Today we will tell you how to select a machine based on load power. You will also find out how dependent the power indicators, the rated current of the device and the cross-section of the electrical wiring are on each other. Let's start with brief definitions of the main concepts:
- power is the rate at which electricity is transmitted or converted;
- rated current of the circuit breaker - the maximum transmitted current to which the thermal release does not respond;
- The wire cross-section is the cut area of the current-carrying core.
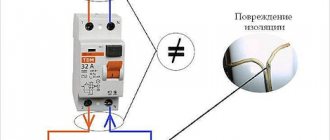
An adequate selection of circuit breakers is made taking into account the cable cross-section, since the wiring must be able to pass the required load and not overheat. And the issue of power depends on peak loads on the line, that is, you need to know how much the amount of power in the network will increase when all consumers simultaneously require power.
When choosing a circuit breaker, pay attention to the current rating, which you need to select as accurately as possible. It’s not worth taking with a large margin, because the wiring melts when the permissible power consumption is exceeded, and the machine itself is in no hurry to disconnect the circuit, because for it the power is quite normal. As a result, a fire or burning of sockets may occur if the owner of the apartment/house does not notice something is wrong and does not smell the characteristic smell. Again, from a rational point of view, spending money on an expensive AV with a high rating is not profitable if the real requirements for protecting your home network are modest or standard.
If you choose a machine in favor of a small nominal value (less than required), you will end up with “knocking out” the light at peak loads. Limitations on electricity consumption will force you to either calculate the total power before each connection of devices to the network, or even abandon the use of powerful equipment.
Circuit breaker functions
From the name it is clear that this is a switch that turns off automatically . That is, himself , in certain cases. From the second name - circuit breaker - it is intuitively clear that this is some kind of automatic device that protects something.
Here are examples of the installation and use of such machines - when installing an apartment meter and when replacing electrical wiring in an apartment.
Now more details. The circuit breaker trips and turns off in two cases - in case of overcurrent , and in case of short circuit (short circuit) .
Overcurrent occurs due to faulty consumers, or when there are too many consumers. A short circuit is a mode when all the power of an electrical circuit is spent on heating the wires, while the current in this circuit is the maximum possible. More details will follow.
In addition to protection (automatic shutdown), machines can be used to manually turn off the load. That is, like a switch or a regular “advanced” switch with additional options.
Another important function (this goes without saying) is the connection terminals. Sometimes, even if the protection function is not particularly needed (and it never hurts), the terminals of the circuit breaker can be very useful. For example, as shown in the article Laying the input cable from the gander to the meter.
The procedure for connecting machines - what you should always remember
It would seem, what could go wrong when connecting a single-pole circuit breaker?
The technician’s task is to strip the wire of insulation, thread it inside the terminal and tighten it! However, we are full of people with arms growing in the wrong places.
Sorry for such open indignation, but sometimes you just can’t say it any other way. And sometimes mistakes happen among professionals (this is less common), since we are all human, we can get sick, get tired, be overwhelmed with problems and other things that will prevent us from doing our work efficiently.
How to change a machine in a panel - working with electricity always requires a responsible attitude to the matter
So, we got carried away with something. Let's get down to business. We will start with the most important thing - the correct connection of the machines in the panel. Such a switch has two contacts through which it is connected to the network.
One of them is movable, and the second is fixed; they are located at the top and bottom of the device. Do you know which one needs power? Imagine, very few people know about this, since there are constantly debates on this topic on “electrical” forums.
We will not engage in introspection and will turn directly to the PUE, 7th edition, paragraph 3.1.6. It says the following. If the device is powered one-way, then the supply conductor must be connected to a fixed contact.
However, it is worth noting that there is a disclaimer in the form of the phrase “as a rule”, this is a little confusing, as if there are cases that allow an exception to this recommendation. But no further explanations are provided.
Excerpt from the PUE - whenever questions arise, you should seek help from the technical documentation
The same rule applies to all protective devices, circuit breakers and RCDs. To understand where the machine is and what contact is located, you need to know how it works from the inside. Let's dive a little deeper into the world of electrical engineering and look at the structure of a simple single-pole circuit breaker.
Here is a cross-section of a single-pole circuit breaker
- You don’t need to be an engineer to notice that the upper contact of such a machine is fixed, and the lower one is movable. It is not necessary to disassemble the device to recognize the types of contacts. You can also use the markings on its body. Look at the next photo.
How to connect machines in a panel - schematic designation of different types of contacts on a machine
The markings on switches from other companies may be slightly different, but, in general, everything is very clear there too. As a last resort, you can always find information on the Internet by making a request for a specific model. In general, almost all modern single-pole circuit breakers have exactly the same arrangement of contacts, but you must make sure of this.
Now let's try to understand the issue from a purely technical approach. So, top or bottom?
- The purpose of the circuit breaker is to protect the line connected to it from short circuits and overloads. It works like this - when overcurrents appear in the circuit, a reaction occurs between the thermal and magnetic releases, which are located inside the device body. At the same time, there is no difference in which side the power cable is connected; the device will work in any case.
- This is confirmed by the fact that some manufacturers, for example, Hager or ABB, allow reverse connection of power to the machine. For these purposes, they are specially equipped with clamps for comb tires.
How the circuit breakers are connected in the panel: ABB - single-pole circuit breaker
- Then why does the PUE indicate different information? Didn’t they just pull it out of thin air? This statement is established in a general manner. Any electrician with the appropriate education will tell you that before performing work, it is necessary to remove voltage from the equipment with which you are going to work. When a master who performs such work regularly approaches the panel, he intuitively, so to speak - mechanically, believes that the phase is at the top. Having disconnected the terminals, he will think that there is no voltage on the lower wires.
- As a result, if some unfortunate electrician, let it be Uncle Vanya, did not act according to this principle during installation, then the situation is fraught with an accident, sometimes with a fatal outcome. Of course, no one exempts an electric train driver, especially a professional one, from the need to know safety precautions, but still, initially you need to do it as prescribed by the standard. This is both safer and faster in the long run.
- The essence of the problem also lies in the fact that previously, all machines always had a fixed contact on top, but now, when products from manufacturers from different countries are presented on the markets, and, as you can see, there are no strict regulations, anything can fall into your hands. That is, in fact, the PUE norm regulates not the technical part, but the “aesthetic” one, and the structure of the connection circuit does not depend in any way on the location of the contacts.
Parallel circuit diagram for connecting the machine in the panel
If you do not agree with this statement, try to describe from a technical point of view the need to connect the power wire to any of the contacts. To be honest, nothing comes to our minds.
Number of poles
Depending on the number of poles, the machines are:
- Single-pole (1p, 1p). This is the most common type. It stands in a circuit and protects one wire, one phase. This is shown at the beginning of the article.
- Bipolar (2p, 2p). In this case, these are two single-pole circuit breakers, with a combined switch (handle). As soon as the current through one of the machines exceeds the permissible value, both will turn off. These are mainly used to completely disconnect a single-phase load when both the zero and the phase break. It is the two-pole circuit breakers that are used at the entrance to our apartments.
- Three-pole (3p, 3p). Used to break and protect three-phase circuits. Just as in the case of two-pole ones, these are actually three single-pole circuit breakers, with a common on/off handle.
- Four-pole (4p, 4p). They are rare, they are installed mainly at the input of three-phase switchgears (switchgears) to break not only the phases (L1, L2, L3), but also the working zero (N). Attention! Under no circumstances should the protective grounding (PE) wire be broken!
Circuit breaker current
Automatic currents come from the following series:
0,5, 1, 1,6, 2, 3,15, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63.
The denominations most often used in everyday life are highlighted in bold. There are other denominations, but we won’t talk about them now.
This current for the circuit breaker is rated. If it is exceeded, the switch will turn off. True, not immediately, as stated below:
Lower level of sockets
The lower level of outlets is planned for most built-in kitchen appliances.
- Microwave;
- Oven;
- Hob;
- Dishwasher;
- Waste shredder (Disposer);
- Washing machine;
- Fridge.
The unspoken rules for installing kitchen outlets state that the height of the bottom row of outlets from the floor is 10 cm. This is the standard level of the bottom outlets behind the kitchen. At this height, the lower sockets fall into the free space between the floor and the beginning of the floor cabinets. 10 cm should not be to the middle, but to the top of the sockets, since the height of the legs of kitchen cabinets is usually 12.5 cm. True, the height of the legs is adjustable, but not by much. In kitchen cabinets without legs, a special cutout is made at the back at the factory, usually at a height of 11.4 cm from the floor (it is clearly visible in the photo).
Related article: Mounting a pendant lamp. Connection of wires in the socket and box
Time-current characteristics
Obviously, the machine does not always turn off instantly, and sometimes it needs to “think and make a decision”, or give the load a chance to return to normal.
The time-current characteristic shows after what time and at what current the machine will turn off. These characteristics are also called tripping curves or current-time characteristics. Which is more accurate, since it depends on the current after what time the machine turns off.
Tripping curves or current-time characteristics
Let me explain these graphs. As I said above, the circuit breaker has two types of protection - thermal (against overcurrent) and electromagnetic (against short circuit). In the graph, the operation of thermal protection is a section that smoothly descends. Electromagnetic - the curve abruptly breaks down.
The thermal one works slowly (for example, if the current is twice the nominal value, the machine will go off in about a minute), and the electromagnetic one works instantly. For graph B, this instant “begins” when the current exceeds the nominal value by 3-5 times, for category C - 6-10 times, for D (not shown, since it is not used in everyday life) - 10-20 times.
How it works - you can imagine what will happen if the current exceeds the nominal value by 5 times, and the protection is with the “C” characteristic, as in all houses. The machine will only go off after 1.5-9 seconds, depending on your luck. In 9 seconds the insulation will melt and the wiring will need to be changed. In this case, therefore, short circuit is better than overload.
Average level of sockets
The middle level of sockets is designed for temporary connection of portable household appliances. This level of outlets is called additional outlet blocks. You can plan any number of such sockets. In this example, two blocks of three sockets are planned above the desktop tabletop.
The height of the middle level sockets is taken to be 10-15 cm above the level of the working surface of the table, which corresponds to 110-115 cm from the floor level for low kitchens or 115-120 cm for kitchen cabinets with a high base.
Selecting a circuit breaker. Basic Rule
It is necessary to select a circuit breaker based on the cross-sectional area of the wire that this circuit breaker protects (which is connected after this circuit breaker). And the cross-section of the wire is based on the maximum current (power) of the load.
The algorithm for selecting a circuit breaker is as follows:
- We determine the power and current of the line consumers that will be fed through the machine. The current is calculated by the formula I=P/220 , where 220 is the rated voltage, I is the current in amperes, P is the power in watts. For example, for a 2.2 kW heater the current will be 10 A.
- We select the wire according to the cross-section selection table depending on the current. A cable with a conductor cross section of 1.5 mm² is suitable for our heater. In the worst conditions in a single-phase network, it holds a current of up to 19A.
- We choose a machine so that it is guaranteed to protect our wire from overload. For our case - 13A. If you install a machine with such a rated thermal current, then at a current of 19A (one and a half times higher), the machine will work in about 5-10 minutes, judging by the time-current characteristics.
Is it a lot or a little? Considering that the cable also has thermal inertia and cannot instantly melt, this is normal. But considering that the load cannot just increase its current by one and a half times, and in these minutes a fire can occur - this is a lot.
Therefore, for a current of 10 A, it is better to use a wire with a cross-section of 2.5 mm² (the current with an open installation is 27 A), and a 13 A machine (if it is exceeded by 2 times, it will work in about a minute). This is for those who want to play it safe.
The main rule will be this:
The wire current must be greater than the current of the machine, and the current of the machine must be greater than the load current
Iload < Iaut < Iprov
This refers to maximum currents.
And if there is such a possibility, the rating of the machine should be shifted towards the load current. For example, the maximum load current is 8 Amperes, the maximum wire current is 27A (2.5mm2). The machine should be chosen not for 13 or 16, but for 10 Amperes.
Here is the machine selection table:
Introduction: where to start calculating electrical wiring in kitchens
If you decided to renovate your kitchen, then most likely you planned to buy new furniture. Kitchen renovation and buying new kitchen furniture are usually interrelated events. They cannot be separated, primarily because a new kitchen also means new kitchen appliances. And new kitchen appliances mean new sockets and, as a result, new electrical wiring. Otherwise, the best option to update the kitchen is to renovate it and buy new furniture, and do the renovation according to the ready-made design of the kitchen furniture being purchased.
In this article I will not talk about all the stages of kitchen renovation. Here I will tell you how to calculate electrical wiring for kitchens when purchasing new modern kitchen furniture and not just a surreal calculation, but a calculation of electrical wiring based on the design of future kitchen furniture with built-in appliances.
Related article: Table of power of household appliances for calculating the cross-section of an electrical cable
As an example, I took a kitchen project that furniture sellers make when making a purchase.
This plan will be the basis for calculating the electrical wiring, and subsequently the plan for performing electrical installation work.
You can say: “Why do I need this, let the workers figure it out.” But in my opinion, to control the work that you will undoubtedly carry out, you need to understand or have an idea about the work that will be done to you. The task is how to calculate electrical wiring for kitchens when purchasing new modern kitchen furniture.
Table for selecting a circuit breaker based on cable cross-section
The choice of circuit breaker clearly depends on the cable cross-section. If the current of the machine is selected more than necessary, then the cable may overheat due to the flow of high current. If the machine is selected correctly, then if the current exceeds it will turn off and the cable will not be damaged.
Table for selecting a machine according to cable cross-section
Pay attention to the cable routing methods (installation type). Depending on where the cable is laid, the current of the selected circuit breaker may differ by 2 times!
According to the table, we have the initial cable cross-section, and select a circuit breaker for it. For us, as electricians, the first three columns of the table are most important.
Now - how to choose a circuit breaker if the power of the devices is known?
Nuances
In general, readers should not have any questions regarding the selection of packages according to the cable cross-section, but there are some subtleties that we did not mention above.
- A machine with which type of electromagnetic release to choose. In everyday life, machines of categories “B” and “C” are most often used. This is due to the fastest possible operation of package switches when the rated current is exceeded. This is extremely important when using appliances such as electric kettles, toasters and irons. Depending on the type of equipment used, you should choose a specific category; it is advisable to give preference to category “B” switches.
- A machine with a maximum switching capacity to choose. Depends on the location of the electricity input from the substation to the apartment, if in close proximity, then you should choose one with a switching capacity of 10,000 amperes, otherwise for city apartments there are enough devices for 5,000–6,000 amperes. You can play it safe and choose the option of 10,000 amperes; ultimately, this indicator only affects whether the machine will be operational after a short circuit.
- What type of wire to choose: aluminum or copper We strongly do not recommend purchasing aluminum conductors. Copper wiring is more durable and can handle higher currents.
Table for selecting a circuit breaker based on load power
Table of consumption and current of the circuit breaker according to the power of devices
It can be seen that the manufacturer recommends different time-current characteristics for different electrical appliances. Where the load is purely active (different types of heaters), the “B” characteristic of the machine is recommended. Where there are electric motors - “C”. Well, where powerful engines with difficult starting are used - “D”.
The time-current characteristic D is not included in this table because it is not for domestic use. More details about starting engines are described in the article about connecting an electric motor through a magnetic starter. And also about turning on the solid-state relay.
Upper level of sockets
The upper level of sockets is designed to connect the hood and built-in kitchen lighting. The placement of sockets in the kitchen is practically not regulated, and the recommended height of their location is 30 cm from the upper kitchen cabinets. At this height, the upper rosettes will not be visible.
Now that we've figured out the location of the sockets, let's move on to the electrical calculations.
Related article: Hob connection diagrams
Table of dependence of the current of the circuit breaker (fuse) on the cross-section
And here is how the Germans treat the circuit breaker current depending on the cross-sectional area of the wire:
Table for selecting a circuit breaker for different wire cross-sections
As you can see, the Germans are playing it safe and are providing for a larger reserve compared to us.
Although, perhaps this is because the table was taken from instructions from “strategic” industrial equipment.
Why does the air conditioner need a separate machine?
Owners of household air conditioners often wonder about the need to install a separate machine for their device and lay a separate line to it from the apartment or floor distribution board. Low-power split systems are often equipped with a wire with a standard plug for connecting to a household outlet, which adds even more questions.
The first thing to do to determine whether you need a separate circuit breaker and line for your device is to read the owner's manual. The instructions for absolutely any air conditioner have a section dedicated to connecting to the electrical network.
If the requirement for a separate line and machine is clearly stated in the manual, then it must be fulfilled unconditionally. Otherwise, you may lose the warranty on the device and face other troubles.
The air conditioner manufacturer specifically stated in its instructions that it is not permissible to connect other devices to the air conditioner switch. If your instructions include a similar requirement, then connect the split system via a separate line with a separate machine
If there is no such requirement, then you have to make the choice yourself. To do this, you need to know what advantages and disadvantages a connection via a separate line has.
Advantages of installing a separate line with a machine:
- You can use powerful air conditioners even in apartments with old, including aluminum, electrical wiring without replacing it;
- Reducing the negative impact of the air conditioner on the operation of other devices: the air conditioner is equipped with a compressor and fans that have significant starting currents that cause voltage fluctuations in the network when it is turned on. Such vibrations, if the wiring is weak, can harm other household appliances;
- Eliminating the possibility of overload during simultaneous operation of the air conditioner and other devices connected to the same line;
- There is no need to test existing electrical wiring for functionality and safety;
- The ability to turn off the air conditioner for maintenance or repair without interrupting the operation of other devices in the apartment;
- You don’t have to install a socket to connect the air conditioner, but run the wire directly into the terminal block of the device, which will look more aesthetically pleasing.
The more powerful the air conditioner and, accordingly, the more current it consumes, the more your choice should lean towards laying a separate line and installing a separate machine for the air conditioner.
If the air conditioner is installed after finishing work has been completed, then a separate line can be connected to it in a cable channel. If the device is equipped with a factory cord and plug, then you need to install a socket with grounding contacts
The list of disadvantages of constructing a separate branch includes only:
- It is necessary to carry out electrical installation work to lay a line from the panel to the device, which can damage the finishing of the apartment;
- It is not always possible to install another machine in an existing switchboard, which may require its replacement or modification.
It is possible not to install a separate machine and a separate line for the climate system, but to get by by connecting the device to an existing household outlet only if this is directly indicated in the instructions.
In this case, the socket must have protective grounding contacts, and the electrical wiring and circuit breaker installed in the switchboard must withstand the total load from the air conditioner and other household devices connected to this line.
In order to find out which devices are connected to the line into which the air conditioner is supposed to be turned on, you need to turn off the circuit breakers in the apartment or floor panel one by one. This makes it easier to check which household appliances are left without power, that is, they do not turn on.
Before connecting the air conditioner to an existing outlet, check what material the electrical wiring is made of and what its cross-section is. If the wiring is old aluminum, it is better not to connect the air conditioner to it
Also, you should not plug the air conditioner into an existing outlet if it is connected to the line that powers a microwave, electric kettle, washing machine or other devices with high power consumption.
If you have a low-power split system, and the choice fell on connecting to an existing outlet, then be sure to inspect the electrical wiring. Make sure that the wire connections in the branch boxes are not oxidized or loose, the bolt clamps in the socket and the machine in the panel are not loose, and the air conditioner plug is tightly inserted into the socket, ensuring reliable contact.
How does a circuit breaker work?
A bonus is the device of the protective circuit breaker, several photos of the circuit breaker, which is given at the beginning of the article.
Circuit breaker device. As you can see, the device is not simple. Top (fixed) contact - right
Circuit breaker. One second before the trash can)
Download
For those who are interested in the topic deeper and more thoroughly, I am posting GOST, which describes in detail all the characteristics and terminology of circuit breakers.
• GOST R 50345-2010 / GOST R 50345-2010 (IEC 60898-1:2003) Small-sized electrical equipment. Automatic switches for overcurrent protection for household and similar purposes. Part 1. Circuit breakers for alternating current. This standard applies to air circuit breakers (hereinafter referred to as circuit breakers) for alternating current for operation at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz with a rated voltage (between phases) of not more than 440 V, a rated current of not more than 125 A and a rated breaking capacity of not more than 25,000 A. , pdf, 1.89 MB, downloaded: 868 times./ • Kharechko V.N., Kharechko Yu.V. Automatic switches of modular design / Kharechko V.N., Kharechko Yu.V. Automatic circuit breakers of modular design: Reference manual. The reference manual sets out the requirements of GOST R 50345-99 (IEC 60898-95) for household circuit breakers intended for overcurrent protection, examines the design of circuit breakers, gives characteristics and their classification. Errors that are partially corrected in the new version of GOST R 50345-2010, pdf, 7.17 MB, downloaded: 837 times are analyzed./ As always, I will be glad to have questions and comments on the article in the comments!