made data will help determine the approximate thickness, but it is better to entrust the calculations to professionals who know the design features and materials Source sargorstroy.ru
It is equally important to choose the right material that will avoid unnecessary heat loss. Now there is no point in considering insulation materials like sawdust or slag, which were so popular at the dawn of frame house construction. There are a lot of more technologically advanced and practical thermal insulation materials on the market.
See also: Catalog of frame house projects presented at the Low-Rise Country exhibition.
Mineral wool
This type of insulation is made using glass or basalt fiber using the following technology:
- First, the basalt is melted in a furnace at high temperatures until it becomes liquid.
- The resulting liquid is pumped into a centrifuge, where under enormous air pressure it turns into fibers.
- These fibers are then put under a press, which compacts them to the desired parameters.
- Next, the resulting material is rolled into rolls or cut into slabs.
The positive aspects when using mineral wool are its low thermal conductivity, which is even lower than that of wood. With a density of 50 kg/m3, its average value will be around 0.045-0.05 W/m oC (depending on the manufacturer). Based on these data, using the formula δ = R. k you can calculate the thickness of the insulation for any region of Russia:
- 3 x 0.05 = 0.15 (m) - for the Moscow region,
- 4.9 x 0.05 = 0.24 (m) - for Yakutsk,
- 1.8 x 0.05 = 0.09 (m) - for Sochi.
Mineral wool is one of the inexpensive and frequently used insulation materials Source konveyt.ru
If we compare it with the thickness of wooden walls without additional insulation, we get:
3 x 0.11 (thermal conductivity coefficient of spruce) = 0.33 m. This is for the Moscow region.
The only disadvantage of mineral fiber thermal insulation is that when wet, its properties deteriorate significantly. Therefore, during installation you need to ensure compliance with waterproofing standards.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the design and construction of turnkey country frame houses.
Ecowool
A material that has recently appeared on the market is based on cellulose obtained by processing waste paper and other paper waste. Non-combustibility is achieved by adding boron compounds to the insulation. For the same reason, insects and rodents do not grow in ecowool. Today on the market this is truly the most environmentally friendly insulation.
To install this material over large areas, special fiber-spraying equipment is required, colloquially called a “vacuum cleaner.” Thanks to it, you can spray cotton wool granules both onto a structure that is not yet sewn up on one side, or pump the material inside an already mounted wall through holes specially made for this purpose. Fiber can be applied to small areas without the use of special means, like plaster.
To spray ecowool you will need a special machine Source keyinsulation.com
Among the disadvantages, it is necessary to note shrinkage, which occurs after some time, and as a result, the insulating properties are lost. This can be eliminated by pumping additional amounts of insulation into an already installed structure, which is not always convenient.
The thermal conductivity of ecowool is approximately equal to the thermal conductivity of mineral insulation at the same density, so the calculation will be the same.
Requirements for thermal insulation material
The frames of houses built using “Canadian” technology are assembled from OSB boards or wood. To prevent the insulation from causing damage to structures, it must have sufficient vapor permeability - at least 0.32 Mg .
Fiber heat insulators – mineral wool materials – absolutely meet this requirement. Popular synthetic insulation materials, such as polystyrene foam and polymer-based analogues, cannot be used in wooden structures for two reasons:
- Firstly, due to the lack of elasticity, the heat insulator will not be able to adapt to temporary deformations of the wood (shrinkage, increase in volume). The result is the formation of cracks and cold bridges.
- Secondly, polystyrene foam and its analogues do not allow wood to “breathe”. This leads to moisture accumulation, mold and rotting of structural elements.
When choosing how to insulate a frame house, in addition to vapor permeability, you should also take into account the additional properties of the heat insulator. The following indicators are welcome:
- fire safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to shrinkage;
- minimal water absorption.
Video description
About the types and features of materials for wall insulation in the video:
Expanded polystyrene
Foam plastic is familiar to everyone from childhood. It has been used in construction technologies for a very long time, but has not yet lost its relevance due to its low thermal conductivity and low weight.
The production technology of expanded polystyrene is quite simple:
- Polystyrene is brought to the melting point and saturated with vapors and gases under pressure. As a result, small balls filled with air are formed.
- The balls are then reheated and pressed into sheets of various shapes.
- To improve the characteristics, the foam is processed with an extruder - again brought to a viscous state, and then molded (extruded through a special hole). This is how extruded polystyrene foam is obtained.
Expanded polystyrene sheets are inserted and fastened between the partitions of the frame Source obrawa.ru
Among the disadvantages of this insulation, one can note its flammability, although if we talk about extruded material, this indicator will be within acceptable limits.
The density of the foam varies from 20 to 160 kg/m3 with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.03-0.05 W/m °C.
Thus, it can be calculated that the minimum thickness of this insulation for the Moscow region should be no less than 150 mm (3 x 0.05).
Floor insulation
The technology of floor insulation largely depends on the foundation on which the frame house is built. But, nevertheless, there is a certain number of activities that must be performed regardless of the type of foundation:
- the subfloor boards should be laid close to each other (this way there will be noticeably fewer drafts)
- it is necessary to install a wind barrier that is laid on the joists and subfloor. After all, to prevent the boards from rotting, the underground must be ventilated. Additionally, OSB boards can be laid on top of the wind barrier, which will eliminate even the slightest drafts
- insulation is placed between the joists (by analogy with insulation of walls and ceilings)
- A wind barrier is laid on top of the insulation, which is nailed to the joists using a stapler.
- the installation of a finishing plank flooring completes the stage of floor insulation work.
To summarize, we note: in order for the insulation in a frame house to last as long as possible and perform its functions properly, choose high-quality, reliable materials. Control the installation process, do not be lazy to check the seams and connections - this will ensure a comfortable microclimate.
On the website you can study various frame house projects, or discuss an individual project by simply leaving a request in the form below.
Example of calculating wall thickness
The thickness of the insulation of a frame house for permanent residence using the example of the Moscow region (this calculation was given above) was 150 mm when using mineral wool with a density of 50 kg/m3. Since most manufacturers produce this insulation in thicknesses of 50 and 100 mm, you will have to put insulation in either three layers of 50 mm thickness, or two layers of 100 and 50 mm. This will not change the thermal conductivity coefficient.
OSB with a thickness of 12 mm with an air gap of 50 mm and plaster of 5 mm was chosen as the external cladding.
The interior is lined with 13 mm plasterboard.
Total: 150 + 12 + 50 + 5 + 13 = 230 (mm).
Now, based on these data, you can now calculate the foundation, but you need to understand that this is just a mathematical calculation and it does not take into account problems that may arise during installation of the structure.
Online foundation calculator
To find out the approximate cost of various types of foundations, use the following calculator:
To make sure that there is no draft anywhere in the house, the structure is checked with a thermal imager Source sargorstroy.ru
Features of frame technologies
Frame construction has been known in our country for quite some time. More than a century ago, frame-fill technologies were used for the construction of lightweight buildings. To build the walls of the house, boards were used, from which they made structures in the form of boxes.
The box walls were filled with available heat-insulating materials, most often sawdust and slag. Such buildings were less durable and comfortable than the same houses made of timber. But in recent years, many technologies have appeared that make frame construction so practical that it is beginning to displace the technology of construction from timber for winter houses and country summer houses.
This is due to the emergence of new materials on the construction market that have improved performance and technical characteristics and are ideal for frame technologies. These are oriented strand boards (OSB), MDF, sandwich panels, etc. They have a number of positive qualities:
- Low weight, allowing the use of lightweight foundations as a load-bearing base.
- Ease of installation, resulting in less expensive and faster construction.
- Durability. If frame walls are installed correctly, they can last no less than timber walls.
- Affordable price. Construction of a frame house will cost much less than construction of a brick, timber or monolithic building.
OSB sheets or boards are attached to the frame, creating external and internal protective layers. The space between them is filled with heat-insulating materials.
The wall is a kind of layer cake
Layered cake