Home / Heating
Back
Published: 12/18/2020
Reading time: 3 min
0
1220
The question of what is the difference between a hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank remains unclear to some consumers, although such equipment has been used in boiler houses for quite a long time.
Water supply and heating systems cannot be imagined without such successful additions; most people are accustomed to distinguishing these devices by their shade.
One of the units is available in blue, and the other in red, but their structure has its own nuances. I want to analyze in detail the differences between the devices and describe the purpose of installing each type of device.
- 1 Design and purpose of the expansion tank
- 2 Design and purpose of the hydraulic accumulator
- 3 What are the differences 3.1 How does the expansion tank work
- 3.2 How a hydraulic accumulator works
What is the difference between a hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank?
Tanks used in heating or hot water supply systems are more correctly called expansion tanks.
Hydraulic accumulators, in turn, are used in cold water supply systems.
In this case, a heating tank is needed to reduce the pressure resulting from the thermal expansion of water, and in the water supply, on the contrary, to increase it and raise the weak pressure to a comfortable value. In other words, their task is to somehow maintain the desired pressure of the working environment.
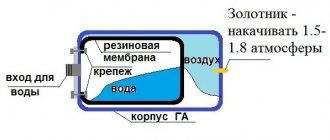
In both cases, pressure regulation is carried out using an elastic membrane and an air chamber in which the gas is under pressure and tends to fill the entire volume of the housing. The type of this membrane is also one of the differences between expansion tanks and hydraulic accumulators.
Differences between tanks by type of membrane
Tanks can have one of two types of membrane: pear-shaped or diaphragm. It is important to distinguish between them since using a tank with an unsuitable design significantly reduces its service life.
The diaphragm (disc-shaped) membrane cuts the body in half and does not isolate the coolant from the metal body. Membranes of this type do not tolerate proximity to the pump and cannot be repaired if they fail. When they break, the entire tank must be replaced, but on the other hand, they are cheaper and, if used correctly, last longer, since the diaphragm distributes the load of the working environment more evenly.
The pear-shaped membrane is attractive primarily because it can be replaced independently if it fails. However, due to its shape and fastening, the load on the membrane is distributed unevenly, which is an additional wear factor. It is mounted inside the housing using a special holder and fixed with a flange.
Moreover, this type of membrane can be used both in a hydraulic accumulator and in the design of an expansion tank. But the requirements for them are different. For the first, the suitability of the membrane material for drinking water is important. For the second, it is important to maintain the required temperature of the working environment.
How to choose
The main working body of the hydraulic tank is the membrane. Its service life depends on the quality of the material. The best membranes today are made from food-grade rubber (vulcanized rubber plates). The housing material matters only in membrane-type tanks. In those in which a “pear” is installed, water comes into contact only with rubber and the material of the body does not matter.
The flange should be made of thick galvanized steel, but better - stainless steel
What's really important about bulb tanks is the flange. It is usually made of galvanized metal. In this case, the thickness of the metal is important. If it is only 1 mm, after about a year and a half of operation, a hole will appear in the metal of the flange, the tank will lose its tightness and the system will stop working. Moreover, the warranty is only one year, although the stated service life is 10-15 years. The flange usually rots after the warranty period expires. There is no way to weld it - the metal is very thin. You have to look for a new flange at service centers or buy a new tank.
So, if you want the accumulator to last a long time, look for a flange made of thick galvanized or thin, but made of stainless steel.
What is a hydraulic accumulator?
From the name of the hydraulic accumulator you can guess that it is used primarily to store water, but it also performs other functions. For example, it dampens water hammer and smoothes out pressure fluctuations that occur during pump operation. In addition, it reduces the number of pump starts, which can significantly extend its life.
The operating cycle of the accumulator is simple: the pump pumps water into it and turns off when the pressure on the relay reaches the maximum permissible value. The next turn on of the pump occurs when, as a result of water intake, the pressure on the relay drops to the value set as the minimum.
It is important to note: since drinking water is used as the working medium in such a system, it should not come into contact with metal parts of the housing, which may rust.
In addition, the membrane in the accumulator must be more wear-resistant than in the expansion tank due to significantly more intense deformation and close placement of the pump.
Causes of breakdowns and ways to eliminate them
Despite the fairly strong and durable design, it happens that the water supply accumulator fails. There are several reasons for this. Very often the water main becomes airy. An air lock forms in the pipeline, preventing normal water circulation. The cause of airing in the water supply system is the accumulation of air inside the membrane. It gets there along with the flow of water, and gradually accumulates, spreading through the pipeline.
In hydraulic tanks with a vertical installation method, a special drain nipple is installed in their upper part to bleed the air accumulated in the membrane. Small storage tanks with a volume of less than 100 liters are usually made horizontally. Bleeding air into them can be somewhat more difficult.
The procedure here is performed in several stages:
- The hydraulic accumulator is disconnected from the power supply.
- All water is drained from the system until the storage tank is completely empty.
- Then all valves in the pipeline system are closed.
- The hydraulic tank is connected to electricity and refilled with water.
The air accumulated inside the storage tank will leave along with the discharged water.
What is an expansion tank in a heating system?
Its name also speaks for itself; it is designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of water in hot water supply and heating systems . The absence of an expansion tank in closed systems would inevitably lead to exceeding the maximum permissible pressure and leaks even with a slight increase in temperature.
If water with a temperature of 0 °C is heated to 100 °C, its density will become less, causing its volume to increase by about 4.3%. Without taking into account the deformation of pipes and other elements of the system, an increase in temperature by one degree increases the pressure by 3 bar.
The expansion tank must be able to operate in high temperature conditions. In addition, it must be of sufficient size to accommodate all excess coolant volume. As a rule, this is about 15-20% of the total coolant volume at room temperature.
What is the difference between a blue expansion tank and a red one?
Often, by the red or blue color of the tank, you can determine whether it is designed to work with a cold or hot working environment. However, the color of the tank depends solely on the preferences of the manufacturer and can be anything. For example, in Arma Shop we sell ProTank tanks (Turkey), painted gray. They are universal and can be used both as expansion tanks and hydraulic accumulators.
Models with bodies of various volumes are available for purchase: from 2 to 10,000 liters. If necessary, you can choose a model with a pump platform and a pressure gauge. Tanks are also available in vertical or horizontal mounting position.
Recommendations for installation and operation
Installing a hydraulic tank is easy; it is simply connected to the water supply system after the pump. Before entering the device, you need to install a good filter to clean the water from impurities. They can accumulate inside and damage the membrane.
A hydraulic accumulator designed for autonomous water supply is best used with a pressure switch that will control the operation of a submersible pump
You need to choose the right place for installation. The HA should be placed where one can freely approach to inspect the device and maintain it. Over time, the device may need to be repaired, so it doesn’t hurt to think in advance about the procedure for dismantling it and the difficulties that may arise at this time.
It is very important that the dimensions of the pipe and the water pipe match. This will avoid hydraulic losses due to narrowing of the route in some area. The use of adapters is acceptable, but not recommended. As water flows in and out, the membrane tank may vibrate.
It is recommended to attach it to the base using shock-absorbing pads. Connection to the water supply is made with a flexible liner. You should make sure that the device is correctly aligned horizontally and vertically; distortions are not allowed.
It is necessary to take care in advance about the possibility of disconnecting the HA from the water supply so that you do not have to completely drain the water from the system. This requirement is met by installing a conventional shut-off valve. For small containers with a capacity of up to 10 liters, which do not have a nipple, it is also necessary to provide for the installation of a drain valve.
You can read more about how to connect a hydraulic accumulator to a water supply system in this material.
Maintenance of the hydraulic tank comes down to a careful inspection of the housing and monitoring the pressure in the air compartment. Sometimes you need to pump up the air or bleed it to restore the correct performance. Typically the pressure should be about two atmospheres or slightly less. In addition, the air that has accumulated behind the membrane in the compartment where the water is stored should be removed.
Sometimes you can even install an automatic air vent here. If there is no hole for this procedure, you need to disconnect the HA from the water supply and completely empty it through the drain tap. The air will come out of the container along with the water. Then you just have to turn on the pump again so that water starts flowing into the tank again.
Speaking about how a membrane accumulator works, it is worth noting that the most common failure in a hydraulic accumulator is a membrane breakthrough. This elastic element is subject to constant tension and compression, and therefore fails over time.
Here are the signs that the membrane has ruptured:
- water comes from the tap in sharp bursts;
- the pressure gauge needle “jumps”;
- After the contents of the “air” compartment are completely bled, water flows out of the nipple.
The last point allows you to accurately determine whether the problem is really with the membrane. If water does not flow out of the nipple, and water enters the system poorly, most likely the housing is depressurized. You need to carefully examine it, find and repair the cracks.
The membrane can deteriorate due to wear or improper use. It needs to be completely replaced; repairing this element is useless
Replacing the membrane is not difficult, but you need to select exactly the same element as the damaged one, since it is designed specifically for this particular HA.
To carry out repairs, you need:
- Disconnect the device from the water supply system.
- Drain the water, bleed the air.
- Unscrew the mounting screws.
- Remove the damaged membrane.
- Install the correct element.
- Secure it with screws.
- Install the GA in place and connect it to the system.
The most difficult part of this procedure is tightening the screws. It should be uniform, so it is recommended to twist them, making one turn on each element in turn. This tactic will allow you to properly secure the membrane to the body and prevent its edge from sliding inward.
Some inexperienced craftsmen, in an effort to improve the quality of the connection, apply sealant to the edge of the membrane. This should not be done, since the composition can destroy the rubber and cause the opposite effect.
Let's sum it up
Hydraulic accumulators and expansion tanks have different purposes, but belong to a common group - expansion tanks. What to choose specifically in your case? First you need to evaluate the entire system and decide what function this device should perform. If you need a pressure tank for drinking water, you should use a hydraulic accumulator with a pear-shaped membrane.
If it is necessary to compensate for the expansion of the coolant in the heating system, then use a membrane expansion tank (expanzomat), in which the diaphragm is designed to operate at high temperatures.
☛ Select expansion tank