Gas shielded arc welding is divided into two categories: metal inert gas welding (MIG) and metal active gas welding (MAG). The market offers endless choice with many solutions for different processes and control options. However, welding torch designs are virtually identical, with minor internal differences depending on the process. So what is a “welding torch” and, in particular, a “MIG/MAG welding torch”?
Burner consumables and wear parts
The welding torch also includes a trigger handle and a torch neck with wear parts such as the gas nozzle, contact tip, nozzle holder and diffuser. The standard burner model can be up to six meters in length.
When purchasing a welding torch, it is important to pay attention to the amount of welding current required to perform the welding task. It makes no sense to use a 600 Amp welding torch with a power source that can handle up to 220 Amp current, nor does it make sense to install a high-performance, high-power welding system with the smallest torch available. The MIG/MAG welding torch must match the maximum power range of your power source.
The length of the sleeve
We proceed from the assigned tasks. The farther the welding torch is used from the semi-automatic machine, the longer the sleeve should be. Typically the length varies from 3 to 5 meters. Masters prefer to take with a reserve, which will certainly come in handy, if not now, then in the future. But all this is individual, because some are convinced that the shorter the sleeve, the less energy loss.
Gas or water cooled?
Another key question is which cooling to choose - air or water? It's a bit like buying a motorcycle - air-cooled one or two cylinder or water cooled four cylinder? The fact is that water-cooled systems are often more durable. Any welder who has used a water-cooled welding system will tell you how much more convenient it was to weld with a water-cooled welding torch and how easy it was to handle. Additionally, water-cooled systems not only last longer, but also provide more power. Air-cooled welding torches are not suitable for high currents and long-term operation, while water-cooled torches continue to perform well at currents well above 200 A.
Naturally, the advantages of water cooling come at a price and the cost of water-cooled burners is on average 20-30% higher. There is also the added cost of installing the water cooling system itself. Replacing welding torch wear parts will be part of the ongoing operating costs, so cost is an important factor when choosing between gas or water cooling.
Care and operation
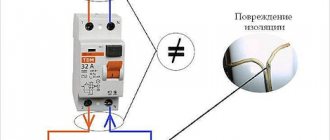
If you expect long-term operation of the welding torch, you must provide it with proper care and maintenance and follow the operating rules. During operation, the burner and its components become dirty and clogged, which negatively affects their performance. The wire feeder needs to be cleaned regularly. For this purpose, compressed air is usually used. It removes metal dust. Regular dust also accumulates on the internal surfaces of working units. This leads to burnout of power transistors and affects the insulation resistance.
If the torch is not working properly, the quality of the weld will deteriorate. Minor breakdowns lead to more significant ones. One of the most common problems is nozzle burning. Under normal conditions, this element is protected from the circuit, so it should not burn. This happens due to metal splashes on the working parts. To extend the life of the nozzle, you should regularly clean the equipment using special metal splash cleaners.
MIG/MAG welding torch control functions
Once you have decided on your preferred cooling option, the next question to ask is what kind of operational controls you want. Do you need something simple or more feature-rich? What controls does your welding torch need to meet your welding requirements? The simplest option is an on-off switch or burner trigger. But even then, there is a choice: do you want the start button on the top or the bottom? Ultimately it comes down to the welder's preference - trigger on the top if you prefer to use your thumb, or the trigger on the bottom if you prefer to use your index finger.
Perhaps you want to be able to increase or decrease the current while welding? A simple rocker switch on the top of the torch allows the welder to adjust the power up and down without stopping the weld or changing the handle grip.
If you are using a digital power source, there are many more sophisticated control functions available for your welding torch. Looking for something more advanced than simple power management? This means you must select a burner with additional controls that relate to all the different settings shown on the power supply display. Each individual parameter can be viewed on the burner's small display and selected or adjusted as needed. There is also the ability to set specific parameters on the power source for a specific welding task or "job". After this, the presets can be activated on the burner itself.
All the settings you need in your daily work can be controlled directly on the MIG/MAG welding torch without having to use the controls of the welding system itself. These multi-function torches are especially beneficial when welding in areas where the power source cannot be located directly next to the weld or where longer hosepacks are required to access hard-to-reach components.
Application area
Shielding gas for semi-automatic welding is used in many areas. Without it, not a single semi-automatic welding process can be carried out, except for those when self-shielding wire is used. Most often it is used by professionals, since the use of a semi-automatic device relates more to highly skilled work. Gas is used in equipment and car repair shops. This is often used when assembling metal structures from non-ferrous metals. Almost all production enterprises where there is a need to work with metal have semi-automatic machines that operate using a gas protective atmosphere. There is no specific connection to the model of the device itself.
Multilock: one welding torch – many options
Multifunctionality means more than just a set of process control tools. The Multilock system has been designed for maximum flexibility, allowing the welder to change the torch jaw depending on the shape of the elements being welded and its availability. By varying torch jaw lengths and angles, you can achieve exceptional welding results no matter how complex the welding task.
Multilock is also very convenient for replacing faulty parts. For example, if the torch jib is damaged, but the hose package is absolutely intact, then only the jib can be quickly and easily replaced thanks to the Multilock connection.
Thanks to the Multilock design, the torch jaw can be rotated 360°. For example, turning it 180° up allows you to easily and conveniently perform welding work in the ceiling position. The burner control remains the same.
Gases used for welding
It is necessary to select gas for semi-automatic welding based on its properties.
Acetylene
Characteristics:
- colorless;
- lighter than air;
- has a specific smell.
This is one of the most common gases used in this field of activity. It has the highest combustion temperature among other types of gas and has high polarity. Often used due to the high combustion temperature when cutting metal structures.
Specialized generators are used to produce acetylene. Acetylene can be obtained by combining water with calcium carbide, which can even absorb moisture from the atmosphere. Therefore, according to the safety requirements for this chemical compound, special storage conditions are provided.
Hydrogen
Characteristics:
- colorless;
- has no smell;
- refers to explosive substances.
When combined with oxygen and air, it forms an explosive gas. According to safety requirements, hydrogen cylinders should not be under pressure more than 15 MPa.
Specialized generators are used to produce hydrogen. Hydrogen is also released due to water synthesis.
Coke gas
Characteristics:
- colorless;
- has a specific smell.
It is a by-product extracted during the extraction of coke, which in turn is extracted from coal. This gas can be transported using pipelines.
Natural gas: methane, butane, propane
Quite common types of gases used for many welding jobs. There are no special requirements for them during transportation and storage. The extraction of these types of gases for semi-automatic welding is carried out at their deposits.
Pyrolysis gas
It is extracted during the breakdown of petroleum products. This gas contributes to the formation of corrosion of the burner mouthpieces, as a result of which they quickly fail. Pyrolysis gas is purified before its direct use. This substance is used both for welding metal structures and for cutting them.
PushPull welding torches
For welding using soft wires, as well as when it is necessary to use a long hose package up to 15 m long, when welding aluminum, where reliable and accurate wire feeding is especially important, a particularly light (weight 1.6 kg) PushPull torch is used, in the handle of which has a built-in powerful motor with a maximum wire feed of up to 20 m/min and feed rollers with continuously adjustable wire pressure.
Semi-automatic gas welding
Gas semi-automatic welding of steel, copper, titanium samples, and their alloys is a procedure for joining individual metal products by supplying filler wire and gas to the joint area, which protects the molten materials from the adverse effects of air.
Advantages of gas welding
- To carry out welded joints of metal structures using gas, there is no need to purchase rather expensive equipment.
- When using carbon dioxide, welding work can be carried out on any areas of buildings and structures. In this case, additional energy consumption is eliminated.
- During welding work, it is possible to change the flame power. This makes it possible to weld different types of samples, for example, titanium with copper, lead with brass, and other metals with different melting points.
- This welding method can not only connect metal structures, but also harden and cut them.
- Semi-automatic gas welds are much stronger than with electric arc welding.
Joining cast iron, copper, brass, and lead workpieces using semi-automatic welding is much faster and of better quality.
Features of the work
- If you set the power correctly on a semi-automatic machine, select the optimal wire, wire feed speed, and carbon dioxide consumption, then the welded joints will be of the best quality.
- The surfaces being welded heat up and cool down rather slowly. When connecting copper, steel, titanium parts, the flame temperature is regulated. The maximum temperature of the flame when it is in a vertical position, and according to a change in the angle of inclination, it will decrease.
- When performing gas semi-automatic welding in carbon dioxide, the use of two equipment options is provided. In the first case, welding units work with argon and other inert gases. In the second case, semi-automatic machines work with carbon dioxide.
- The use of a high-pressure gas cylinder significantly complicates body work and welding of pipeline communications in open areas. But, for stationary work, this technique is considered the most effective.
- When gas welding, wire containing silicon and manganese is used. Its consumption is strictly controlled, and it is supplied to the welded zone along with gas, which protects the wire and metals being connected from the negative influences of air. The standards define the grades of wire that are recommended for use for specific welding equipment.
FumeEx - forced removal of gases
Gases and aerosols released during welding have a harmful effect on health, so it is important to provide a set of measures to reliably protect the welder and surrounding people. For these purposes, a fume extraction option is provided, which is suitable for any type of welding torch, has an adjustable length of the exhaust nozzle with a special geometry for optimal fume capture without affecting the gas protection.
Ease of maintenance of the torch for semi-automatic welding
The structural elements of this accessory, when exposed to high temperatures, require periodic replacement due to wear. This is especially true for the nozzle, diffuser and contact tip. The wear of these parts is largely determined by the quality of the seam. Therefore, they need regular cleaning and maintenance.
If there is a need to replace them, then it would be nice if not only branded elements were suitable for the welding tool for the inverter. Universal ones are usually cheaper and more common. Therefore, it is worth asking in advance whether the semi-automatic burner design allows the use of universal components.
Having heeded the listed recommendations, you certainly will not regret your choice of accessory. But if it is not possible to buy a burner for a semi-automatic device during a visit to the store, which will allow you to evaluate first of all the ergonomics of the device, place an order remotely. The catalog of the online store “1001 Welding” provides a wide selection of everything necessary for high-quality and productive welding of various types.
Types and markings
For semi-automatic welding, a gearbox with a different number of chambers can be used. In the vast majority of cases, single-chamber modifications are used. But in some cases, the stability of equipment use at low temperatures is critical. In such a situation, two-chamber models are the most attractive. The compartments are usually arranged in a sequential pattern.
In any case, the gearbox must meet the following standards:
Carbon dioxide welding gearboxes are also distinguished according to the conditions of use. Ramp models are used in multi-station welding areas. Network devices receive gas flow from a stationary main, which communicates with a carbon dioxide industrial station. At small work sites, on construction sites and in everyday life, balloon gear units are used. They are mainly designed for a slightly lower specific consumption of CO2 and a small spread of gas pressure.
Opening and sealing of the intake valve assembly can occur using a direct or reverse method. The second variety has just been described above. In the “direct scenario,” the work steps change order. This solution is much less convenient. It is therefore used much less frequently.
The oxygen reducer is designed in almost the same way as its carbon dioxide analogue. The difference concerns mainly the methods of connection to the valves and the number of pressure gauges used (1 or 2). Oxygen reducers must meet increased performance requirements. The reason is simple: oxygen cannot be in a liquefied state, and therefore the pressure inside the cylinder sometimes reaches 200 atmospheres. For comparison: for carbon dioxide this figure is 70-80 atmospheres.
If you try to direct oxygen into the carbon dioxide reducer, the sealing membranes will gradually collapse. But the opposite replacement (injecting carbon dioxide through an oxygen reducer) is quite acceptable. You just need to understand that the oxygen reducer unit is connected to the cylinder via a clamp. Carbon dioxide, which is safe in terms of explosions and fires, is supplied when connected with a folding nut.
If the purity of the incoming substance is critical, special filters are needed.
Russian industry supplies various models of gearboxes. Level 6-6 is popular. The body is formed from a special alloy that perfectly withstands thermal and mechanical influences. Other parameters:
- gas pressure heterogeneity maximum 0.3;
- the safety block is triggered at 1200 kPa;
- thanks to two manometric units it is easier to influence the carbon dioxide pressure;
- maximum gas flow - 6 m3 per hour.
If the usual functionality is not enough, it is necessary to use not simple gearboxes, but control devices with rotameters . They show gas consumption immediately. The cost of such devices, however, is noticeably higher. The hole inside the throttle is carefully calibrated.
Sometimes the gas flow is heated by an electrical module.
Selection of components and accessories
You should not make certain spare parts yourself, since installing them on the burner will automatically deprive you of the right to warranty service for the product. You will also be deprived of warranty service if you use certain non-branded parts. Almost everything can be purchased on the spare parts market at the moment, but the quality of the products offered does not always meet the requirements.
The part may only have a visual resemblance to the required element, but the material used to make it does not meet the requirements and can quickly melt or change its physical properties after the first weld. In any case, the user will not be insured against substandard spare parts. But if you buy them in a company store, a person will at least be insured against troubles when the product is repaired at a service center.
The torch for semi-automatic welding is connected to the machine itself using a cable. It can be of different lengths (from 2.5 to 7 meters). The choice of train length is not spontaneous. Usually the user believes that the longer the cable, the more convenient it is to work, since you can reach the surfaces to be welded far from the semi-automatic machine itself. This is the right idea, but you also need to remember that electrical cables (and the cable is an electrical cable) are subject to certain requirements, and the rules when working with welding may depend on the length:
- When passing electric current, the cable should not have twists in the form of rings; each such ring is a kind of inductor; accordingly, heat will be generated at the twisted points, which leads to damage to the insulation;
- the longer the electrical cable, the higher the likelihood of mechanical damage;
- storing such a cable is not entirely convenient for the user.
The choice of burner for semi-automatic machines should be carried out in accordance with the work that you mainly plan to carry out.
There is no need to buy a product designed for industrial production. For an ordinary user, it will be enough to have a middle-class semi-automatic machine and a corresponding burner. It will cost less, and you can make repairs yourself, if necessary.
Advantages of semi-automatic carbon dioxide welding for automotive repairs
- The technology for welding in carbon dioxide is easy to learn and, if necessary, can be quickly learned.
- A limited zone of thermal influences makes it possible to connect thin metal products.
- Carbon dioxide is the most accessible of all types of gases used for welding.
- quite high melting rate of filler wire, correspondingly high productivity.
- The paint on the product fades in a narrow stripe. This allows preparatory and finishing work to be reduced to a minimum.
- Welds are of high quality for parts of different thicknesses.
- There is no need to pre-fit the welded samples.
Selecting a gearbox for welding
A reducer, in the global sense of the word, is a device that changes any physical indicator, usually in the direction of decreasing or lowering it (reduction).
A welding reducer is a device that is designed to release gas from a nozzle under reduced pressure, since it is highly compressed in the cylinder. Specific pressure indicators depend on the type of gas or gas mixture.
What to choose
It is believed that for domestic welding conditions - short-term, occasional operations - any device that matches the thread of the cylinder is suitable.
Even a carbon dioxide reducer screwed onto an oxygen cylinder (if gas welding is used) or onto a cylinder for a welding mixture of 80% argon and 20% carbon dioxide can withstand an operation like welding a barbecue for a summer house. Another thing is that later this mechanism will have to be thrown away.
A typical example of such a gearbox designed to work with CO2 is the very well-known and popular among old-school welders UR 6-6.
It is compact, inexpensive, and thanks to the presence of two pressure gauges, it makes it quite convenient to determine the flow rate “by eye.” For household welding, high precision is not needed. One pressure gauge shows the residual pressure in the cylinder, and the second is aimed at demonstrating gas flow - liters per minute.
Oxygen and argon welding regulators are theoretically interchangeable. In this case, oxygen will work worse as the pressure in the cylinder drops to a critical point of about 1 atmosphere.
An example of an argon gearbox for welding is the domestically produced AR-40-2. There is also a truly universal pressure regulator - AR-40/U-30 (argon reducer/carbon dioxide). It will withstand both temperature changes and high pressure.
If there are no financial restrictions, and the volume of welding work is expected to be high, then you should prefer a device not with an additional pressure gauge, but with a rotameter.
The rotameter shows the flow rate of the gas mixture much more accurately, since it works on different principles - it takes measurements in real time. These devices are used by professionals.
Source
Peculiarities
The main function that any gearbox for a semi-automatic machine has is the precise regulation of the pressure of carbon dioxide or other gas supplied to the semi-automatic machine. It is regulated not only in terms of lowering or increasing, but also in terms of stabilization. The gear unit at the welding station contains:
- intake and exhaust valves;
- chambers with adjustable membranes;
- sealing elements;
- upper and control springs;
- fittings for connection;
- outer casing;
- pressure gauges;
- a valve that provides manual opening or closing of the line.
A simple device has one working chamber. Gas from the cylinder moves into the device under pressure set by the inlet pressure gauge. Then it ends up in the initial fitting, and after passing through the chamber, the gas flow meets the resistance of a special spring. Since the pressure turns out to be sufficiently large, the spring is pressed off, and the free flow of the jet into a special cavity begins. The cross-section of the chamber is many times larger than the diameter at the inlet to the fitting, and therefore the second pressure gauge registers the reduction in pressure.
A special screw allows you to adjust the tension of the main spring. It adapts to the initial balloon pressure. The control spring goes down at the same time as the diaphragm. Therefore, the gas flow can freely flow to the shut-off valve. Next it goes to the burner. The gearbox diaphragm is made of oil-resistant rubber and is precisely positioned in relation to the outlet.
Reducer for welding mixture
A welding reducer is a must if you use gas cylinders in your work. This simple compact device is designed to reduce pressure and monitor its indicators. There are several types of reducers, each of which is designed for a specific type of gas.
In this article we will briefly but clearly explain what gas reducers are, what they are like and how to choose them for your tasks.