Modern aluminum heating radiators are very popular. Such equipment can be seen both in city apartments and in offices. They are especially often installed by owners of private and country houses. The technical parameters of the batteries make them an excellent option for one-, two- and three-story buildings. The article discusses the device, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, the main models of aluminum batteries, and also describes how to disassemble, assemble and wash an aluminum radiator.
Aluminum heating radiators: types and characteristics
There are three main types of aluminum radiators. Despite the same raw materials, manufacturing technology and degree of purification lead to significant differences in performance characteristics, and therefore in the specific application of these batteries.
Die cast
The raw material is high-silicon alloy EN AB 46100 (AlSi9Cu2(Fe)), where the silicon (Si) content should not exceed 10-12%. European and most domestic manufacturers use certified primary aluminum in the manufacture of such radiators. This makes it possible to obtain products with the declared strength characteristics and reduce the risk of corrosion processes. In contrast, almost all Chinese manufacturers use recycled aluminum obtained from scrap. This results in a low-quality alloy, and the radiators themselves, compared to the standard, turn out to be more fragile. In addition, due to the high porosity of the material, heat transfer is significantly reduced. At the moment, radiators made of die-cast aluminum are the most popular in the Russian market.
Die-cast, regular and reinforced version
Extrusion sectional
Unlike cast ones, the production technology of extruded aluminum radiators involves the production of individual elements of sections, as well as the upper and lower manifold separately. Although each part is stronger, multiple joints significantly reduce the overall strength of the product. In addition, some manufacturers, to reduce the cost of the production process, use composite glue rather than argon welding during assembly. The likelihood of leaks in such batteries is much higher, even at standard operating pressure. It should be noted that many sellers pass off extrusion radiators as high-pressure cast ones. It is quite easy to distinguish such products. By the presence of characteristic seams at the junction of the ribs and collectors.
Extruded aluminum heating radiator in section. The connection lines of the elements are clearly visible
Anodized
Made from high purity aluminum (up to 98%). The technology involves anodic oxidation of the entire internal working surface of the radiator. Oxidation changes the structure of the metal surface, as a result of which the product receives protection from almost any type of corrosion. The main technical characteristics of anodized aluminum radiators are significantly higher than those of previous varieties. However, this manufacturing technology is quite expensive, which affects the cost of the final product. Therefore, anodized aluminum radiators have not found wide distribution on the Russian heating products market.
Anodized aluminum radiators
A comparative analysis of the main technical characteristics of aluminum radiators of various types is given in the table.
| Radiator type | Performance characteristics | ||
| Working pressure, atmospheres | Maximum temperature, ºС | Heat dissipation (for one section), W | |
| Die cast | 16-20 | 110 | 100-150 |
| Sectional extrusion | 10-40* | 110*** | 80-100 |
| Anodized | 215** | 140 | 150-200 |
* - In practice, the amount of “return” on extrusion radiators is much greater than on cast ones.
** - Most manufacturers of anodized radiators indicate the maximum pressure to destroy one section. However, prefabricated connections significantly reduce this figure. As a rule, the working pressure does not exceed 50-60 atm.
*** — Extruded sectional radiators assembled using composite gluing technology have a much lower maximum temperature threshold, no more than 85-90ºС.
Anodized radiators can also be produced in the form of panels with a fairly wide selection of standard sizes
Related article:
Which heating radiators are best for an apartment . In this publication we will look at the types of radiators, their advantages and disadvantages, selection criteria, how to correctly calculate the number of radiators and how to install them correctly.
How to assemble a radiator?
Aluminum heating radiators are assembled according to the following algorithm:
- place the battery on a flat surface;
- Inspect each threaded connection for chips, cracks and thoroughly clean with sandpaper. Degrease the ends using gasoline. Gaskets can be washed in soapy water;
- connect the sections. To do this, you need to put the seals on the nipple nut and place them on both sides of the device section. Make a couple of turns with the key in the upper and lower holes. When the key stops turning, you can pull it out using the lever;
- A plug should be placed on the unused hole. And on the other side, attach a Mayevsky valve to remove excess air from the system. Now the radiator can be connected to the system according to the selected scheme.
Advantages and disadvantages of use
Aluminum radiators have become widely popular due to their undeniable technical and operational advantages:
- high heat transfer with relatively compact dimensions;
- light weight, greatly facilitating transportation and installation;
- good ratio of cost and heat transfer power;
- aesthetic appearance and durable protective coating (no need for periodic painting).
There are certain technical limitations:
- low resistance to high pressure, especially to water hammer during pressure testing of the heating system;
- sensitivity to coolant quality.
It should be noted that anodized aluminum radiators are completely devoid of these disadvantages.
Decorative design of aluminum radiators using a grille
Special attention should be paid to such a parameter as thermal inertia. On the one hand, unlike cast iron radiators, aluminum radiators will not be able to maintain heat in the room after the boiler is turned off. On the other hand, this gives the widest possibilities for monitoring and managing the temperature in the room. Ultimately, the widespread use of heat regulators and the economic effect of their use turn the low thermal inertia of aluminum radiators into an advantage.
Manufacturers offer various color solutions that fit perfectly into the interior.
Aluminum die-cast batteries
The price of injection molding equipment is higher. During its production, each section is cast under pressure from silumin - the name of an aluminum alloy that contains about 12% silicon to enhance strength.
All components of injection molding devices are connected by welding in an inert gas atmosphere. This technology for the production of aluminum radiators makes the equipment more durable. Products having the required thermal power are assembled from separate sections.
The advantages of such devices:
- the presence of sealed connections;
- the ability to add or subtract the number of sections.
Their main disadvantage is their high cost.
Features of application
As already mentioned, aluminum and its alloys used in the manufacture of radiators are highly sensitive to the quality of the coolant. Namely, to its acidity. The normal acidity of the coolant should be within pH=7-8. If there is a deviation from the norm, the protective oxide film is washed away, and as a result of the formation of a new one, hydrogen is released (champagne effect). This causes a lot of troubles, ranging from the formation of air locks to battery failure due to accelerated corrosion. This is especially noticeable in the summer months, when the coolant is drained from the general system and the pipelines are clogged. A large amount of hydrogen released simply ruptures the housing from the inside.
Using a radiator with insufficient strength in a city apartment
When choosing aluminum radiators, it is also necessary to take into account the operating pressure in the system. For centralized networks, the standard is 10-15 atmospheres. However, this is the working pressure. When starting up and checking heating systems for leaks, the pressure test is increased to 1.5-2 times. Thus, for apartments with a centralized system, only anodized aluminum radiators are allowed.
Aluminum radiators are sold in a wide range of standard sizes. In addition, you can independently add and remove sections, optimizing the heat transfer of the battery
In individual heating systems, the operating pressure rarely exceeds 1.5-2 atm. Therefore, any type of aluminum radiators can be used there.
Galvanic couple effect. There is a fairly well-founded opinion among thermal engineers and installers that aluminum radiators cannot be used in conjunction with boilers that are equipped with copper heat exchangers. The reason is the formation of a galvanic aluminum-copper pair, leading to electrochemical corrosion. If it is formed, copper attracts aluminum ions, and, within just a few years of operation, the aluminum on the radiator turns into foil.
Galvanic couple effect. Intense hydrogen release can not only destroy batteries, but also cause a fire
However, this effect can only be achieved in the case of direct contact between copper and aluminum. If PVC pipes are used to transfer coolant or special cadmium-plated, chrome-plated or nickel-plated adapters are used during installation, the galvanic couple is broken.
Selection of heating radiators
When choosing heating batteries, you need to consider the following parameters:
- The pressure and temperature conditions in the heating system to which the batteries will be connected - these indicators directly affect the characteristics of heating devices;
- The ability of radiators to withstand the effects of the coolant used in the system;
- The total thermal power that the radiators installed in the room must have - this indicator allows you to determine the required number of radiators and their characteristics;
- Decorative properties of radiators and their compatibility with the existing or planned interior of the premises where they will be installed.
Manufacturers: black and white list
Of the main manufacturers whose products are deservedly popular, many Italian companies can be noted:
- Global;
- Fondital;
- Nova;
- Florada;
- Radiatori;
- Sira.
Nami also deserve attention .
Among domestic companies, it is worth noting radiators from Ankor , Rifar (under Global license) and Thermal .
Some Chinese manufacturers operating under a Global license were also included in the white list: Alltermo , Tianrun .
Also, we would like to draw your attention to the list of companies (mostly Chinese), about whose products we found the most negative reviews:
- Oasis;
- Conner;
- Radena;
- Warma.
In addition, during tests carried out in 2021 in the Moscow Vitaterm laboratory, discrepancies between real parameters and declared indicators from 22% to 34.75% were found in the products of the listed companies.
Classification of batteries by manufacturing technology
For the production of heating radiators, it is not aluminum in its pure form that is used, but its alloys with silicon. Separate sections and whole products are obtained from blanks. The main methods of metal processing are extrusion and casting.
Type #1 – extrusion
On production lines, the main tool for the manufacture of extrusion devices is a molding extruder, which literally extrudes the required profile onto metal blanks.
The disadvantage of the technology is the production of separate parts, which are subsequently connected by pressing. Of course, the seams on the structure make it vulnerable to pressure changes and unclean coolant.
Sections and manifolds are made using extrusion. After the parts undergo pressing processing, it is not possible to change their size, therefore, during installation, the length of the finished products cannot be changed
Extrusion models are the most inexpensive among aluminum ones. They are characterized by a smaller working surface area, which reduces the heat transfer of devices. The seams obtained as a result of pressing are gradually destroyed by contact with low-quality coolant.
The corrosion process is also more active because secondary aluminum is used as a raw material for extrusion, a characteristic feature of which is the presence of rapidly oxidizing impurities.
Type #2 – cast
Radiators produced by casting technology have higher performance indicators. They are safer, stronger and more resistant to aggressive environments than their extrusion counterparts, and therefore more expensive. For manufacturing, aluminum (from 88%) and alloys with the introduction of silicon (up to 12%) are used.
Production occurs as follows. The molten metal enters the casting molds, where it acquires a given profile. The parts that have received the design configuration are cooled, processed and checked for leaks. The walls of the workpieces are treated on all sides with an anti-corrosion compound.
After further cooling and drying, the almost finished sections are painted with protective polymer enamel with the addition of epoxy resins. Final stage – assembly and testing
Various manufacturers are experimenting with casting technology, resulting in new types of radiators. Let's say the Faral Trio company has released a line of two-channel radiators that have not lost strength and cope well with burst pressure of more than 55 atm.
And Italian Raden radiators have vertical fins of 6 rows, due to which there is an increase in heat transfer.
If you want your heating system to be equipped with truly reliable and protected devices, pay attention to anodized batteries. These are radiators made of aluminum coated with a durable oxide film, which has two purposes - protection and decoration.
The oxidation process several times increases the metal’s resistance to corrosion and other negative changes or reactions to the poor quality of the liquid circulating through the channels of the devices.
Popular models and reviews of them
The editors of HomeMyHome present to your attention some consumer reviews of the most popular models of aluminum radiators:
Feedback on the use of aluminum heating radiators “Lammin”:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_7663127.html
Aluminum heating radiators Lammin
Review of the aluminum radiator “Konner”:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_7043504.html
Review of the aluminum radiator “Royal Thermo Evolution 350”:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_4064173.html
Royal Thermo Evolution 350
Review of the aluminum radiator “Mirado Al 500/96”:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_4043505.html
Feedback on the operation of the Monlan radiator:
More details on Otzovik: https://otzovik.com/review_4154747.html
Methods for making radiators
Injection molding and extrusion are traditionally used to make radiators .
Injection molding and extrusion
The most commonly used method for making radiators, injection molding , involves pouring pre-molten metal under pressure into steel molds at a certain speed. The result is solid sections with thin-walled fins. The sections are then connected by nipples. The injection molding method can be used to make a radiator of any, even the most complex configuration. In this case, the resulting part will have high uniformity of material throughout the entire volume of the product
The extrusion method is used to produce large, tall heating radiators.
First, blocks and manifolds are made, and then they are connected using various technologies. Some manufacturers make vertical channels using extrusion and manifolds using injection molding. Such radiators can be either block or sectional.
Selection criteria and calculation of the number of sections
When choosing an aluminum heating radiator, pay attention to the following parameters:
- the presence of a protective oxide film or additional treatment on internal surfaces;
- mandatory availability of a technical passport for the product indicating the main technical characteristics;
- the seller has a certificate of conformity to prevent the purchase of counterfeit products;
- As a rule, prefabricated heating radiators are supplied in 10 sections. Some manufacturers offer radiator options from 3 to 15 sections. Remember that factory assembly is more reliable than one made at home. Therefore, it is advisable to purchase batteries assembled;
- if, according to calculations, a radiator with a number of sections exceeding 10 is needed to heat the room, then it is more efficient to purchase two batteries with the corresponding number of sections;
- Most European manufacturers are very jealous of the quality of their products, so they order various examinations. The presence of an independent test report is a significant advantage of this manufacturer’s products.
Additional parameters of the form factor of an aluminum heating radiator
Important! It is strictly not recommended to purchase aluminum radiators (mainly made in China) marked NF/68/. Research by the independent laboratory AIRAL has revealed a critical asbestos content in such products.
Temperature control
When determining the number of sections for heating a room, the following nuance must be taken into account. Manufacturers indicate the heat transfer rate of one section at a certain temperature. As a rule, it is 70-75ºС. However, in most cases, the temperature of the coolant in heating systems rarely rises above 60ºC. Therefore, the indicator indicated in the technical passport must be reduced by 15-20%.
Correct location in the niche under the window
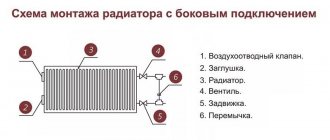
Installation
Almost all recommendations for installing aluminum radiators are related to its chemical properties. Firstly, you cannot use copper and galvanized pipes for wiring. Secondly, you need to select shut-off and control valves that are also neutral. If you find stainless steel , install them, but they cost a lot and are rare. Copper-based alloys - bronze and brass - are incompatible in their pure form; only nickel-plated ones are suitable. So we are looking for nickel-plated ball valves and control valves.
In the table you can see what materials aluminum is compatible with and select the components of the system accordingly.
Metal compatibility table. Useful when planning a heating system and when selecting fittings (Click on the picture to enlarge its size)
Another feature is the mandatory installation of air vents on each radiator. You can install a manual (Maevsky crane) or an automatic device, but it must be required. The fact is that when water and aluminum come into contact, a chemical reaction occurs with the release of gases. A large number of them can disrupt the circulation of the coolant, which is why the radiator may not heat up completely. All the features, the standard recommendations remain:
- When installed in a one-pipe system, a bypass is required.
- To allow maintenance without stopping and draining the system, it is advisable to install ball valves at the inlet and outlet.
- It is possible to install thermostatic fittings.
- For normal air convection it is necessary to leave gaps: from the rear panel of the radiator to the wall - 3-5 cm;
- from the floor - 10-12 cm;
- from the windowsill 8-10 cm.
The heat transfer can also decrease or increase depending on how the radiators are connected.
If we talk about connection diagrams, they are no different. If the radiator has less than 8 sections, the connection can be any, from 10 pieces the most effective is diagonal, a little worse - lateral. With a horizontal layout, the bottom one looks better, but if there are a large number of sections, you need to do it diagonally.
Features of self-installation of aluminum heating radiators
If the heating system pipes have appropriate threaded fittings, then replacing any radiators with aluminum ones can be done with your own hands:
- first of all, it is necessary to shut off the heating circuit and drain the water;
- on the purchased radiator you need to find the plugs and pull them out;
- If the heating system is single-pipe, a bypass must be installed. If it is two-pipe, then you can do without it;
- to connect the radiator, it is used in a fitting with a valve, which is screwed on using pipe wrenches;
- To seal the threaded connection, tow or more modern sealing materials are used: Unipack, silicone tape, etc.;
- The packaging shell is removed only after all installation work is completed, which will protect against damage to the front panel.
For positioning on the wall, it is better to purchase brackets with the ability to adjust the height of the position
Securing the radiator with a pipe wrench
Comparison with other types of radiators
A potential buyer is always interested: which radiators are better: aluminum, copper or something else? It is impossible to answer unequivocally, since each type is designed for specific operating conditions. We will try to name the leaders based on their most important performance characteristics.
Thermal power
The best performance is for copper and aluminum, slightly lower for bimetal. They deliver up to 200 W. This figure is slightly lower for cast iron and steel. Overall, any of these devices will be good. The only caveat is inertia. It is maximum for cast iron, so it takes a very long time to heat up. But it also releases the accumulated heat slowly. Therefore, the operation of such devices is difficult to regulate.
Liquid temperature
In systems where sudden changes in the temperature of the transported liquid are possible, it is important that the metal can withstand them without compromising its characteristics. Copper and cast iron do this best. If, based on this indicator, we compare which radiators are better, steel or aluminum, then it turns out that the former lose. It is better not to install them where the liquid can heat up to 110C.
Operating pressure
An important characteristic that determines the scope of application of the equipment. The bimetal withstands the most, from 16 to 36 bar. It can be used in any systems. Copper is not far behind it with its 16 bar. Steel batteries can carry a slightly smaller load. This is 10-12 bar. Aluminum “holds” from 6 to 25 bar. It all depends on the manufacturer and model.
Coolant type
In a centralized system, only water can be used, while in autonomous systems other liquids are also used. This is possible for cast iron, copper and steel. It is not advisable to use aluminum devices in such cases, although there are mixtures specifically for such batteries.
Instagram batareya.rostov
When choosing a radiator, it is important to decide on the type of connection. It can be bottom or top
Purpose of thermostat elements
All functional elements included in the thermostat include:
- thermal valve;
- thermal element;
- thermal sensitivity element;
- connector;
- transmission rod;
- spool valve;
- union type nut;
- compensator;
- fixation ring;
- scale.
The thermoelement has the form of an element that is equipped with a cylinder filled with a working composition that strongly reacts to any changes in temperature around, and its walls from the inside are made in compliance with corrugation technology. This mechanism is called a bellows.
When the temperature increases, the volume of the working medium also increases, which, in turn, causes the working rod to move and block the movement of the coolant. If the temperature drops, the volume of the working medium, on the contrary, decreases, thereby compressing the bellows itself. This leads to reverse movement of the rod, which opens the way for the coolant to the heating radiator. A similar cycle of compression and expansion in modern devices is repeated a huge number of times, which makes it possible to operate them for a very long time.
Three-way valve
An unconventional device for regulating the temperature of heating devices is a three-way valve. It is placed at the connection between the bypass and the supply pipe that goes to the battery. In order for the valve to perform the function of stabilizing the heating level of the radiator, it must have a thermostatic head. If the temperature near the head rises above the required value, the supply of coolant to the battery stops, and the liquid flow moves through the bypass. When cooling occurs, the valve opens again and the radiator heats up. This adjustment method is suitable for single-pipe systems with vertical wiring.
Important! In homes with a central heating system, the coolant usually contains foreign particles that clog thermostats. Therefore, you can safely install manual taps or valves, as well as three-way valves in your apartment.
If you want to install automatic heat regulators, you must install filters in front of them, which will have to be cleaned regularly.