Basics of exhaust and supply ventilation
Ventilation systems are designed to ensure air purity and humidity. Ventilation must maintain temperature and replace dirty air. The basic requirements for such systems are established by certain standards. Individual hygiene standards have also been developed for the functioning of ventilation. The presence of toxic vapors in the air is clearly regulated. Concentration limits have been established that do not harm human health. The permissible temperature is limited by conditions that support good health.
Ventilation system diagram.
The basics of ventilation, when designing for plants and factories, are based precisely on air purification and maintaining the desired temperature. All parameters depend on the specifics of the technological process, each value is set by SNiP. Sometimes the room temperature, when ventilation is operating, must be maintained within certain limits so that the materials in the building are completely safe.
The air conditioning system is not a vital item and does not need to be installed. But ventilation systems are required to be installed in every building. Ventilation systems must be installed in industrial enterprises. Technical indicators are established by law and regulated by building codes.
Exhaust ventilation diagram.
In the absence of a ventilation and air conditioning system, the carbon dioxide content begins to increase. This is very dangerous for closed premises. People's well-being deteriorates sharply and they lose their ability to work. To avoid such problems, ventilation and air conditioning systems are installed.
The ventilation system must maintain standardized meteorological parameters. Each room has ventilation configured according to individual parameters.
Some characteristics
The foundations of various types of air conditioning rest on the properties of technological characteristics. They depend on the specialization of the room. Ventilation and air conditioning devices have distinctive features that classify them:
- A method of creating pressure to start air flow. Excitation can be of two types:
- mechanical;
- artificial.
- The principle of operation of ventilation. It is divided into:
- exhaust;
- supply air
- Service area.
- Design. It can be produced in two types:
Supply ventilation diagram.
- channel;
- ductless.
The natural ventilation system is distinguished by certain characteristic individual characteristics:
- The movement of air flow is carried out due to the discrepancy between the heating of the air in and around the room. This phenomenon is called aeration.
- The movement of the air stream is carried out due to the occurrence of a pressure difference between the mounted exhaust devices. One is on the roof, and the other serves the building.
- Air masses move due to the appearance of wind pressure.
The development and installation of natural ventilation is carried out in those buildings where large heat emissions are observed. The presence of toxic substances contained in the air is allowed no more than 30% of a certain standard for the place where the work is performed. Aeration is not done if, according to the technological process, it is necessary to pre-clean the incoming air flow.
Where there is a lot of heat, the air has a temperature much higher than outside. Heavier street air entering through the installed ventilation system begins to displace warm air flow, which has a lower density. The air circulation caused by the heat source begins. This is very similar to the operation of a fan.
When natural ventilation works, the movement of the air mass occurs due to the resulting pressure difference, and the altitude difference should reach 3 m. When such air conditioning is developed, the length of the air shaft, stretching in one line, is taken into account. It must exceed 3.5 m. The air flow must move at a speed not exceeding 1 m/s.
Layout diagram of a duct ventilation system.
The wind creates high pressure on the walls of the building facing the wind. The source of the vacuum becomes the leeward side.
The fencing of the room is sometimes equipped with openings. Then the air supply starts from the other side. The magnitude of the air flow velocity in such openings strongly depends on the velocity of the air mass blowing through the building. The resulting pressure difference also affects the speed.
This natural system is considered the simplest. It does not require particularly complex, expensive equipment. This system consumes a minimal amount of electricity. In such a system, individual factors greatly influence work productivity. Air temperature, wind strength, etc. play an important role. As a result, it is impossible to solve the most diverse tasks included in the ventilation bases.
Mechanical ventilation
This ventilation and air conditioning system uses equipment that makes it possible to move air masses over long distances. This type can create an air flow directed to specific areas, as well as its subsequent removal in the required quantity. The system operates regardless of any type of environment. When the need arises, air purification is carried out in a variety of ways. For example, the air is cooled, humidified, and so on. Such processes cannot be performed with systems operating on the principle of natural excitation.
Engineers very often have to develop air conditioning systems that combine several types of ventilation systems: natural, mechanical.
For each case, the optimal type of ventilation is determined. The most rational one is selected, which meets the technological requirements of hygiene and sanitation.
Scheme of operation of a ductless ventilation system.
By the way, supply ventilation is designed to pump fresh air into the room. If necessary, the air undergoes special treatment, with special purification.
The performance indicator of the system directly depends on the available ability to direct a stream of air into combined rooms. Sometimes only one specific type of ventilation is installed. Air supply is carried out through special openings. Air removal is carried out in a similar way. Such a system, similar to the supply system, can be installed at the place where technological operations are performed.
And, for example, local ventilation is designed specifically to direct fresh air directly to the work area. It is called supply ventilation, which has an individual purpose. Bad air is removed only from those places where harmful gases appear. This ventilation is called “local exhaust”.
What formulas are used in calculations
The main parameter that needs to be calculated in any system is how much air should be changed within an hour.
For residential apartments, the value is determined according to the living area: V=2xSxH, where S is the area of the living room, 2 is the coefficient of air mass exchange rate per 1 hour, H is the height of the room.
For work premises, the calculation is made based on the number of personnel: V=Nx35, where N is the number of people simultaneously present in the room.
When calculating the power of a ventilation station, the formula is used: P=ΔT * V * Сv/1000, where V is the volume of air mass consumed per hour, Сv is the heat capacity of the air mass, ΔT is the temperature difference of the air mass at the ends of the pipeline. The accepted value of heat capacity is 0.336 W * h/m³ * °C.
Another important indicator is the cross-sectional area of the duct, measured in square centimeters. There are 2 types of sections: square and round. By calculating the cross-sectional area, it is possible to determine the width and height of a rectangular pipe or the diameter of a round one.
Special supply ventilation capable of working in a specific location
This system is called the “air shower”. In other words, it is an air flow that has a certain direction and high speed. These systems must direct fresh air directly to the work site. Reducing the heating of the environment depends on their work. Such ventilation is capable of blowing workers who are forced to work under powerful thermal radiation.
Local ventilation is installed in areas of the building that are fenced off with sliding screens, where air at a low temperature is pumped.
Natural ventilation schemes.
Most often, this type of air conditioning is used in industry. Ventilation becomes an air curtain, a kind of air partition separating gates or hot stoves.
With its help you can direct the air flow in the desired direction. Installation of such ventilation is less expensive when compared with general ventilation. In factory workshops, when there is an abundance of harmful impurities, a mixed system is most often installed.
General ventilation handles toxic substances; local ventilation only serves individual work areas.
Exhaust ventilation: nuances
This system is used only if toxic substances are released in specific places where a ban on the spread of toxic gases in the room is required. Industrial ventilation, installed in factory workshops, removes toxic substances that are formed as a result of the operation of thermal equipment. To remove all harmful emissions, local hoods are installed:
- umbrellas;
- side hoods;
- curtains;
- machine casings.
All such protective elements must fulfill certain conditions:
- The place where harmful secretions occur must be completely closed.
- Local exhaust of any kind should not have any impact on human performance.
- Removal of harmful vapors generated is carried out according to the direction of movement. Heated gases go up, accumulated dust goes down.
General exchange supply ventilation
Such forced ventilation is designed to combat humidity and reduce the concentration of toxic substances that local ventilation could not remove. The use of such a system makes it possible to comply with sanitary standards and fulfill all hygienic requirements. When there is a lack of heat, this general ventilation is supplied with mechanical stimulation. It has the ability to heat the entire volume of incoming air. The entire volume of incoming air is purified from dust.
If the air is polluted by toxic emissions, the volume of fresh air must be equal to the volume that can completely replace the activity of the local ventilation system.
The most affordable type of such a ventilation system is considered to be a fan that has an electric motor installed on its axis. It is mounted in a window opening or a niche in the wall. As a result, air begins to be removed from the area close to the fan. In this case, only general air exchange is carried out.
Such a system is sometimes equipped with a long air duct. If it is more than 40 m, the network begins to lose pressure. To compensate for this phenomenon, a centrifugal fan is installed.
If heavy gases become toxic substances, there is no heat generation from the installed equipment, exhaust air ducts are laid directly on the floor surface or special underground ducts are made.
Air is supplied to production workshops in a variety of ways:
- concentrated;
- dispersed;
- delivery depends on the level of location.
Exhaust ventilation is very often installed in several types simultaneously in factory workshops. For example, local ventilation is installed together with general ventilation.
Ventilation for beginners: what you need to know
Contaminated air
When cleaning and washing, tiny particles of cleaning products get into the air we breathe. If air circulation is insufficient, there is a real health hazard.
Another problem in our premises is high humidity , which is inevitable not only in bathrooms, but also in the kitchen, where people constantly steam, fry and wash.
To the above air pollution you can add combustion products produced by gas stoves, fireplaces and stoves. The conclusion suggests itself - the most contaminated areas of the house are the kitchen and bathroom. We'll talk about their ventilation.
Natural ventilation
The simplest method of room ventilation is natural . This type of ventilation requires minimal costs, since air circulation in the room occurs without the use of any electromechanical devices, and, therefore, without the cost of electricity. Air movement in natural ventilation systems occurs:
- Due to the temperature difference between the outside (atmospheric) air and the indoor air, the so-called aeration.
- Due to the pressure difference in the “air column” between the lower level (the room served) and the upper level - the exhaust device installed on the roof of the building. This type of ventilation is called convection.
- As a result of the influence of the so-called wind pressure.
The dependence of natural ventilation on variable factors (air temperature, wind direction and speed) makes it unsuitable.
Artificial ventilation
To increase the efficiency of room ventilation, forced ventilation is used in combination with natural ventilation.
In the case of an economical solution to improve the quality of ventilation of the monastery, it is customary to use low-power duct fans.
Through their use, the following types of ventilation can be provided:
Supply systems are used to supply clean air to ventilated rooms. In this case, a fan installed on the inlet in one of the windows pumps in fresh air, which disperses throughout all rooms.
Yes, in the cold season you will have to limit such ventilation, because the fan does not heat the street air. But in warm weather you can ventilate as much as you like. The main thing is that the fan is equipped with filters.
Exhaust ventilation removes polluted or heated air from the room.
Combined ventilation is the most common and effective option for installing a ventilation system, in which air is supplied to the room by a supply system, and air is removed by an exhaust system. Both systems operate simultaneously. At the same time, their performance must be the same in order to eliminate the difference in air pressure inside and outside the room, leading to the “slamming doors” effect.
Calculation programs
Since carrying out calculations and building a ventilation scheme manually is a very labor-intensive and time-consuming process, simple programs have been developed that can do all the actions independently. Let's look at a few. One such ventilation system calculation program is Vent-Clac. Why is she so good?
A similar program for calculations and network design is considered one of the most convenient and effective. The operating algorithm of this application is based on the use of the Altschul formula. The peculiarity of the program is that it copes well with both natural and mechanical ventilation calculations.
Since the software is constantly updated, it is worth noting that the latest version of the application is also capable of carrying out such work as aerodynamic calculations of the resistance of the entire ventilation system. It can also effectively calculate other additional parameters that will help in the selection of preliminary equipment. In order to make these calculations, the program will need data such as air flow at the beginning and end of the system, as well as the length of the main air duct of the room.
Since manually calculating all this takes a long time and you have to break the calculations into stages, this application will provide significant support and save a lot of time.
Supply and exhaust ventilation: operating principle and design features
In a room filled with fresh air, you can breathe easier, work more productively, and sleep better. But opening the window for ventilation every 2-3 hours is problematic, do you agree? Especially at night, when all family members are sleeping soundly.
One of the automated solutions for this task is supply and exhaust ventilation (PVV) of the room. But how to do it correctly? We will help you study the principle of operation and understand the features of the arrangement.
Our article discusses the components of the supply and exhaust system, the rules for their calculation and air exchange standards in rooms of various types.
Ventilation arrangement diagrams, photographs depicting individual elements of the system, and useful video recommendations for installing a ventilation system in a private home with your own hands are provided.
Types of systems by purpose
Ventilation structures are classified according to a variety of criteria: ducted and ductless, general local, with and without a heat exchanger. They are also distinguished by the direction of influence.
Air circulation involves removing gases from the building and replacing the exhaust air with new air. In practice, these processes are separated. In some cases, air flow can occur passively - an open door or window. To remove the air, you need to apply force. The reverse is also possible. In such cases, it is necessary to install devices on part of the system that increase the air flow speed: fans, diffusers.
Supply
Supply ventilation is a system of devices that provides air input . It can be one module - a fan with a pipe fragment for installation. May include blowers, grilles, diffusers, filters, valves, etc.
The simplest option is often found on plastic windows. This is a ventilation valve mounted directly into the frame. Without opening the window, it provides fresh air. However, its power is low.
In the kitchen, in the bathroom, if there is no ventilation shaft, install an inlet. Mount the block on the wall next to the window, at a distance of at least 2–2.2 m from the floor. Another option is to use radiators under the windowsill. In the latter case, the air from the street will be immediately heated, and the fan will provide sufficient air flow. The breather performs the same function.
Exhaust
Used to remove polluted air. The simplest option is a kitchen hood. The fan is built directly into the device or installed on a tee; the air is discharged into the general ventilation shaft of the house or directly to the street.
The need for an exhaust structure is usually higher. In modern apartments with sealed windows, natural circulation is difficult. In rooms such as the bathroom and kitchen, its power is not enough to remove moisture, heat and odors.
If necessary, build a system serving several rooms. To do this, install a network of air intake pipes and a fan at the outlet of the hood.
Supply and exhaust
In apartments there is rarely a need for it. In private houses, where there are many internal isolated rooms and cellars, it comes in handy.
The main element of the system is a module with two fans operating in the opposite direction . Additional accessories: blowers, grilles, check valves - you can’t do without them, diffusers, etc.
Since such a system runs on electricity, it is often equipped with heaters, humidifiers, and purifiers.
All blowers in a building must have the same cross-section.
What is ventilation?
How often do we ventilate the room? The answer should be as honest as possible: 1-2 times a day, if you remember to open the window. And how many times at night? A rhetorical question.
According to sanitary and hygienic standards, the total air mass in a room where people are constantly present must be completely renewed every 2 hours.
Conventional ventilation refers to the process of exchange of air masses between a confined space and the environment. This molecular kinetic process provides the ability to remove excess heat and moisture using a filtration system.
Ventilation also ensures that the air in the room meets sanitary and hygienic requirements, which imposes its own technological limitations on the equipment that will generate this process.
The ventilation subsystem is a set of technological devices and mechanisms for intake, exhaust, movement and purification of air. It is part of a comprehensive communications system for premises and buildings.
We recommend not to compare the concepts of ventilation and air conditioning - very similar categories that have a number of differences.
- Main idea. Air conditioning ensures the maintenance of certain air parameters in a confined space, namely temperature, humidity, degree of particle ionization, and the like. Ventilation produces a controlled replacement of the entire volume of air through inflow and outlet.
- Main feature. The air conditioning system works with the air that is in the room and the flow of fresh air itself may be completely absent. The ventilation system always operates at the boundary between the enclosed space and the environment through exchange.
- Means and methods. Unlike ventilation in a simplified form, air conditioning is a modular scheme of several blocks that processes a small part of the air and thus maintains sanitary and hygienic air parameters in the specified range.
The ventilation system in the house can be expanded to any required scale and ensures, in the event of an emergency in the room, a fairly quick replacement of the entire volume of air mass. What happens with the help of powerful fans, heaters, filters and an extensive piping system.
You may be interested in the information on arranging a ventilation pipeline from plastic air ducts, discussed in our other article.
There are several classes of ventilation, which can be divided according to the method of generating pressure, distribution, architecture and purpose.
Artificial air injection in the system is carried out using injection units - fans, blowers. By increasing the pressure in the pipeline system, it is possible to move the gas-air mixture over long distances and in significant volumes.
This is typical for industrial facilities, production premises and public facilities with a central ventilation system.
Local (local) and central ventilation systems are considered. Local ventilation systems are “spot”, narrowly targeted solutions for specific premises where strict compliance with standards is necessary.
Central ventilation provides the opportunity to create a regular exchange of air for a significant number of rooms with the same purpose.
And the last class of systems: supply, exhaust and combined. Supply and exhaust ventilation systems provide simultaneous supply and exhaust of air in a space. This is the most common subgroup of ventilation systems.
Such designs provide easy scaling and maintenance for a wide variety of industrial, office and residential premises.
Acoustic calculation of the ventilation system
Acoustic calculation is a mandatory operation that is attached to the calculation of any room ventilation system. This operation is carried out in order to perform several specific tasks:
- determine the octave spectrum of airborne and structural ventilation noise at design points;
- compare the existing noise with the permissible noise according to hygienic standards;
- determine a way to reduce noise.
All calculations must be carried out at strictly established design points.
After all measures have been selected according to building and acoustic standards, which are designed to eliminate excess noise in the room, a verification calculation of the entire system is carried out at the same points that were determined earlier. However, the effective values obtained during this noise reduction measure must also be added to this.
To carry out calculations, certain initial data are needed. They became the noise characteristics of the equipment, which were called sound power levels (SPL). For calculations, geometric mean frequencies in Hz are used. If an approximate calculation is carried out, then correction noise levels in dBA can be used.
If we talk about design points, they are located in human habitats, as well as in places where the fan is installed.
Physical basis of the ventilation system
The supply and exhaust ventilation system is a multifunctional complex for ultra-fast processing of the gas-air mixture. Although this is a system of forced gas transportation, it is based on completely understandable physical processes.
The word “ventilation” itself is closely related to the concept of convection. It is one of the key elements in the movement of air masses.
Convection is the phenomenon of circulation of thermal energy between cold and warm gas flows. There is natural and forced convection.
A little school physics to understand the essence of what is happening. The temperature in the room is determined by the air temperature. Molecules are carriers of thermal energy.
Air is a multimolecular gas mixture that consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%) and other impurities (1%).
Being in a closed space (room), we have inhomogeneity of temperature relative to height. This is due to the heterogeneity of the concentration of molecules.
Considering the uniformity of gas pressure in a closed space (room), according to the basic equation of molecular kinetic theory: pressure is proportional to the product of the concentration of molecules and their average temperature.
If the pressure is the same everywhere, then the product of the concentration of molecules and the temperature at the top of the room will be equivalent to the same product of concentration and temperature:
The lower the temperature, the greater the concentration of molecules, and therefore the greater the total mass of the gas. This is why they say that warm air is “lighter” and cold air is “heavier”.
In connection with the above, the basic principle of arranging ventilation becomes clear: the air supply (supply) is usually equipped from below the room, and the outlet (exhaust) is from above . This is an axiom that must be taken into account when designing a ventilation system.
Video description
More about the calculation of ventilation in the video:
Ssection = V * 2.8/w, where Ssection is the cross-sectional area, V is the volume of air mass (m³/hour), w is the air flow speed inside the highway (m/sec) (average from 2 to 3), 2.8 – dimensional matching coefficient.
For installation, it is necessary to calculate how many diffusers (intake and outlet openings) and their parameters are required. The dimensions of the nozzles are calculated based on the cross-sectional area of the main pipeline, multiplied by 1.5 or 2. To calculate the number of diffusers, use the formula: N=V/(2820 * W * d2), where V is the volume of air mass consumed per hour, W is speed of movement of the air mass, D – diameter of the round diffuser.
For rectangular diffusers, the formula is transformed as follows: N=π * V/(2820 * W * 4 * A * B), π is the number pi, A and B are the section parameters.
Useful program
The TURKOV company has developed a program for calculating the necessary parameters and selecting suitable equipment.
In any case, calculations of ventilation systems should be carried out by professionals - if something is forgotten or not taken into account, then the cost of the mistake is the need to redo the calculations and work.
A full calculation of supply ventilation is done using specific software Source ventisam.ru
Features of supply and exhaust ventilation
Supply and exhaust ventilation interacts with two air flows of different composition and purpose, which are subsequently processed.
In the PVV, all the necessary equipment and additional systems are placed in a single frame, which can be installed inside the loggia, in the attic, on the wall outside the house, etc.
The special design of the installation provides ample opportunities to provide ventilation for almost any number of rooms in the building.
In addition to the main function of moving air, supply and exhaust ventilation includes the following arsenal of auxiliary subsystems and additional functions.
Among which are the following:
- air cooling and heating;
- ionization and humidification of particles;
- air disinfection and filtration.
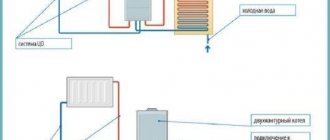
Let's consider a typical operating cycle of a supply and exhaust ventilation system, which is based on a two-circuit transportation model.
At the first stage, cold air is taken in from the environment and warm air is extracted from the room. On both sides the air passes through a cleaning system.
Afterwards, the cold air is transferred to the heater (heater) - typical for PVH with heat recovery. In addition, heat is transferred to the cold gas from the warm exhaust air - typical for conventional systems.
Main parameters of the ventilation system
The main working element is a fan, but not the usual propeller, but an impeller, which is a wheel with blades - this design allows you to reduce the size of the equipment.
The efficiency of the installed structure directly depends on the accuracy and correctness of the preliminary calculations. For example, it is equally bad if insufficient or excessive engine power is selected. In the first case, the engine will wear out and soon enough it will have to be replaced. If the power is excessive, this means regularly inflated maintenance and electricity costs.
Calculations of performance and dynamic parameters of air flows are made using algebraic formulas. It is recommended to entrust the calculations to a specialist who will not only do it correctly, but also obtain the necessary approvals from the fire inspectorate.
Firefighters check the operation of the supply and exhaust ventilation
The calculations take into account the following data:
- Premises parameters: purpose - residential or non-residential, internal area, number of floors, humidity level.
- The number and type of activity of people simultaneously present inside the building.
- Required level of air exchange according to SNiP 2.04.05-91. For example, in living rooms it is 3 cubic meters per hour per 1 meter of living space.
- Pipeline cross-section and installation diagrams.
Exhaust ventilation: types, diagrams and general information
Modern technology copes with solving almost any problem related to room ventilation, doing it at a high level. Working conditions in production premises can be fully ensured in accordance with the requirements.
Modern comprehensive equipment is also installed in residential buildings and buildings, as well as commercial areas, providing a comfortable environment. Exhaust ventilation successfully removes waste air. Moreover, at production facilities it is capable of performing targeted removal of harmful contaminants. And in residential interiors it functions as part of the overall complex system.
Classification
The types of exhaust ventilation considered differ based on the method of induction. These are the following types:
- Natural.
- Mechanical (or forced).
There are also differences in the volume of premises and ventilated areas:
- Local (local), air drawn out on the site.
- General exchange (capable of ensuring the exchange of air masses in a house, building or apartment).
Whatever the classification, exhaust ventilation is included with the supply type. Such a system exchanges air, creates a microclimate and comfort. Also, any exhaust ventilation is classified as duct ventilation, since waste materials always exit through air ducts. The latter form a network of branches.
What standards exist for ventilation systems?
Recommended air exchange parameters depend on various conditions and are prescribed in the relevant regulations, which must be taken into account during design. In general, for domestic premises, when rooms for different purposes are concentrated on one floor, the following amount of air should change in an hour:
- office – 60 cubic meters;
- common living rooms or halls – 40 cubic meters;
- corridors – 10 cubes;
- bathrooms and showers – 70 cubic meters;
- smoking rooms - over 100 cubic meters.
In living rooms, air mass exchange is calculated per person. It should be more than 30 cubic meters per hour. If the calculation is made based on living space, then the standard is 3 cubic meters per 1 meter.
For non-residential premises, the average standard is 20 cubic meters per meter of area. If the area is large, then ventilation systems include a multi-component system of paired fans.
Natural exhaust ventilation
The exhaust system can be part of a complex responsible for natural air circulation. The process of mass exchange in it is based on the difference in external and internal parameters of temperature, pressure, and is driven by gusts of wind. All these physical phenomena are engines of circulation. The influence of weather on operation is a disadvantage of such structures. So in summer there is no air exchange. After all, the temperature is the same indoors and outdoors. In winter, there is a big difference in these indicators. Cold air comes in from outside, the heating of which loads the heating system at great expense.
Efficiency can be increased by opening the windows and making gaps under the doors. In residential buildings, ductwork is located in kitchens and bathrooms. Basically, natural exhaust ventilation is practically uncontrollable. It is necessary to note many “advantages” of such systems. But shortcomings can create difficulties for operation, during which nothing can be changed. However, natural ventilation can be optimized. If there is a lack of draft, fans and valves are placed in the ducts at a number of points, preventing the masses from escaping not to the street, but to the neighbors.
How are large volumes of air purified?
The pre-chamber is a preliminary room located in front of the cleaning system; free movement of air occurs in it, its exchange with the atmosphere; for this there is a special air valve. There is also a filter that allows you to pre-clean the atmospheric air by separating internal and external ventilation. This makes it possible to deliver an already partially filtered air stream to the cleaning system.
Thanks to this, most of the oxygen-clogging particles remain outside and do not initially enter the ventilation system. Excess volatile compounds will be released back into the atmosphere thanks to the valve.
Prechamber operation diagram
Fans
A special fan is installed in the preliminary chamber; depending on how large the volume of the room is and what quality characteristics the air has, the equipment of this room may change. An engine-driven fan helps accelerate the flow and create the necessary draft; The larger the area, the more powerful the device should be.
If the room is small, then a directional fan will suffice: as a rule, it does not have a powerful motor, makes less noise and is cheaper. Its task is to separate the air into channels, incoming and outgoing. Often the system is supplemented with special filters that allow you to create a noise barrier, otherwise the fan will be heard in the main room, which is not very pleasant if you are constantly there. You can find out more about how to deal with ventilation noise in this publication https://ventilation-conditioning.ru/zdorove/shum-ventilyacii.html.
Read more: KAMAZ power take-off catalog
Forced exhaust systems
A forced-type exhaust ventilation system is based on the draft created by additional equipment located in the shaft that exhausts the air.
Effective operation with the required efficiency is possible only if there is a sufficient supply of external air. Otherwise, the fan will function in vain. The most popular systems are supply and exhaust systems, supplemented with mechanical drive.
In such a complex, air exchange will be complete in all rooms of the building. There is balance in a properly designed structure. Air is removed from the structure at the same speed as it enters it. The exhaust ducts are not overloaded.
When creating a system, the following data is taken into account:
- dimensions of the premises (calculation of the required air volume);
- their purpose (the frequency of air exchange will depend on this);
- number of employees or residents (there are standards per person);
- equipment parameters (here you will need to take into account the characteristics of all elements of the system).
The norm is to replace all the air within an hour (multiplicity = 1).
During the winter, there is a problem with the need for heating costs to heat large air masses. To reduce costs, a recuperator is used, which transfers heat from the exhaust air to the heat exchanger. Masses from outside also come there and are heated by the same energy. The efficiency of such devices is 30-90%.
An exhaust ventilation system equipped with a recuperator can also be equipped with a heater. This device additionally heats the influent masses with water, electricity or cools them with water or freon. Such installations take up very little space. With the use of such air conditioning systems, the microclimate in the room can be idealized.
Sanitary standards
Another option for calculating ventilation is according to sanitary standards. Similar calculations are carried out for public and administrative facilities. To make correct calculations, you need to know the average number of people who will constantly be inside the building. If we talk about regular consumers of indoor air, they need about 60 cubic meters per hour per person. But since public facilities are also visited by temporary persons, they must also be taken into account. The amount of air consumed by such a person is about 20 cubic meters per hour.
If you carry out all the calculations based on the initial data from the tables, then when you receive the final results, it will become clearly visible that the amount of air coming from the street is much greater than that consumed inside the building. In such situations, they most often resort to the simplest solution - installing a ventilation hood at approximately 195 cubic meters per hour. In most cases, adding such a network will create an acceptable balance for the existence of the entire ventilation system.
Local exhaust ventilation
A local exhaust system solves the problem of air purification in hazardous production areas. Contaminants such as aerosols, smoke, gases, and abrasive dust can be removed from the employee’s workplace. This will save him from prolonged exposure to harmful emissions on the body. Health and performance will be ensured. In everyday life, many people know an example of local ventilation - a kitchen hood.
This type of system is different from the general exchange type, since it solves problems in a point-by-point manner. For example, if a release is concentrated in a specific location, ventilation will remove it, preventing spread. Laboratory fume hoods and air intakes in hazardous industries operate on this principle.
In almost all cases, the design contains a filter that filters out impurities typical for a given location. So in the kitchen it is a grease and carbon filter, and in a lathe there are several dust filters. Industrial emissions are also thoroughly cleaned, because the atmosphere cannot be polluted. Exhaust ventilation through the wall to the street is often used in such equipment. But air can also pass into the general ventilation network.
Harmful substances are removed by local extraction using suction. The latter must meet the following requirements.
- Coverage of the emission location.
- The device does not interfere with the employee’s normal activities at his workplace.
- Gases and emissions are eliminated in natural directions. If they are hot - up, and dust - down.
Local exhaust helps to maintain safe work, reduces the risk of disease, does not pollute the environment and saves costs on general house or industrial ventilation.
How to make exhaust ventilation with your own hands
Installing exhaust ventilation yourself is a completely feasible idea. First, they make calculations and select components, after which they begin assembly. For residential premises, a local hood in the kitchen is popular. It can be installed not only by a specialist, but also by the apartment owners on their own. Air and steam will be removed forcibly through air ducts, of which the flexible version is easy to install. In this case, control is carried out manually using a switch.
The hood is placed above the stove. It is preferable to take the outlet out to the outside. Otherwise, reverse draft is possible from the natural ventilation of the building. Installation instructions and a list of components can be found in our article on installing a kitchen hood.
Results
Systems that include exhaust ventilation are used in all types of industry, both in mechanical engineering and in construction. Ensuring sanitary standards is very important for enterprises. These are the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation. The exhaust type of ventilation replaces natural ventilation, which may be less effective and cost more. It also acts in combination with it, including thermoregulation capabilities. Exhaust structures are the most effective systems and devices.
We put a lot of time and effort into helping you with your ventilation needs. Please help us answer: